IPv6 地址分类、地址格式及其寻址方式
An Internet Protocol Version 6 address (IPv6 address) is a numeric label that is used to identify and locate a network interface of a computer or a network node participating in a computer network using IPv6. IP addresses are included in the packet header to indicate the source and the destination of each packet. The IP address of the destination is used to make decisions about routing IP packets to other networks.
IPv6 is the successor to the first addressing infrastructure of the Internet, Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4). In contrast to IPv4, which defined an IP address as a 32-bit value, IPv6 addresses have a size of 128 bits. Therefore, in comparison, IPv6 has a vastly enlarged address space.

Addressing methods寻址方法[edit]
IPv6 addresses are classified by the primary addressing and routing methodologies common in networking: unicast addressing, anycast addressing, and multicast addressing.[1]
A unicast address identifies a single network interface. The Internet Protocol delivers packets sent to a unicast address to that specific interface.
An anycast address is assigned to a group of interfaces, usually belonging to different nodes. A packet sent to an anycast address is delivered to just one of the member interfaces, typically the nearest host, according to the routing protocol's definition of distance. Anycast addresses cannot be identified easily, they have the same format as unicast addresses, and differ only by their presence in the network at multiple points. Almost any unicast address can be employed as an anycast address.
A multicast address is also used by multiple hosts that acquire the multicast address destination by participating in the multicast distribution protocol among the network routers. A packet that is sent to a multicast address is delivered to all interfaces that have joined the corresponding multicast group. IPv6 does not implement broadcast addressing. Broadcast's traditional role is subsumed by multicast addressing to the all-nodes link-local multicast group ff02::1. However, the use of the all-nodes group is not recommended, and most IPv6 protocols use a dedicated link-local multicast group to avoid disturbing every interface in the network.
Address formats地址格式[edit]
An IPv6 address consists of 128 bits.[1] For each of the major addressing and routing methodologies, various address formats are recognized by dividing the 128 address bits into bit groups and using established rules for associating the values of these bit groups with special addressing features.
一个IPv6地址 由128 bit构成,在每类主要的寻址和路由协议/方法中 IPv6地址的128bit 会被区分为不同的 bit组(即IPv6地址的格式构成),各bit组中的 值 基于特定的映射规则 分别对应着不同的特殊寻址/路由特性。(不同格式的IPv6 对应着不同的 路由/寻址规则)
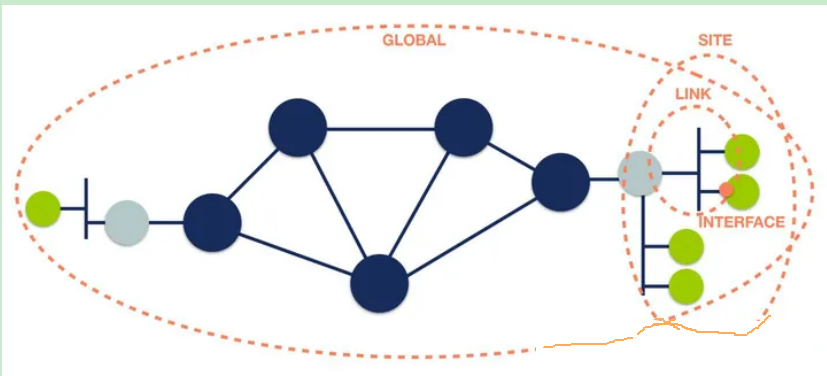
一、Unicast and anycast address format单播和任播地址[edit]
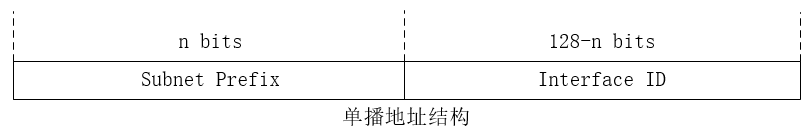
Unicast and anycast addresses are typically composed of two logical parts: a 64-bit network prefix used for routing, and a 64-bit interface identifier used to identify a host's network interface.
| bits | 48 (or more) | 16 (or fewer) | 64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| field | routing prefix | subnet id | interface identifier |
The network prefix (the routing prefix combined with the subnet id) is contained in the most significant 64 bits of the address. The size of the routing prefix may vary; a larger prefix size means a smaller subnet id size. The bits of the subnet id field are available to the network administrator to define subnets within the given network. The 64-bit interface identifier is automatically established randomly, obtained from a DHCPv6 server, or assigned manually. (Historically, it was automatically generated from the interface's MAC address using the modified EUI-64 format, but this method is now deprecated for privacy reasons.)
General unicast address ,,也叫全局单播地址吧,global unicast addres (GUA)
网络前缀(路由前缀 + 子网ID)被包括在 这类地址最重要的 64 bit中。其中的 路由前缀 长度各异:大一点的路由前缀意味着小一些的子网ID 范围。网络管理员可以通过 子网ID 的bit位 在给定的网络中划分子网。64位的网络接口ID 是随机建立的,从DHCPv6服务器上获取到,或者,也可以手动分配。(在历史上,他是基于接口主机 的MAC地址 使用修正后的 EUI-64标准 自动生产的。这个方法基于MAC,通过特定逻辑,生成接口标识 ID, 出于隐私保护的原因 已经不建议使用此方法)
1、单播地址
单播地址只能分配给一个节点上的一个接口,即寻址到该单播地址的数据报文最终会被发送到一个唯一的接口。
单播地址可以分为链路本地地址,站点本地地址,可聚合全球单播地址(全球单播地址)、全球唯一本地地址(Unique local address )等。

Unique local addresses are addresses analogous to IPv4 private network addresses. 本地唯一地址 是 类似于 IPv4中的私有网络地址 的一类地址;这类地址网络前缀(IPv4中的网络号)是固定的,主要依赖网络接口部分的不同来 进行通信 和 主机识别
| bits | 7 | 1 | 40 | 16 | 64 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| field | prefix | L | random | subnet id | interface identifier |
The prefix field contains the binary value 1111110. The L bit is one for locally assigned addresses; the address range with L set to zero is currently not defined. The random field is chosen randomly once, at the inception of the /48 routing prefix. 本球 唯一本地地址 的前缀部分包括了固定的 值: 1111 110,第8位 L位,为1表示本地分配,为0当前未定义;随机部分的40位,作为Global ID,它由 获取/48位路由前缀时随机生成。【因此,本地IPv6局域网地址,均为 FCxx::/7, 前面8位用十六进制表示时固定为 FC,紧接着后面一个8位 的十六进制默认使用 00,

A link-local address is also based on the interface identifier, but uses a different format for the network prefix. 与本地唯一地址一样,链路本地地址,也是基于 网络接口部分 来工作的,但是它的网络前缀 与 本地唯一地址还是不一样的。如下:
| bits | 10 | 54 | 64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| field | prefix | zeroes | interface identifier |
The prefix field contains the binary value 1111111010. The 54 zeroes that follow make the total network prefix the same for all link-local addresses (fe80::/64 link-local address prefix), rendering them non-routable. 链路本地地址的 网络前缀 部分包括了 10位的 1111 1110 10 即 fe-10, 后边接着54位固定为 0,因此,固定前缀为 fe80::/64

站点本地地址
站点本地地址是另一种应用范围受限的地址,它只能在一个站点内使用。目前已被废弃,不再使用。
二、Multicast address format 多播地址 格式/有些地方 也翻译为 组播[edit]
Multicast addresses are formed according to several specific formatting rules, depending on the application. 多播地址的结构格式 要看基体的格式规则而定,格式规则取决于特定的应用。
| bits | 8 | 4 | 4 | 112 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| field | prefix | flg | sc | group ID |
For all multicast addresses, the prefix field holds the binary value 11111111. 在所有的多播地址格式中,网络前缀 均固定为 1111 1111, 因此前缀固定为 FFxx::/8, 通常为 FF00::/8
Currently, three of the four flag bits in the flg field are defined;[1] the most-significant flag bit is reserved for future use. 当前,flag 4位中,后三位已定义,第1位预留给将来使用,具体如下;
| bit | flag | Meaning when 0 | Meaning when 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | reserved | reserved | reserved |
| 9 | R (Rendezvous)[3] | Rendezvous point not embedded | Rendezvous point embedded |
| 10 | P (Prefix)[4] | Without prefix information | Address based on network prefix |
| 11 | T (Transient)[1] | Well-known multicast address | Dynamically assigned multicast address |
The four-bit scope field (sc) is used to indicate where the address is valid and unique. sc 的4位,用来标识在什么范围内 本多播地址合法和唯一,如下表
In addition, the scope field is used to identify special multicast addresses, like solicited node. 同时,sc位也用于标识 一些 特殊的多播地址,如 solicited node.
| Value | Scope name | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0 | reserved | |
| 0x1 | interface-local | Interface-local scope spans only a single interface on a node, and is useful only for loopback transmission of multicast. |
| 0x2 | link-local | Link-local scope spans the same topological region as the corresponding unicast scope. |
| 0x3 | realm-local | Realm-local scope is defined as larger than link-local, automatically determined by network topology and must not be larger than the following scopes.[13] |
| 0x4 | admin-local | Admin-local scope is the smallest scope that must be administratively configured, i.e., not automatically derived from physical connectivity or other, non-multicast-related configuration. |
| 0x5 | site-local | Site-local scope is intended to span a single site belonging to an organisation. |
| 0x8 | organization-local | Organization-local scope is intended to span all sites belonging to a single organization. |
| 0xe | global | Global scope spans all reachable nodes on the internet - it is unbounded. |
| 0xf | reserved |
All other scopes are unassigned and available to administrators for defining additional regions. 其余的 sc 值,暂未分配/定义,管理员可用 其来定义多播地址的额外的合法/唯一 范围/区域;
| bits | 8 | 4 | 4 | 79 | 9 | 24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| field | prefix | flg | sc | zeroes | ones | unicast address |
The sc(ope) field holds the binary value 0010 (link-local). Solicited-node multicast addresses are computed as a function of a node's unicast or anycast addresses. A solicited-node multicast address is created by copying the last 24 bits of a unicast or anycast address to the last 24 bits of the multicast address.
| bits | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 64 | 32 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| field | prefix | flg | sc | res | riid | plen | network prefix | group ID |
Link-scoped multicast addresses use a comparable format.[5]

被请求节点组播地址
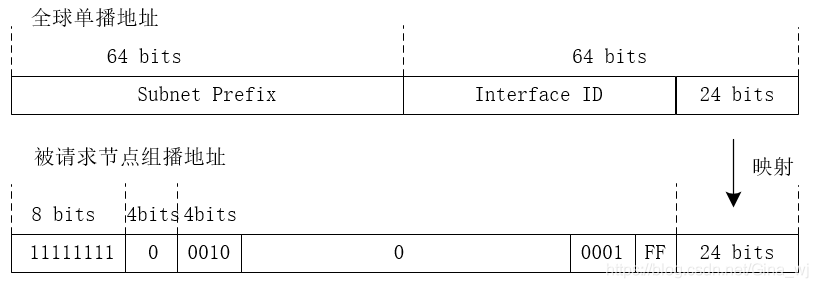
众所周知的组播地址
IPv6具有一些众所周知的组播地址,他们具有特殊的含义,如下表所示:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号