spark源码分析, 任务提交及序列化
简易基本流程图如下
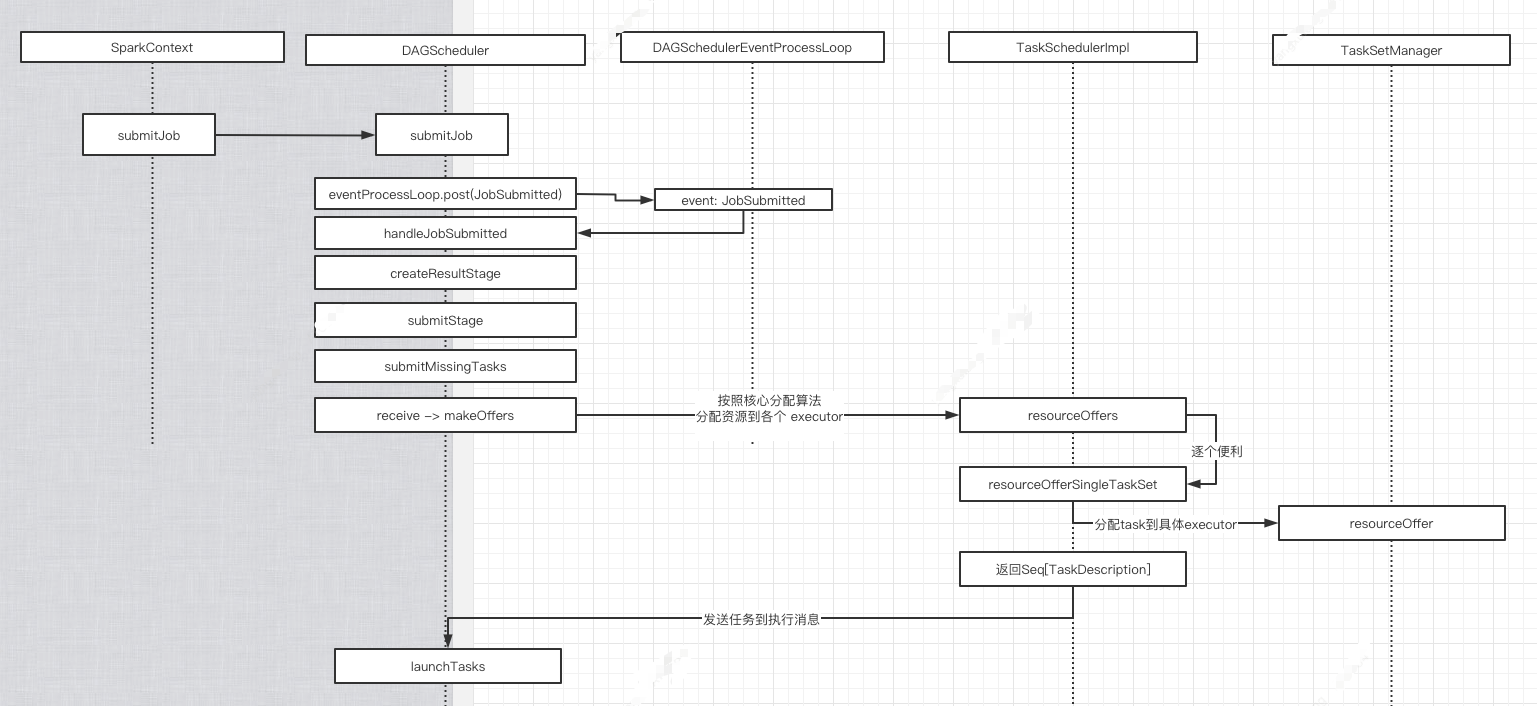
1. org.apache.spark.scheduler.DAGScheduler#submitMissingTasks
2. => org.apache.spark.scheduler.TaskSchedulerImpl#submitTasks
// First figure out the indexes of partition ids to compute.
val partitionsToCompute: Seq[Int] = stage.findMissingPartitions()
// Use the scheduling pool, job group, description, etc. from an ActiveJob associated
// with this Stage
val properties = jobIdToActiveJob(jobId).properties
runningStages += stage
// SparkListenerStageSubmitted should be posted before testing whether tasks are
// serializable. If tasks are not serializable, a SparkListenerStageCompleted event
// will be posted, which should always come after a corresponding SparkListenerStageSubmitted
// event.
stage match {
case s: ShuffleMapStage =>
outputCommitCoordinator.stageStart(stage = s.id, maxPartitionId = s.numPartitions - 1)
case s: ResultStage =>
outputCommitCoordinator.stageStart(
stage = s.id, maxPartitionId = s.rdd.partitions.length - 1)
}
val taskIdToLocations: Map[Int, Seq[TaskLocation]] = try {
stage match {
case s: ShuffleMapStage =>
partitionsToCompute.map { id => (id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, id))}.toMap
case s: ResultStage =>
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val p = s.partitions(id)
(id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, p))
}.toMap
}
}
//序列化 RDD
// TODO: Maybe we can keep the taskBinary in Stage to avoid serializing it multiple times.
// Broadcasted binary for the task, used to dispatch tasks to executors. Note that we broadcast
// the serialized copy of the RDD and for each task we will deserialize it, which means each
// task gets a different copy of the RDD. This provides stronger isolation between tasks that
// might modify state of objects referenced in their closures. This is necessary in Hadoop
// where the JobConf/Configuration object is not thread-safe.
var taskBinary: Broadcast[Array[Byte]] = null
var partitions: Array[Partition] = null
try {
// For ShuffleMapTask, serialize and broadcast (rdd, shuffleDep).
// For ResultTask, serialize and broadcast (rdd, func).
var taskBinaryBytes: Array[Byte] = null
// taskBinaryBytes and partitions are both effected by the checkpoint status. We need
// this synchronization in case another concurrent job is checkpointing this RDD, so we get a
// consistent view of both variables.
RDDCheckpointData.synchronized {
taskBinaryBytes = stage match {
case stage: ShuffleMapStage =>
JavaUtils.bufferToArray(
closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.shuffleDep): AnyRef))
case stage: ResultStage =>
JavaUtils.bufferToArray(closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.func): AnyRef))
}
partitions = stage.rdd.partitions
}
taskBinary = sc.broadcast(taskBinaryBytes)
}
//生成 taskset
val tasks: Seq[Task[_]] = try {
val serializedTaskMetrics = closureSerializer.serialize(stage.latestInfo.taskMetrics).array()
stage match {
case stage: ShuffleMapStage =>
stage.pendingPartitions.clear()
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val locs = taskIdToLocations(id)
val part = partitions(id)
stage.pendingPartitions += id
new ShuffleMapTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptNumber,
taskBinary, part, locs, properties, serializedTaskMetrics, Option(jobId),
Option(sc.applicationId), sc.applicationAttemptId, stage.rdd.isBarrier())
}
case stage: ResultStage =>
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val p: Int = stage.partitions(id)
val part = partitions(p)
val locs = taskIdToLocations(id)
new ResultTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptNumber,
taskBinary, part, locs, id, properties, serializedTaskMetrics,
Option(jobId), Option(sc.applicationId), sc.applicationAttemptId,
stage.rdd.isBarrier())
}
}
}
//最终提交 taskset
if (tasks.size > 0) {
logInfo(s"Submitting ${tasks.size} missing tasks from $stage (${stage.rdd}) (first 15 " +
s"tasks are for partitions ${tasks.take(15).map(_.partitionId)})")
taskScheduler.submitTasks(new TaskSet(
tasks.toArray, stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptNumber, jobId, properties))
}
3. => org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend#reviveOffers ,发送消息
def reviveOffers() {
// 类型 CoarseGrainedClusterMessage
driverEndpoint.send(ReviveOffers) }
4. => 自己处理消息org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.DriverEndpoint#receive
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case StatusUpdate(executorId, taskId, state, data) =>
.....
case ReviveOffers =>
makeOffers()
case KillTask(taskId, executorId, interruptThread, reason) =>
....
case KillExecutorsOnHost(host) =>
.....
case UpdateDelegationTokens(newDelegationTokens) =>
.....
case RemoveExecutor(executorId, reason) =>
...
removeExecutor(executorId, reason)
}
5.=> org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.DriverEndpoint#makeOffers
// Make fake resource offers on all executors private def makeOffers() { // Make sure no executor is killed while some task is launching on it val taskDescs = withLock { // Filter out executors under killing val activeExecutors = executorDataMap.filterKeys(executorIsAlive) val workOffers = activeExecutors.map { case (id, executorData) => new WorkerOffer(id, executorData.executorHost, executorData.freeCores, Some(executorData.executorAddress.hostPort)) }.toIndexedSeq scheduler.resourceOffers(workOffers) } if (!taskDescs.isEmpty) { launchTasks(taskDescs) } }
6.=> org.apache.spark.scheduler.TaskSchedulerImpl#resourceOffers. 按照核心分配算法分配各 task 到 executor 上.
// Take each TaskSet in our scheduling order, and then offer it each node in increasing order
// of locality levels so that it gets a chance to launch local tasks on all of them.
// NOTE: the preferredLocality order: PROCESS_LOCAL, NODE_LOCAL, NO_PREF, RACK_LOCAL, ANY
for (taskSet <- sortedTaskSets) {
var launchedAnyTask = false
// Record all the executor IDs assigned barrier tasks on.
val addressesWithDescs = ArrayBuffer[(String, TaskDescription)]()
for (currentMaxLocality <- taskSet.myLocalityLevels) {
var launchedTaskAtCurrentMaxLocality = false
do {
launchedTaskAtCurrentMaxLocality = resourceOfferSingleTaskSet(taskSet,
currentMaxLocality, shuffledOffers, availableCpus, tasks, addressesWithDescs)
launchedAnyTask |= launchedTaskAtCurrentMaxLocality
} while (launchedTaskAtCurrentMaxLocality)
}
}
=>org.apache.spark.scheduler.TaskSchedulerImpl#resourceOfferSingleTaskSet
=>org.apache.spark.scheduler.TaskSchedulerImpl#resourceOfferSingleTaskSet private def resourceOfferSingleTaskSet( taskSet: TaskSetManager, maxLocality: TaskLocality, shuffledOffers: Seq[WorkerOffer], availableCpus: Array[Int], tasks: IndexedSeq[ArrayBuffer[TaskDescription]], addressesWithDescs: ArrayBuffer[(String, TaskDescription)]) : Boolean = { var launchedTask = false //分配任务 for (i <- 0 until shuffledOffers.size) { val execId = shuffledOffers(i).executorId val host = shuffledOffers(i).host if (availableCpus(i) >= CPUS_PER_TASK) { for (task <- taskSet.resourceOffer(execId, host, maxLocality)) { tasks(i) += task val tid = task.taskId taskIdToTaskSetManager.put(tid, taskSet) taskIdToExecutorId(tid) = execId executorIdToRunningTaskIds(execId).add(tid) availableCpus(i) -= CPUS_PER_TASK launchedTask = true } } } return launchedTask } ==> org.apache.spark.scheduler.TaskSetManager#resourceOffer @throws[TaskNotSerializableException] def resourceOffer( execId: String, host: String, maxLocality: TaskLocality.TaskLocality) : Option[TaskDescription] = { val offerBlacklisted = taskSetBlacklistHelperOpt.exists { blacklist => blacklist.isNodeBlacklistedForTaskSet(host) || blacklist.isExecutorBlacklistedForTaskSet(execId) } if (!isZombie && !offerBlacklisted) { val curTime = clock.getTimeMillis() var allowedLocality = maxLocality if (maxLocality != TaskLocality.NO_PREF) { allowedLocality = getAllowedLocalityLevel(curTime) if (allowedLocality > maxLocality) { // We're not allowed to search for farther-away tasks allowedLocality = maxLocality } } dequeueTask(execId, host, allowedLocality).map { case ((index, taskLocality, speculative)) => // Found a task; do some bookkeeping and return a task description //找到一个任务,然后封装task的信息,包括序列化 val task = tasks(index) //原子自增 val taskId = sched.newTaskId() // Do various bookkeeping copiesRunning(index) += 1 val attemptNum = taskAttempts(index).size val info = new TaskInfo(taskId, index, attemptNum, curTime, execId, host, taskLocality, speculative) taskInfos(taskId) = info taskAttempts(index) = info :: taskAttempts(index) // Serialize and return the task val serializedTask: ByteBuffer = try { ser.serialize(task) } //添加到运行Map中 addRunningTask(taskId) sched.dagScheduler.taskStarted(task, info) new TaskDescription( taskId, attemptNum, execId, taskName, index, task.partitionId, addedFiles, addedJars, task.localProperties, serializedTask) } } else { None } }
7.=> org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.DriverEndpoint#launchTasks
// Launch tasks returned by a set of resource offers
private def launchTasks(tasks: Seq[Seq[TaskDescription]]) {
for (task <- tasks.flatten) {
val serializedTask = TaskDescription.encode(task)
...
executorData.executorEndpoint.send(LaunchTask(new SerializableBuffer(serializedTask)))
}
8. => org.apache.spark.scheduler.TaskDescription#encode TaskDescription作为 message 发送给 executor
def encode(taskDescription: TaskDescription): ByteBuffer = {
val bytesOut = new ByteBufferOutputStream(4096)
val dataOut = new DataOutputStream(bytesOut)
dataOut.writeLong(taskDescription.taskId)
dataOut.writeInt(taskDescription.attemptNumber)
dataOut.writeUTF(taskDescription.executorId)
dataOut.writeUTF(taskDescription.name)
dataOut.writeInt(taskDescription.index)
dataOut.writeInt(taskDescription.partitionId)
// Write files.
serializeStringLongMap(taskDescription.addedFiles, dataOut)
// Write jars.
serializeStringLongMap(taskDescription.addedJars, dataOut)
// Write properties.
dataOut.writeInt(taskDescription.properties.size())
taskDescription.properties.asScala.foreach { case (key, value) =>
dataOut.writeUTF(key)
// SPARK-19796 -- writeUTF doesn't work for long strings, which can happen for property values
val bytes = value.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)
dataOut.writeInt(bytes.length)
dataOut.write(bytes)
}
// Write the task. The task is already serialized, so write it directly to the byte buffer.
Utils.writeByteBuffer(taskDescription.serializedTask, bytesOut)
dataOut.close()
bytesOut.close()
bytesOut.toByteBuffer
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号