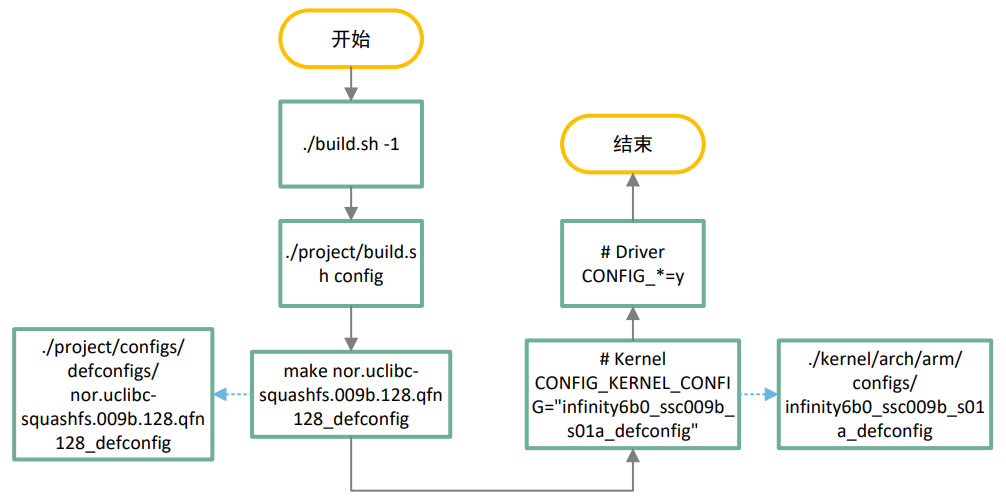
1 编译流程顺序
- 开发板编译时,文件的指定编译流程顺序
- 在kernel目录下make ARCh=arm menuconfig 配置选项后,生成的是.config,也只能在当前目录下直接make ARCH=arm编译才会生效
- 想要整个项目的生效生成KO文件或者编译进去内核,需要同步到项目编译的mk文件中
![]()
2 驱动hello代码
![]()
2.1 hello.c
Code
#include
#include
#include
static int __init funcIn_init(void)
{
int a = 9;
printk("hello world in module a=%d\n", a++);
return 0;
}
static void __exit funcOut_exit(void)
{
printk("hello world out module\n");
}
module_init(funcIn_init);
module_exit(funcOut_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("st");
2.2 Makefile
Code
obj-$(CONFIG_HELLO)+=hello.o
2.3 kconfig
Code
config HELLO
tristate "hello world"
help
hello hello
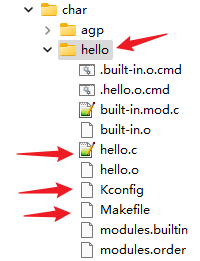
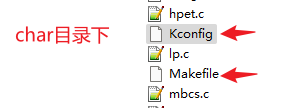
3.4 ./driver/char目录下
![]()
![]()
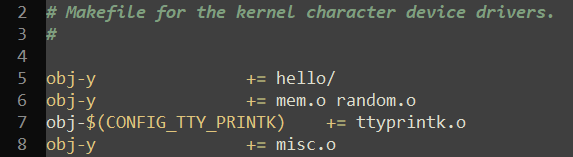
Makefile
obj-y += mem.o random.o
![]()
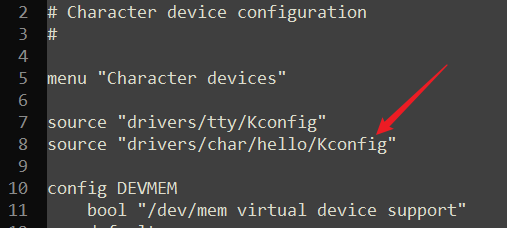
Kconfig
source "drivers/char/hello/Kconfig"
- driver目录下的Kconfig和Makefile不需要修改
- 只需要修改Driver/char子模块修改即可
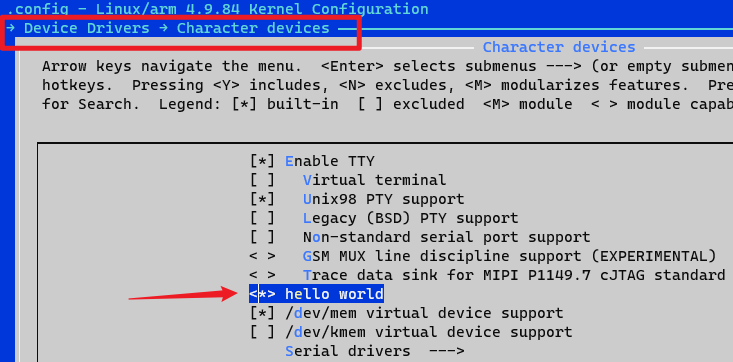
4 图形化编译kernel保存.config
![]()
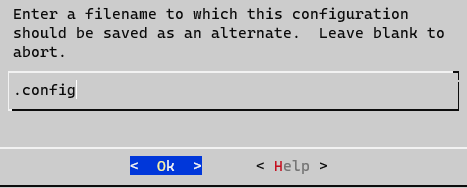
4.1 保存
![]()
5 配置选项同步
- 因为嵌入式开发板是指定配置文件进行编译的,不是按照.config去编译的,所以按照文章开头的编译流程,找到内核编译选项文件进行添加和修改即可。
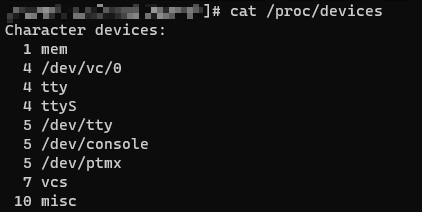
- 然后,回到开发板主目录下,运行build.sh等编译脚本进行整体系统编译,之后将固件烧录到开发板,cat /proc/kmsg 查看
6 驱动加载之后察看
![]()
语法参考链接
![]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号