vue学习笔记(六)— 关于Vuex可以这样简单理解
关于Vuex可以这样简单理解
作者:狐狸家的鱼
本文链接:关于Vuex
GitHub:sueRimn
概念理解
和大多数文章都一样,从概念解释到引出问题再举例解决问题。
官网中,Vuex是状态管理模式,将所有组件的状态集中式存储管理,并在相应的规则中发生变化。
在我的理解中,组件的状态就是数据,Vuex就是一个集中存储管理所有组件的数据的仓库,当组件需要数据时,从仓库中获取对应数据。
如果Vuex是一个仓库,那将整个项目比作超市,每个组件比作超市里不同的货架,货架上要摆放的货物就是状态(数据),货物从仓库获取。
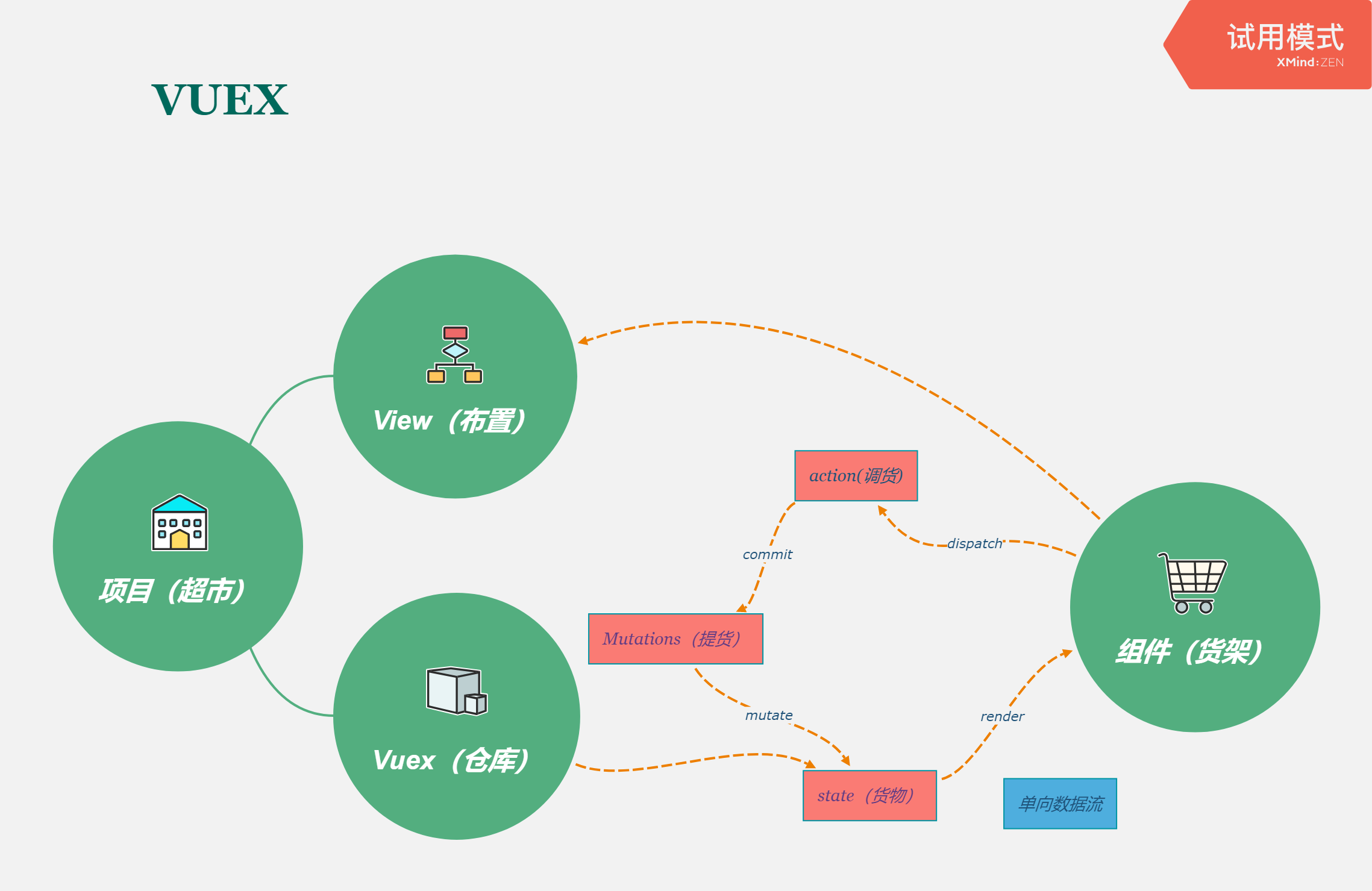
整个流程可以这样理解:
1、超市(项目)建好后,需要在店内(View)布置多个货架(components),仓库(Vuex)存储货物(State),仓库清点货物后(声明全局变量),提取筛选后(getter)的货物,然后摆放在货架(components)上;
2、如果有人买走了货物,就会挪动货架已有的货物重新摆放(mutation),如果缺货了就会重新补货,通知调货(action)
应用场景
当多个组件拥有共享状态时,可以将它们存储在仓库中,而不用单独每个组件内声明获取。
核心概念
1、State
字面上来理解,State就是状态,可以理解为数据,数据都在计算属性中获取得到。
数据在State中声明存储,组件通过this.$store.state.数据名获取相应数据。
如果获取多个数据,可以使用辅助函数mapState
state: { list: { tableData: [], total: 0, currentPage: 1, pageSize: 20, listLoading: false, id: 1 } }
组件中获取数据:
import { mapState } form 'vuex' computed: {// 计算属性中获取数据 ...mapState(['list']) } <el-table :data="list.tableData" highlight-current-row style="width: 100%;margin-bottom: 20px;" height="800px" v-loading="list.listLoading" size="medium" class="planListTable el-table__column-filter-trigger" @cell-dblclick="rowDbClick" >
2、Getter
有时候需要对State中的状态进行派生,就是进行一些额外的筛选操作,就需要在getter里定义。
getter接受state作为第一个参数:
getters: { list: state => state.list }
直接返回state的list数据
可以直接在组件中使用this.$store.getters.list进行获取,也可以使用mapGetter辅助函数。
computed: { ...mapGetters(['list']) },
3、Mutation
更改Vuex的store中状态的唯一方法式提交mutation,在 Vuex 中,mutation 都是同步事务。类似于事件,每个mutation都有一个字符串的类型事件(type)和一个回调函数(handler)。这个回调函数就是对状态进行更改的地方,接受state作为第一个参数。
mutations: { INCREMENT: state => state.list.id++ } methods: { add () { this.$store.commit('INCREMENT') } }
也可以使用辅助函数mapMutations
methods: { ...mapMutations(['INCREMENT']) // 或者 add: 'INCREMENT' }
如果在组件中调用时有额外传入的参数,就是mutation的载荷(payLoad)。
mutations: { INCREMENT: (state, payload) => { state.list.id += payload } } methods: { ...mapMutations(['INCREMENT'], 3) }
4、Action
Action类似mutation,不同在于:
-
Action提交的是mutation,而不能直接变更状态 -
可以包含任何异步操作
mutations: { INCREMENT: (state, payload) => { state.list.id += payload.amount } }, actions: { incrementAsync: context => { context.commit('INCREMENT') } }
Action函数接受context对象,即上下文,包含store实例具有的相同方法和属性,但不是store本身,可以使用context.commit提交mutation。
Action通过store.dispatch分发,Actions 支持同样的载荷方式和对象方式进行分发:
// 以载荷形式分发 store.dispatch('incrementAsync', { amount: 10 }) // 以对象形式分发 store.dispatch({ type: 'incrementAsync', amount: 10 })
在组件中使用 this.$store.dispatch('xxx') 分发 action,或者使用 mapActions 辅助函数将组件的 methods 映射为 store.dispatch 调用
methods: { ...mapActions(['incrementAsync']) }
5、Module
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。
可以将store分割为好几个模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割。
const moduleA = { state: { ... }, mutations: { ... }, actions: { ... }, getters: { ... } } const moduleB = { state: { ... }, mutations: { ... }, actions: { ... } } const store = new Vuex.Store({ modules: { a: moduleA, b: moduleB } }) store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态 store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
对于模块内部的 mutation 和 getter,接收的第一个参数是模块的局部状态对象
默认情况下,模块内部的 action、mutation 和getter 是注册在全局命名空间的——这样使得多个模块能够对同一 mutation或 action作出响应。
如果希望你的模块具有更高的封装度和复用性,你可以通过添加 namespaced: true 的方式使其成为带命名空间的模块。当模块被注册后,它的所有 getter、action 及 mutation 都会自动根据模块注册的路径调整命名。
// module1.js export default { namespaced: true, state: { }, getters: { }, mutations: { }, actions: { } } // store.js import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' import module1 from './module/module1' // const strict = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' const strict = false Vue.use(Vuex) export default new Vuex.Store({ modules:{ module1 }, strict: strict }) // 组件调用 computed: { ...mapGetters('module1', ['list']) },


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号