k8s flannel插件
CNI:
规定了容器和网络插件之间的协议,协议规定了CNI插件的输入和输出。
CNI需要提供将网络接口加入指定网络和从指定网络删除的命令,分别在创建容器和销毁容器时候调用。
类似docker的容器runtime会为容器分配网络命名空间和容器ID,然后结合一些其他CNI配置参数传给网络驱动,网络驱动会将容器添加到网络并为其分配ip地址。
Flannel:
flanne为每个pod都会被分配唯一的ip地址,且每个K8s node的subnet各不重叠;
flanneld将本主机获取的subnet以及用于主机间通信的Public IP通过etcd存储起来;
flannel利用各种机制,例如udp,vxlan等等,跨主机转发容器间的网络流量,完成容器间的跨主机通信;
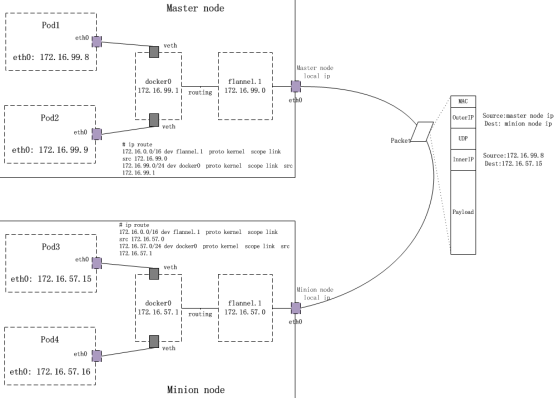
Cni0:
与docker0一样,是linux bridge,每创建一个pod都会创建一对 veth pair。其中一端是pod中的网卡,另一端是Cni0网桥中的端口,Pod中从网卡发出的流量都会发送到Cni0网桥设备的端口上。
Flannel.1
overlay网络的设备,用来进行 vxlan 报文的处理(封包和解包)。不同node之间的pod数据流量都从overlay设备以隧道的形式发送到对端
Flanneld
flannel在每个主机中运行flanneld作为agent,它会为所在主机从集群的网络地址空间中,获取一个小的网段subnet,本主机内所有容器的IP地址都将从中分配。同时Flanneld监听K8s集群数据库,为flannel.1设备提供封装数据时必要的mac,ip等网络数据信息。
我们这边ping 10.122.1.6;
容器中的路由信息:
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 10.122.1.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
10.122.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
10.244.0.0 10.122.1.1 255.255.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0`
可以看到,容器的数据包会通过eth0走到10.122.1.1,我们的pod在node上,我们去node上看一下:
cni0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1450
inet 10.122.1.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 10.122.1.255
ether 3e:20:d1:d4:39:96 txqueuelen 0 (Ethernet)
RX packets 15734 bytes 915230 (893.7 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 4580 bytes 415120 (405.3 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
10.122.1.1就是cni0的地址
[root@VM-91-167-centos ~]# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 9.135.88.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
9.0.0.0 9.135.88.1 255.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
9.135.88.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.248.0 U 0 0 0 eth1
10.0.0.0 9.135.88.1 255.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
10.122.0.0 10.122.0.0 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 flannel.1
10.122.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 cni0
100.64.0.0 9.135.88.1 255.192.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1002 0 0 eth1
172.16.0.0 9.135.88.1 255.240.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
192.168.0.0 9.135.88.1 255.255.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
192.168.10.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 docker0
因为目的也在本机,所以根据路由信息,这边会直接走到回到cni0,并且根据内部路由转发到对应地址;
如果ping 10.122.0.3;
就会走到flannel.1,
[root@VM-91-167-centos ~]# ip n
9.135.88.1 dev eth1 lladdr fe:ee:7e:31:3a:5a REACHABLE
10.122.0.0 dev flannel.1 lladdr 02:b9:d7:59:0e:82 PERMANENT
10.122.1.2 dev cni0 lladdr 1a:a1:f0:c5:0a:36 REACHABLE
169.254.0.34 dev eth1 lladdr fe:ee:7e:31:3a:5a STALE
10.122.1.4 dev cni0 lladdr 02:bf:90:fb:ca:d0 STALE
169.254.0.35 dev eth1 lladdr fe:ee:7e:31:3a:5a STALE
169.254.128.5 dev eth1 lladdr fe:ee:7e:31:3a:5a REACHABLE
169.254.169.254 dev eth1 lladdr fe:ee:7e:31:3a:5a STALE
169.254.128.10 dev eth1 lladdr fe:ee:7e:31:3a:5a REACHABLE
10.122.1.7 dev cni0 lladdr c2:dc:12:50:4d:f9 STALE
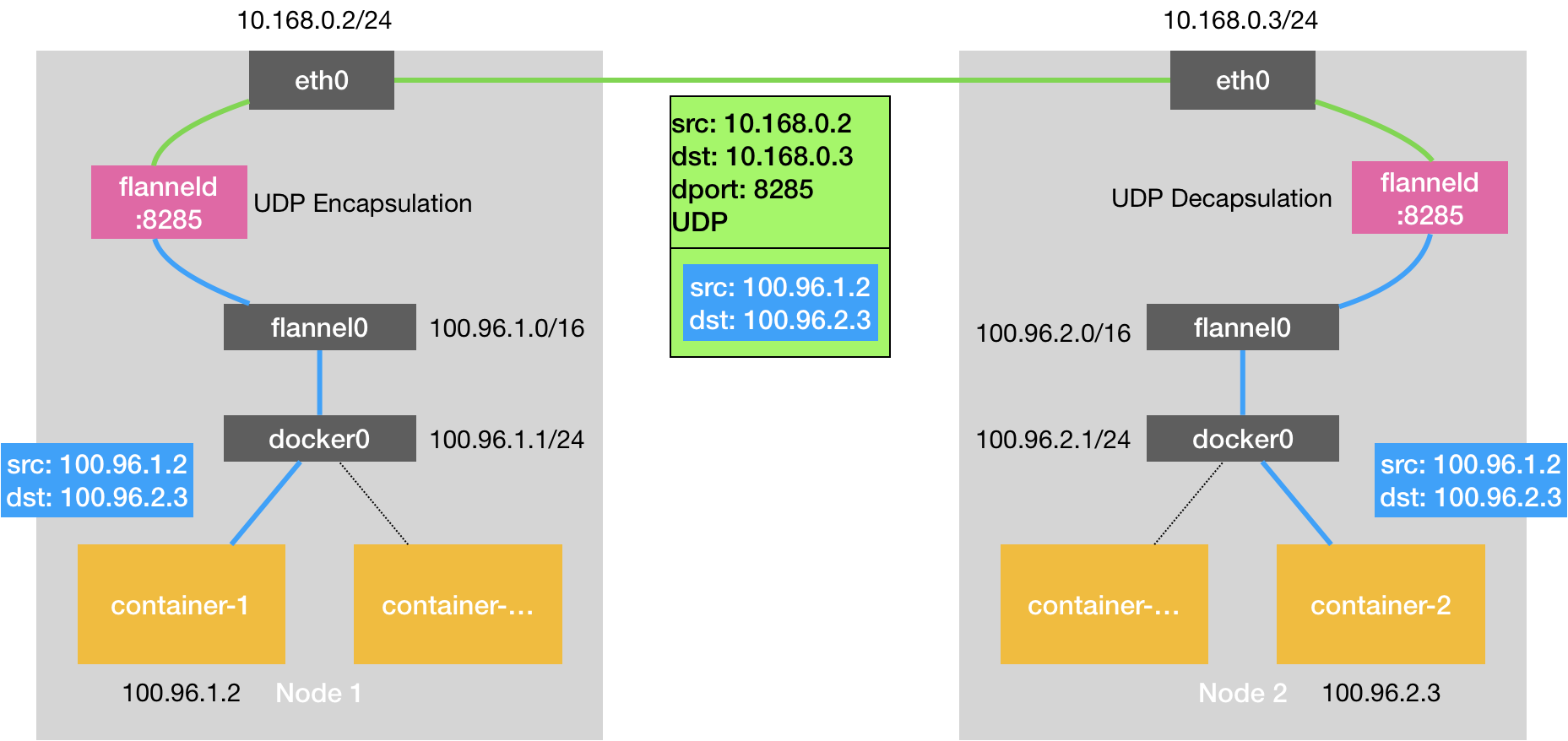
flannel.1根据目的网关地址查到对应节点网卡的mac,然后进行封内部包,再根据节点ip地址封外部包:

换到另一个节点:
[root@lai ~]# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 9.134.64.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
9.0.0.0 9.134.64.1 255.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
9.134.64.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.240.0 U 0 0 0 eth1
10.0.0.0 9.134.64.1 255.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
10.122.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 cni0
10.122.1.0 10.122.1.0 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 flannel.1
100.64.0.0 9.134.64.1 255.192.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1002 0 0 eth1
172.16.0.0 9.134.64.1 255.240.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
192.168.0.0 9.134.64.1 255.255.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
192.168.10.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 docker
flannel.1进行解包,然后根据路由转发给cni0,
[root@lai ~]# arp -n
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
169.254.128.10 ether fe:ee:c6:38:ee:a8 C eth1
10.122.1.0 ether 6e:59:fa:2c:9c:02 CM flannel.1
169.254.0.34 ether fe:ee:c6:38:ee:a8 C eth1
169.254.0.35 ether fe:ee:c6:38:ee:a8 C eth1
10.122.0.4 (incomplete) cni0
169.254.169.254 ether fe:ee:c6:38:ee:a8 C eth1
9.134.64.1 ether fe:ee:c6:38:ee:a8 C eth1
10.122.0.3 ether ca:37:43:1b:fc:4d C cni0
169.254.128.5 ether fe:ee:c6:38:ee:a8 C eth1
10.122.0.2 ether 06:d9:33:5c:6e:3e C cni0
9.134.73.10 ether fe:ee:c6:38:ee:a8 C eth1
查找到目的mac地址,转发到对应网卡:
[root@lai ~]# kubectl exec -it iperf-clients-q7lh2 sh
kubectl exec [POD] [COMMAND] is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl kubectl exec [POD] -- [COMMAND] instead.
# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1450 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether ca:37:43:1b:fc:4d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.122.0.3/24 brd 10.122.0.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
交互大致是这样的:
负载均衡:
Service
Service定义了Pod的逻辑集合和访问该集合的策略,是真实服务的抽象。Service提供了一个统一的服务访问入口以及服务代理和发现机制,关联多个相同Label的Pod,用户不需要了解后台Pod是如何运行。
外部系统访问Service的问题,首先需要弄明白Kubernetes的三种IP:Node IP:Node节点的IP地址, 是Kubernetes集群中节点的物理网卡IP地址,所有属于这个网络的服务器之间都能通过这个网络直接通信;Pod IP:Pod的IP地址, 是Docker Engine根据docker0网桥的IP地址段进行分配的,通常是一个虚拟的二层网络;Cluster IP:Service的IP地址,一个虚拟的IP,作用于Kubernetes Service这个对象,并由Kubernetes管理和分配IP地址
kube-proxy:
service在逻辑上代表了后端的多个Pod,外界通过service访问Pod。service接收到的请求是如何转发到Pod的呢?这就是kube-proxy要完成的工作。每个Node都会运行kube-proxy 服务,它负责将访问service的TCP/UPD数据流转发到后端的容器。如果有多个副本,kube-proxy会实现负载均衡。kube-proxy使用etcd的watch机制,监控集群中service和endpoint对象数据的动态变化,并且维护一个service到endpoint的映射关系,从而保证了后端pod的IP变化不会对访问者造成影响。
etcd:
etcd 负责保存 Kubernetes Cluster 的配置信息和各种资源的状态信息。当数据发生变化时,etcd 会快速地通知 Kubernetes 相关组件。







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号