Q1:What is the expected output?(Python)
b = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
print(b[::3])
列表的切片,3表示间隔3个,index+3,输出 b[0] b[3] b[6] b[9] = 0 3 6 9
实际运行结果
>>> b = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
>>> print(b[::3])
[0, 3, 6, 9]
Q2:What is the expected output?(Python)
对于切片的间隔,直接在index上加上对应的间隔即可
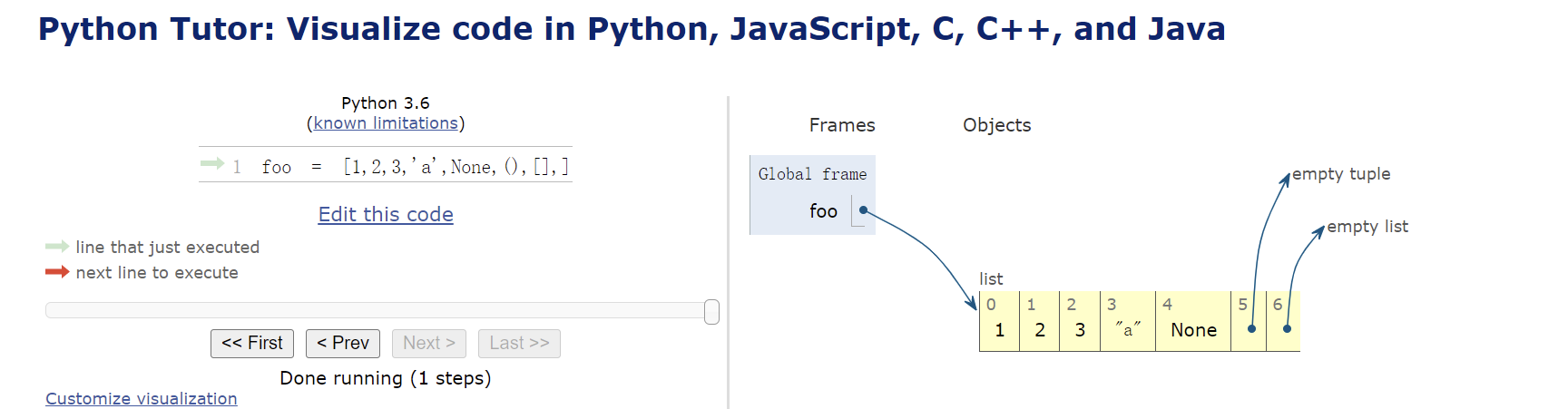
foo = [1,2,3,'a',None,(),[],]
print(len(foo))
考察最后一个,后面的内容没写,长度是多少。
foo = [1,2,3,'a',None,(),[],]
print(foo)
print(len(foo))
结果;
[1, 2, 3, 'a', None, (), []]
7
列表最后一个,后面没有值,为空
Q3:What is the output of the following?
ans = -4//1.5
print ans
>>> -4//1.5
-3.0
思路:
1、地板除,会向下取整;40/15,计算得到2.6666.. 40//15地板除,相当于floor(2.6666) = 2
同样对于-40/15,计算得到-2.66666,-40//15,地板除,相当于floor(-2.66666) =-3
2、衍生到求余数,余数都是正整数,知道这点基本就明白怎么取余数。
比如 -40%15,商-2的话,根据除法公式-40-(15-2),得到的结果是负数, 所以成绩的值本身要小于-40,商-3,得到:-40-(-153)等于-40+45 = 5
Q4:如何合并两个字典
同类问题:如何合并list 如何合并tuple
1、字典增加键值对
d = {'name':'Jhon','age':22,'gender':'Female'}
d['phone_num'] = '02018978383'
print(d)
输出:
{'name': 'Jhon', 'age': 22, 'gender': 'Female', 'phone_num': '02018978383'}
2、合并2个字典
d1 = {'name':'Jhon','age':22,'gender':'Female'}
d2 = {'weight':None,'Height':180,'addr':'Beijing'}
d1.update(d2)
print(d1)
print(d2)
输出;
{'name': 'Jhon', 'age': 22, 'gender': 'Female', 'weight': None, 'Height': 180, 'addr': 'Beijing'}
{'weight': None, 'Height': 180, 'addr': 'Beijing'}
3、更新字典中的一个值
使用update更新一个字典到已经存在的字典,如果有相同的key就会更新
d1 = {'name':'Jhon','age':22,'gender':'Female'}
d1.update({'age':44})
print(d1)
输出;
{'name': 'Jhon', 'age': 44, 'gender': 'Female'}
接使用键值对引用索引的方式
d1 = {'name':'Jhon','age':22,'gender':'Female'}
d1['age'] = 55
print(d1)
输出:
{'name': 'Jhon', 'age': 55, 'gender': 'Female'}
4、能够使用两个字典相加?--不支持
d1 = {'name':'Jhon','age':22,'gender':'Female'}
d2 = {'weight':None,'Height':180,'addr':'Beijing'}
print(d1+d2)
输出:
TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for +: 'dict' and 'dict'
5、如何把一个字典整个作为 一个字典元素合并到另外一个字典
字典作为value,使用update()方法
d1 = {'name':'Jhon','age':22,'gender':'Female'}
d2 = {'weight':None,'Height':180,'addr':'Beijing'}
d1.update({'d2':d2})
print(d1)
输出:
{'name': 'Jhon', 'age': 22, 'gender': 'Female', 'd2': {'weight': None, 'Height': 180, 'addr': 'Beijing'}}
6、list和tuple的操作
l = ['monitor','mouse','harddisk','cpu','memory']
t = ('c','c++','java','python')
la = ['speaker','motherboard','usb-interface']
ta = ('ruby','go','swift')
# list和tuple的元素合并
l = l + la
t += ta
print(l)
print(t)
# 新list和tuple作为列表和元组合并
l.append(la)
print(l)
t.append(ta)
print(t)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Users\lily\PycharmProjects\pythonProject\test.py", line 14, in <module>
t.append(ta)
tuple无append()方法
AttributeError: 'tuple' object has no attribute 'append'
['monitor', 'mouse', 'harddisk', 'cpu', 'memory', 'speaker', 'motherboard', 'usb-interface']
('c', 'c++', 'java', 'python', 'ruby', 'go', 'swift')
列表以字典形式更新到了新的list
['monitor', 'mouse', 'harddisk', 'cpu', 'memory', 'speaker', 'motherboard', 'usb-interface', ['speaker', 'motherboard', 'usb-interface']]
如果要更新2list,则无法append
l = ['monitor','mouse','harddisk','cpu','memory']
la = ['speaker','motherboard','usb-interface']
lb = ['wire','mic','lan']
l.append(la,lb)
输出;
TypeError: list.append() takes exactly one argument (2 given)
使用list.extend()方法
l = ['monitor','mouse','harddisk','cpu','memory']
l.extend(['wire','mic','lan'])
print(l)
la = ['speaker','motherboard','usb-interface']
lb = ['wire','mic','lan']
l.extend([la,lb])
print(l)
输出:
['monitor', 'mouse', 'harddisk', 'cpu', 'memory', 'wire', 'mic', 'lan']
['monitor', 'mouse', 'harddisk', 'cpu', 'memory', 'wire', 'mic', 'lan', ['speaker', 'motherboard', 'usb-interface'], ['wire', 'mic', 'lan']]
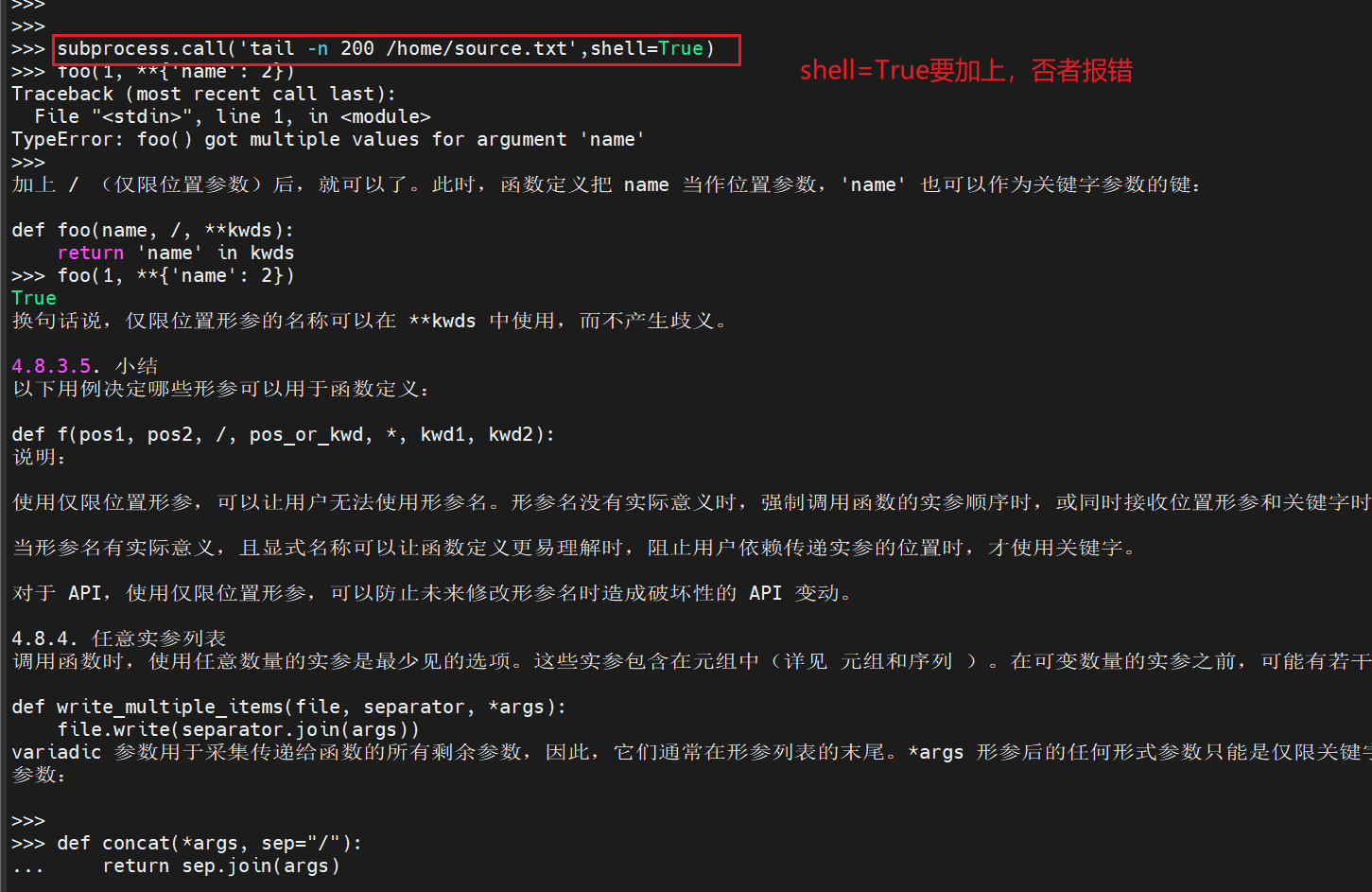
Q5:如何读取一个文件的最后200行
1、使用readlines来进行读取
2、如果是linux ,使用subprocess
# 方法1:简单粗暴,直接用readlines读取成列表,然后读取最后200行
with open(r'./source.txt','r',encoding='utf-8') as f:
stri = f. readlines()
print(''.join(stri[len(stri)-200:]))
# 方法2:使用subprocess模块,仅限于linux
import subprocess
subprocess.run('tail -n 200 source.txt',shell=True)
# 方法3:使用seek()
seek()方法用于文件读取,将文件读取的指针移动到指定的位置。
fileObject.seek(offset[, whence])
offset -- 开始的偏移量,也就是代表需要移动偏移的字节数
whence:可选,默认值为 0。给offset参数一个定义,表示要从哪个位置开始偏移;
0代表从文件开头开始算起;
1代表从当前位置开始算起;
2代表从文件末尾算起;
tell()函数返回当前的偏移量的位置
这里是读取的是最后2行的内容
```python
# 方法1:简单粗暴,直接用readlines读取成列表,然后读取最后200行
with open(r'./source.txt','r',encoding='utf-8') as f:
stri = f. readlines()
print(''.join(stri[len(stri)-200:]))
# 方法2:使用subprocess模块,借助tail命令,仅限于linux
import subprocess
subprocess.run('tail -n 200 source.txt',shell=True)
# 方法3:移动文件读取指针seek
'''
基本思路是尝试,移动文件读取指针,相对于文件末尾移动,然后再通过readlines()判断是否有2行
'''
with open(r'source.txt','rb') as f:
offset_num ,i = -5 , 1
while True:
f.seek(offset_num,2) #2表示相对于文件末尾移动
s = f.readlines()
if len(s) > 2:
print(s[-2].decode()+s[-1].decode())
break
else:
print(f'开始第{i}次循环,不满足条件,继续')
i=i+1
offset_num += -5
推荐阅读:f_seek()相关用法
</font size>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号