3-6如何在一个for语句中迭代多个可迭代对象
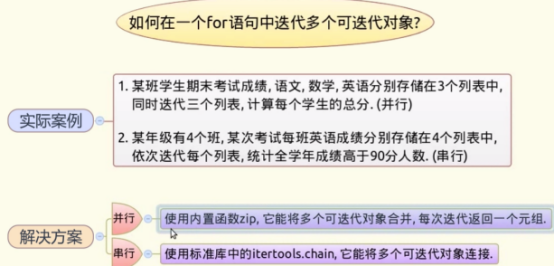
1、并行迭代
迭代元组可以进行拆包迭代。
>>> zip([1,2,3,4],('a','b','c','d')) [(1, 'a'), (2, 'b'), (3, 'c'), (4, 'd')] >>> zip([1,2,3,4],('a','b','c')) #当元素个数不一致时,以少的为准 [(1, 'a'), (2, 'b'), (3, 'c')] >>> zip([1,2,3,4],('a','b','c','d'),"7890") [(1, 'a', '7'), (2, 'b', '8'), (3, 'c', '9'), (4, 'd', '0')] >>> zip([1,2,3,4],('a','b','c'),"7890") [(1, 'a', '7'), (2, 'b', '8'), (3, 'c', '9')]
实现并行迭代例子实现
(1)生成三科成绩的3个列表
>>> from random import randint >>> math = [randint(60,100) for _ in xrange(40)] >>> english = [randint(60,100) for _ in xrange(40)] >>> chinese = [randint(60,100) for _ in xrange(40)]
(2)由zip()函数将三科成绩的3个列表,组成一个元组。迭代元组可以进行拆包迭代
>>> for m,e,c in zip(math,english,chinese): print (m+e+c),
输出结果:285 234 207 204 272 268 234 280 241 232 202 241 236 262 231 206 238 246 236 224 254 248 258 234 246 227 216 240 216 214 224 250 222 228 223 248 252 201 265 192
2、串行迭代
>>> from itertools import chain

>>> help(chain) Help on class chain in module itertools: class chain(__builtin__.object) | chain(*iterables) --> chain object | | Return a chain object whose .next() method returns elements from the | first iterable until it is exhausted, then elements from the next | iterable, until all of the iterables are exhausted. | | Methods defined here: | | __getattribute__(...) | x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name | | __iter__(...) | x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) | | from_iterable(...) | chain.from_iterable(iterable) --> chain object | | Alternate chain() constructor taking a single iterable argument | that evaluates lazily. | | next(...) | x.next() -> the next value, or raise StopIteration | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Data and other attributes defined here: | | __new__ = <built-in method __new__ of type object> | T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T
>>> for x in chain([1,2,3,4],"abc"): print x,
输出结果:1 2 3 4 a b c
串行迭代例子实现
(1)生成四个班级的学习的成绩列表,每班的人数不同
>>> from random import randint >>> e1= [randint(60,100) for _ in xrange(40)] >>> e2= [randint(60,100) for _ in xrange(46)] >>> e3= [randint(60,100) for _ in xrange(50)] >>> e4= [randint(60,100) for _ in xrange(40)]
(2)串行对各个班级进行迭代,判断每个学生成绩,大于90的将人数加1
>>> count = 0 >>> for x in chain(e1,e2,e3,e4): if x>90: count +=1 >>> count
输出结果:49
posted on 2018-04-16 09:02 石中玉smulngy 阅读(174) 评论(0) 收藏 举报




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号