代码随想录Day12
题目列表
- 150.逆波兰表达式求值(LeetCode)
- 239.滑动窗口最大值(LeetCode)
- 347.前 K 个高频元素(LeetCode)
解题过程
150.逆波兰表达式求值
题目描述

解题思路
之前上编译原理课程时有接触过逆波兰式,逆波兰式就是后序遍历表达式对应的二叉树的结果,它的特点是操作符总是在两个操作数的后面,也就是说不管怎么样,一个操作符的前面的“两大块”就是这个操作符对应的操作数。
逆波兰式可以通过栈计算。从左到右扫描表达式,遇到操作数就压入栈中,遇到操作符就从栈中弹出相应数量的操作数进行计算,然后将结果压回栈中。最终栈顶的元素就是表达式的计算结果。
代码展示
class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int result = 0;
for(String s : tokens){
if(isDigit(s)){
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(s));
}
else{
int a = stack.pop();
int b = stack.pop();
if(s.equals( "+")){
stack.push(a + b);
}
else if(s.equals("-")){
stack.push(b - a);
}
else if(s.equals("*")){
stack.push(b * a);
}
else if(s.equals("/")){
stack.push(b / a);
}
}
}
return stack.pop();
}
public boolean isDigit(String s){
try {
Integer.parseInt(s);
return true;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
return false;
}
}
}
239.滑动窗口最大值
题目描述

解题思路
看了代码随想录的视频和题解,写了个数组模拟了下。
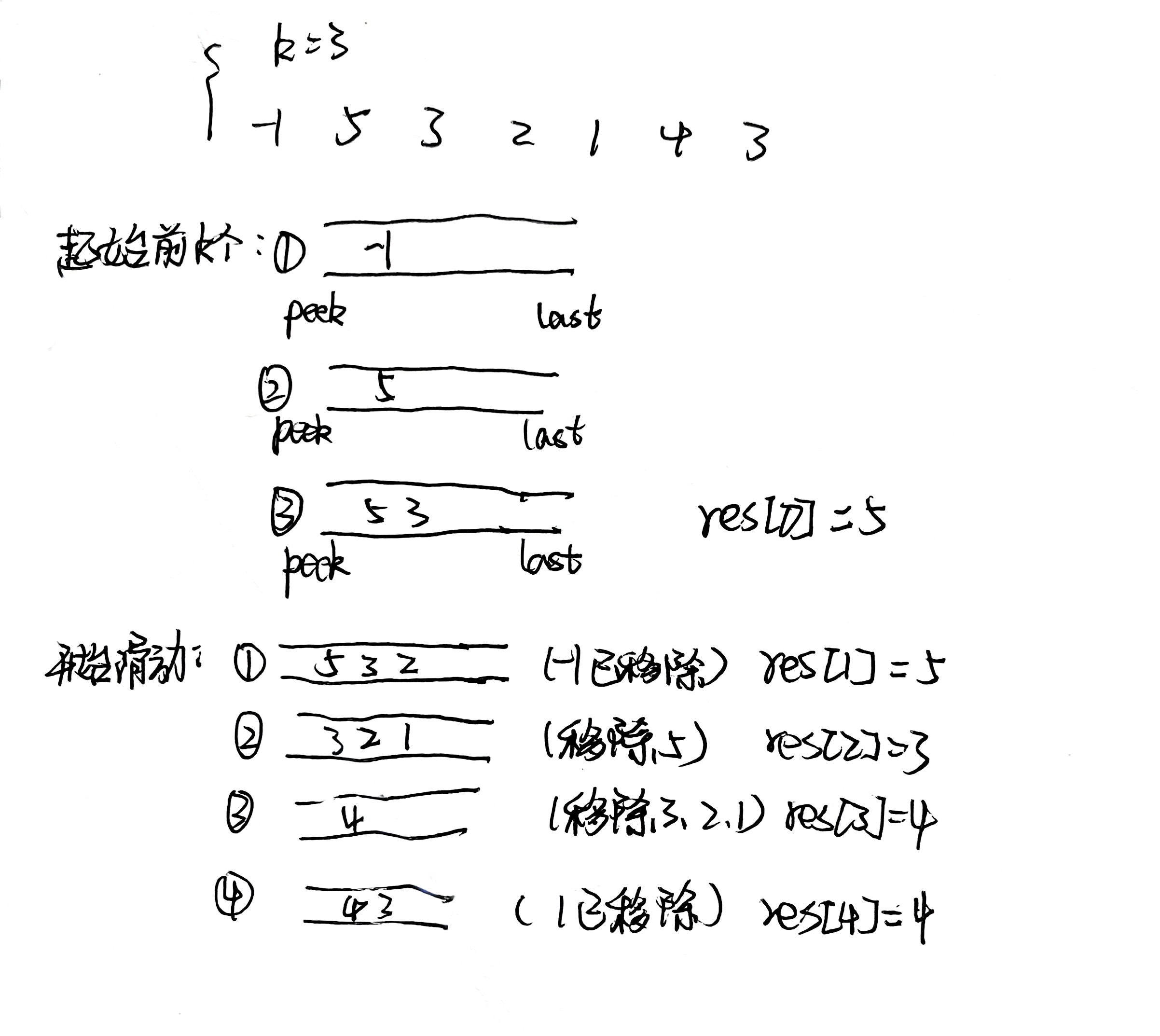
代码展示
class MyQueue{
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();
void poll(int val){
if(!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekFirst() == val){
//队头出
deque.pollFirst();
}
}
void push(int val){
while(!deque.isEmpty() && val > deque.getLast()){
//删队尾
deque.removeLast();
}
//队尾进
deque.offerLast(val);
}
int peek(){
return deque.peek();
}
}
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
MyQueue myqueue = new MyQueue();
int res[] = new int[nums.length - k + 1];
//处理前k个元素
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
myqueue.push(nums[i]);
}
res[0] = myqueue.peek();
//滑动窗口开始移动
for(int i = k; i < nums.length; i++){
myqueue.poll(nums[i - k]);
myqueue.push(nums[i]);
res[i - k + 1] = myqueue.peek();
}
return res;
}
}
347.前 K 个高频元素
题目描述

解题思路
https://programmercarl.com/0347.前K个高频元素.html#算法公开课
注意事项
小顶堆
优先队列比较规则
代码展示
class Solution {
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i : nums){
map.put(i, map.getOrDefault(i, 0)+1);
}
/*
*Lambda 表达式,用于定义 PriorityQueue(优先队列/堆)的 比较规则。
pair1 和 pair2 是优先队列中的两个元素(这里是 int[2] 数组,存储 [数字, 出现次数])。
pair1[1] - pair2[1] 表示按 出现次数(pair[1])从小到大排序(小顶堆)。
如果 pair1[1] - pair2[1] < 0,说明 pair1 的出现次数更少,应该排在前面。
如果 pair1[1] - pair2[1] > 0,说明 pair2 的出现次数更少,应该排在前面。
如果 = 0,则两者相等,顺序无关紧要。
*/
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((pair1, pair2) -> pair1[1] - pair2[1]);
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()){
if (pq.size() < k) {
pq.add(new int[]{entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()});
} else {
if (entry.getValue() > pq.peek()[1]) {
pq.poll();
pq.add(new int[]{entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()});
}
}
}
int res[] = new int[k];
for(int i = k - 1; i >= 0;i--){
res[i] = pq.poll()[0];
}
return res;
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号