算法笔记之N叉树的最大深度(用队列、栈和递归实现)
给定一个 N 叉树,找到其最大深度。
最大深度是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点总数。
N 叉树输入按层序遍历序列化表示,每组子节点由空值分隔(请参见示例)。
示例 1:
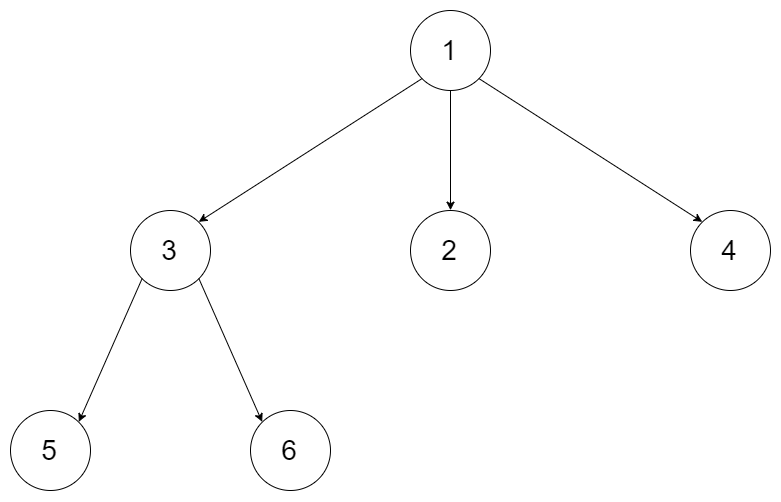
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
输出:3
解题
这个跟求二叉树的最大深度相似,不过是子节点数变成了N。求解的时候可以参考层序遍历用队列实现,比较好理解。也可以用栈实现的后序遍历,但觉得不太好理解。
- 用队列
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
import collections
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
que = collections.deque() # 定义一个队列
que.append(root) # 把根节点添加至队列
depth = 0
while que: # 迭代处理,直到队列为空
size = len(que) # 每次处理一层
depth += 1 # 深度+1
for i in range(size): # 处理一层的所有节点
node = que.popleft() # 从左到右取该层的一个节点
if node.children: # 把该节点的所有子节点加入队列。所有这些子节点属于同一层。计算完毕后进入下一个while循环。
for j in range(len(node.children)):
que.append(node.children[j])
return depth
- 栈
这里采用的后序遍历。
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
import collections
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:
stack = []
depth = 0
tmp = 0
if root:
stack.append(root)
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
if node: # 节点不为空,重新入栈,但是在后面添加一个空节点,标记一下该节点的子节点已经做过了处理
tmp += 1 # 当还有节点时,tmp会一直增加,直到到达最下面一层
stack.append(node) # 重新入栈
stack.append(None) # 添加一个空节点作为标记
if node.children: # 所有子节点入栈
for i in range(len(node.children)):
stack.append(node.children[i])
else: # 节点为空,说明下一个节点被标记为了不作处理,直接跳过
stack.pop()
tmp -= 1
depth = max(depth,tmp)
return depth
- 递归
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
depth = 0
for i in range(len(root.children)):
depth = max(depth, self.maxDepth(root.children[i]))
return depth + 1
'''
如果是二叉树,因为最多只有2个子节点,可以省去for循环,直接返回左右子树的最大深度即可
return 1 + max(self.maxDepth(root.left), self.maxDepth(root.right))
'''




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号