Day41 of learning python --web框架的本质及初识Django框架
1.web框架的本质
自己开发web框架必备的知识点 --socket --http协议 --HTML知识 --数据库(pymysql,SQLALchemy)
HTTP:无状态,短连接 TCP:不断开 WEB应用(网站)的简单连接过程 浏览器(socket客户端) 2.在网站输入框输入:www.cnblogs.com sk.socket() sk.connect() sk.send('我想要xxx') 5.收到 6.连接断开 博客园(socket服务端) 1.监听IP和端口 3.收到'我想要xxx' 4.响应:'好',返回想要的内容 7.断开,等待下一个连接
网站构成的基本原理:
a.socket服务器 b.根据URL不同返回不同的内容 路由系统: URL -> 函数 c.字符串返回给用户 模板引擎渲染: HTML充当模板(特殊字符) 自己创造任意数据 返回字符串
web框架分类:
框架种类: -a,b,c --> Tornado -[第三方a],b,c --> wsgiref -> Django -[第三方a],b,[第三方c] --> flask,bottle.
两个重要的例子:
静态网站:发送给浏览器端的内容不变的,根据输入不同的网站得到不同的页面展示,可以查看URL路由系统

import socket import time sock = socket.socket() sock.bind(('127.0.0.1',8080)) sock.listen(5) def func1(request): with open('information.html','rb') as f: data = f.read() return data def func2(request): with open('login.html','rb') as f: data = f.read() return data def func3(request): with open('active.html','r',encoding='utf-8') as f: data = f.read() active_time = time.ctime() current_data = data.replace('@time',active_time) return bytes(current_data,encoding='utf-8') relation_list = [ ('/information.html',func1),('/login.html',func2),('/active.html',func3) ] def run(): while 1: conn,addr = sock.accept() # hang 住 #有人来连接了 #获取用户发送的数据 data = conn.recv(8096) data = str(data,encoding='utf-8') headers,bodys = data.split('\r\n\r\n') temp_list = headers.split('\r\n') method,url,protocal = temp_list[0].split(' ') conn.send(b'HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n\r\n') # 此句不能少,否则浏览器不能识别,因为html的识别需要依据http协议传输才行 func_name = None # 要先定义了,才能使用 for item in relation_list: if url == item[0]: func_name = item[1] break if func_name: response = func_name(bodys) else: response = b'404' conn.send(response) conn.close() if __name__ =='__main__': run()

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>active</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, maximum-scale=1, user-scalable=no"> <!--<link rel="stylesheet" href="bootstrap/css/bootstrap.min.css">--> </head> <body> <table border="1"> <thead> <tr> <th>id</th> <th>name</th> <th>mail</th> <th>time</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr> <th>1</th> <th>alex</th> <th>123@qq.com</th> <th>@time</th> </tr> </tbody> </table> <!--<script src="jQuery-3.3.1.js"></script>--> <!--<script src="bootstrap/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>--> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>infomation</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, maximum-scale=1, user-scalable=no"> <!--<link rel="stylesheet" href="bootstrap/css/bootstrap.min.css">--> </head> <h3>基本信息</h3> <body> <table border="1"> <thead> <tr> <th>id</th> <th>name</th> <th>mail</th> <th>time</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr> <th>1</th> <th>alex</th> <th>123@qq.com</th> <th>2019.1.19</th> </tr> </tbody> </table> <!--<script src="jQuery-3.3.1.js"></script>--> <!--<script src="bootstrap/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>--> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>login</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, maximum-scale=1, user-scalable=no"> <!--<link rel="stylesheet" href="bootstrap/css/bootstrap.min.css">--> </head> <body> <h3>Login</h3> <form action=""> <p> <label for="username">用户名:</label> <input type="text" id="username" name="username"> </p> <p> <label for="password">密码:</label> <input type="password" id="password" name="password"> </p> </form> <!--<script src="jQuery-3.3.1.js"></script>--> <!--<script src="bootstrap/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>--> </body> </html>
动态网站:从数据库中获取数据,把数据库的内容替换到html模板进行渲染,通过修改数据库的数据,从而页面展示不同的数据

import socket import time sock = socket.socket() sock.bind(('127.0.0.1',8080)) sock.listen(5) def func1(request): with open('information.html','rb') as f: data = f.read() return data def func2(request): with open('login.html','rb') as f: data = f.read() return data def func3(request): with open('active.html','r',encoding='utf-8') as f: data = f.read() active_time = time.ctime() current_data = data.replace('@time',active_time) return bytes(current_data,encoding='utf-8') def func4(request): import pymysql # 创建连接 conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='baicells', db='school') # 创建游标 cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 执行SQL,并返回收影响行数 effect_row = cursor.execute("select * from student ") user_list = cursor.fetchall() # 关闭游标 cursor.close() # 关闭连接 conn.close() print(user_list) """ <tr> <td>%s</td> <td>%s</td> <td>%s</td> <td>%s</td> </tr> """ content_list = [] for row in user_list: tp = "<tr><td>%s</td><td>%s</td><td>%s</td><td>%s</td></tr>" %(row['sid'],row['sname'],row['gender'],row['class_id']) content_list.append(tp) content = "".join(content_list) with open('userlist.html', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: template = f.read() # 模板渲染(模板+数据) data = template.replace('@@content@@',content) return bytes(data,encoding='utf-8') # 基于第三方工具实现模板渲染 def func5(request): import pymysql from jinja2 import Template # 创建连接 conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='baicells', db='school') # 创建游标 cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 执行SQL,并返回收影响行数 effect_row = cursor.execute("select * from student ") host_list = cursor.fetchall() # 关闭游标 cursor.close() # 关闭连接 conn.close() print(host_list) with open('hostlist.html', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: data = f.read() # 模板渲染(模板+数据) template = Template(data) data = template.render(hostlist=host_list) return bytes(data,encoding='utf-8') relation_list = [ ('/information.html',func1),('/login.html',func2),('/active.html',func3),('/mysql.html',func4),('/hostlist.html',func5) ] def run(): while 1: conn,addr = sock.accept() # hang 住 #有人来连接了 #获取用户发送的数据 data = conn.recv(8096) data = str(data,encoding='utf-8') headers,bodys = data.split('\r\n\r\n') temp_list = headers.split('\r\n') method,url,protocal = temp_list[0].split(' ') conn.send(b'HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n\r\n') # 此句不能少,否则浏览器不能识别,因为html的识别需要依据http协议传输才行 func_name = None # 要先定义了,才能使用 for item in relation_list: if url == item[0]: func_name = item[1] break if func_name: response = func_name(bodys) else: response = b'404' conn.send(response) conn.close() if __name__ =='__main__': run()

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>hostlist</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, maximum-scale=1, user-scalable=no"> <!--<link rel="stylesheet" href="bootstrap/css/bootstrap.min.css">--> </head> <body> <table border="1"> <thead> <tr> <th>id</th> <th>name</th> <th>gender</th> <th>class_id</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> {% for row in hostlist %} <tr> <td>{{row.sid}}</td> <td>{{row.sname}}</td> <td>{{row.gender}}</td> <td>{{row.class_id}}</td> </tr> {% endfor %} </tbody> <!--<script src="jQuery-3.3.1.js"></script>--> <!--<script src="bootstrap/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>--> </body> </html>
2.Django框架(通过框架,主要实现业务)
1)安装,在CMD上输入:pip install django
2)创建一个Django项目:django-admin startproject mysite(可以在不同的盘内创建,例如:D:)
3)在CMD上切换到mysite目录下:cd mysite
4)启动服务器:Python manage.py runserver 127.0.0.1:8080
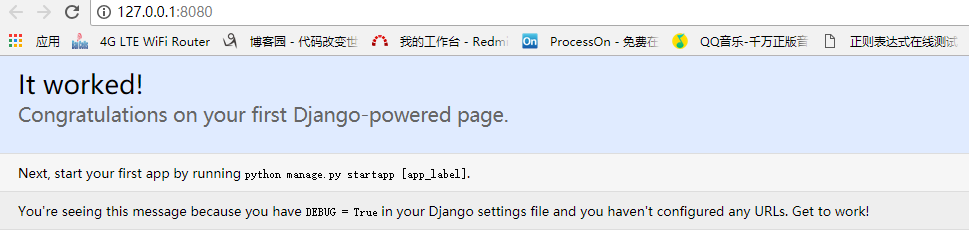
5)检查该简单的网站是否建立成功,打开浏览器,输入:127.0.0.1:8080,如果显示的是该页面,则已经检查成功了。
Django程序目录: mysite -settings.py # Django配置文件 -url.py # 路由系统:URL -> 函数 -wsgi.py #用于定义Django用的socket:wsgiref,uwsgi manage.py #对当前Django程序所有操作可以基于Python manage.py xxxx
3.利用pycharm创建Django框架
1)创建Project
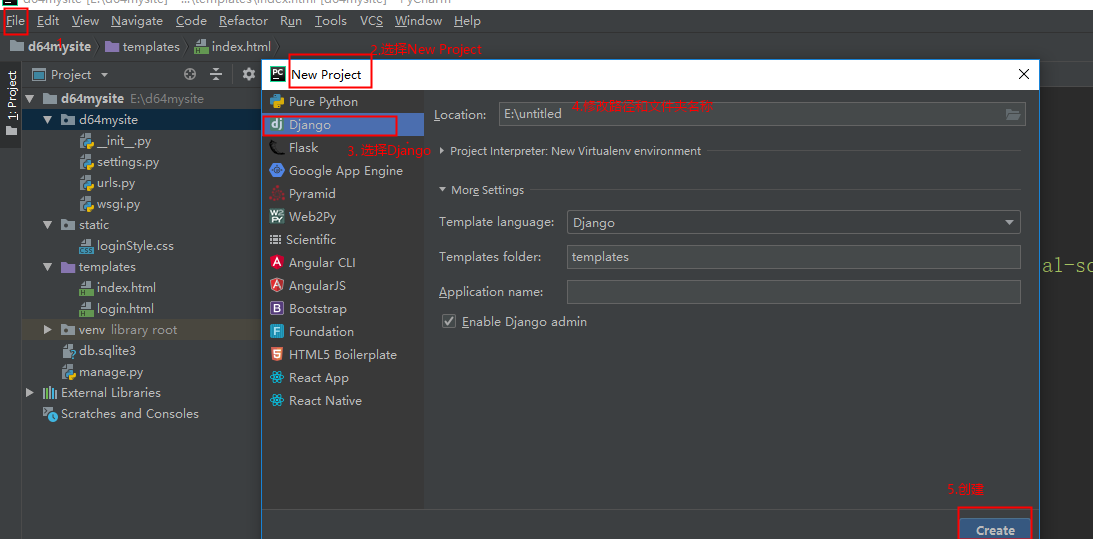
2.配置:
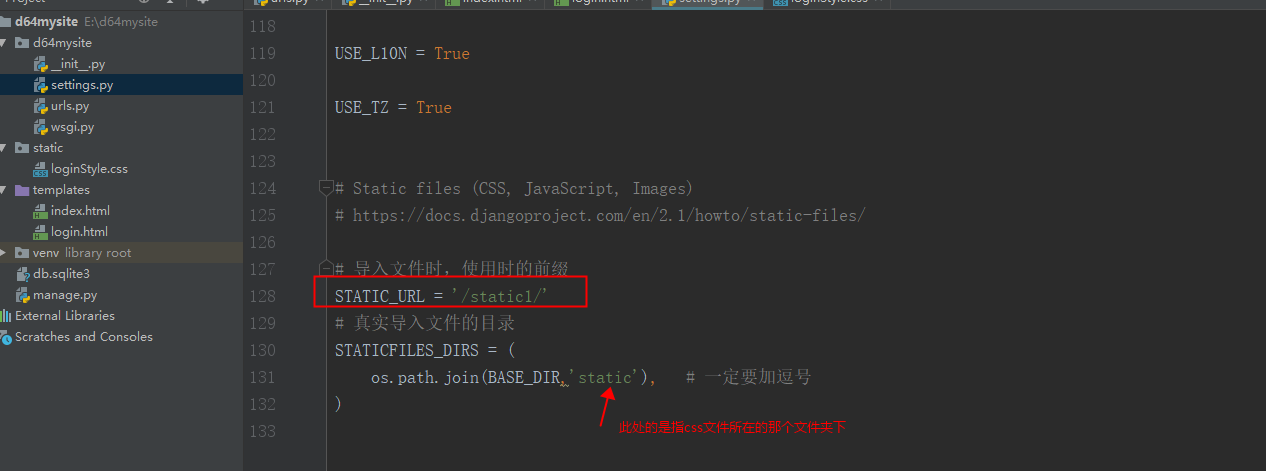
模板路径:template目录,用来存放html文件的(render显示)


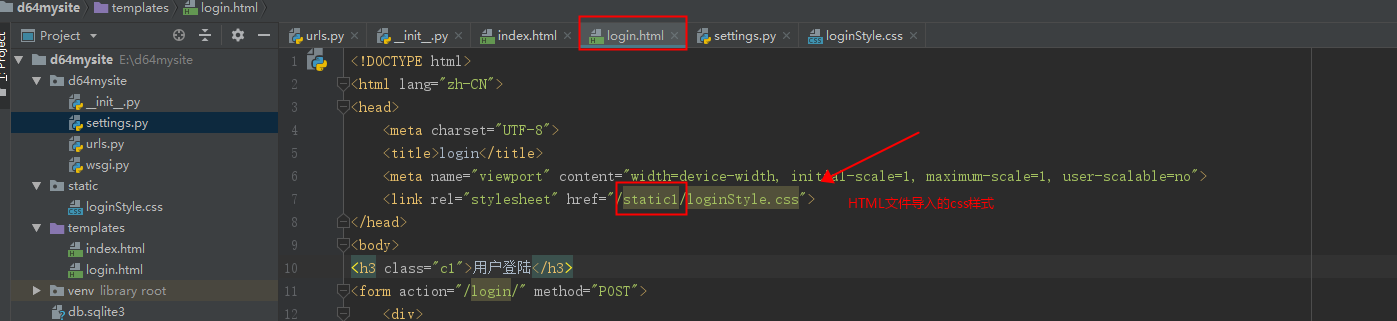
静态文件路径:static 用来导入css,js,等文件的。HTML文件导入的CSS/JS文件时的文件路径前缀/static1/要与settings.py文件的STATIC_URL = '/static1/'一致
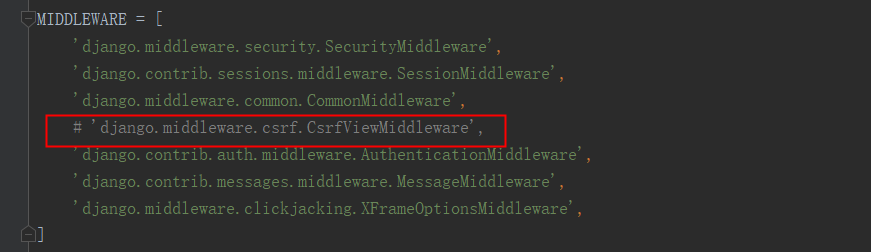
3.额外的配置
在setting文件中注释掉这个字符串
Django框架例子:
Django框架的相关语句和语句 def login(request): # request为请求体的内容参数 request.method request.POST -> 请求体 request.GET -> 请求头的url return HttpResponse(..) return render(request,'login.html',{...} return redirect('网址') GET请求 -> request.GET POST请求 -> request.GET(网址的?开始分割的数据)和request.POST get方式提交的数据会放在url之后,以?分割url和传输数据,参数之间以&相连;post方式提交的数据会放在http包的请求体中,请求体和请求首部字段中间用一行空白相连。 get提交的数据大小有限制(因为浏览器对url的长度有限制),而post方法提交的数据没有限制
重点要学会:for循环和html结合起来,以及模板引擎中的特殊标记{{内容}}
例子:
url.py
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse,render,redirect def login(request): ''' 处理用户请求,并返回内容 :param request: 用户请求相关的所有信息 :return: ''' # HttpResponse只能返回的是字符串类型的 # return HttpResponse('login') # return HttpResponse('<input type="text" />') # 自动找到模板路径下的login.html文件,读取内容并返回给用户 # 模板路径配置 if request.method == "GET": return render(request,'login.html') else: # 用户POST 提交的数据 # print(request.POST) u = request.POST.get('username') # 不同于字典获取request.POST['username'],此不会报错 p = request.POST.get('password') # 数据库连接 import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='baicells', db='userinformation') cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) effect_row = cursor.execute("select * from user") host_list = cursor.fetchall() # 得到的是一个带有字典的列表 cursor.close() conn.close() print(host_list) for item in host_list: if item['name'] == u and item['password'] == p: # 登陆成功 # return redirect('http://www.cnblogs.com') # 重定向到某个页面 return redirect('/index/') else: # 登陆失败 return render(request,'login.html',{'error':'用户名或密码错误'}) def index(request): return render(request,'index.html',{'name':'alex','users':['林聪','燕子'],'user_dict':{'k1':'v1','k2':'v2'}, 'user_list_dict':[ {'id':1,'name':'alex','email':'alex3714@163.com'}, {'id':2,'name':'alex2','email':'alex3714@1632.com'}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'alex3', 'email': 'alex3714@1633.com'}, ]}) urlpatterns = [ # path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('login/', login), path('index/',index), ]
index.html :标记语言与for循环的应用
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, maximum-scale=1, user-scalable=no"> </head> <body> <h1>标记模板</h1> <p>{{ name }}</p> <P>{{ users }}</P> <p><h2>{{ users.0 }}</h2></p> <p><h2>{{ users.1 }}</h2></p> <p>{{ user_dict.k1 }}</p> <p>{{ user_dict.k2 }}</p> <h1>循环</h1> {% for item in users %} <p>{{ item }}</p> {% endfor %} {% for item in user_dict.values %} <p>{{ item}}</p> {% endfor %} <table border="1"> <thead> <tr> <th>id</th> <th>name</th> <th>email</th> <th>操作</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> {% for row in user_list_dict %} <tr> <td>{{ row.id}}</td> <td>{{ row.name }}</td> <td>{{ row.email }}</td> <td> <a href="">编辑</a> | <a href="">删除</a> </td> </tr> {% endfor %} </tbody> </table> </body> </html>
login.html:Django框架的发送数据显示
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>login</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, maximum-scale=1, user-scalable=no"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static1/loginStyle.css"> </head> <body> <h3 class="c1">用户登陆</h3> <form action="/login/" method="POST"> <div> <label for="username">用户名</label> <input type="text" id="username" name="username"> </div> <div> <label for="password">密码</label> <input type="password" id="password" name="password"> </div> {{ error }} <div> <input type="submit" value="登陆"> </div> <!--提交数据的时候是以字典的形式提交--> <!-- username:输入的username password:输入的密码--> </form> </body> </html>
loginStyle.css样式:
.c1 { color: green; }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号