JUC学习-15-线程6种的状态
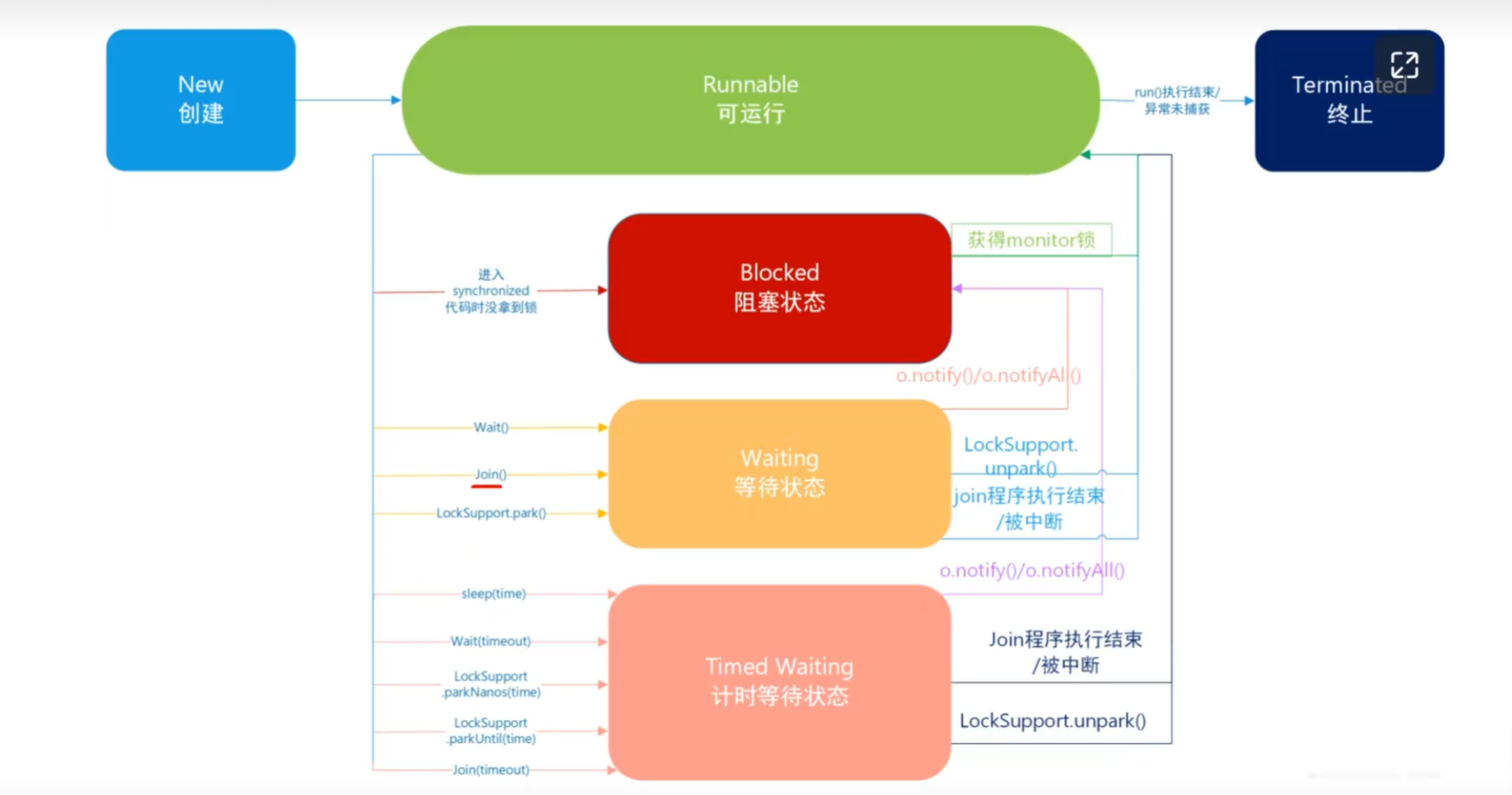
JUC学习-15-线程的6种状态
通过getState()方法来获取线程的状态
public state getState()
Java中 线程状态时用6个Enum表示,分别是
NEW, 初始状态,线程被构建。但是还没有调用start()方法
RUNNABLE, 运行状态,已经调用了start()方法,Java将操作系统中的就绪和运行的两种状态成为“运行中”
BLOCKED, 阻塞状态,表示线程阻塞于锁
WAITING,等待状态,表示线程进入<等待状态>,进入该状态的线程表示当前线程需要其他线程通知(notify或者notifyAll)
TIMED_WAITING,超时等待状态,可以指定等待时间自己返回
TERMINATED, 终止状态 表示当前线程已经执行完毕
相关代码:
一、State —> NEW(创建)
class StateThead {
public void test1() {
// 创建一个线程 此时state是 NEW
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("Thread1----");
});
System.out.println(t1.getState());
}
}
二、State —> TERMINATED(线程终止)
public void test2() throws InterruptedException {
// 线程终止状态 TERMINATED
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("线程开始执行");
System.out.println("线程执行结束");
});
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(t1.getState());
}
三、State —> RUNNABLE (正在运行)
public void test3 () {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
});
t1.start();
System.out.println(t1.getState());
}
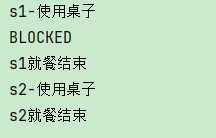
四、State —> BLOCKED
线程stud1执行start()方法后,运行table.use()方法并开始睡眠。 -> 线程stud2执行start()方法后,同样要运行table.use()方法,但是由于方法被synchronized锁修饰,导致无法进入到方法体内,此时线程状态为BLOCKED(阻塞状态)。等待线程stud1睡眠结束后,线程stud2正常执行table.use()方法。直到结束
public static void test4() throws InterruptedException {
// 局部内部类
class Table {
public synchronized void use() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-使用桌子");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "就餐结束");
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
Table table = new Table();
Thread stud1 = new Thread(() -> {
table.use();
}, "s1");
Thread stud2 = new Thread(() -> {
table.use();
}, "s2"
);
stud1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
stud2.start();
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println(stud2.getState());
}
结果如下:
五、State —> WAITING/TIMED WAITING
public static void test5() {
class Table1 {
public synchronized void use() throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-使用桌子");
// 忘记点餐了
System.out.println("忘记点餐了");
wait();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "就餐结束");
}
}
Table1 table1 = new Table1();
Thread stud1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
table1.use();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "s1");
stud1.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(stud1.getState());
}
结果如下:

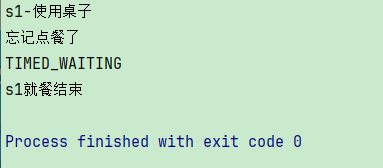
计时等待(TIMED WAITING)
public static void test5() {
class Table1 {
public synchronized void use() throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-使用桌子");
// 忘记点餐了
System.out.println("忘记点餐了");
wait(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "就餐结束");
}
}
Table1 table1 = new Table1();
Thread stud1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
table1.use();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "s1");
stud1.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(stud1.getState());
}
结果如下:
本文来自博客园,作者:skystrivegao,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/skystrive/p/18978451
整理不易,如果对您有所帮助 请点赞收藏,谢谢~

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号