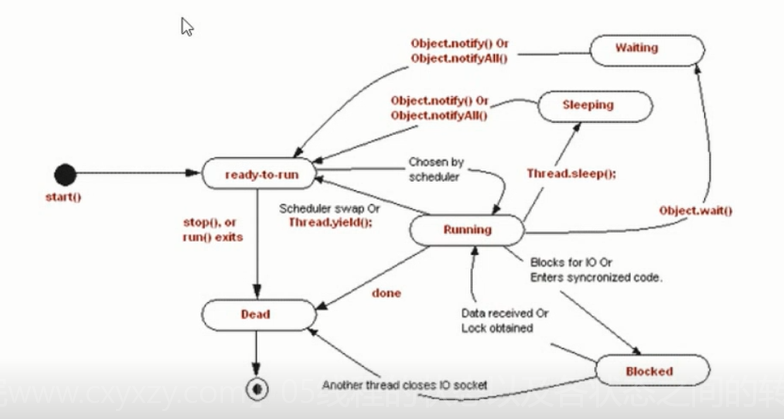
Java 线程状态


状态:
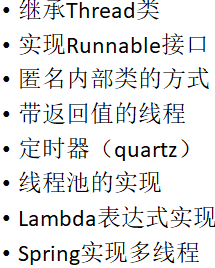
创建线程的方法:
public class NewThread implements Runnable{
@Override
public synchronized void run(){
while(true){
try {
//Thread.sleep(100);
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程运行中...");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
NewThread n=new NewThread();
//初始化状态
Thread thread =new Thread(n); //创建线程,并执行线程任务
thread.start(); //启动线程
while(true){
synchronized (n) {
System.out.println("主线程执行了....");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
n.notifyAll();
}
}
}
}
public class Demo1 extends Thread{
public Demo1(String name){
super(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
// while(true){
while(!interrupted()){ //中断线程的推荐用法
System.out.println(getName()+"线程执行了。。");
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo1 demo1=new Demo1("first-thread");
Demo1 demo2=new Demo1("second-thread");
//守护线程
//demo1.setDaemon(true);
//deom2.setDaemon(true);
demo1.start();
demo2.start();
//中断线程
//demo1.stop();
demo1.interrupt();
// try {
// Thread.sleep(2000);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
}
}
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//匿名内部类,只是用一次
new Thread(){
public void run(){
System.out.println("thread start...");
};
}.start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("thread start...");
}
}).start();
//两个同时使用
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("runnable");
}
}){
public void run(){
System.out.println("sub");
};
}.start();
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
//线程的返回值类型
public class Demo4 implements Callable<Integer>{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Demo4 demo4=new Demo4();
FutureTask<Integer> task=new FutureTask<>(demo4);
Thread t=new Thread(task);
t.start();
task.get();
System.out.println("我先干点别的。。。。");
Integer result=task.get();
System.out.println("线程执行的结果为:"+result);
}
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("正在进行紧张的计算");
Thread.sleep(300);
return 1;
}
}
定时器:
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer=new Timer();
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
//实现定时任务
System.out.println("timertask is run");
}
},0,1000);
}
}
线程池:
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//固定容量的线程池
//Executor threadPool=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//ExecutorService threadPool=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
ExecutorService threadPool=Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
spring使用线程:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.roocon.thread.t1") //扫描的包
@EnableAsync
public class Config {
}
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service //交给spring管理
public class DemoService {
@Async //异步调用的注解
public void a() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("a");
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void b() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("b");
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac=new
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);
DemoService ds=ac.getBean(DemoService.class);
ds.a();
ds.b();
}
}
使用lambda表达式:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> value=Arrays.asList(10,20,30,40);
int res=new Demo7().add(value);
System.out.println("计算结果:"+res);
}
public int add(List<Integer> values){
//打印集合中的值 并行执行
//values.parallelStream().forEach(System.out::println);
//不是并行执行
//values.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
//并行执行排序
values.parallelStream().forEachOrdered(System.out::println);
return 0;
//并发的流
//return values.parallelStream().mapToInt(a->a).sum();
}
}
线程带来的风险:
1.线程安全问题
2.活跃性问题(死锁、饥饿、活锁)
3.性能问题
饥饿与公平



同时启动三个线程执行会有重复性数据:(与字节码有关)
public class Sequence {
private int value;
public int getNext(){
value=value+1;
return value++;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sequence sq=new Sequence();
//一个执行
// while(true){
// System.out.println(sq.getNext() );
// }
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()+""+
sq.getNext());
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()+""+
sq.getNext());
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()+""+
sq.getNext());
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
}
}
解决方法:让方法变成同步方法。
public synchronized int getNext(){
return value++;
}
线程安全问题:
1.多线程环境下
2.多个线程共享一个资源
3.对资源进行非原子性操作
内置锁:每个对象都可以用同步的锁 synchronized 放在普通方法上,内置锁就是当前类的实例。修饰静态方法,内置锁是当前Class字节码对象,修饰代码块。
互斥锁:一个线程进来,另一个线程就不能就来,保证了原子性
任何对象都可以作为锁,锁的信息又存在对象的什么地方呢?
存在对象头中
对象头中的信息包括:
1.Mark Word
2.Class Metadata Address
3.Array Length
偏向锁:每次获取锁和释放锁会浪费资源
很多情况下,竞争锁,不是由多个线程,而是由一个线程在使用。
只有一个线程在访问同步代码块的场景
轻量级锁:自旋,多个线程可以同时
重量级锁:只能等当前线程执行完了,其他线程才能进去。
锁重入:使用同一个对象才能锁的住,不同的对象是锁不住的。
public class Demo {
public synchronized void a(){
System.out.println("a");
//b();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public synchronized void b(){
System.out.println("b");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Demo demo=new Demo();
Demo demo1=new Demo();
Demo demo2=new Demo();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
demo2.a();
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
demo1.b();
}
}).start();
}
}
自旋锁的应用:
import java.util.Random;
//多个线程执行完毕后,打印一句话,结束
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行开始....");
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(2000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行完毕了...");
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行开始....");
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(2000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行完毕了...");
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行开始....");
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(2000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行完毕了...");
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行开始....");
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(2000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行完毕了...");
}
}).start();
while(Thread.activeCount()!=1){
//自旋
}
//if(Thread.activeCount()==1)//活动线程的数量
System.out.println("所有的线程执行完毕了");
}
}
死锁:当一个线程永远的持有一把锁,并且其他线程尝试获取这把锁,也就发生了死锁
public class Demo3 {
private Object obj1=new Object();
private Object obj2=new Object();
public void a(){
synchronized (obj1) {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (obj2) {
System.out.println("a");
}
}
}
public void b(){
synchronized(obj2){
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (obj1) {
System.out.println("b");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo3 demo3=new Demo3();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
demo3.a();
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
demo3.b();
}
}).start();
}
}
单例中出现线程安全问题,懒汉和饿汉方式:
public class Singleton {
//私有化构造方法,不让new
private Singleton(){
}
//饿汉式,创建的时候实例化(没有线程安全性问题)
private static Singleton instance=new Singleton();
public static Singleton getInstance(){
return instance;
}
//出现线程安全性问题的条件
//多线程的环境下
//必须有共享资源
//对资源进行非原子性操作
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Singleton s1=Singleton.getInstance();
Singleton s2=Singleton.getInstance();
Singleton s3=Singleton.getInstance();
Singleton s4=Singleton.getInstance();
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
}
}
public class Singleon2 {
private Singleon2(){}
//懒汉式
private static volatile Singleon2 instance;
// public static Singleon2 getInstance(){
public static synchronized Singleon2 getInstance(){ //synchronized没有性能保证
//自旋 while(true)
if(instance ==null){
// try {
// Thread.sleep(100);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
synchronized(Singleon2.class){ //锁住有问题的代码
if(instance==null){
instance =new Singleon2(); //双重检查加锁,还有指定重排序的问题
//申请一块空间 1.
//在这块空间中实例化对象2.
//instance的引用指向这块空间地址3.
//但是不一定这样执行,这就引发指令重排序
//volatile 不会出现指令重排序
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class MultiThreadMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//固定线程池
ExecutorService threadPool=
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20);
for(int i=0;i<20;i++){
threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+":"+Singleon2.getInstance());
}
});
}
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号