需求背景
公司做的数据分析系统中想要将Excel中的条件格式功能搬过来。原因:纯表格中的数据展示只有字符没有样式,比较难发现更多维度的信息,当有了色阶效果后分析人员可以更容易在数据中发现更多信息如:是否波动剧烈、是否呈聚合趋势、是否有规律等
下面我们试着分析如何实现这样的效果。
实现逻辑
需要先获得每列的最大值max和最小值min,并且计算当前值在最大值和最小值之间的位置;
先来实现一个获取色阶颜色值的方法,关于色阶的计算使用到的是线性插值的方式,有一个标准的公式,下面是 ChatGPT 回答:

实现代码
设置excel中表格的自定义背景颜色
// 创建一个 workbook 对象
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
// 创建一个 sheet对象
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
//创建一行对象
Row row = sheet.createRow((short) 1);
//获取样式对象
XSSFCellStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
//自定义颜色对象
XSSFColor color = new XSSFColor();
//根据你需要的rgb值获取byte数组
color.setRGB(intToByteArray(getIntFromColor(255,255,255)));
//自定义颜色
style.setFillForegroundColor(color);
style.setFillPattern(CellStyle.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
Cell cell = row.createCell((short) 1);
cell.setCellValue("X1");
cell.setCellStyle(style);
/**
* rgb转int
*/
private static int getIntFromColor(int Red, int Green, int Blue){
Red = (Red << 16) & 0x00FF0000;
Green = (Green << 8) & 0x0000FF00;
Blue = Blue & 0x000000FF;
return 0xFF000000 | Red | Green | Blue;
}
/**
* int转byte[]
*/
public static byte[] intToByteArray(int i) {
byte[] result = new byte[4];
result[0] = (byte)((i >> 24) & 0xFF);
result[1] = (byte)((i >> 16) & 0xFF);
result[2] = (byte)((i >> 8) & 0xFF);
result[3] = (byte)(i & 0xFF);
return result;
}
获取RGB的值
/**
* 获取RGB值
* @param value 当前值
* @param min 最小值
* @param max 最大值
* @return rgb的数组
List<Integer[]> colors=new ArrayList<>();
colors.add(new Integer[]{90,138,198});
colors.add(new Integer[]{252,252,255});
colors.add(new Integer[]{248,105,107});
*/
private Integer[] getRGB(double valueDou,BigDecimal min,BigDecimal max,List<Integer[]> colorsRgbList)
{
//将colors的hex值转换为rgb的值
// List<Integer[]> colorsRgbList=new ArrayList<>();
// for (String color : colors) {
// Integer[] rgbValue = hexToRgb(color);
// colorsRgbList.add(rgbValue);
// }
BigDecimal value=new BigDecimal(valueDou);
//集合的长度
BigDecimal colorsSize = new BigDecimal(colorsRgbList.size());
//判断传过来的值是否大于最大值或者小于最小值
if(value.compareTo(min)==-1) return colorsRgbList.get(0);
if(value.compareTo(max)==1)return colorsRgbList.get(colorsRgbList.size()-1);
//计算当前值在最大值最小值之间的位置
BigDecimal rang=max.subtract(min);
BigDecimal weight=BigDecimalUtils.divide(value.subtract(min), rang,1);
//计算颜色列表的最后一个索引值
BigDecimal qian= colorsSize.subtract(BigDecimal.ONE).multiply(weight);
qian=qian.setScale(0,BigDecimal.ROUND_UP);
BigDecimal endIndex;
if(qian.compareTo(BigDecimal.ONE)==1) {
endIndex=qian;
}else {
endIndex=BigDecimal.ONE;
}
//通过最后一个索引值获取两个颜色的最小颜色(起始色)和最大颜色(结束色)
Integer[] minColor=colorsRgbList.get(endIndex.subtract(BigDecimal.ONE).intValue());
Integer[] maxColor=colorsRgbList.get(endIndex.intValue());
//计算色阶比例
BigDecimal C=colorsSize.subtract(BigDecimal.ONE);
weight= weight.multiply(C).subtract(endIndex.subtract(BigDecimal.ONE));
//线性差值公式 c=(1-t)*c1+t*c2 c1、c2是起始色和结束色的rgb的值 t是一个介于0到1之间的值 c是计算出来的中间颜色
BigDecimal t1=BigDecimal.ONE.subtract(weight);
Integer r=(t1.multiply(new BigDecimal(minColor[0])).add(weight.multiply(new BigDecimal(maxColor[0])))).intValue();
Integer g=(t1.multiply(new BigDecimal(minColor[1])).add(weight.multiply(new BigDecimal(maxColor[1])))).intValue();
Integer b=(t1.multiply(new BigDecimal(minColor[2])).add(weight.multiply(new BigDecimal(maxColor[2])))).intValue();
return new Integer[]{r,g,b};
}
/**
* 将hex值转换为RGB的值(颜色)
* @param hex hex的值
* @return RGB的值
*/
private Integer[] hexToRgb(String hex) {
Integer r = Integer.parseInt(hex.substring(1, 3), 16);
Integer g = Integer.parseInt(hex.substring(3, 5), 16);
Integer b = Integer.parseInt(hex.substring(5, 7), 16);
return new Integer[]{r, g, b};
}
最终效果
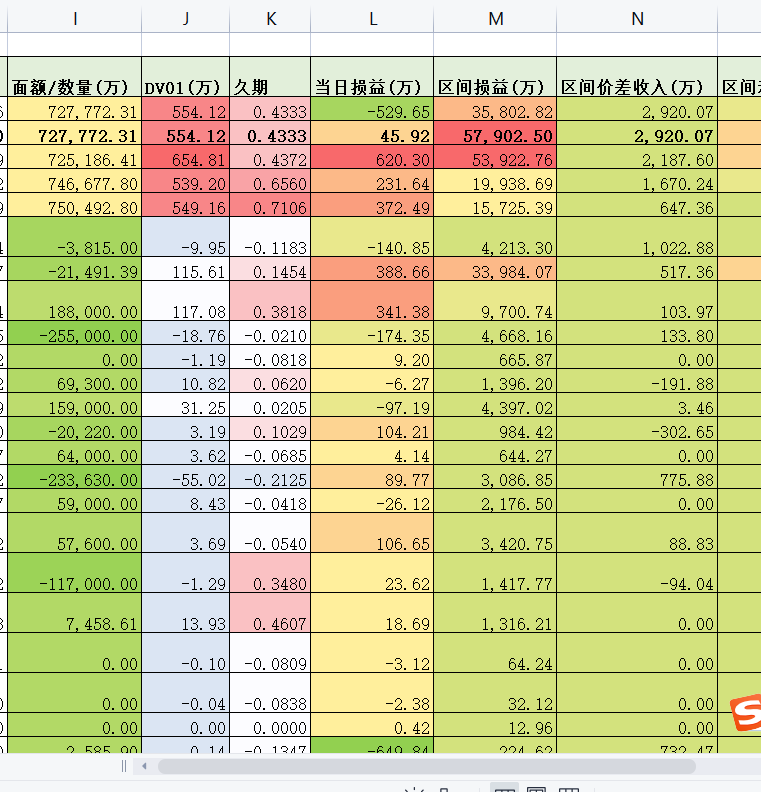
总结
- 实现此功能中最重要也是最难的点就是在于色阶值的计算、线性插值公式的理解,这一步理解透了其他的就简单了。




 posted on
posted on


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号