future task cancel (二)向下传递中断【重要】- (java object多大 java对象内存模型 数组有多长(十三))
1 测试用例
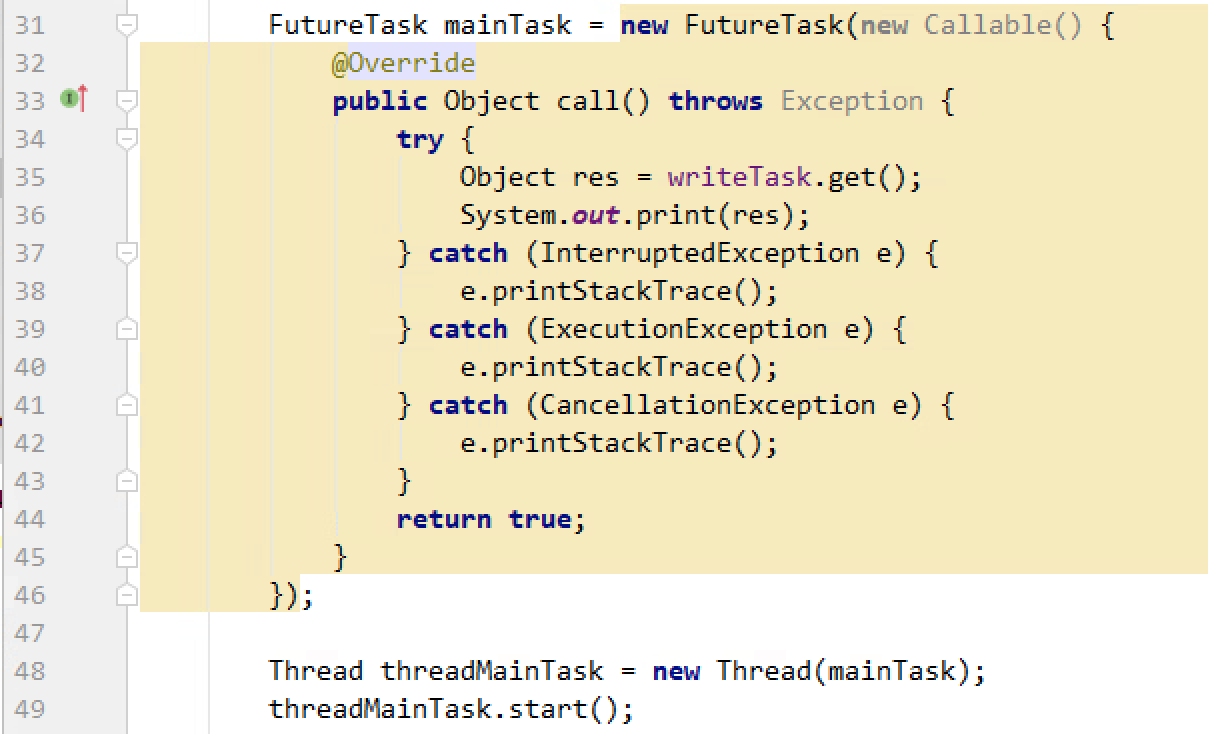
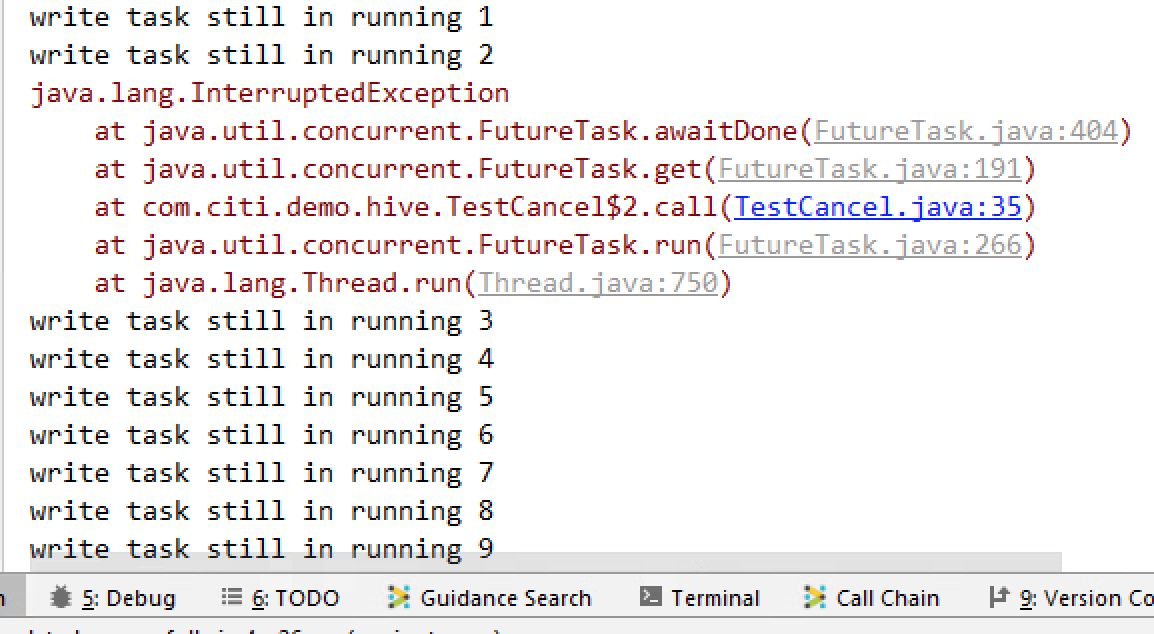
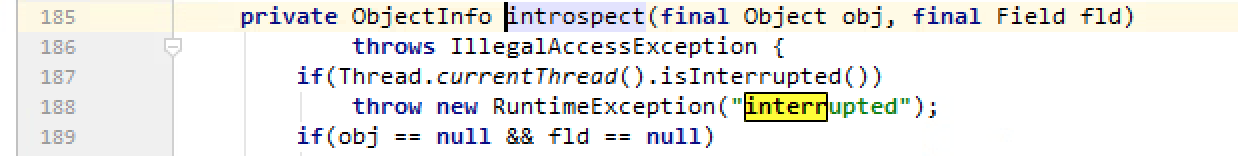
当future.get响应interruptedexception时,意味着外界想要中断你这个线程和所有子任务
那么应当在interruptedexception响应中对future进行cancel


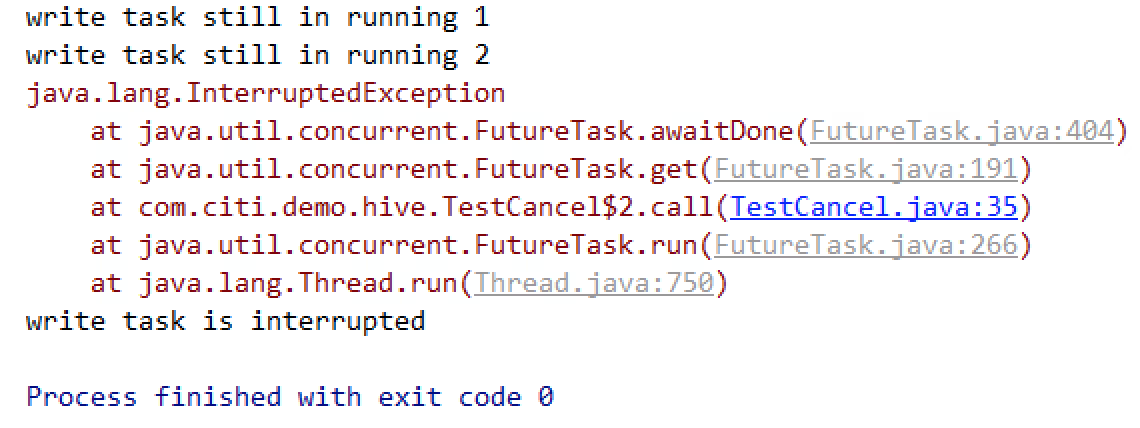
60 61 行一样结果
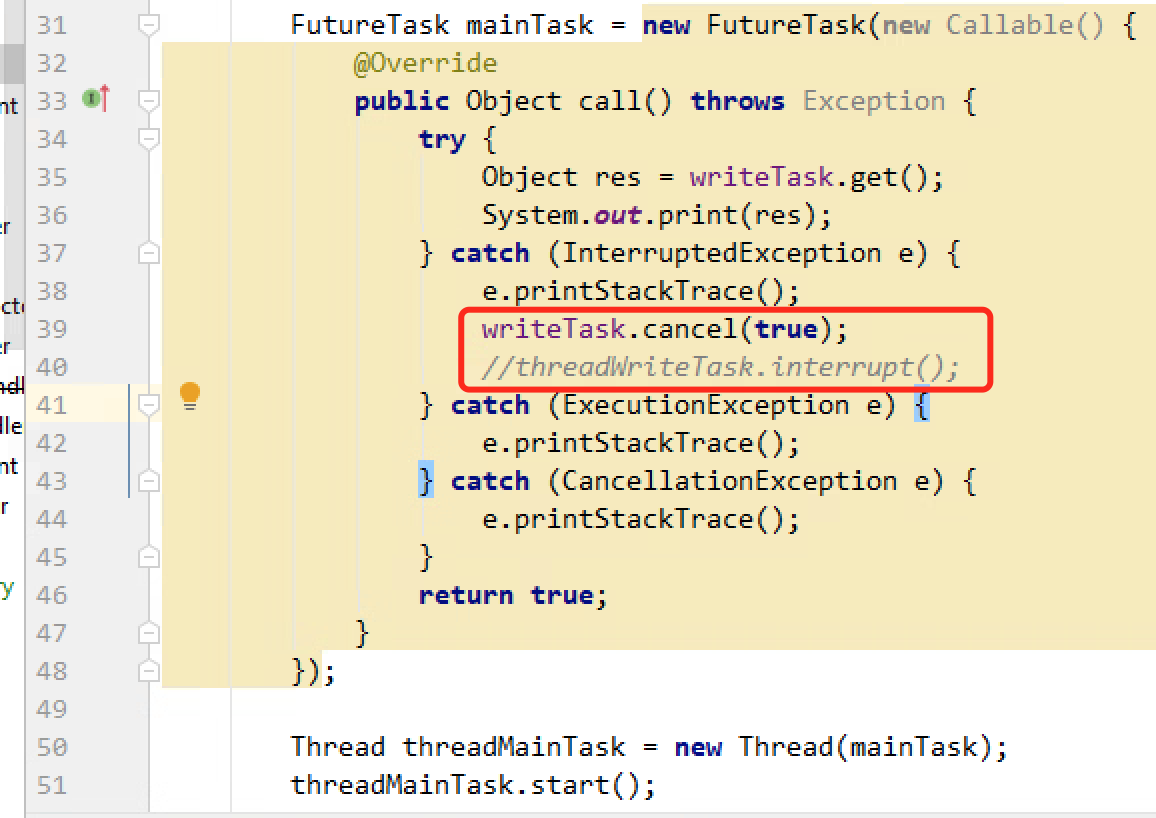
应当在38行处中断子任务writeTask
2 实例

1)主线程被interrupt,135行,重置主线程旗标,并且cancel子线程
2)主线程cancel,同1)
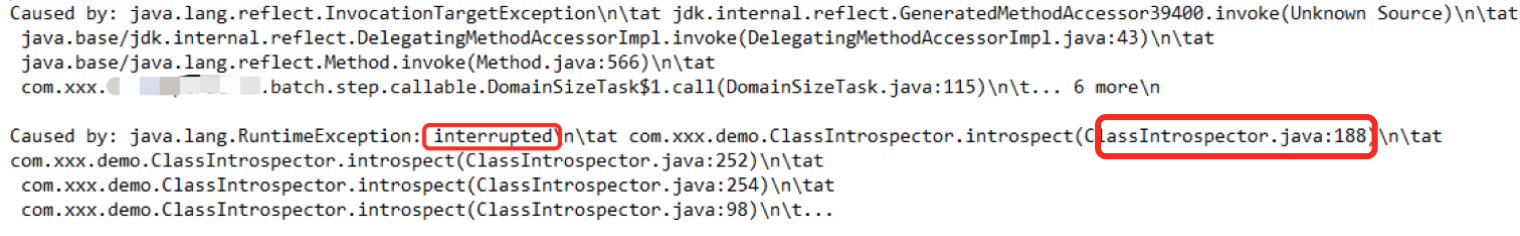
3)子线程被interrupt,114行-127行-139行
4)子线程被cancel,141行
子线程
主线程
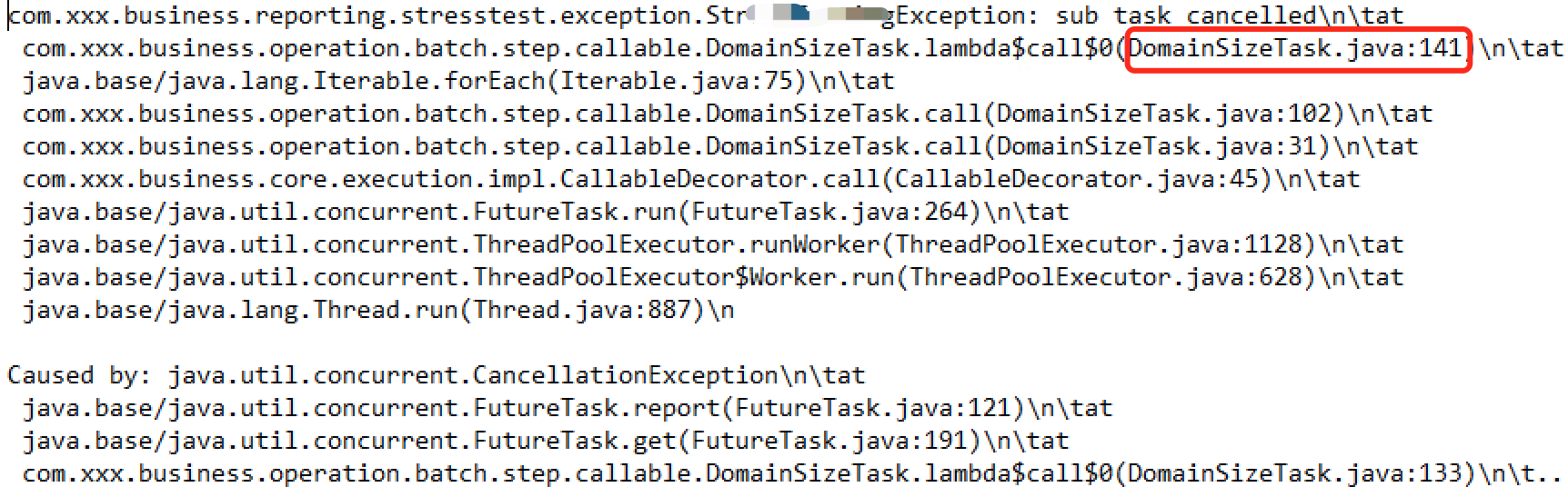
没有线程泄漏
![]()
testcase:
package markdown.memory;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class TestCancel {
private static AtomicInteger no = new AtomicInteger(0);
private static List<Boolean> assertRes = new ArrayList<>();
private static Map<Integer, FutureTask> tasksLeak = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static Map<Integer, Thread> threadsLeak = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static BlockingQueue<Exception> queueException = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5);
private static BlockingQueue<Boolean> queueIsInturruped = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5);
private static int time = 2000;
private static CountDownLatch assertLock = new CountDownLatch(1);
public static void main(String []f) throws Exception {
int no = registerSubTask();
runMainTask(no);
Thread.sleep(time);
FutureTask cancelSubTask = tasksLeak.get(no);
cancelSubTask.cancel(true);
assertLock.await(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
assertRes.add(!tasksLeak.containsKey(no));
assertRes.add(!threadsLeak.containsKey(no));
Exception eMainTask = queueException.poll(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
assertRes.add(eMainTask.getCause() instanceof CancellationException);
assertRes.add(eMainTask.getMessage().equalsIgnoreCase("sub task cancelled"));
assertRes.add(queueIsInturruped.poll(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
assertLock = new CountDownLatch(1);
no = registerSubTask();
runMainTask(no);
Thread.sleep(time);
Thread interruptedThread = threadsLeak.get(no);
interruptedThread.interrupt();
assertLock.await(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
assertRes.add(!tasksLeak.containsKey(no));
assertRes.add(!threadsLeak.containsKey(no));
eMainTask = queueException.poll(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
assertRes.add(eMainTask.getCause() instanceof ExecutionException);
assertRes.add(eMainTask.getMessage().equalsIgnoreCase("Error when domain size"));
assertRes.add(!queueIsInturruped.poll(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
assertLock = new CountDownLatch(1);
no = registerSubTask();
Thread mainThread = runMainTask(no);
Thread.sleep(time);
mainThread.interrupt();
assertLock.await(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
assertRes.add(!tasksLeak.containsKey(no));
assertRes.add(!threadsLeak.containsKey(no));
eMainTask = queueException.poll(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
assertRes.add(eMainTask.getCause() instanceof InterruptedException);
assertRes.add(eMainTask.getMessage().equalsIgnoreCase("main task cancelled"));
assertRes.add(queueIsInturruped.poll(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
assertLock = new CountDownLatch(1);
no = registerSubTask();
runMainTask(no);
Thread.sleep(7000);
assertLock.await(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
assertRes.add(!tasksLeak.containsKey(no));
assertRes.add(!threadsLeak.containsKey(no));
eMainTask = queueException.poll(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
assertRes.add(eMainTask.getCause() instanceof TimeoutException);
assertRes.add(eMainTask.getMessage().equalsIgnoreCase("main task timeout"));
assertRes.add(queueIsInturruped.poll(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
for(Boolean res : assertRes) {
print(res);
}
}
private static Thread runMainTask(int no) {
Thread mainThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
runSubTask(no);
} catch (Exception e) {
queueException.add(e);
print("status of main task " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
queueIsInturruped.add(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
}
}
});
mainThread.start();
return mainThread;
}
private static void runSubTask(int no) {
FutureTask future = tasksLeak.get(no);
Thread thread = new Thread(future);
threadsLeak.put(no, thread);
thread.start();
try {
future.get(4, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// 对主线程interrupt或canceL,进去这里
print("status of main task after interrupted " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
// 响应InterruptedException后重置,以在不抛错的情况下后续资源回收,表明主线程被人canceL了
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
print("status of main task after interrupted 2 " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
// 同时干掉子线程从
future.cancel(true);
throw new RuntimeException("main task cancelled", e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
// 子线程被interrupt,进入这里
// 理论上应判别子线程是执行错误还是被人interrupt了,如果是后者,最后加上Thread.currentThread().interrupt(),因为子线程被人干掉了
// 本例4个case中,只有这个case没有中断主线程
throw new RuntimeException("Error when domain size", e);
} catch (CancellationException e) {
// 子线程被interrupt,进入这里
// 同时干掉主线程
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new RuntimeException("sub task cancelled", e);
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
// 主线程超时
print("status of main task after timeout " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
// 上一句isInterrupted是false,无论是抛TimeoutException后重置角度还是从表明主线程放弃了的角度,都中断下主线程
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
print("status of main task after timeout 2 " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
// 同时干掉子线程
future.cancel(true);
throw new RuntimeException("main task timeout", e);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("unknown Error when domain size", e);
}
}
private static int registerSubTask() {
int num = no.incrementAndGet();
FutureTask future = new FutureTask(new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
while(true) {
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
tasksLeak.remove(num);
threadsLeak.remove(num);
assertLock.countDown();
throw new RuntimeException("sub task interrupted");
}
}
}
});
tasksLeak.put(num, future);
return num;
}
private static void print(Object o) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号