Java 阻塞队列

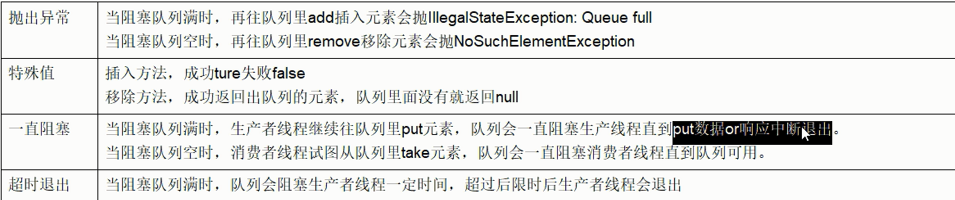
线程1往阻塞队列中添加元素,而线程2从阻塞队列中移除元素
当阻塞队列是空,从队列中获取元素的操作将会被阻塞,直到其他线程往空的队列插入新的元素
当阻塞队列是满,往队列里添加元素的操作将会被阻塞.直到其他线程从队列中移除一个或多元素或者完全清空队列,是队列变得空闲起来才能新增.
分类:
ArrayBlockingQueue :由数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列
LinkedBlockingQueue:由链表结构组成的有界(但大小默认值为Inter.MAX_VALUE)阻塞队列
PriorityBlockingQueue:支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列
DelayQueue:使用优先级队列实现的延迟无阻塞队里.
SynchronousQueue:不存储元素的阻塞队列,即单个元素的队列
LinkedTransferQueue:由链表组成的无界阻塞队列
LinkedBlockingDeque:右于链表构成的双向阻塞队列

同步队列的代码:
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class SynchronouQueueDemo {
//SynchronousQueue没有容量
//与其他的BlockingQueue不同,SynchronousQueue是一个不存储元素的BlockingQueue
//每一个put操作必须等待一个take操作,反之不能继续添加元素
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t put 1");
blockingQueue.put("1");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t put 2");
blockingQueue.put("2");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t put 3");
blockingQueue.put("3");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"AAA").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t "+ blockingQueue.take());
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t "+ blockingQueue.take());
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t "+ blockingQueue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"BBB").start();
}
}
lock生产一个消费一个代码:
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
class SharData {
private int number = 0;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
public void increment() throws Exception {
lock.lock();
try {
//1.判断
while (number != 0) {
//等待,不生产
condition.await();
}
//2.干活
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + number);
//3.通知唤醒
condition.signalAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void decrement() throws Exception {
lock.lock();
try {
//判断
while (number == 0)
condition.await();
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + number);
//3.通知唤醒
condition.signalAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
//1.线程操作资源类
public class ProduConsumer_TraditionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SharData sharData = new SharData();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) {
try {
sharData.increment();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "AA").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) {
try {
sharData.decrement();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "BB").start();
}
}
//多线程中的判断不要用if,用while

import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
class ShareResoure {
private int number = 1;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition c1 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition c2 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition c3 = lock.newCondition();
//1.判断
public void print5() {
lock.lock();
try {
while (number != 1) {
c1.await();
}
//干活
for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + i);
}
//3.通知
number=2;
c2.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//2.干活
public void print10() {
lock.lock();
try {
while (number != 2) {
c1.await();
}
//干活
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + i);
}
//3.通知
number=3;
c3.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//3.通知
public void print15() {
lock.lock();
try {
while (number != 3) {
c1.await();
}
//干活
for (int i = 0; i <= 15; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + i);
}
//3.通知
number=1;
c1.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public class SyncAndReentrantLockDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareResoure shareResoure=new ShareResoure();
new Thread(()->{
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
shareResoure.print5();
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(()->{
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
shareResoure.print10();
}
},"B").start();
new Thread(()->{
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
shareResoure.print15();
}
},"C").start();
}
}
线程池
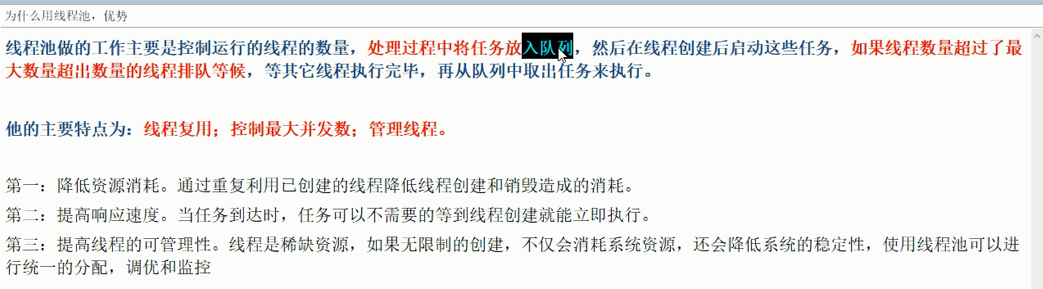
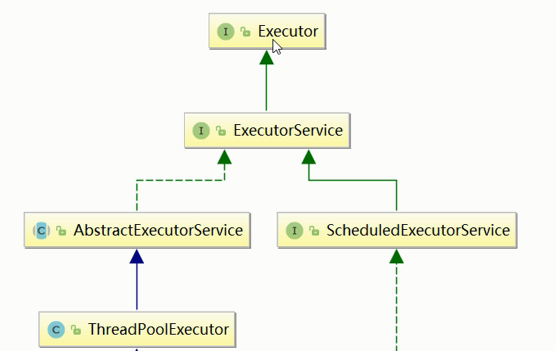
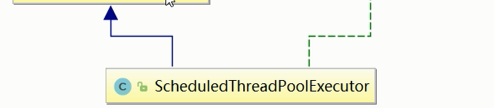
Java 中的线程池是通过Excutor框架来实现的,该框架中用到了Excutor,Excutors,ExcutorService,ThreadPoolExecutor这几个类
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class MyThreadPoolDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//cpu核数
//System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
// ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);//一池5个处理线程
// ExecutorService threadPool=Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();//一池1個處理線程
ExecutorService threadPool=Executors.newCachedThreadPool();//一池N个线程
try {
for(int i=0;i<=10;i++){
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 辦理業務");
});
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}



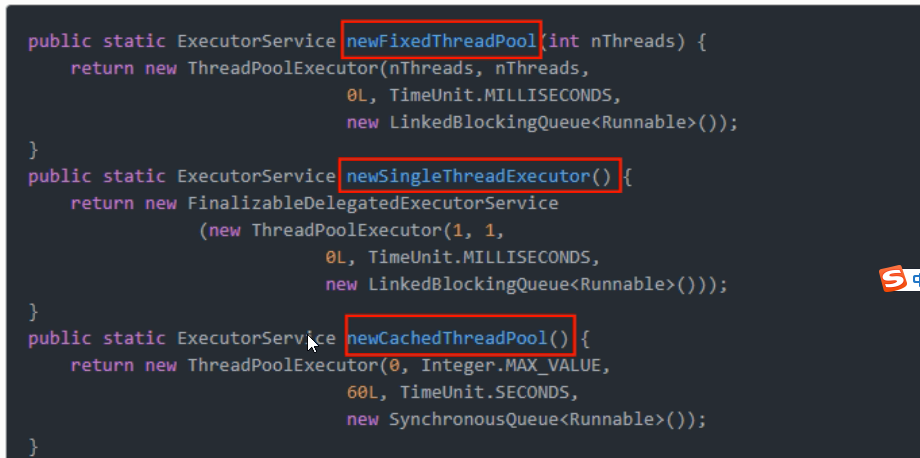
七大参数:

七大参数描述:

拒绝请求执行的runnable的策略。
corePoolSize:


拒绝策略:

jdk内置的拒绝策略划分:



手写线程池:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2,
5,
1L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
);
try {
for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 辦理業務");
});
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号