代码随想录Day13
题目列表
- 递归法:144.二叉树的前序遍历|94.二叉树的中序遍历|145.二叉树的后序遍历(LeetCode)
- 迭代法:144.二叉树的前序遍历|94.二叉树的中序遍历|145.二叉树的后序遍历(LeetCode)
- 统一迭代:144.二叉树的前序遍历|94.二叉树的中序遍历|145.二叉树的后序遍历(LeetCode)
- 102.二叉树层序遍历(LeetCode)
解题过程
递归法:144.二叉树的前序遍历|94.二叉树的中序遍历|145.二叉树的后序遍历
题目描述
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 前序遍历 。
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 中序遍历 。
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 后序遍历 。
解题思路
- 首先明确前中后序遍历二叉树是什么顺序:
前序遍历:中左右
中序遍历:左中右
后序遍历:左右中 - 然后知道左子树右子树这种形式适合递归,使用递归要明确三个要点:
递归函数的参数和返回值类型;
递归结束条件:也就是边界条件;
一次递归的逻辑。
代码展示
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
//前序递归遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
preorder(root,list);
return list;
}
public void preorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list){
if(root == null){
return;
}
list.add(root.val);
preorder(root.left,list);
preorder(root.right,list);
}
}
//中序递归遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root,list);
return list;
}
public void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list){
if(root == null){
return;
}
inorder(root.left,list);
list.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right,list);
}
}
//后序递归遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
postorder(root,list);
return list;
}
public void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list){
if(root == null){
return;
}
postorder(root.left,list);
postorder(root.right,list);
list.add(root.val);
}
}
迭代法:144.二叉树的前序遍历|94.二叉树的中序遍历|145.二叉树的后序遍历
题目描述
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 前序遍历 。
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 中序遍历 。
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 后序遍历 。
解题思路
- 前序
前序遍历是中左右的顺序,在不使用递归的情况下,可以借助栈来保存遍历过的节点,并且在恰当时间返回。
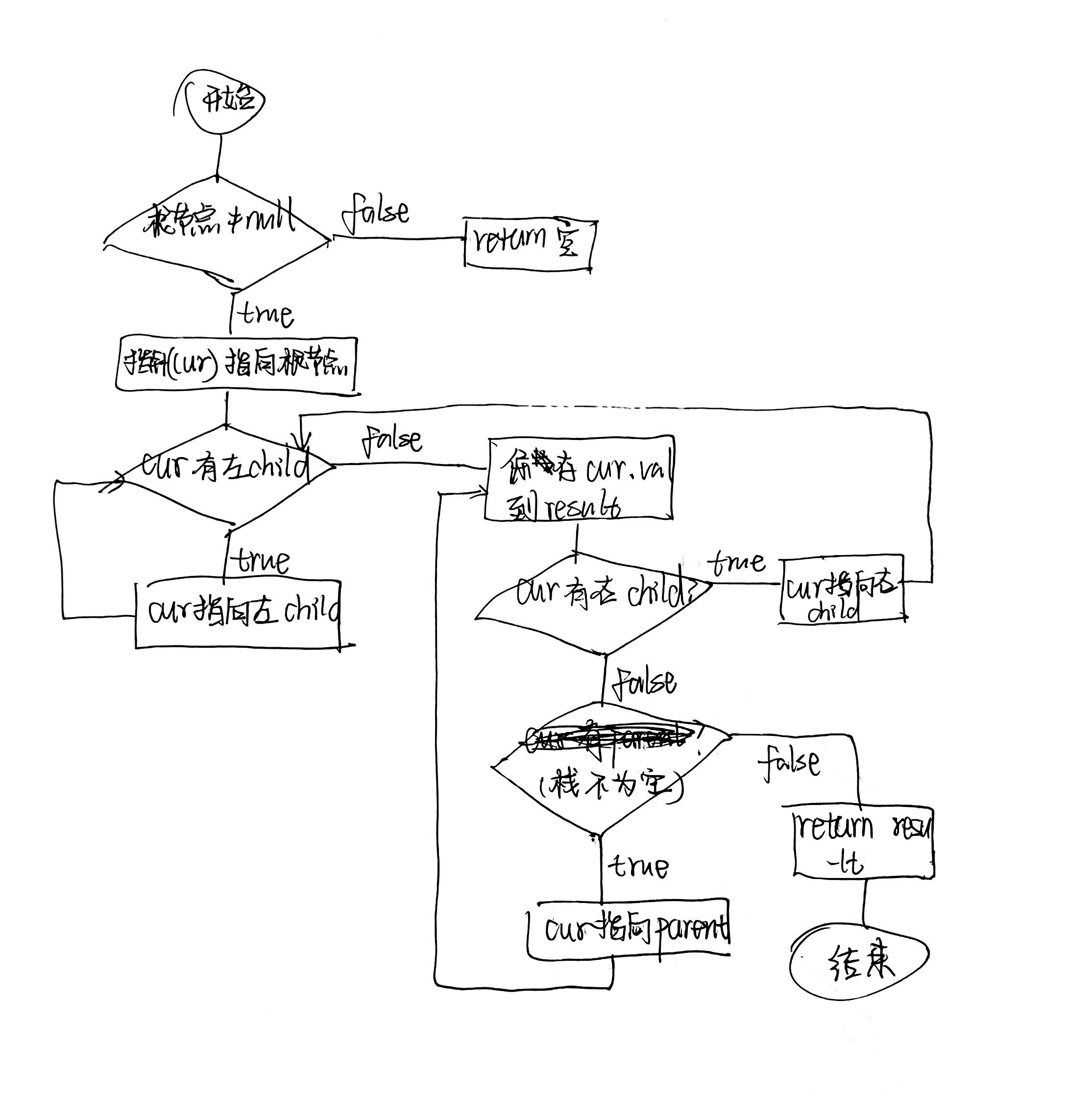
首先将根节点放到栈中,然后在循环中先处理栈顶元素(每次循环中处理的子树的中间节点),然后让右节点入栈,再让左节点入栈,左节点此时是栈顶元素,也就是下一次循环要处理的子树的中间节点,左子树处理完之后再处理右子树,一直到遍历完最后一个右节点,此时栈为空,循环结束。 - 中序
中序遍历是左中右的顺序,可以想象我们是从根节点开始遍历这棵树的,但是在第一次遍历中间节点的时候我们不能对其做出处理,而是要继续寻找它的左 child 。
流程图大致如下(代码中是先让 cur 指向左右 child 再判断 cur 是否为空的,流程图不大严谨)
![image]()
- 后序
后序是左右中的顺序,那么可以按照倒过来“中右左”的顺序进行遍历和保存,结束之后反转结果即可。
代码展示
//前序
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
//迭代
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
if(root == null){
return result;
}
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
result.add(cur.val);
if(cur.right != null){
stack.push(cur.right);
}
if(cur.left != null){
stack.push(cur.left);
}
}
return result;
}
}
//中序
//迭代
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return result;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
if (cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}else{
cur = stack.pop();
result.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return result;
}
}
//后序
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return result;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
result.add(node.val);
//出栈顺序:右左
if (node.left != null){
stack.push(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null){
stack.push(node.right);
}
}
Collections.reverse(result);
return result;
}
}
统一迭代:144.二叉树的前序遍历|94.二叉树的中序遍历|145.二叉树的后序遍历(待做)
题目描述
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 前序遍历 。
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 中序遍历 。
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 后序遍历 。
解题思路
代码展示
102.二叉树层序遍历
题目描述
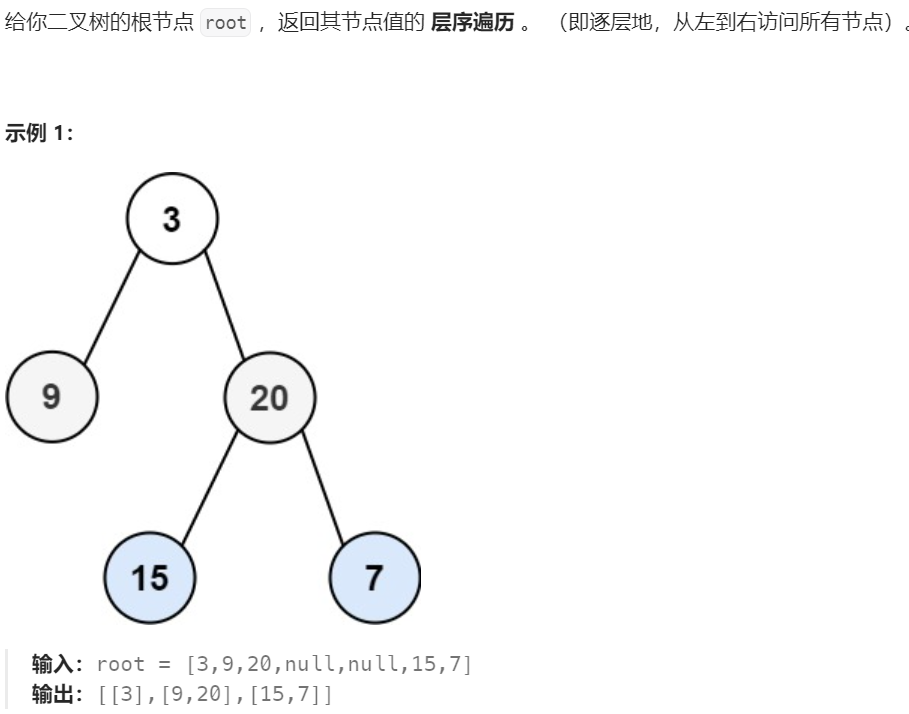
解题思路
使用一个队列,先将第一层放进去,记录第一层的大小 size ,每次遍历这一层的下一层,同时根据 size 将这一层放入结果中并弹出队列,此时队列大小作为下一次循环中弹出元素数目的依据。
代码展示
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null) return result;
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> levelList = new ArrayList<>();
while(size > 0){
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
levelList.add(cur.val);
if(cur.left != null) queue.add(cur.left);
if(cur.right != null) queue.add(cur.right);
size--;
}
result.add(levelList);
}
return result;
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号