第四次作业:结对编程
第四次作业:结对编程
| Git项目地址 | 项目地址 |
|---|---|
| 姓名 | 曲晨阳 |
| 学号 | 201831061313 |
| 结对伙伴 | 潘伟键 |
| 伙伴博客地址 | https://www.cnblogs.com/pwj1278634240/ |
| 学号 | 201831061312 |
| 1.结对编程照片 |

2.PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 43 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 1200 | 1500 |
| Development | 开发 | 60 | 90 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 30 | 60 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 40 | 20 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 30 | 30 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | 30 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 120 | 150 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 600 | 800 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 200 | 300 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 120 | 150 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 30 | 60 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 20 | 20 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 30 | 35 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 30 |
| 合计 | 2560 | 3318 |
3.解题过程
Wordcount需求描述:
统计input.txt中的以下几个指标
1.统计文件的字符数:
只需要统计Ascii码,汉字不需考虑
空格,水平制表符,换行符,均算字符
英文字母:A-Z,a-z
字母数字符号:A-Z,a-z,0-9
分割符:空格,非字母数字符号
例;file123是一个单词,123file不是一个单词。file,File和FILE是同一个单词输出的单词统一为小写格式
2.统计文件的单词总数,单词:至少以4个英文字母开头,跟上字母数字符号,单词以分隔符分割,不区分大小写。
3.统计文件的有效行数:任何包含非空白字符的行,都需要统计。
4.统计文件中各单词的出现次数,最终只输出频率最高的10个。频率相同的单词,优先输出字典序靠前的单词。
输出的格式为
· characters: number
· words: number
· lines: number
· <word1>: number
· <word2>: number
· ...
解题思路:
题目要求统计一个文本文档中的字符数,单词数等,我们的思路是先把文档中的字符全部取出来,存在一个string类的字符串里,然后再进行计数等操作。
在解题过程中,我和我的搭档首先进行了分工,我负责写出main函数和计算字符的函数,我的搭档潘伟键负责写出单词统计和输出十个高频词汇的函数。
分工完成后,我和伟键同时进行编码活动,这个过程不是独立的,在编代码时我们经常交流,互相给出意见,这样最终的代码吻合度高,开发效率也很不错。
思路图:

详细代码:
- 判断是不是有效单词
- 把大写字母转换成小写字母
- 把储存在string里的字符转换为单词
- 统计字符数
总代码:
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//写入文件
ofstream tongji("output.txt", ios::app);
class word_count
{
private:
string str;
public:
//输出原文
void output()
{
cout << "原文:" << endl;
cout << str << endl;
}
//统计字符数
int countzifu()
{
int i = 0;
int sum = 0;
while (str[i] != '\0')
{
if (str[i] <= 126 && str[i] >= 32 || str[i] == 10 || str[i] == 13)
sum++;
i++;
}
return sum;
cout << endl << "字符个数:" << sum << endl;
tongji << "字符个数:" << sum << '\n';
}
//将文件中的字符存入一个string字符串
void getinstr(stringstream &s)
{
str = s.str();
}
//判断是不是有效单词
int judgeword(string a)
{
int i = a.size(), n;
if (i < 4)
{
return 0;
}
for (n = 0; n < 4; n++)
{
if (a[n] < 65 || 91 <= a[n] && a[n] < 96 || a[n]>123 && a[n] < 127)
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
//把大写字母转化为小写字母
void turn(string& a)
{
int n = 0;
while (a[n] != '\0')
{
if ('A' <= a[n] && a[n] <= 'Z')
a[n] = a[n] + 32;
n++;
}
}
//输出前十个高频词汇
void tenword(string a[500], int n)
{
int j, k, p = 0, t = 0, i;
string b[500];
int count[500];
int count1[500];
int count3[500];
for (k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
count[k] = 1;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (b[j] == a[k])
{
count[j]++;
break;
}
}
if (j == n)
{
b[p] = a[k];
p++;
}
}
for (k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
count1[k] = count[k];
count3[k] = k;
}
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i)
{ // 二重循环完成选择排序
k = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
if (count1[k] < count1[j]) k = j;
}
if (k != i) {
t = count1[k];
count1[k] = count1[i];
count1[i] = t;
t = count3[i]; // 辅助数组同步操作
count3[i] = count3[k];
count3[k] = t;
}
}
for (k = 0; k < 10; k++) {
cout << '<' << b[count3[k]] << ">: " << count[count3[k]] << endl;
tongji << '<' << b[count3[k]] << ">: " << count[count3[k]] << '\n';
}
}
//把string a转化为单词
int readword()
{
int n = 0;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int count = 0;
string b[500];
string c[500];
while (str[i] != '\0')
{
if (str[i] != 32 && str[i] != 44 && str[i] != 46)
{
b[n] = b[n] + str[i];
i++;
}
else
{
n++;
i++;
}
}
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (judgeword(b[j]) == 1)
{
turn(b[j]);
c[count] = b[j];
count++;
}
}
tenword(c, count);
return count;
}
};
int main()
{
int a;
fstream wordfill("input.txt");//打开文档文件
stringstream ss;
ss << wordfill.rdbuf();
word_count count1;
ofstream tongji("output.txt", ios::app);//写入文件
count1.getinstr(ss);//将文件中的字符存入一个string字符串
count1.output();//输出原文
a = count1.countzifu();//调用统计字符函数
cout << endl << "字符个数:" << a << endl;
tongji << "字符个数:" << a << '\n';
a = count1.readword();//调用单词统计函数
cout << "单词个数:" << a << endl;
tongji << "单词个数:" << a << '\n';
tongji.close();
}
代码复审:
我和我的同伴把写好的函数合并起来,然后共同封装成一个wordcount类,其中发现了一些输出错误,进行了改正。
运行截图:
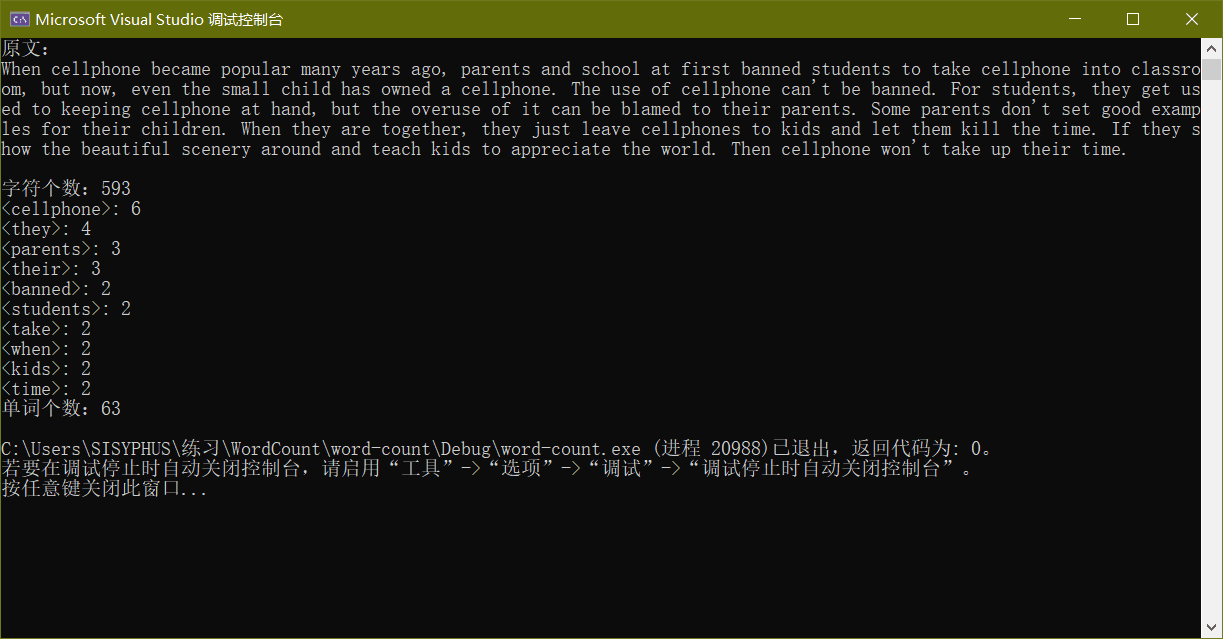
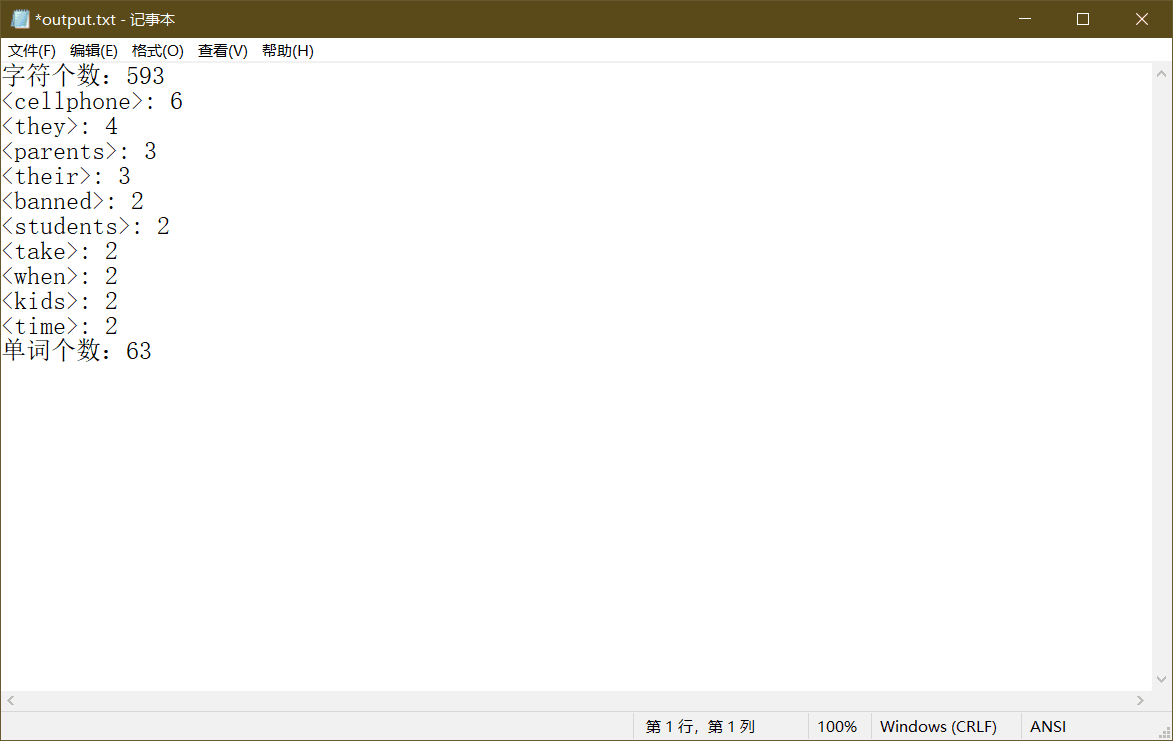
4.性能分析及单元测试:
- 性能分析:

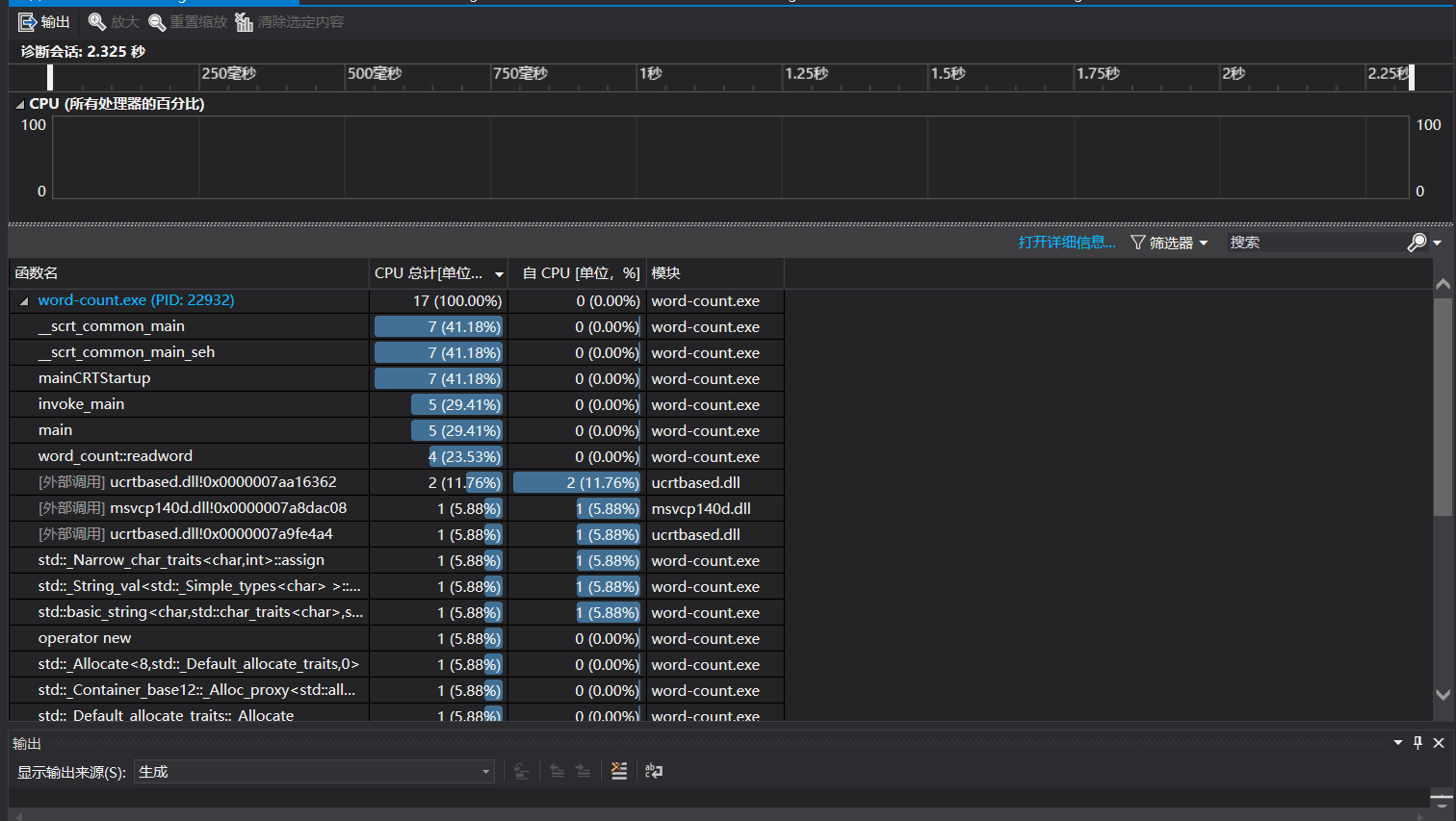
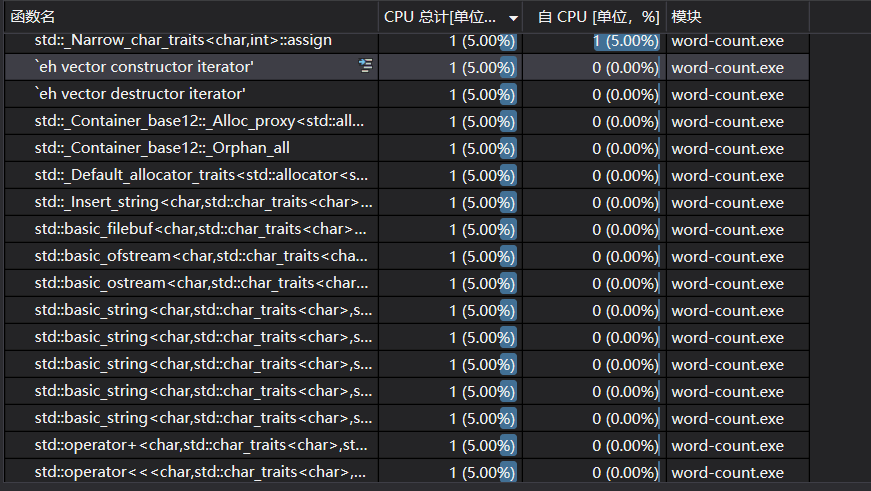
- 单元测试:
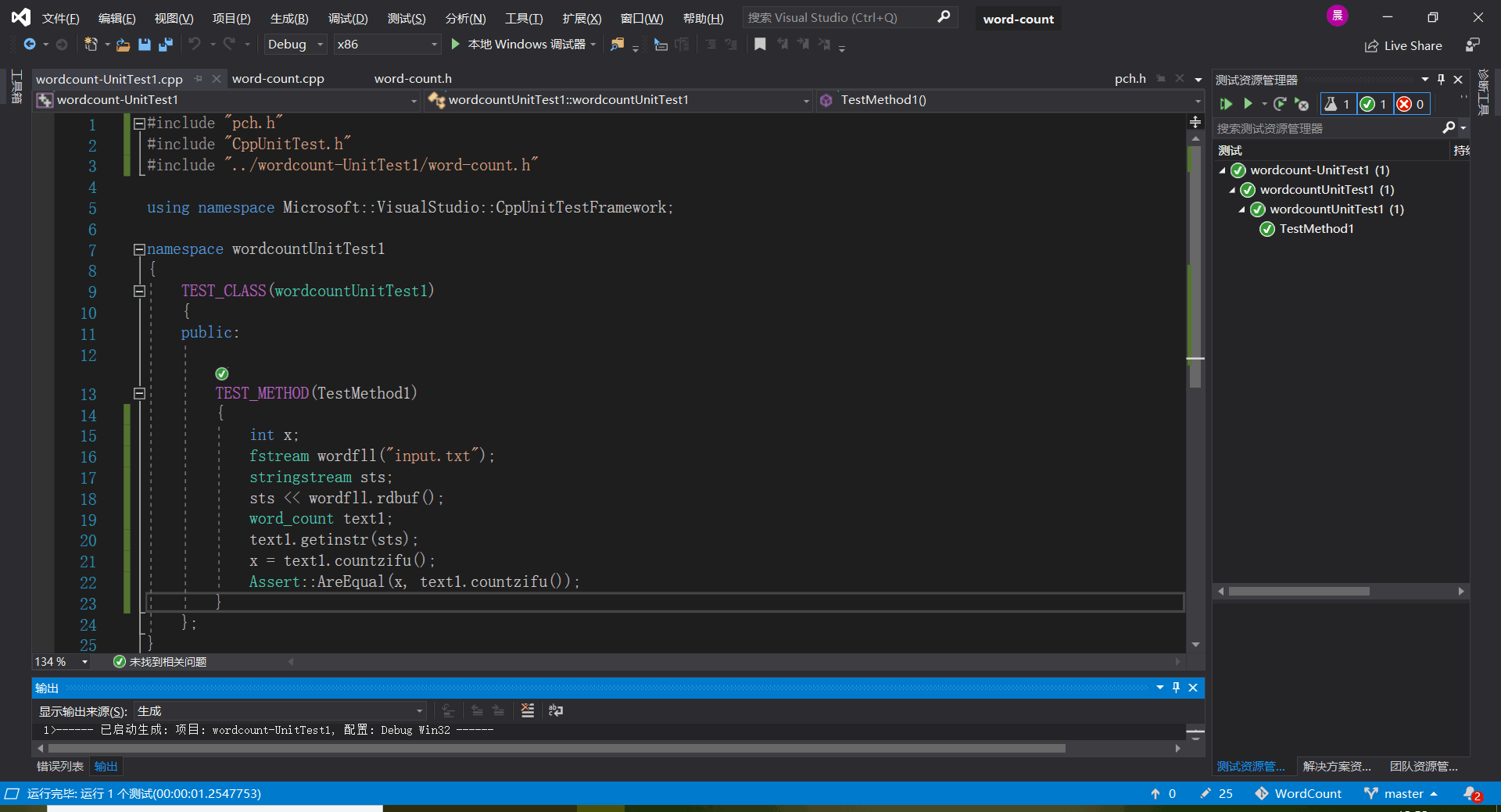
5:小结:
这次作业可以说是第二次作业的一次升级,使用第二次学习的工具,通过结对编程的方式完成这个题目,我的结对搭档潘伟键非常认真负责,写的代码很完美,都完成了要求的功能,最后在单元测试上面卡了很久很久,最后询问了同学才得以解决,在第二次作业时就没有学好,在以后的作业中还要更加认真去学习。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号