2-4字典排序
1、实现方法
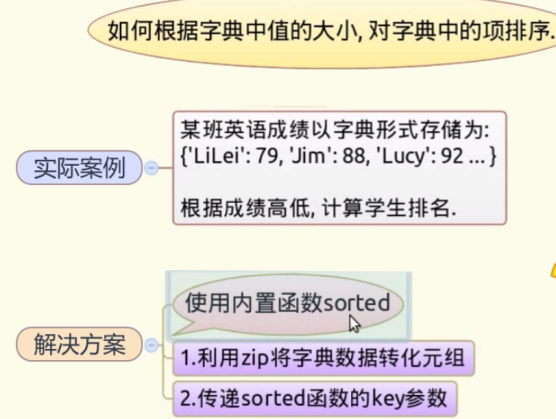
两种方法:1、利用zip将字典数据转化为元组数据;2、传递sorted函数的key参数
1.1利用zip将字典数据转化为元组数据
分为三步:
1、生成学生姓名分别为xyzabc六个学生的随机成绩字典

>>> from random import randint >>> d = {x:randint(60,100) for x in 'xyzabc'} >>> d {'a': 75, 'c': 72, 'b': 87, 'y': 71, 'x': 67, 'z': 77}
2、生成元组列表(成绩(值)放在前面,名字(键)放在后面。)在排序中先按第1个位置排序,这个相同时再按照第2个位置排序

>>>dic = zip(d.itervalues(),d.iterkeys()) [(75, 'a'), (72, 'c'), (87, 'b'), (71, 'y'), (67, 'x'), (77, 'z')]
3、对元组列表进行排序

>>> sorted(dic) [(67, 'x'), (71, 'y'), (72, 'c'), (75, 'a'), (77, 'z'), (87, 'b')]
1.2传递sorted函数的key参数

>>> sorted(d.iteritems(),key = lambda x : x[1]) [('x', 67), ('y', 71), ('c', 72), ('a', 75), ('z', 77), ('b', 87)]
sorted()排序时,每次都迭代他的参数(可迭代对象)
sorted(d.iteritems(),key = lambda x : x[1])
把每次迭代对象d.iteritems()传给 key的函数lambda 的参数x,并把x的第1项(即字典的值)作为key来比较。
2、扩展知识
1、zip使用方法
>>> help(zip) Help on built-in function zip in module __builtin__: zip(...) zip(seq1 [, seq2 [...]]) -> [(seq1[0], seq2[0] ...), (...)] Return a list of tuples, where each tuple contains the i-th element from each of the argument sequences. The returned list is truncated in length to the length of the shortest argument sequence.
help(zip)
字典的items()返回元组列表
2、字典的键值迭代
>>> d.items()
[('a', 75), ('c', 72), ('b', 87), ('y', 71), ('x', 67), ('z', 77)]
>>> d.keys()
['a', 'c', 'b', 'y', 'x', 'z']
>>> d.values()
[75, 72, 87, 71, 67, 77]
下面这三个是可迭代的对象,更节省内存,尽量使用下面的形式。
>>> d.iteritems()
<dictionary-itemiterator object at 0x02BC5690>
>>> d.iterkeys()
<dictionary-keyiterator object at 0x02C5E2A0>
>>> d.itervalues()
<dictionary-valueiterator object at 0x02BC5630>
posted on 2018-04-02 10:31 石中玉smulngy 阅读(139) 评论(0) 收藏 举报




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号