tensorflow 1.4学习
tensorflow已经更新到2.0版本了,大多数公司还在用1.4的版本,去过了一遍网上tensorflow1.4的教程,记录下。1.4版本的官网教程貌似已下架,主要是api参考:https://github.com/tensorflow/docs/tree/r1.14/site/en/api_docs/python
Tensorflow数据的核心单位是张量 (tensor),就像numpy中的array一样。Tensorflow中还有一个核心知识点就是计算图(computation graph), tensorflow的大多数程序都可以认为包含两部分:
1. 构建计算图
2. 执行计算图
1. 计算图
tensorflow的代码中,有一个默认图概念(default graph),当我们开始一个线程时,tensorflow就会为我们创造一张默认图,在线程中进行的操作(加减乘除),定义的变量和常量,都会被加入到这张默认图中,成为默认图的节点,这个默认图就是常说的计算图,是为了记录各给节点之前的关系,方便tensorflow进行前向的计算和反向的梯度计算。当我们构建完计算图后,需要运行这张图,才能执行图上的操作(即我们定义的加减乘除, 变量赋值等)。如下代码所示:
默认图理解:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# tensorflow 创建了一张默认图
# print(tf.get_default_graph()) # 可以获取默认图对象
# 1. 下面的两个matrix常量,和一个矩阵成分操作,会被加入到默认图中
matrix1 = tf.ones(shape=(2, 2), dtype=np.float32) # 构建一个tensor,值全为1
matrix2 = tf.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4]], dtype=tf.dtypes.float32) # 构建一个常量tensor, 值为[1, 2], [3, 4]
product = tf.matmul(matrix1, matrix2)
# 默认图现在有三个节点, 两个 constant() op, 和一个matmul() op.
# 显示shape,dyupe,没有具体的值
print(matrix1)
print(matrix2)
print(product)
# 2. 创建一个会话session,在session中,可以运行默认图
ses = tf.Session() # 有一个参数graph, 可以传入需要计算的图,不传参数时,表示默认图
# 3. 在session中计算默认图中的操作
# 调用 sess 的 'run()' 方法来执行矩阵乘法 op, 传入 'product' 作为该方法的参数.
# 'product' 代表了矩阵乘法 op 的输出, 传入它是向方法表明, 我们希望取回矩阵乘法 op 的输出.
# 整个执行过程是自动化的, 会话负责传递 op 所需的全部输入. op 通常是并发执行的.
# 函数调用 'run(product)' 触发了图中三个 op (两个常量 op 和一个矩阵乘法 op) 的执行.
result = ses.run(product) # 计算product的值,并返回, 注意返回值 'result' 是一个 numpy `ndarray` 对象.
# tensor, 只显示shape,dyupe,没有具体的值
print(matrix1)
print(matrix2)
print(product)
# np.array, 有具体的值
print(result, type(result))
# 4. 关闭session
ses.close() # 关闭会话
'''
session对象在使用完后需要关闭以释放资源. 除了显式调用 close 外, 也可以使用 “with” 代码块来自动完成关闭动作.
with tf.Session() as sess:
result = sess.run([product])
print (result)
'''
2.计算图获取数据和输入数据
上面已经了解到了,可以从计算图中获取计算得到的数据,可以一次性计算和获取多个数据,如下代码中同时获取计算图中两个节点的值:
import tensorflow as tf
matrix1 = tf.constant([[1, 1], [2, 2]])
value1 = tf.constant(3)
value2 = tf.constant(4)
inter_value = tf.add(matrix1, value1)
product = tf.multiply(inter_value, value2)
with tf.Session() as sess:
result = sess.run([inter_value, product]) #需要获取的多个 tensor 值,在 op 的一次运行中一起获得(而不是逐个去获取 tensor)
print(result, type(result)) # 输出为两个np.array组成的list; 注意:若run输入的为list,返回结果则为list,
print(sess.run(product)) # [product]:返回结果则为list; product:返回结果为单个array
上面计算图中,输入的数据都是固定值,我们可以采用占位符来代替这些数据,构建完计算图后,可以通过向计算图中输入数据,从而实习动态数据,如下代码所示:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
x_value = tf.random.normal((2, 3), 0, 1)
y_value = tf.random.uniform((2, 1), 0, 2)
x = tf.placeholder(dtype=np.float32, shape=(2, 3))
y = tf.placeholder(dtype=np.float32, shape=(2, 1))
weight = tf.constant([[1, 1.5, 0.5]])
bias = tf.constant(0.5)
loss = tf.matmul(x, tf.transpose(weight)) + bias - y
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 1. 输入数据为np.array类型
result = sess.run([loss], feed_dict={x: np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]),
y: np.array([[1], [2]])}) #np.array数据
print(result, type(result))
# 2. 输入数据为list
result = sess.run([loss], feed_dict={x: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]],
y: [[1], [2]]}) # 自动转化为np.array
print(result, type(result))
# 3. 输入数据为np.array
result = sess.run([loss], feed_dict={x: sess.run(x_value),
y: sess.run(y_value)}) # 随机数据
print(result, type(result))
3. 变量数据
上述数据中涉及到了常量constant,占位符placeholder, tensorflow中还有一种数据:变量Variable。tf.Variable表示的数据,其值时可以更改的,一般用来存储网络的参数,变量在进行计算前,必须进行初始化,下面代码展示了变量和常量的区别:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
constant_value = tf.constant([2, 3])
variable_value = tf.Variable(initial_value=[1, 2], name="x") # 设置初始化值为【1, 2】
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
result = variable_value.assign_add(constant_value)
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 1. 必须先初始化全部全局变量, 否则会报错:Attempting to use uninitialized value x
sess.run(init)
print(sess.run(variable_value))
print(sess.run(constant_value))
# 2.相加,并更新变量的值
print(sess.run(result))
print(sess.run(variable_value)) #变量的值可以更新
print(sess.run(constant_value)) # 常量的值保持不变
4.计算图可视化
tensorfboard能用来绘制和可视化tensorflow中的计算图,安装tensorflow的过程中应该会自动安装tensorboard。(也可以直接安装:pip install tensorbaord)
使用tensorboard可视化计算图包括两步:
1. 在代码中将计算图绘制到文件中
2. 在命令中使用tensorboard指向绘制的文件,示例命令如:tensorboard --logdir="./logs"。 随后在浏览器打开指定的网址即可,一般是http://localhost:6006/
下面打代码中,实现了一个简单的线性模型,并绘制了其计算图,如下所示:
import tensorflow as tf
# import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
w = tf.Variable([0.3], dtype=tf.float32)
b = tf.Variable([-0.3], dtype=tf.float32)
x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
y = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
linear_model = w*x+b
square_deltas = tf.square(linear_model-y)
loss = tf.reduce_sum(square_deltas)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init) # 初始权重值
print("初始loss:", sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x: [1, 2, 3, 4], y: [0, -1, -2, -3]}))
fix_w = tf.assign(w, [-1])
fix_b = tf.assign(b, [1])
sess.run([fix_w, fix_b]) # 更新权重值
print("更新权重后loss: ", sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x: [1, 2, 3, 4], y: [0, -1, -2, -3]}))
tf.summary.FileWriter("./logs", sess.graph) # 在tensorboard中绘制计算图
对应的计算图:
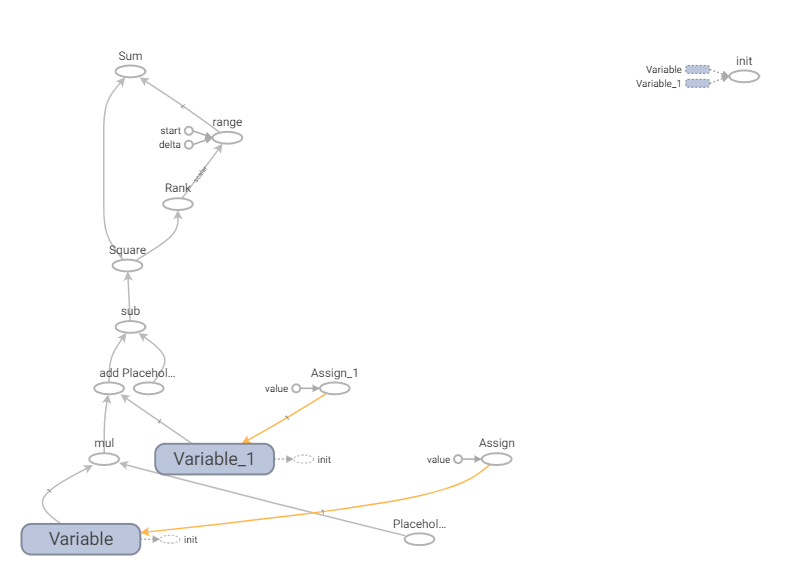
5. tf.train 相关API
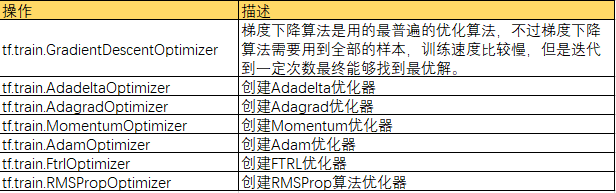
了解上述知识点后,可以开始搭建简单的网络,并进行训练。tf.train提供了关于优化器相关的函数,可以实现梯度梯度下降和参数更新。
常用优化器:
常用损失函数:
- tf.nn
在tensorflow原生库中,只有最常见的几种loss函数。
上面是softmax交叉熵loss,参数为网络最后一层的输出和onehot形式的标签。切记输入一定不要经过softmax,因为在函数中内置了softmax操作,如果再做就是重复使用了。在计算loss的时候,输出Tensor要加上tf.reduce_mean(Tensor)或者tf.reduce_sum(Tensor),作为tensorflow优化器(optimizer)的输入。
这个函数和上面的区别就是labels参数应该是没有经过onehot的标签,其余的都是一样的。另外加了sparse的loss还有一个特性就是标签可以出现-1,如果标签是-1代表这个数据不再进行梯度回传。
sigmoid交叉熵loss,与softmax不同的是,该函数首先进行sigmoid操作之后计算交叉熵的损失函数,其余的特性与 一致。
这个loss与众不同的地方就是加入了一个权重的系数,其余的地方与 这个损失函数是一致的,加入的pos_weight函数可以适当的增大或者缩小正样本的loss,可以一定程度上解决正负样本数量差距过大的问题。
- tf.keras
中是全部的loss函数库,但是也只是非常普通有限的函数。
下面代码中采用tensorflow实现了一个多层感知机,并对minist数据集进行分类:(minist数据集:手写数字灰度图片)

import tensorflow as tf from keras.datasets import mnist (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data() # print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape, x_test.shape) nClass = tf.placeholder(tf.int32) x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 784]) y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None]) y_hot = tf.one_hot(indices=y, depth=nClass, on_value=1.0, off_value=0.0, axis=-1) # 网络层 w1 = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal(shape=[784, 100], stddev=0.1), name="weight1") b1 = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.constant(0.1, shape=(1, 100)), name="bias1") h1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(x, w1)+b1) w2 = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal(shape=[100, 20], stddev=0.1), name="weight2") b2 = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.constant(0.1, shape=(1, 20)), name="bias2") h2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h1, w2)+b2) w3 = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal(shape=[20, 10], stddev=0.1), name="weight2") b3 = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.constant(0.1, shape=(1, 10)), name="bias2") h3 = tf.matmul(h2, w3)+b3 cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_hot, logits=h3)) # train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(cross_entropy) # 梯度下降法,学习率为0.01 train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.0001).minimize(cross_entropy) # 梯度下降法,学习率为0.01 # 测试 prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(h3, axis=1), tf.argmax(y_hot, axis=1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(prediction, dtype=tf.float32)) with tf.Session() as sess: epochs = 300 batch_size = 8 n = x_train.shape[0] # n = 10000 sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) for epoch in range(epochs): epoch_loss = 0.0 iter_count = 0 for i in range(0, n, batch_size): j = min(i + batch_size, n) batch_data = x_train[i:j, :, :].reshape(-1, 28 * 28) batch_label = y_train[i:j] _, loss = sess.run([train_step, cross_entropy], feed_dict={x: batch_data, y: batch_label, nClass: 10}) # if epoch % 40 == 0: # train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={ # x: batch_data, y: batch_label, nClass: 10}) # print('step %d, training accuracy %g' % (i, train_accuracy)) epoch_loss += loss iter_count += 1 print("[Epoch {}/{}], train loss: {}".format(epoch, epochs, epoch_loss/iter_count)) # 测试: acc = 0 iter_count = 0 n = x_test.shape[0] for i in range(0, n, batch_size): j = min(i + batch_size, n) batch_data = x_test[i:j, :, :].reshape(-1, 28 * 28) batch_label = y_test[i:j] acc += sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x:batch_data, y:batch_label, nClass:10}) iter_count += 1 print('Test accuracy {:.4f}%'.format(100*acc/iter_count)) # Test accuracy 92.3077%
6. 正则化损失
一般为了防止过拟合,会采用L2正则化,tensorflow中的L2正则化使用起来有点特别。
下面代码中实现了cifar10数据集的分类,并采用了tf.nn.l2_loss来实现网络参数的L2正则化,限制网络规模,从而达到抑制过拟合的目的:

import tensorflow as tf # import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf import Cifar10_data import time import math import numpy as np # 创建一个variable_with_weight_loss()函数,该函数的作用是: # 1.使用参数w1控制L2 loss的大小 # 2.使用函数tf.nn.l2_loss()计算权重L2 loss # 3.使用函数tf.multiply()计算权重L2 loss与w1的乘积,并赋值给weights_loss # 4.使用函数tf.add_to_collection()将最终的结果放在名为losses的集合里面,方便后面计算神经网络的总体loss, def variable_with_weight_loss(shape, stddev, w): var = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=shape, stddev=0.1)) # 截断的正态分布,超过两倍标准偏差的被舍弃掉 if w is not None: weight_loss = tf.multiply(tf.nn.l2_loss(var), w, name="weight_loss") tf.add_to_collection("losses", weight_loss) return var def conv2d(x, w, strides): return tf.nn.conv2d(x, w, strides, padding='SAME') #图片X:shape(batch,h,w,channel); 卷积核w:(h,w,in_channel, out_channel); strides:[1, stride, stride, 1]; # padding: 'SAME'考虑边界,填充0,'VALID'不填充边界 # 1. 参数设置 batch_size = 32 cifar_data_dir = r"./cifar_data/cifar-10-batches-bin" # 二进制文件格式存放 num_examples_for_eval = 10000 # 10000张测试图片 num_examples_for_train = 50000 # 50000 张训练图片; (一个epoch训练:50000/8 个batch) max_steps = int(math.ceil(num_examples_for_train)/batch_size)*300 # 训练300个epoch # 2. 数据加载 # from keras.datasets import cifar10 # (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = cifar10.load_data() images_train, labels_train = Cifar10_data.inputs(data_dir=cifar_data_dir, batch_size=batch_size, distorted=True) images_test, labels_test = Cifar10_data.inputs(data_dir=cifar_data_dir, batch_size=batch_size, distorted=None) print(images_train.shape, labels_train.shape, images_test.shape, labels_test.shape) # 3. 网络搭建 x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[batch_size, 24, 24, 3]) # cifar10: 32*32*3, 前处理crop到24*24*3 y_ = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.int32, shape=[batch_size]) # 卷积层1 w_conv1 = variable_with_weight_loss(shape=[5, 5, 3, 64], stddev=5e-2, w=0) # 卷积核输入channel是3,输出channel是64 b_conv1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64])) # 初始化为0 h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x, w_conv1, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1])+b_conv1) h_pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(h_conv1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') # 卷积层2 w_conv2 = variable_with_weight_loss([5,5,64,64], stddev=5e-2, w=0) b_conv2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[64])) h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, w_conv2, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1])+b_conv2) h_pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(h_conv1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') # reshape x_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, shape=[batch_size, -1]) # h_pool2:shape(7,7,64),需要reshape,方便全连接 dim = x_flat.get_shape()[1].value # 全连接层1 w_fc1 = variable_with_weight_loss([dim, 384], stddev=0.04, w=0.004) b_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[384])) h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(x_flat, w_fc1) + b_fc1) # 全连接层2 w_fc2 = variable_with_weight_loss([384, 192], stddev=0.04, w=0.004) b_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[192])) h_fc2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_fc1, w_fc2) + b_fc2) # dropout keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) # train是设置丢弃概率;eval时可以设置为1 h_fc2_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc2, keep_prob) # 全连接层3,预测输出 w_fc3 = variable_with_weight_loss([192, 10], stddev=1 / 192.0, w=0.0) b_fc3 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[10])) y_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(h_fc2_drop, w_fc3), b_fc3) # 损失函数 #loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_logits(labels=y_, logits=y_output)) cross_entropy=tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=tf.cast(y_,tf.int64), logits=y_output) weights_with_l2_loss = tf.add_n(tf.get_collection("losses")) loss = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy) + weights_with_l2_loss # 训练优化器 train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss) # 测试 top_k_op = tf.nn.in_top_k(y_output, y_, 1) # 计算输出结果中top k的准确率,函数默认的k值是1,即top 1的准确率,也就是输出分类准确率最高时的数值 # correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_output, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1)) # accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, dtype=tf.float32)) # cast数据转换 with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) # 初始化定义的变量 # 启动线程操作,这是因为之前数据增强的时候使用train.shuffle_batch()函数的时候通过参数num_threads()配置了16个线程用于组织batch的操作 tf.train.start_queue_runners() for step in range(max_steps): t1 = time.time() image_batch, label_batch = sess.run([images_train, labels_train]) #返回一个batch的数据 # print(step, image_batch.shape, label_batch) loss_value, _ = sess.run([loss, train_step], feed_dict={x: image_batch, y_: label_batch, keep_prob: 0.5}) duration = time.time() - t1 if step % 100 == 0: # train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={ # x: image_batch, y_: label_batch, keep_prob: 1.0}) print("[Step {}/{}] loss={:.4f}, {:.1f} images/sec, {} sec/batch".format( step, max_steps, loss_value, batch_size/duration, duration)) # 测试阶段 num_batch = int(math.ceil(num_examples_for_eval/batch_size)) # 有多少个batch true_count = 0 total_sample_count=num_batch * batch_size # 若最后一个batch,图片不够一个batch_size时,注意是如何处理的? for i in range(num_batch): image_batch, label_batch = sess.run([images_test, labels_test]) predictions = sess.run([top_k_op], feed_dict={x: image_batch, y_: label_batch, keep_prob: 1}) true_count += np.sum(predictions) print("Test accuracy: {:.4f}%".format(100*true_count/total_sample_count))

# 该文件负责读取Cifar-10数据并对其进行数据增强预处理 import os import tensorflow as tf num_classes = 10 # 设定用于训练和评估的样本总数 num_examples_pre_epoch_for_train = 50000 num_examples_pre_epoch_for_eval = 10000 # 定义一个空类,用于返回读取的Cifar-10的数据 class CIFAR10Record(object): pass # 定义一个读取Cifar-10的函数read_cifar10(),这个函数的目的就是读取目标文件里面的内容 def read_cifar10(file_queue): result = CIFAR10Record() label_bytes = 1 # 如果是Cifar-100数据集,则此处为2 result.height = 32 result.width = 32 result.depth = 3 # 因为是RGB三通道,所以深度是3 image_bytes = result.height * result.width * result.depth # 图片样本总元素数量 record_bytes = label_bytes + image_bytes # 因为每一个样本包含图片和标签,所以最终的元素数量还需要图片样本数量加上一个标签值 reader = tf.FixedLengthRecordReader( record_bytes=record_bytes) # 使用tf.FixedLengthRecordReader()创建一个文件读取类。该类的目的就是读取文件 result.key, value = reader.read(file_queue) # 使用该类的read()函数从文件队列里面读取文件 record_bytes = tf.decode_raw(value, tf.uint8) # 读取到文件以后,将读取到的文件内容从字符串形式解析为图像对应的像素数组 # 因为该数组第一个元素是标签,所以我们使用strided_slice()函数将标签提取出来,并且使用tf.cast()函数将这一个标签转换成int32的数值形式 result.label = tf.cast(tf.strided_slice(record_bytes, [0], [label_bytes]), tf.int32) # 剩下的元素再分割出来,这些就是图片数据,因为这些数据在数据集里面存储的形式是depth * height * width,我们要把这种格式转换成[depth,height,width] # 这一步是将一维数据转换成3维数据 depth_major = tf.reshape(tf.strided_slice(record_bytes, [label_bytes], [label_bytes + image_bytes]), [result.depth, result.height, result.width]) # 我们要将之前分割好的图片数据使用tf.transpose()函数转换成为高度信息、宽度信息、深度信息这样的顺序 # 这一步是转换数据排布方式,变为(h,w,c) result.uint8image = tf.transpose(depth_major, [1, 2, 0]) return result # 返回值是已经把目标文件里面的信息都读取出来 def inputs(data_dir, batch_size, distorted): # 这个函数就对数据进行预处理---对图像数据是否进行增强进行判断,并作出相应的操作 filenames = [os.path.join(data_dir, "data_batch_%d.bin" % i) for i in range(1, 6)] # 拼接地址 file_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filenames) # 根据已经有的文件地址创建一个文件队列 read_input = read_cifar10(file_queue) # 根据已经有的文件队列使用已经定义好的文件读取函数read_cifar10()读取队列中的文件 reshaped_image = tf.cast(read_input.uint8image, tf.float32) # 将已经转换好的图片数据再次转换为float32的形式 num_examples_per_epoch = num_examples_pre_epoch_for_train if distorted != None: # 如果预处理函数中的distorted参数不为空值,就代表要进行图片增强处理 cropped_image = tf.random_crop(reshaped_image, [24, 24, 3]) # 首先将预处理好的图片进行剪切,使用tf.random_crop()函数 flipped_image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right( cropped_image) # 将剪切好的图片进行左右翻转,使用tf.image.random_flip_left_right()函数 adjusted_brightness = tf.image.random_brightness(flipped_image, max_delta=0.8) # 将左右翻转好的图片进行随机亮度调整,使用tf.image.random_brightness()函数 adjusted_contrast = tf.image.random_contrast(adjusted_brightness, lower=0.2, upper=1.8) # 将亮度调整好的图片进行随机对比度调整,使用tf.image.random_contrast()函数 float_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization( adjusted_contrast) # 进行标准化图片操作,tf.image.per_image_standardization()函数是对每一个像素减去平均值并除以像素方差 float_image.set_shape([24, 24, 3]) # 设置图片数据及标签的形状 read_input.label.set_shape([1]) min_queue_examples = int(num_examples_pre_epoch_for_eval * 0.4) print("Filling queue with %d CIFAR images before starting to train. This will take a few minutes." % min_queue_examples) images_train, labels_train = tf.train.shuffle_batch([float_image, read_input.label], batch_size=batch_size, num_threads=4, capacity=min_queue_examples + 3 * batch_size, min_after_dequeue=min_queue_examples, ) # 使用tf.train.shuffle_batch()函数随机产生一个batch的image和label return images_train, tf.reshape(labels_train, [batch_size]) else: # 不对图像数据进行数据增强处理 resized_image = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(reshaped_image, 24, 24) # 在这种情况下,使用函数tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad()对图片数据进行剪切 float_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(resized_image) # 剪切完成以后,直接进行图片标准化操作 float_image.set_shape([24, 24, 3]) read_input.label.set_shape([1]) min_queue_examples = int(num_examples_per_epoch * 0.4) images_test, labels_test = tf.train.batch([float_image, read_input.label], batch_size=batch_size, num_threads=4, capacity=min_queue_examples + 3 * batch_size) # 这里使用batch()函数代替tf.train.shuffle_batch()函数 return images_test, tf.reshape(labels_test, [batch_size])
7. 数据集加载
tensorflow中tf.data.Dataset 和tf.train.slice_input_producer都提供了数据集的批量加载方式。
1. tf.train.slice_input_producer
如果我们的数据保存在txt文件中,txt文件格式如下, 即每一行是图片路径和label
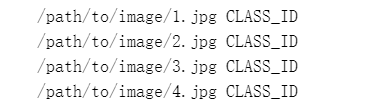
则加载图片的dataloder,数据加载代码如下:

def read_images(dataset_path, batch_size, transform=False): # 1. slice_input_producer构建一个任务队列 imagepaths, labels = list(), list() with open(dataset_path) as f: data = f.read().splitlines() for d in data: imagepaths.append(d.split(' ')[0]) labels.append(int(d.split(' ')[1])) # Convert to Tensor imagepaths = tf.convert_to_tensor(imagepaths, dtype=tf.string) labels = tf.convert_to_tensor(labels, dtype=tf.int32) # Build a TF Queue, shuffle data image, label = tf.train.slice_input_producer([imagepaths, labels], shuffle=True) # 2. 对图片和lable可以进行预处理 # Read images from disk image = tf.read_file(image) image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image, channels=CHANNELS) if transform: # 是否要进行图片增强处理 cropped_image = tf.random_crop(image, [24, 24, 3]) # 首先将预处理好的图片进行剪切,使用tf.random_crop()函数 flipped_image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right( cropped_image) # 将剪切好的图片进行左右翻转,使用tf.image.random_flip_left_right()函数 adjusted_brightness = tf.image.random_brightness(flipped_image, max_delta=0.8) # 将左右翻转好的图片进行随机亮度调整,使用tf.image.random_brightness()函数 adjusted_contrast = tf.image.random_contrast(adjusted_brightness, lower=0.2, upper=1.8) # 将亮度调整好的图片进行随机对比度调整,使用tf.image.random_contrast()函数 float_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization( adjusted_contrast) # 进行标准化图片操作,tf.image.per_image_standardization()函数是对每一个像素减去平均值并除以像素方差 image = float_image image.set_shape([24, 24, 3]) # 设置图片数据及标签的形状 label.set_shape([1]) # Resize images to a common size image = tf.image.resize_images(image, [IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH]) # Normalize image = image * 1.0 / 127.5 - 1.0 # 3. 创建一个batch生成器 # Create batches X, Y = tf.train.batch([image, label], batch_size=batch_size, capacity=batch_size * 8, # 任务队列的大小 num_threads=4) # 四个线程进行数据加载 # X,Y = tf.train.shuffle_batch([image, label], batch_size=batch_size, # num_threads=4, # capacity=min_queue_examples + 3 * batch_size, # min_after_dequeue=min_queue_examples, # ) return X, Y
图片加载和整个训练代码如下,使用tf.train.slice_input_producer()产生队列后,注意在训练时得通过tf.train.start_queue_runners()开始队列

import tensorflow as tf import os # Dataset Parameters - CHANGE HERE MODE = 'folder' # or 'file', if you choose a plain text file (see above). DATASET_PATH = '/path/to/dataset/' # the dataset file or root folder path. # Image Parameters N_CLASSES = 2 # CHANGE HERE, total number of classes IMG_HEIGHT = 64 # CHANGE HERE, the image height to be resized to IMG_WIDTH = 64 # CHANGE HERE, the image width to be resized to CHANNELS = 3 # The 3 color channels, change to 1 if grayscale def read_images(dataset_path, batch_size, transform=False): # 1. slice_input_producer构建一个任务队列 imagepaths, labels = list(), list() with open(dataset_path) as f: data = f.read().splitlines() for d in data: imagepaths.append(d.split(' ')[0]) labels.append(int(d.split(' ')[1])) # Convert to Tensor imagepaths = tf.convert_to_tensor(imagepaths, dtype=tf.string) labels = tf.convert_to_tensor(labels, dtype=tf.int32) # Build a TF Queue, shuffle data image, label = tf.train.slice_input_producer([imagepaths, labels], shuffle=True) # 2. 对图片和lable可以进行预处理 # Read images from disk image = tf.read_file(image) image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image, channels=CHANNELS) if transform: # 是否要进行图片增强处理 cropped_image = tf.random_crop(image, [24, 24, 3]) # 首先将预处理好的图片进行剪切,使用tf.random_crop()函数 flipped_image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right( cropped_image) # 将剪切好的图片进行左右翻转,使用tf.image.random_flip_left_right()函数 adjusted_brightness = tf.image.random_brightness(flipped_image, max_delta=0.8) # 将左右翻转好的图片进行随机亮度调整,使用tf.image.random_brightness()函数 adjusted_contrast = tf.image.random_contrast(adjusted_brightness, lower=0.2, upper=1.8) # 将亮度调整好的图片进行随机对比度调整,使用tf.image.random_contrast()函数 float_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization( adjusted_contrast) # 进行标准化图片操作,tf.image.per_image_standardization()函数是对每一个像素减去平均值并除以像素方差 image = float_image image.set_shape([24, 24, 3]) # 设置图片数据及标签的形状 label.set_shape([1]) # Resize images to a common size image = tf.image.resize_images(image, [IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH]) # Normalize image = image * 1.0 / 127.5 - 1.0 # 3. 创建一个batch生成器 # Create batches X, Y = tf.train.batch([image, label], batch_size=batch_size, capacity=batch_size * 8, # 任务队列的大小 num_threads=4) # 四个线程进行数据加载 # X,Y = tf.train.shuffle_batch([image, label], batch_size=batch_size, # num_threads=4, # capacity=min_queue_examples + 3 * batch_size, # min_after_dequeue=min_queue_examples, # ) return X, Y # Parameters learning_rate = 0.001 num_steps = 10000 batch_size = 128 display_step = 100 # Network Parameters dropout = 0.75 # Dropout, probability to keep units # Build the data input X, Y = read_images(DATASET_PATH, MODE, batch_size) # 模型搭建 # Create model def conv_net(x, n_classes, dropout, reuse, is_training): # Define a scope for reusing the variables with tf.variable_scope('ConvNet', reuse=reuse): # Convolution Layer with 32 filters and a kernel size of 5 conv1 = tf.layers.conv2d(x, 32, 5, activation=tf.nn.relu) # Max Pooling (down-sampling) with strides of 2 and kernel size of 2 conv1 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(conv1, 2, 2) # Convolution Layer with 32 filters and a kernel size of 5 conv2 = tf.layers.conv2d(conv1, 64, 3, activation=tf.nn.relu) # Max Pooling (down-sampling) with strides of 2 and kernel size of 2 conv2 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(conv2, 2, 2) # Flatten the data to a 1-D vector for the fully connected layer fc1 = tf.contrib.layers.flatten(conv2) # Fully connected layer (in contrib folder for now) fc1 = tf.layers.dense(fc1, 1024) # Apply Dropout (if is_training is False, dropout is not applied) fc1 = tf.layers.dropout(fc1, rate=dropout, training=is_training) # Output layer, class prediction out = tf.layers.dense(fc1, n_classes) # Because 'softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits' already apply softmax, # we only apply softmax to testing network out = tf.nn.softmax(out) if not is_training else out return out # 训练代码 # Because Dropout have different behavior at training and prediction time, we # need to create 2 distinct computation graphs that share the same weights. # Create a graph for training logits_train = conv_net(X, N_CLASSES, dropout, reuse=False, is_training=True) # Create another graph for testing that reuse the same weights logits_test = conv_net(X, N_CLASSES, dropout, reuse=True, is_training=False) # Define loss and optimizer (with train logits, for dropout to take effect) loss_op = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits( logits=logits_train, labels=Y)) optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate) train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss_op) # Evaluate model (with test logits, for dropout to be disabled) correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(logits_test, 1), tf.cast(Y, tf.int64)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32)) # Initialize the variables (i.e. assign their default value) init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # Saver object saver = tf.train.Saver() # Start training with tf.Session() as sess: # Run the initializer sess.run(init) # Start the data queue tf.train.start_queue_runners() # Training cycle for step in range(1, num_steps+1): if step % display_step == 0: # Run optimization and calculate batch loss and accuracy _, loss, acc = sess.run([train_op, loss_op, accuracy]) print("Step " + str(step) + ", Minibatch Loss= " + \ "{:.4f}".format(loss) + ", Training Accuracy= " + \ "{:.3f}".format(acc)) else: # Only run the optimization op (backprop) sess.run(train_op) print("Optimization Finished!") # Save your model saver.save(sess, 'my_tf_model')
2. tf.data.Dataset:
如果我们的数据和标签都是np.array类似,可以采用如下的加载方式:

import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf evens = np.arange(0, 100, step=2, dtype=np.int32) evens_label = np.zeros(50, dtype=np.int32) odds = np.arange(1, 100, step=2, dtype=np.int32) odds_label = np.ones(50, dtype=np.int32) # Concatenate arrays features = np.concatenate([evens, odds]) # 数据:shape(100, ) labels = np.concatenate([evens_label, odds_label]) # 标签:shape(100,) # print(features.shape, labels.shape) def dataloader(features, labels): # Slice the numpy arrays (each row becoming a record). data = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((features, labels)) # Refill data indefinitely. data = data.repeat() # Shuffle data. data = data.shuffle(buffer_size=100) # Batch data (aggregate records together). data = data.batch(batch_size=4) # Prefetch batch (pre-load batch for faster consumption). data = data.prefetch(buffer_size=1) # Create an iterator over the dataset. iterator = data.make_initializable_iterator() return iterator # # Initialize the iterator. # sess.run(iterator.initializer) # # # Get next data batch. # d = iterator.get_next() # # return d with tf.Session() as sess: iterator = dataloader(features, labels) sess.run(iterator.initializer) # Initialize the iterator. dataloader = iterator.get_next() # Display data. for i in range(5): x, y = sess.run(dataloader) print(x, y)
如果我们加载如下的图片数据, 下面有一个加载 Oxford Flowers dataset的示例代码:

d = requests.get("http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/data/flowers/17/17flowers.tgz") with open("17flowers.tgz", "wb") as f: f.write(d.content) # Extract archive. with tarfile.open("17flowers.tgz") as t: t.extractall() # Create a file to list all images path and their corresponding label. with open('jpg/dataset.csv', 'w') as f: c = 0 for i in range(1360): f.write("jpg/image_%04i.jpg,%i\n" % (i+1, c)) if (i+1) % 80 == 0: c += 1 with tf.Graph().as_default(): # Load Images. with open("jpg/dataset.csv") as f: dataset_file = f.read().splitlines() # Create TF session. sess = tf.Session() # Load the whole dataset file, and slice each line. data = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(dataset_file) # Refill data indefinitely. data = data.repeat() # Shuffle data. data = data.shuffle(buffer_size=1000) # Load and pre-process images. def load_image(path): # Read image from path. image = tf.io.read_file(path) # Decode the jpeg image to array [0, 255]. image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image) # Resize images to a common size of 256x256. image = tf.image.resize(image, [256, 256]) # Rescale values to [-1, 1]. image = 1. - image / 127.5 return image # Decode each line from the dataset file. def parse_records(line): # File is in csv format: "image_path,label_id". # TensorFlow requires a default value, but it will never be used. image_path, image_label = tf.io.decode_csv(line, ["", 0]) # Apply the function to load images. image = load_image(image_path) return image, image_label # Use 'map' to apply the above functions in parallel. data = data.map(parse_records, num_parallel_calls=4) # Batch data (aggregate images-array together). data = data.batch(batch_size=2) # Prefetch batch (pre-load batch for faster consumption). data = data.prefetch(buffer_size=1) # Create an iterator over the dataset. iterator = data.make_initializable_iterator() # Initialize the iterator. sess.run(iterator.initializer) # Get next data batch. d = iterator.get_next() for i in range(1): batch_x, batch_y = sess.run(d) print(batch_x, batch_y)
8. 模型的保存和加载
Tensorflow有专门保存模型的tf.train.Saver(). 使用Saver保存模型的参数时,一定要将saver = tf.train.Saver定义在你保存的的参数定义之后,定义在saver之后的参数无法被保存。
如下面的代码,能将当前模型和其权值参数保存在tmp目录下
saver = tf.train.Saver() saver.save(sess, "./tmp/model.ckpt")
上述代码会保存的文件如下:

其中后三个文件比较重要,依次存储的信息如下:
- .data文件:保存了当前参数值
- .index文件:保存了当前参数名
- .meta文件:保存了当前图结构
saver.save() 保存模型示例代码:

import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf class Network(): x = tf.placeholder(shape=[1, None], dtype=tf.float32) y = tf.placeholder(shape=[1, None], dtype=tf.float32) inputW = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10, 1])) inputB = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10, 1])) hideW = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1, 10])) hideB = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1, 1])) h1 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(inputW, x), inputB)) output = tf.add(tf.matmul(hideW, h1), hideB) loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(y - output))) opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1) train_step = opt.minimize(loss) if __name__ == '__main__': x_data = np.linspace(-1, 1, 100).reshape(1, 100) noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape) y_data = x_data ** 3 + 1 + noise net = Network() sess = tf.Session() init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init) saver = tf.train.Saver() train_step = 200 for step in range(train_step): print('第', step + 1, '次训练') sess.run(net.train_step, feed_dict={net.x: x_data, net.y: y_data}) pre = sess.run(net.output, feed_dict={net.x: x_data}) saver.save(sess, "./tmp/model.ckpt")
saver.load()载入上面保存的模型:

import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import pylab as pl from tensorflowtest import Network sess = tf.Session() saver = tf.train.Saver().restore(sess, "./tmp/model.ckpt") net = Network() x_data = np.linspace(-1,1,100).reshape(1,100) pre = sess.run(net.output,feed_dict={net.x:x_data}) pl.plot(x_data.T,pre.T) pl.grid() pl.show()
参考: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/333791572
https://www.cnblogs.com/hellcat/p/6925757.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/31362241








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号