Django(06):Django 表单
HTML表单是网站交互性的经典方式。 本章将介绍如何用Django对用户提交的表单数据进行处理。
一、HTTP 请求
HTTP协议以"请求-回复"的方式工作。客户发送请求时,可以在请求中附加数据。服务器通过解析请求,就可以获得客户传来的数据,并根据URL来提供特定的服务。
1、GET 方法
我们在之前的项目中创建一个 search.py 文件,用于接收用户的请求:
/HelloWorld/HelloWorld/search.py 文件代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from django.http import HttpResponse from django.shortcuts import render_to_response # 表单 def search_form(request): return render_to_response('search_form.html') # 接收请求数据 def search(request): request.encoding='utf-8' if 'q' in request.GET and request.GET['q']: message = '你搜索的内容为: ' + request.GET['q'] else: message = '你提交了空表单' return HttpResponse(message)
在模板目录 templates 中添加 search_form.html 表单:
/HelloWorld/templates/search_form.html 文件代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>菜鸟教程(runoob.com)</title> </head> <body> <form action="/search" method="get"> <input type="text" name="q"> <input type="submit" value="搜索"> </form> </body> </html>
urls.py 规则修改为如下形式:
/HelloWorld/HelloWorld/urls.py 文件代码:
from django.conf.urls import url from . import view,testdb,search urlpatterns = [ url(r'^hello$', view.hello), url(r'^testdb$', testdb.testdb), url(r'^search-form$', search.search_form), url(r'^search$', search.search), ]
访问地址 http://127.0.0.1:8000/search-form 并搜索,结果如下所示:
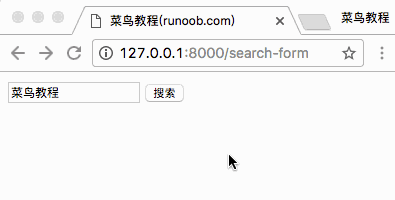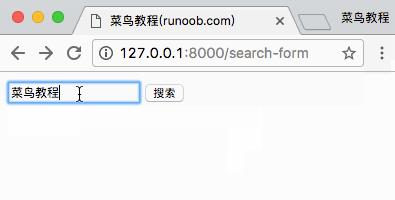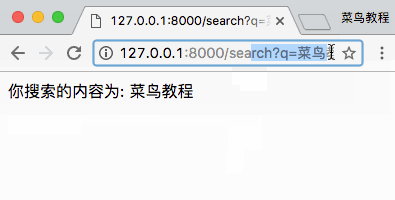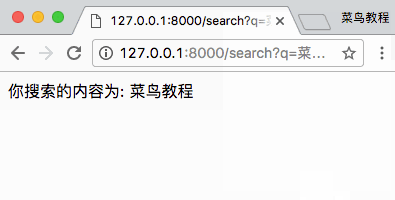
2、POST 方法
上面我们使用了GET方法。视图显示和请求处理分成两个函数处理。
提交数据时更常用POST方法。我们下面使用该方法,并用一个URL和处理函数,同时显示视图和处理请求。
我们在 templates 创建 post.html:
/HelloWorld/templates/post.html 文件代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>菜鸟教程(runoob.com)</title> </head> <body> <form action="/search-post" method="post"> {% csrf_token %} <input type="text" name="q"> <input type="submit" value="Submit"> </form> <p>{{ rlt }}</p> </body> </html>
在模板的末尾,我们增加一个 rlt 记号,为表格处理结果预留位置。
表格后面还有一个{% csrf_token %}的标签。csrf 全称是 Cross Site Request Forgery。这是Django提供的防止伪装提交请求的功能。POST 方法提交的表格,必须有此标签。
在HelloWorld目录下新建 search2.py 文件并使用 search_post 函数来处理 POST 请求:
/HelloWorld/HelloWorld/search2.py 文件代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from django.shortcuts import render from django.views.decorators import csrf # 接收POST请求数据 def search_post(request): ctx ={} if request.POST: ctx['rlt'] = request.POST['q'] return render(request, "post.html", ctx)
urls.py 规则修改为如下形式:
/HelloWorld/HelloWorld/urls.py 文件代码:
from django.conf.urls import url from . import view,testdb,search,search2 urlpatterns = [ url(r'^hello$', view.hello), url(r'^testdb$', testdb.testdb), url(r'^search-form$', search.search_form), url(r'^search$', search.search), url(r'^search-post$', search2.search_post), ]
访问 http://127.0.0.1:8000/search-post 显示结果如下:
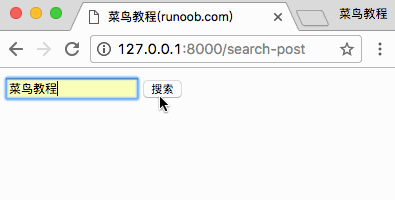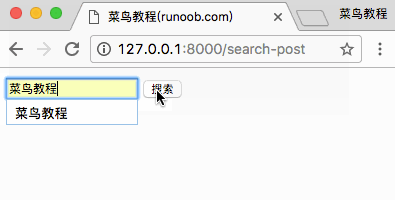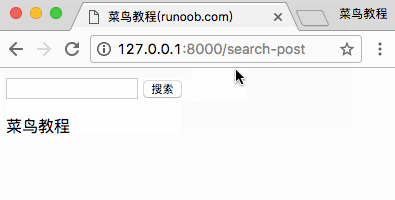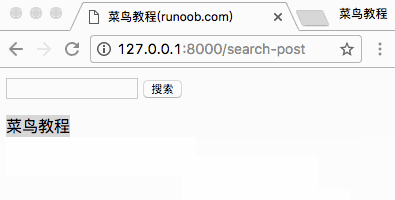
完成以上实例后,我们的目录结构为:
HelloWorld
|-- HelloWorld
| |-- __init__.py
| |-- __init__.pyc
| |-- search.py
| |-- search.pyc
| |-- search2.py
| |-- search2.pyc
| |-- settings.py
| |-- settings.pyc
| |-- testdb.py
| |-- testdb.pyc
| |-- urls.py
| |-- urls.pyc
| |-- view.py
| |-- view.pyc
| |-- wsgi.py
| `-- wsgi.pyc
|-- TestModel
| |-- __init__.py
| |-- __init__.pyc
| |-- admin.py
| |-- admin.pyc
| |-- apps.py
| |-- migrations
| | |-- 0001_initial.py
| | |-- 0001_initial.pyc
| | |-- __init__.py
| | `-- __init__.pyc
| |-- models.py
| |-- models.pyc
| |-- tests.py
| `-- views.py
|-- db.sqlite3
|-- manage.py
`-- templates
|-- base.html
|-- hello.html
|-- post.html
`-- search_form.html二、Request 对象
每个 view 函数的第一个参数是一个 HttpRequest 对象,就像下面这个 hello() 函数:
from django.http import HttpResponse
def hello(request):
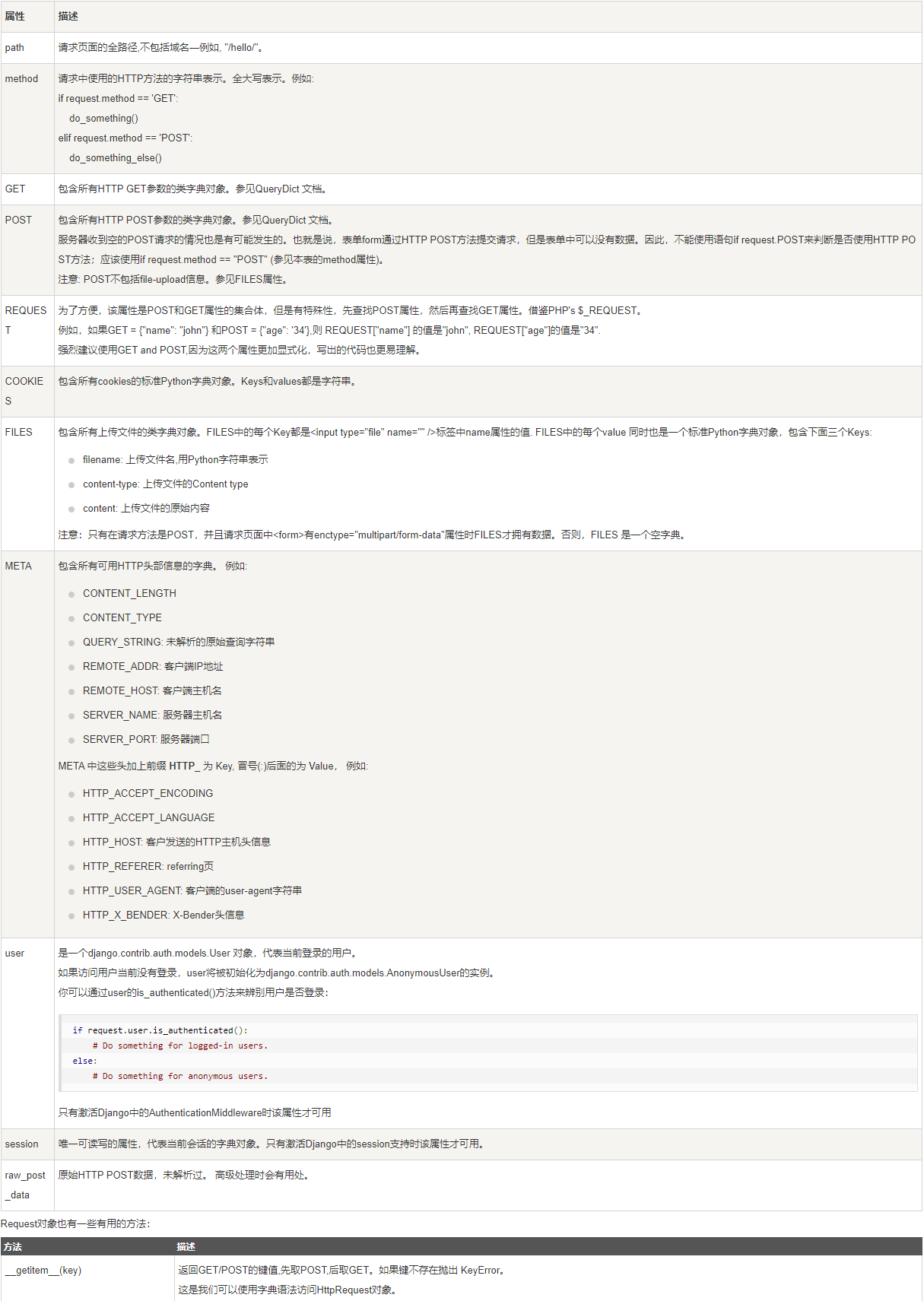
return HttpResponse("Hello world")HttpRequest对象包含当前请求URL的一些信息:
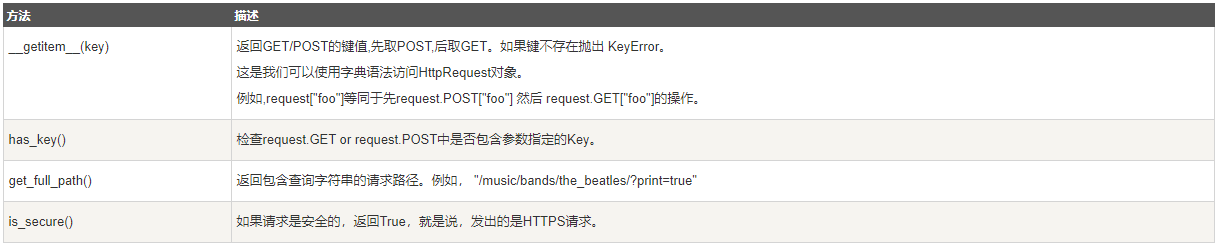
Request对象也有一些有用的方法:
1、QueryDict对象
在HttpRequest对象中, GET和POST属性是django.http.QueryDict类的实例。
QueryDict类似字典的自定义类,用来处理单键对应多值的情况。
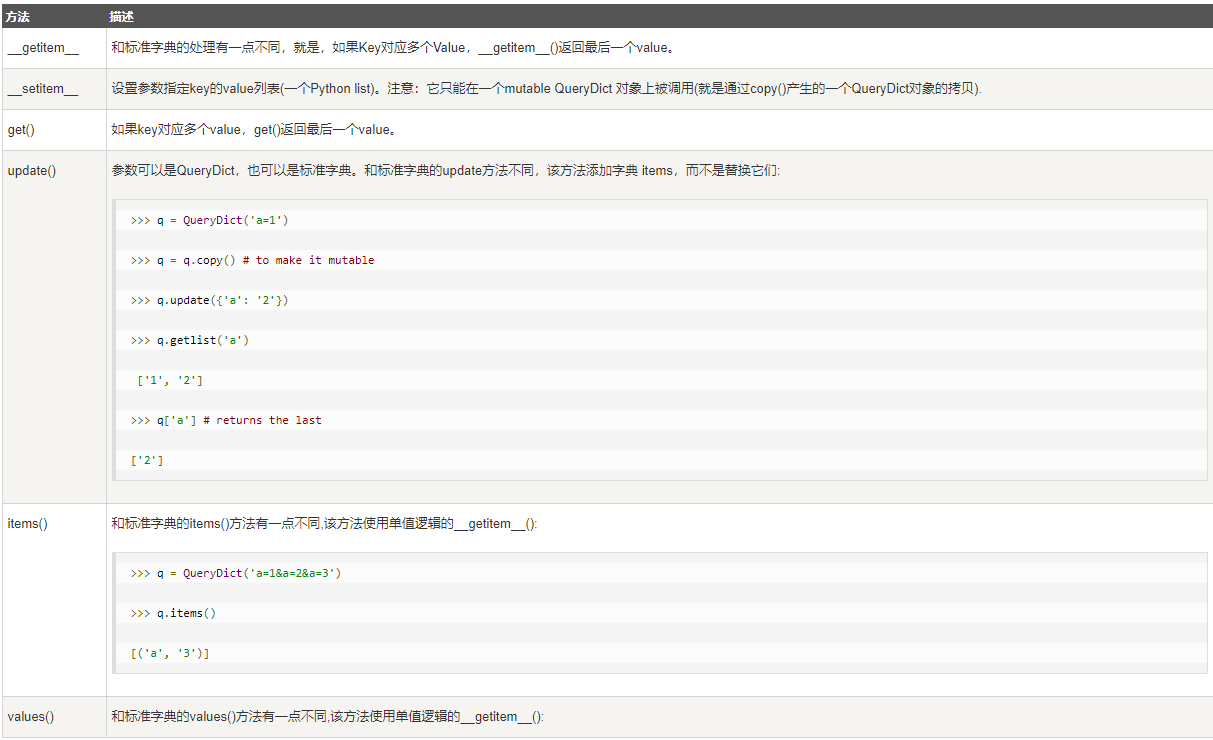
QueryDict实现所有标准的词典方法。还包括一些特有的方法:
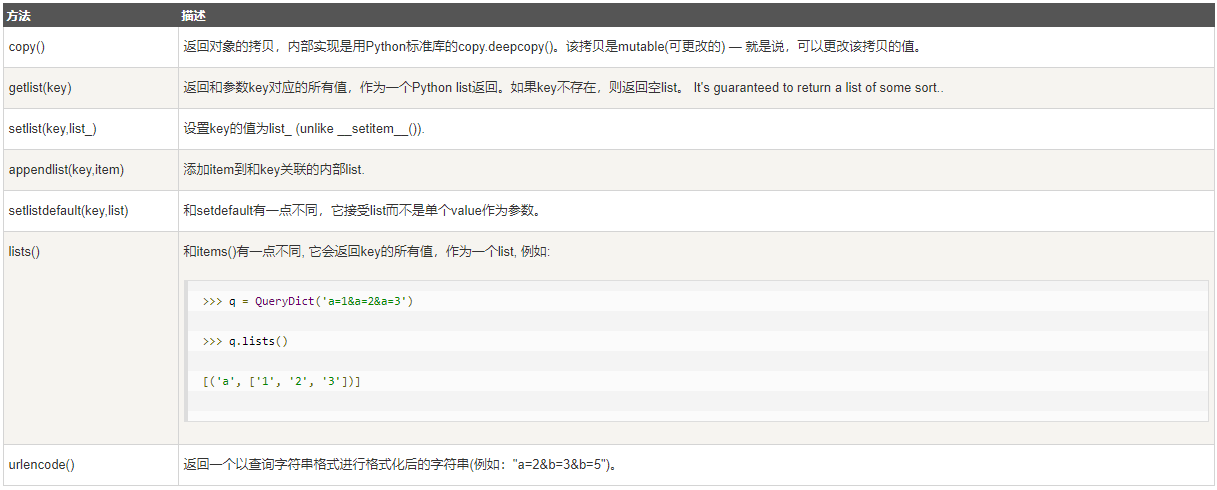
此外, QueryDict也有一些方法,如下表:
posted on 2020-06-20 19:39 springsnow 阅读(273) 评论(0) 收藏 举报


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号