接口隔离原则
官方定义
接口隔离原则(Interface Segregation Principle),又称ISP原则
1、 客户端不应该依赖它不需要的接口
2、 类间的依赖关系应该建立在最小的接口上
基本介绍
通俗的来讲,不要在一个接口中定义多个方法,接口应该尽量细化
以下案例就是实现接口隔离
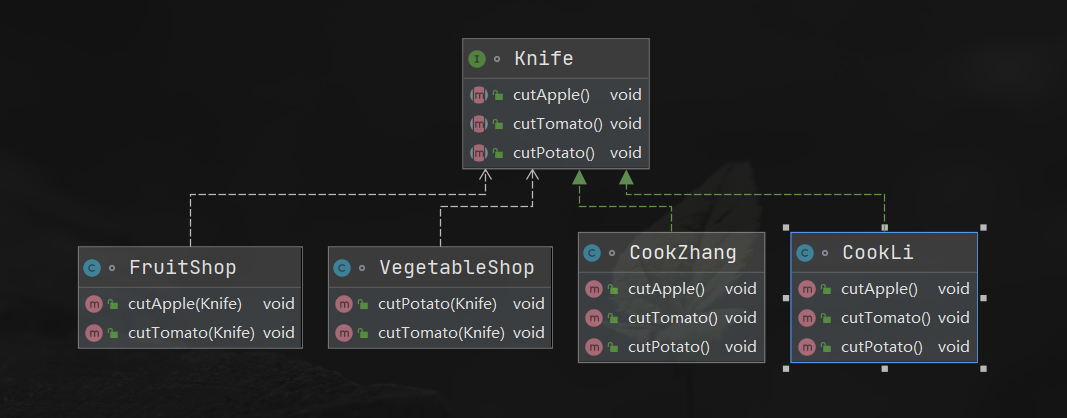
package jiekogeli;
public class SegregationDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new FruitShop().cutApple(new CookZhang());
new FruitShop().cutTomato(new CookZhang());
new VegetableShop().cutTomato(new CookLi());
new VegetableShop().cutPotato(new CookLi());
}
}
interface Knife {
void cutApple();
void cutTomato();
void cutPotato();
}
class CookZhang implements Knife {
@Override
public void cutApple() {
System.out.println("张师傅在切苹果");
}
@Override
public void cutTomato() {
System.out.println("张师傅在切土豆");
}
@Override
public void cutPotato() {
System.out.println("张师傅在切番茄");
}
}
class CookLi implements Knife {
@Override
public void cutApple() {
System.out.println("李师傅在切苹果");
}
@Override
public void cutTomato() {
System.out.println("李师傅在切土豆");
}
@Override
public void cutPotato() {
System.out.println("李师傅在切番茄");
}
}
class FruitShop {
public void cutApple(Knife knife) {
knife.cutApple();
}
public void cutTomato(Knife knife) {
knife.cutTomato();
}
}
class VegetableShop {
public void cutPotato(Knife knife) {
knife.cutPotato();
}
public void cutTomato(Knife knife) {
knife.cutTomato();
}
}
修改后
package jiekogeli;
public class SegregationDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new FruitShop().cutApple(new CookZhang());
new FruitShop().cutTomato(new CookZhang());
new VegetableShop().cutTomato(new CookLi());
new VegetableShop().cutPotato(new CookLi());
}
}
interface AppleKnife {
void cutApple();
}
interface TomatoKnife {
void cutTomato();
}
interface PotatoKnife {
void cutPotato();
}
class CookZhang implements AppleKnife, TomatoKnife {
@Override
public void cutApple() {
System.out.println("张师傅在切苹果");
}
@Override
public void cutTomato() {
System.out.println("张师傅在切番茄");
}
}
class CookLi implements TomatoKnife, PotatoKnife {
@Override
public void cutTomato() {
System.out.println("李师傅在切土豆");
}
@Override
public void cutPotato() {
System.out.println("李师傅在切番茄");
}
}
class FruitShop {
public void cutApple(AppleKnife knife) {
knife.cutApple();
}
public void cutTomato(TomatoKnife knife) {
knife.cutTomato();
}
}
class VegetableShop {
public void cutPotato(PotatoKnife knife) {
knife.cutPotato();
}
public void cutTomato(TomatoKnife knife) {
knife.cutTomato();
}
}
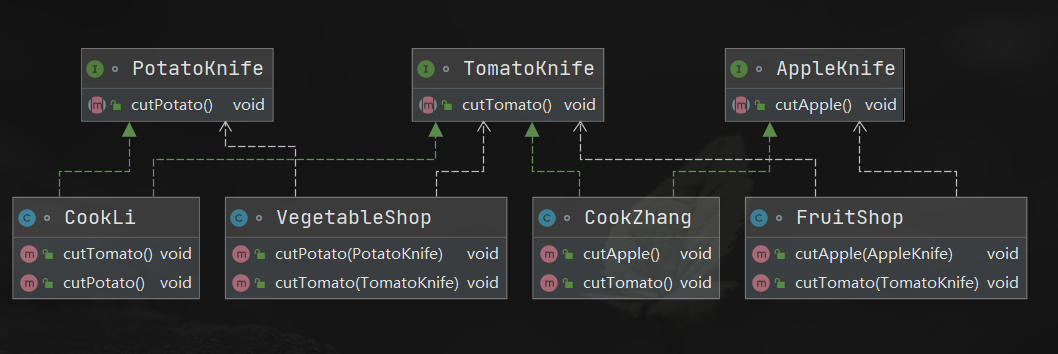
案例总结:
接口隔离原则就是当我一个类通过接口依赖(使用)另一个类的时候,要保证依赖的该接口是最小的,接口里面有方法是用不到的,就进行隔离,而隔离的做法就是,对原来的接口进行拆分,拆分为最小粒度,来避免耦合。
与单一职责原则对比
单一职责原则:合理的职责分解,一个类只负责一项职责
接口隔离原则:类间的依赖关系应该建立在最小的接口上
相同点
- 都要求对结构进行拆分,都要求最小的粒度,都希望减少耦合
不同点
- 单一职责原则:类与接口职责单一,注重的是职责
- 接口隔离原则:要求我们尽量使用多个专门的接口,注重的是接口的设计。
当然了,我们使用接口隔离原则进行拆分的时候,要遵循单一职责原则
转载请注明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/stu-jyj3621



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号