nodejs中的全局对象以及系统模块
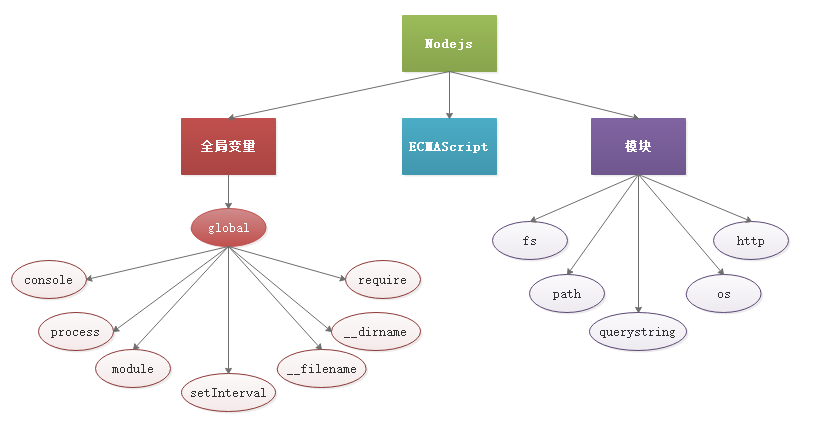
一。node中有一个全局变量global,是node中最大的一个对象,相当于浏览器中的window对象,global中的成员在使用时,可以省略global ,下面介绍几个全局对象global中的成员:
-
console打印
-
process,和进程相关的对象
-
setInterval,同理,也是node中的,不是浏览器中的
-
require(),它是全局对象global中的一个方法,用于在js文件中引入另外的文件
-
__dirname,当前执行文件的绝对路径(在js文件中使用)
-
__filename,当前执行文件的绝对路径,包含文件名(在js文件中使用)
二,系统模块
>path模块:处理路径的模块
//使用前首先要加载
let path = require('path');
//调用path模块中的方法,来处理相应的问题,下面列举path模块中的几个方法
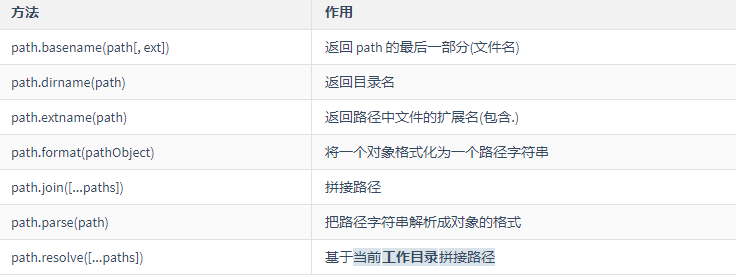
// extname -- 获取文件后缀
console.log(path.extname('index.html')); // .html
// join -- 智能拼接路径
console.log(path.join('/a', 'b', 'c')); // \a\b\c
>fs模块:文件操作模块
//使用前引入模块
const fs = require('fs');
调用fs模块的方法
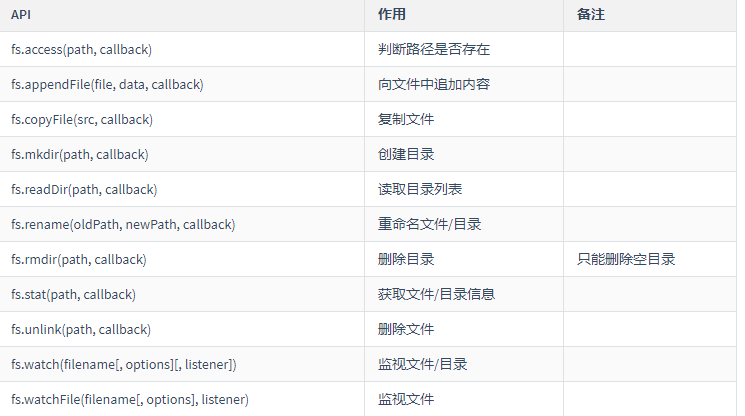
// 功能:判断文件或路径是否存在
// fs.access(需要判断的路径, 检测路径是否存在的一个回调函数);
fs.access(' 路径', (err) => {
// err 为 null,表示没有错误;意思是表示判断的文件 存在
// err 为 错误对象,意思判断的文件 不存在
if (err) {
console.log('文件不存在');
} else {
console.log('文件存在');
}
});
// readFile -- 异步读取文件
fs.readFile('./test.json', 'utf-8', (err, data) => {
if (err) {
console.log('读取文件出错');
} else {
console.log(data); // 读取到的原始数据
}
});
// writeFile -- 异步写入文件
fs.writeFile('./abc.html', 'hello world', (err) => {
if (err) {
console.log('写入文件失败');
} else {
console.log('文件写入成功');
}
});
//加载模块
const querystring = require('querystring');
//调用querystring模块中的方法
// parse -- 将查询字符串解析成JS对象
console.log(querystring.parse('id=1&name=zs&age=20'));
// { id: '1', name: 'zs', age: '20' }
// stringify -- 将JS对象转成查询字符串
console.log(querystring.stringify({ id: '1', name: 'zs', age: '20' }));
// id=1&name=zs&age=20
>
//加载模块
const url = require('url');
// 直接提供一个完整的url
let myURL = new URL('http://www.xxx.com/test.html?id=11&age=22');
// 或
// 提供两个参数,一是文件路径及参数部分,二是域名,总之,二者组合必须是完整的url
let myURL = new URL('/test.html?id=11&age=22', 'http://www.xxx.com');
// 得到的myURL是一个对象,包含url中的各个部分
// 如果需要解析参数部分,则使用querystring模块,或使用URL的一个子对象searchParams中的get方法
let age = myURL.searchParams.get('age'); // 22
>http模块:http服务器处理模块,可以使用http模块搭建服务器
// 1. 加载http模块
const http = require('http');
// 2. 创建服务对象,一般命名为server
const server = http.createServer(); // create创建、server服务器
// 3. 设置端口,开启服务
server.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('服务器启动了');
});
// 4. 给server对象注册请求(request)事件,监听浏览器的请求。只要有浏览器的请求,就会触发该事件
server.on('request', (req, res) => {
});




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号