381,合并两个有序链表(易)
想了解更多数据结构以及算法题,可以关注微信公众号“数据结构和算法”,每天一题为你精彩解答。也可以扫描下面的二维码关注

将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例:
输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
问题分析
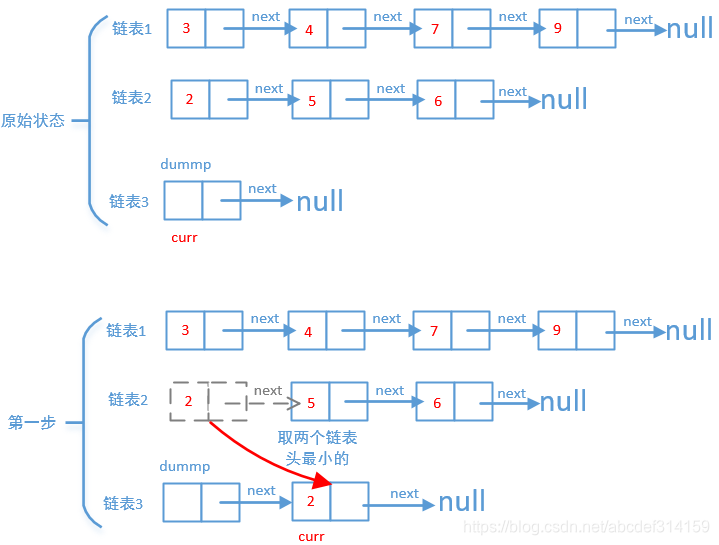
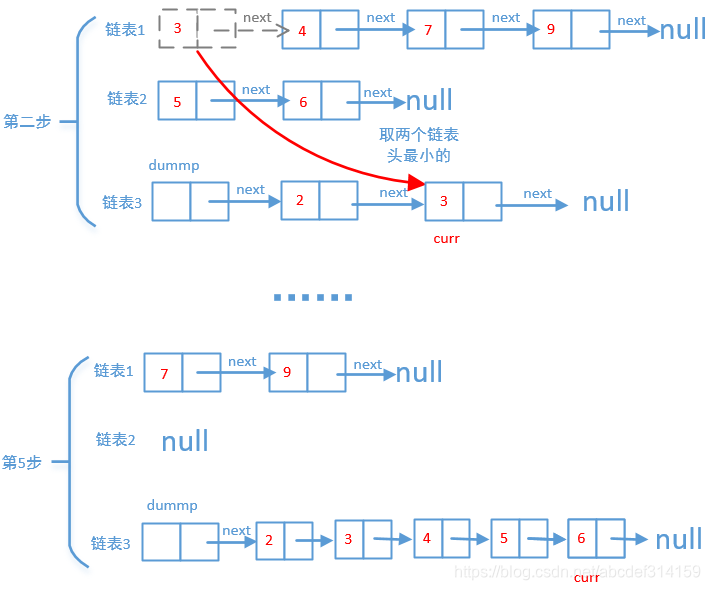
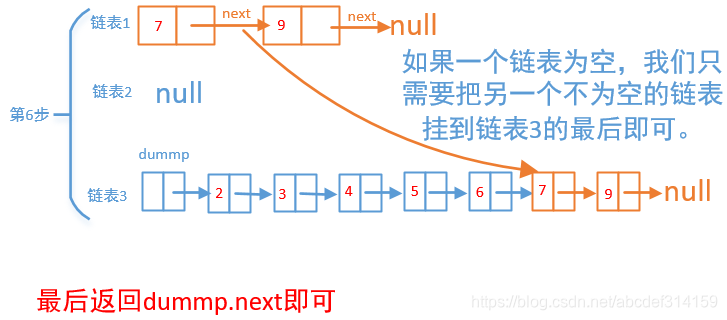
这题比较简单,因为链表是升序的,我们只需要遍历每个链表的头,比较一下哪个小就把哪个链表的头拿出来放到新的链表中,一直这样循环,直到有一个链表为空,然后我们再把另一个不为空的链表挂到新的链表中。我们就以3→4→7→9和2→5→6两个链表来画个图看一下是怎么合并的。
01
链表合并代码
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode linked1, ListNode linked2) {
//下面4行是空判断
if (linked1 == null)
return linked2;
if (linked2 == null)
return linked1;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode curr = dummy;
while (linked1 != null && linked2 != null) {
//比较一下,哪个小就把哪个放到新的链表中
if (linked1.val <= linked2.val) {
curr.next = linked1;
linked1 = linked1.next;
} else {
curr.next = linked2;
linked2 = linked2.next;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
//然后把那个不为空的链表挂到新的链表中
curr.next = linked1 == null ? linked2 : linked1;
return dummy.next;
}
02
链表合并递归写法
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode linked1, ListNode linked2) {
if (linked1 == null)
return linked2;
if (linked2 == null)
return linked1;
if (linked1.val < linked2.val) {
linked1.next = mergeTwoLists(linked1.next, linked2);
return linked1;
} else {
linked2.next = mergeTwoLists(linked1, linked2.next);
return linked2;
}
}
递归写法其实我们还可以写的更简洁一些
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode linked1, ListNode linked2) {
//只要有一个为空,就返回另一个
if (linked1 == null || linked2 == null)
return linked2 == null ? linked1 : linked2;
//把小的赋值给first
ListNode first = (linked2.val < linked1.val) ? linked2 : linked1;
first.next = mergeTwoLists(first.next, first == linked1 ? linked2 : linked1);
return first;
}

关注微信公众号“数据结构和算法”,查看更多算法题



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号