代码随想录Day23
题目列表
- 39.组合总和(LeetCode)
- 40.组合总和II(LeetCode)
- 131.分割回文串(LeetCode)
解题过程
39.组合总和
题目描述

解题思路
回溯中的组合问题,但是该问题中允许组合里的元素重复使用,所以在回溯三部曲中,startIndex 不需要在递归中排除当前已使用的元素,也就是在循环中调用递归函数时传参是 i.
剪枝操作:排序之后,如果 sum + 当前 已经大于 target,那么证明已经不符合条件。(本题代码中没有使用)。
代码展示
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0);
return result;
}
public void backtracking(int[] candidates, int target, int sum,int start){
if(sum > target) return;
if(sum == target){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++){
path.add(candidates[i]);
sum += candidates[i];
backtracking(candidates, target, sum, i);
path.removeLast();
sum -= candidates[i];
}
}
}
40.组合总和II
题目描述

解题思路
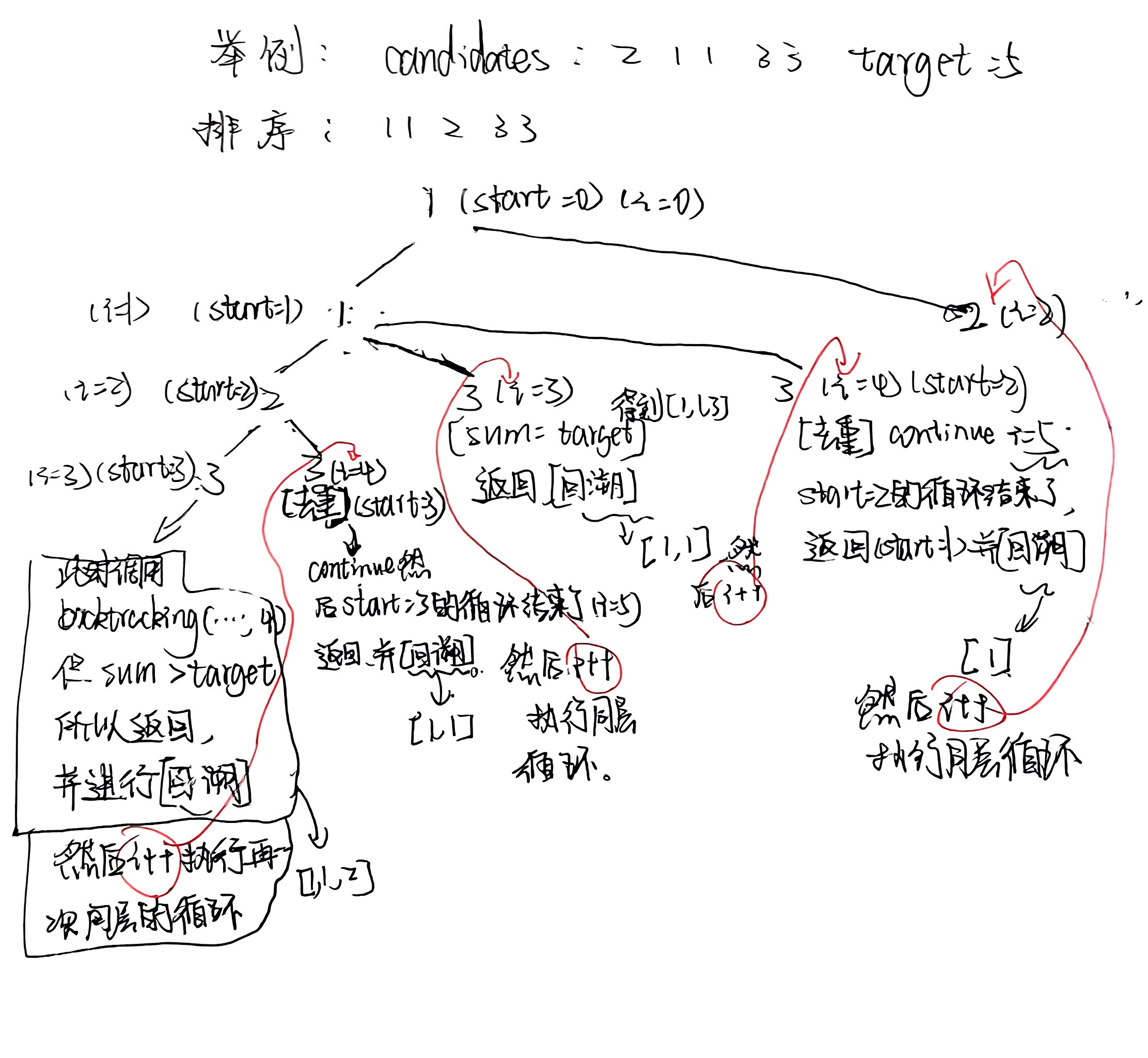
去重
根据题目给的示例可以看出,同一条“路径”上仅仅不允许使用已经使用过的元素(不能重复使用数组中下标相同的元素,下标不同数值相同是允许使用的)
而不同“路径”(也就是另一个结果集)中,不允许使用之前“路径”使用过的数值。因为如果允许的话,会出现两个或两个以上一样的组合,这是不正确的。
对于一条路径中的去重:
一条路径在代码中体现为“每一次元素的使用”都是在不同的循环体中(start不同的for循环),只需要保证下标相同的元素不重复使用,所以让 start == i + 1即可。
不同路径的去重:
不同路径在代码中体现为:在同一层for循环(start相同,也就是同一层递归中),要判断当前元素与前一个元素数值是否相同(i > start 且 candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]),相同就跳过,继续 i++.
代码展示
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0);
return result;
}
public void backtracking(int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int start){
if(sum == target){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = start; i < candidates.length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++) {
if(i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]){
continue;
}
path.add(candidates[i]);
sum += candidates[i];
backtracking(candidates, target, sum, i + 1);
path.removeLast();
sum -= candidates[i];
}
}
}
131.分割回文串
题目描述

解题思路
代码展示
class Solution {
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
backtracking(s, new StringBuilder(), 0);
return result;
}
public void backtracking(String s, StringBuilder sb, int start) {
if(start == s.length()){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = start; i < s.length(); i++){
sb.append(s.charAt(i));
if(isPalindrome(sb)){
path.add(sb.toString());
}else{
continue; //同层递归中寻找下一个组合(重新切割)
}
//只有当前sb是回文子串才会继续这条路径
backtracking(s, new StringBuilder(), i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
public boolean isPalindrome(StringBuilder sb){
for(int i = 0; i < sb.length()/2; i++){
if(sb.charAt(i) != sb.charAt(sb.length() - 1 - i)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号