集合
-
什么是集合
-
·概念:对象的容器,定义了对多个对象进行操作的常用方法。可实现数组的功能。
-
-
和数组区别:
-
数组长度固定,集合长度不固定
-
数组可以存储基本类型和引用类型,集合只能存储引用类型。
-
-
位置: java.util.*;
Collection体系集合
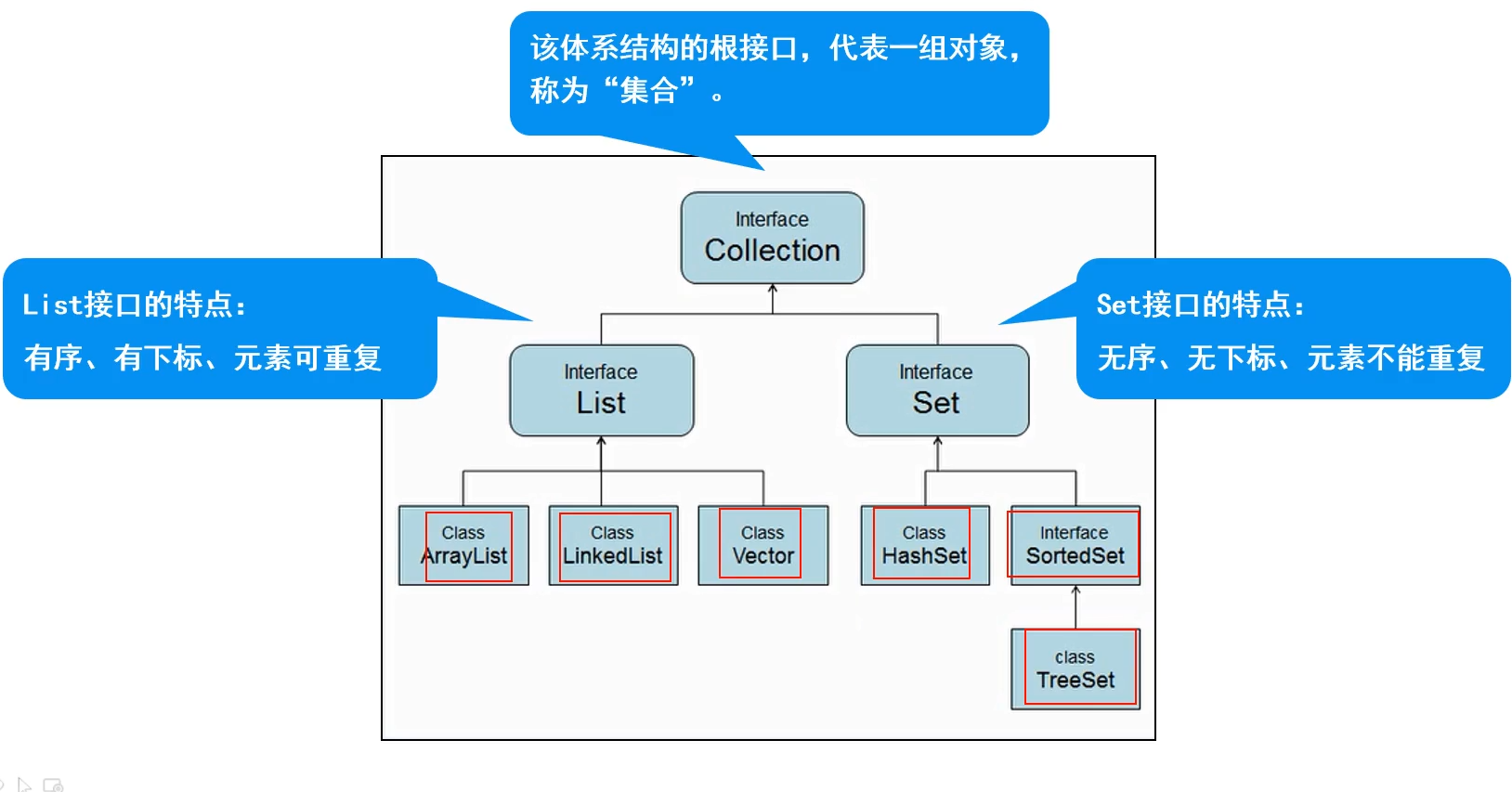
Collection父接口
-
特点:代表一组任意类型的对象,无序、无下标、不能重复
-
方法:
-
boolean add (Object obj)//添加一个对象。
-
boolean addAll(Collection c)//将一个集合中的所有对象添加到此集合中。
-
void clear()//清空此集合中的所有对象。
-
boolean contains(0bject o)//检查此集合中是否包含o对象
-
boolean equals (Object o)/ /比较此集合是否与指定对象相等。
-
boolean isEmpty()//判断此集合是否为空
-
boolean remove(Object o)//在此集合中移除o对象
-
int size()//返回此集合中的元素个数。
-
0bject[] toArray()//将此集合转换成数组。
-
//创建集合
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
Collection collection1 = new ArrayList();
//添加元素
collection.add("大西瓜");
collection.add("小苹果");
collection.add("色茄子");
collection1.add("香蕉");
collection1.add("橘子");
collection1.add("橙子");
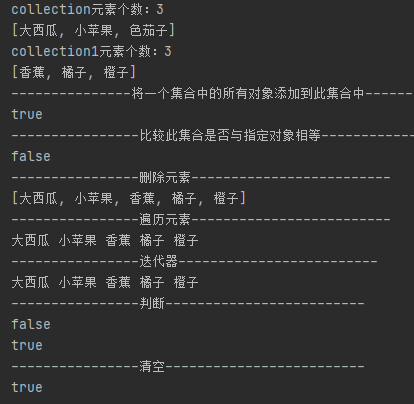
System.out.println("collection元素个数:"+collection.size());
System.out.println(collection);
System.out.println("collection1元素个数:"+collection1.size());
System.out.println(collection1);
System.out.println("---------------将一个集合中的所有对象添加到此集合中------------------");
boolean b = collection.addAll(collection1);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println("----------------比较此集合是否与指定对象相等-------------------------");
boolean equals = collection.equals(collection1);
System.out.println(equals);
//删除元素
System.out.println("----------------删除元素-------------------------");
collection.remove("色茄子");
System.out.println(collection);
//遍历元素
System.out.println("----------------遍历元素-------------------------");
for (Object o : collection) {
System.out.print(o+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----------------迭代器-------------------------");
//不能使用collection.remove删除元素
//使用iterator.remove删除元素
Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.print(next+" ");
}
//判断
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----------------判断集合是否为空-------------------------");
boolean empty = collection.isEmpty();
System.out.println(empty);
System.out.println("----------------判断元素是否存在-------------------------");
System.out.println(collection.contains("香蕉"));
System.out.println("----------------清空-------------------------");
collection.clear();
boolean empty1 = collection.isEmpty();
System.out.println(empty1); -
-
List子接口
-
特点:有序、有下标、元素可以重复。
-
方法:
-
void add(int index,0bject o)//在index位置插入对象o。
-
boolean addAll(int index,Collection c)//将一个集合中的元素添加到此集合中的index位置。
-
0bject get(int index)//返回集合中指定位置的元素。
-
List subList(int fromIndex,int toIndex)//返回fromIndex和toIndex之间的集合元素。
-
List list = new ArrayList();
List list1 = new ArrayList();
list.add("一加");
list.add("小米");
list.add("魅族");
list.add(3,"锤子");
list.add(1,"apple");
list1.add("华硕");
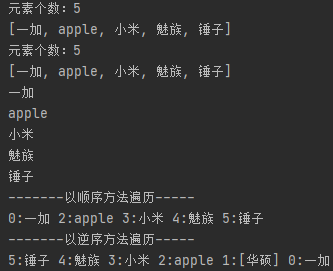
System.out.println("元素个数:"+list.size());
System.out.println(list.toString());
// list.remove("apple");
// list.remove(2);
System.out.println("元素个数:"+list.size());
System.out.println(list.toString());
for (Object o : list) {
System.out.println(o);
}
//以顺序方法遍历
System.out.println("-------以顺序方法遍历-----");
ListIterator listIterator = list.listIterator();
while (listIterator.hasNext()){
if (listIterator.previousIndex()==0) {
listIterator.add(list1);
}
System.out.print(listIterator.nextIndex()+":"+listIterator.next()+" ");
}
//以逆序方法遍历
System.out.println();
System.out.println("-------以逆序方法遍历-----");
while (listIterator.hasPrevious()){
System.out.print(listIterator.previousIndex()+":"+listIterator.previous()+" ");
}
List实现类
-
ArrayList【重点】:
-
数组结构实现,查询快、增删慢;
-
JDK1.2版本,运行效率快、线程不安全。
-
-
Vector:
-
数组结构实现,查询快、增删慢;
-
JDK1.0版本,运行效率慢、线程安全。
-
-
LinkedList:
-
链表结构实现,增删快,查询慢
-
泛型
-
Java泛型是JDK1.5中引入的一个新特性,其本质是参数化类型,把类型作为参数传递。
-
常见形式有泛型类、泛型接口、泛型方法。
-
语法:
-
<T,...>T称为类型占位符,表示一种引用类型
-
-
好处:
-
提高代码的重用性
-
防止类型转换异常,提高代码的安全性
-
//泛型类的创建
public class MyGeneric<T> {
T t;
public void show(T t){
System.out.println(t);
}
public T getT() {
return t;
}
}
//创建泛型对象
MyGeneric<String> myGeneric =new MyGeneric<String>();
myGeneric.t="Hello";
myGeneric.show("Whorld");
String t = myGeneric.getT();
MyGeneric<Integer> integerMyGeneric = new MyGeneric<>();
integerMyGeneric.t=100;
integerMyGeneric.show(600);
Integer t1 = integerMyGeneric.getT();
//泛型接口
public interface Myinterface<T> {
String name = "小火龙";
T serve(T t);
}
//实现类1
public class MyInterface1 implements Myinterface<String>{
//实现类2
public class MyInterface2<T> implements Myinterface<T>{
//创建对象
MyInterface1 myInterface1 = new MyInterface1();
myInterface1.serve("张三");
MyInterface2<String> stringMyInterface2 = new MyInterface2<>();
stringMyInterface2.serve("李四");
//泛型方法
public class Myinterface3 {
public <T> T show(T t){
System.out.println("中国加油"+t);
return t;
}
}
//会随着类型的变换而变换
myinterface3.show("加油");
myinterface3.show(314);
myinterface3.show(3.14);
泛型集合
-
概念:参数化类型、类型安全的集合,强制集合元素的类型必须一致。
-
特点:
-
编译时即可检查,而非运行时抛出异常。
-
访问时,不必类型转换(拆箱)。
-
不同泛型之间引用不能相互赋值,泛型不存在多态。
set集合
-
Set实现类
-
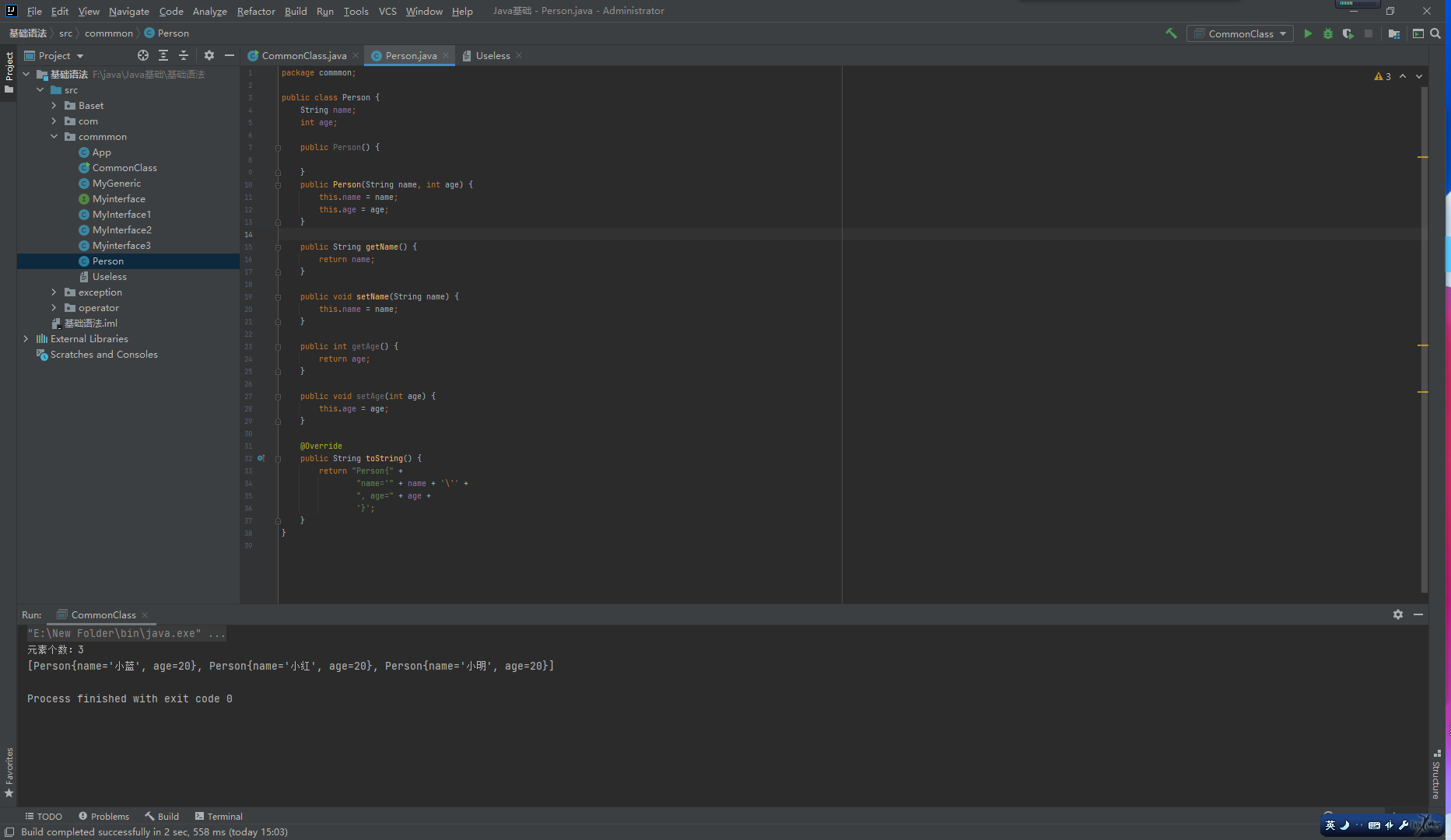
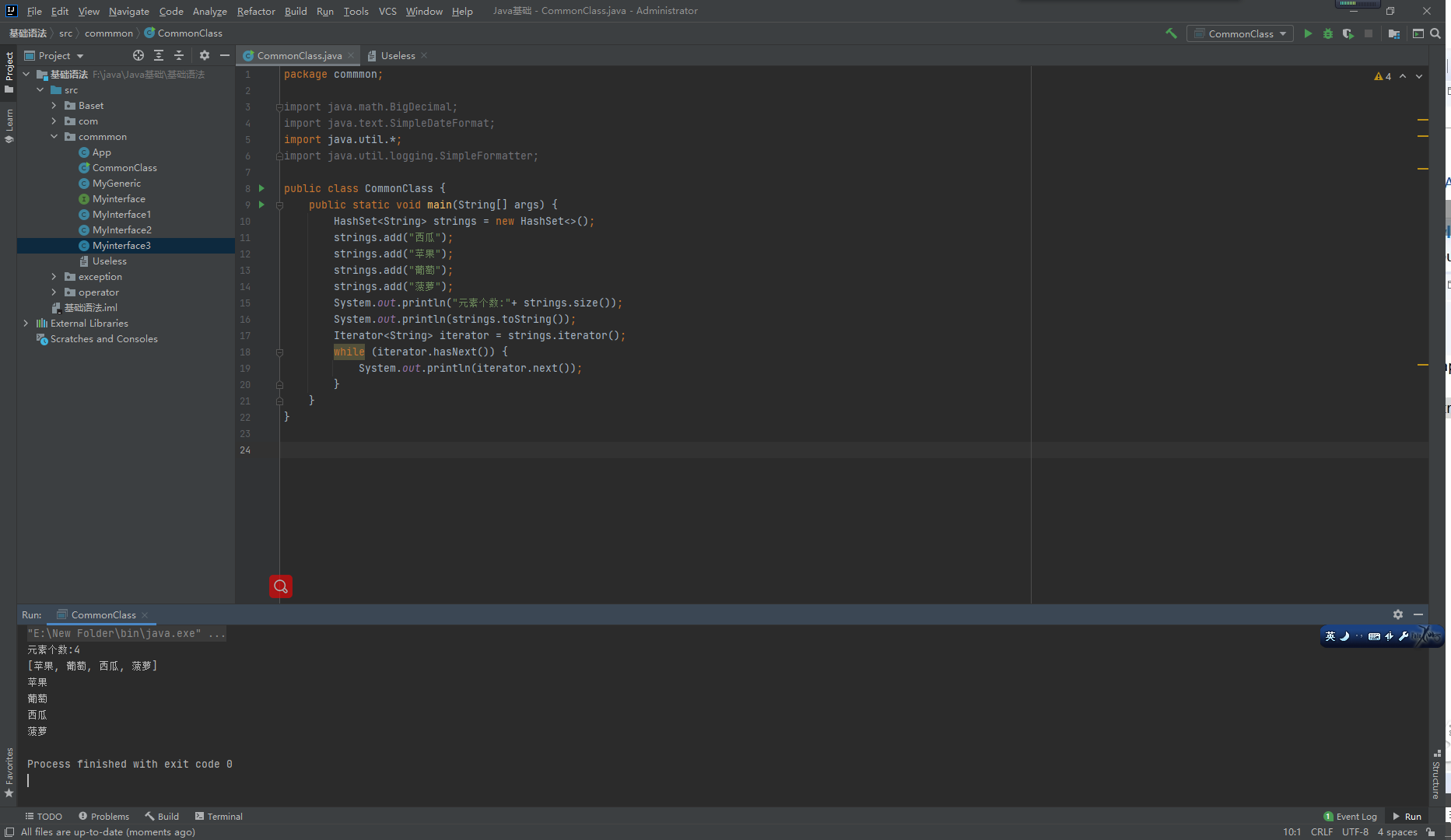
HashSet【重点】:
-
基于HashCode实现元素不重复。
-
当存入元素的哈希码相同时,会调用equals进行确认,如结果为true,则拒绝后者存入。
-
-
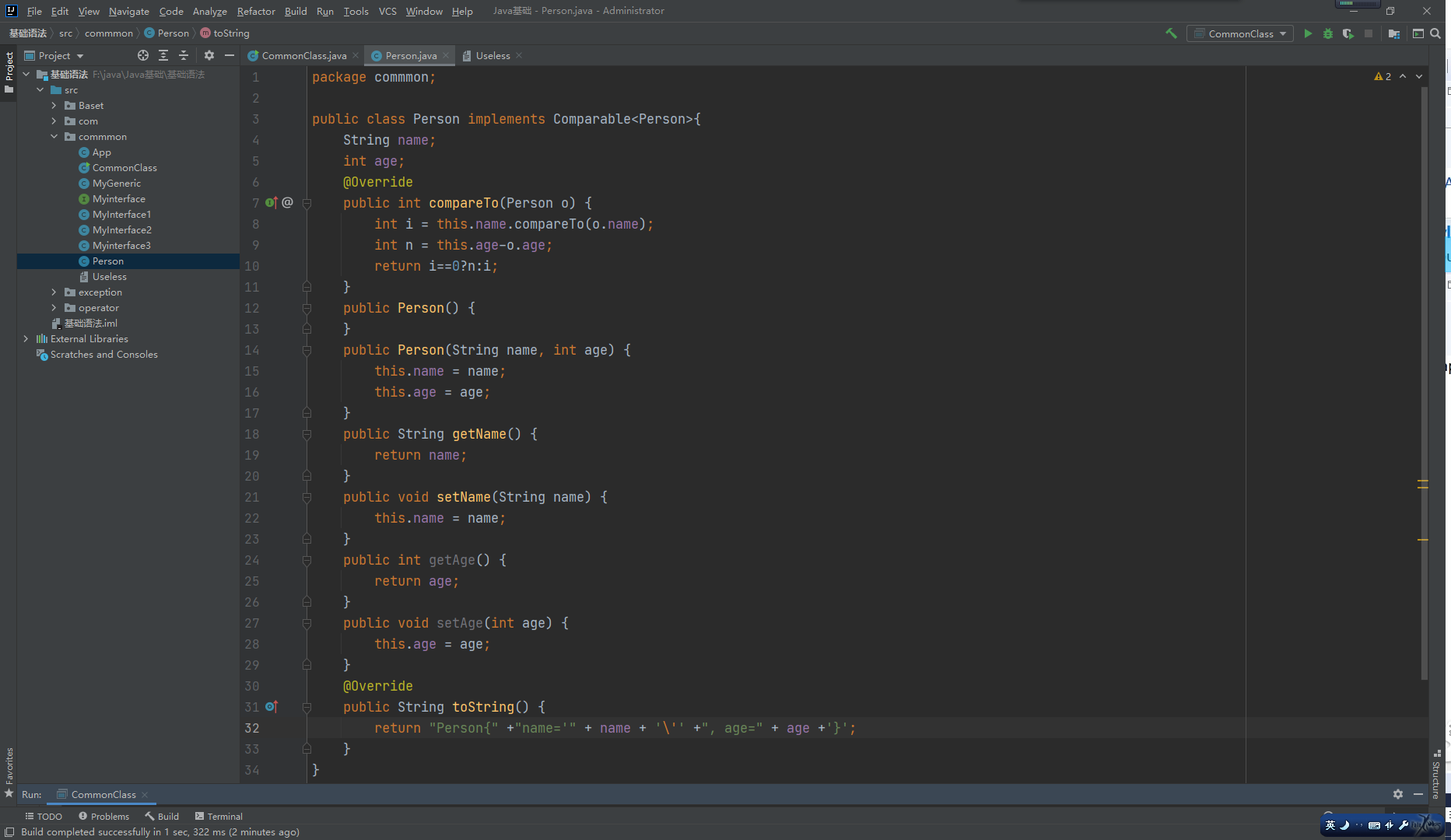
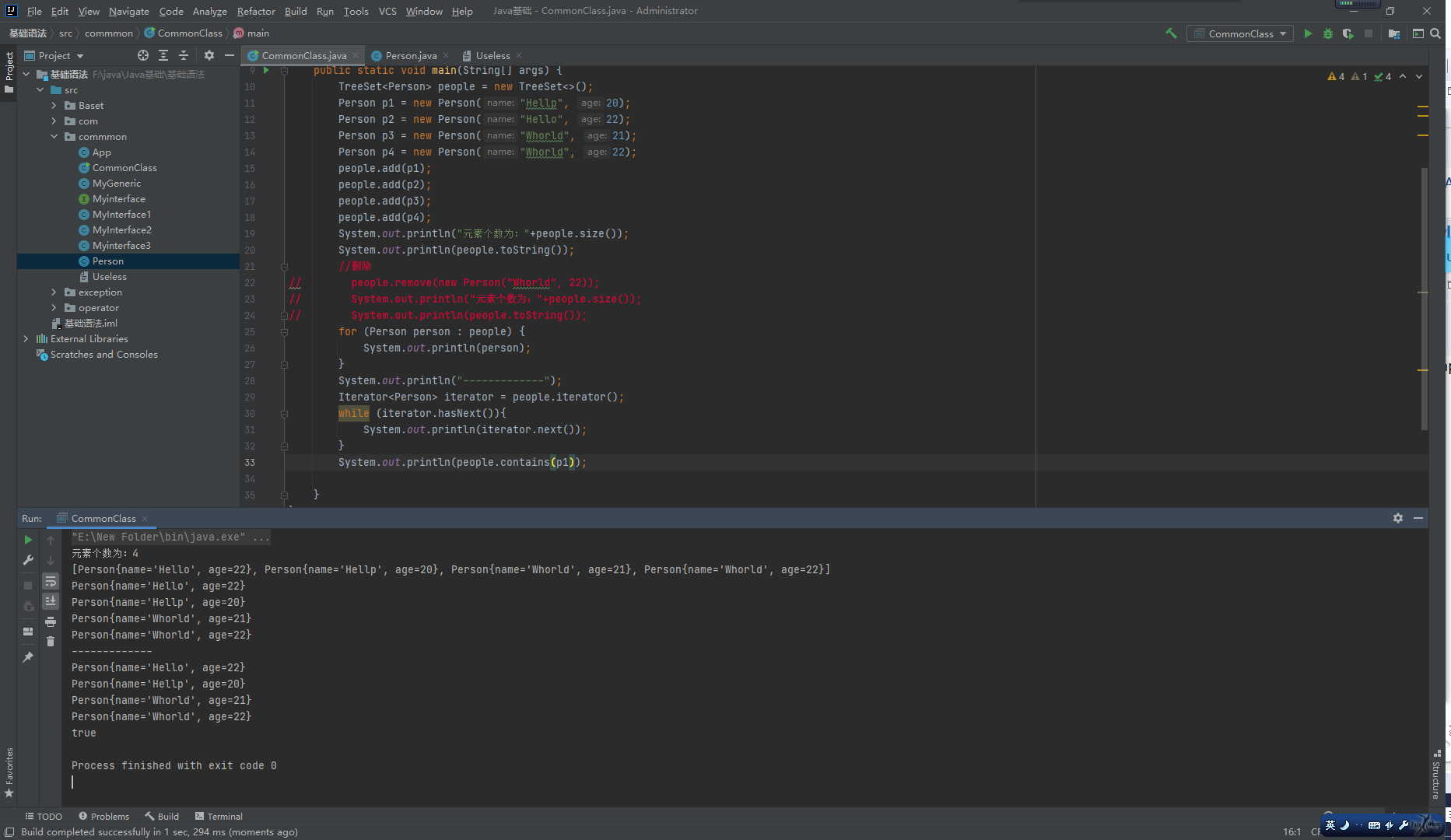
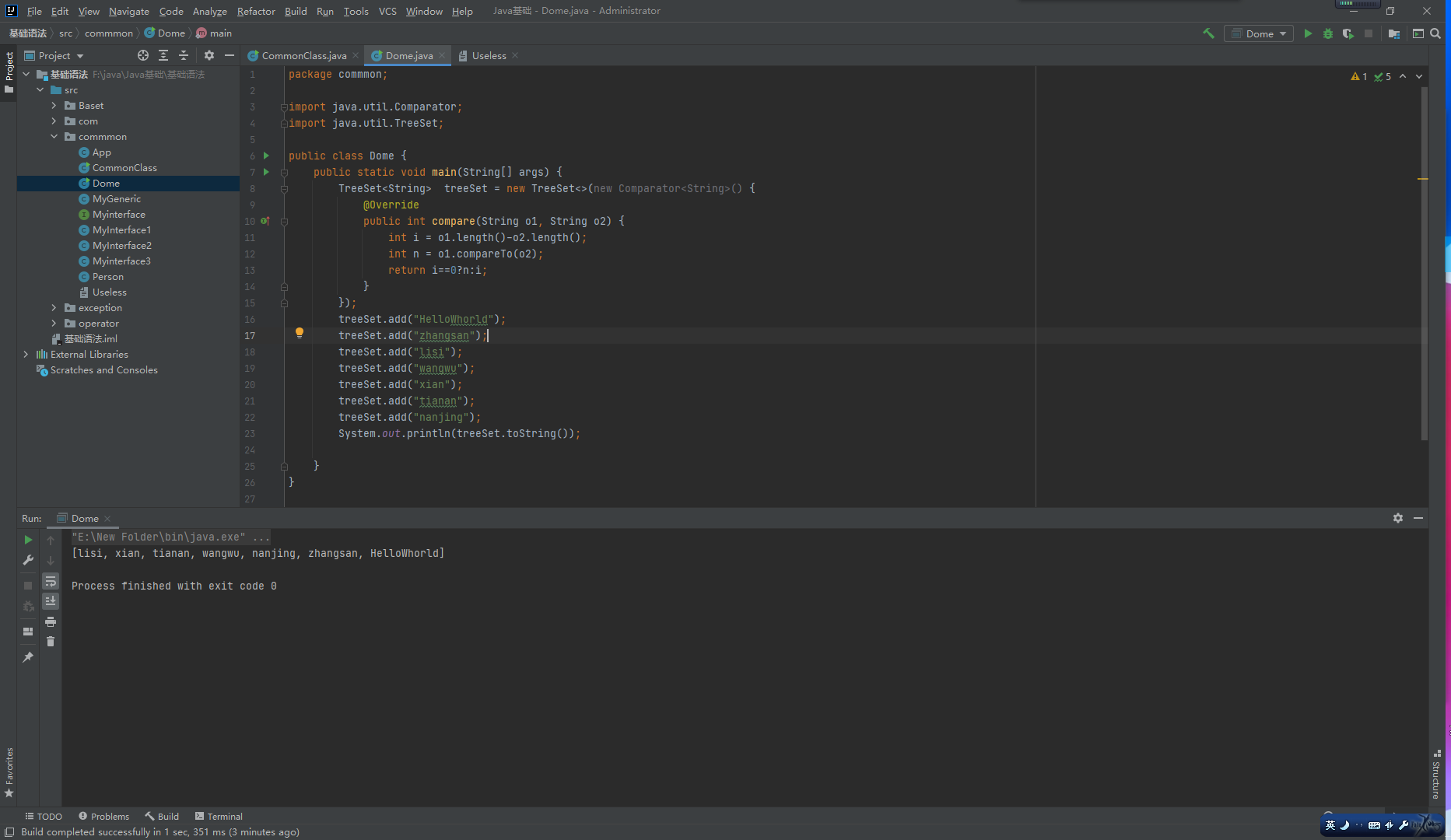
TreeSet:
-
基于排列顺序实现元素不重复。
-
实现了SortedSet接口,对集合元素自动排序。
-
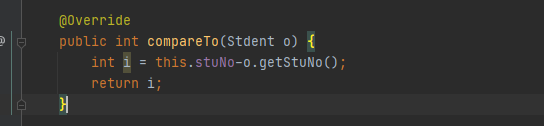
元素对象的类型必须实现Comparable接口,指定排序规则。
-
通过CompareTo方法确定是否为重复元素。
-
-
HashSet:
TreeSet:
Map集合
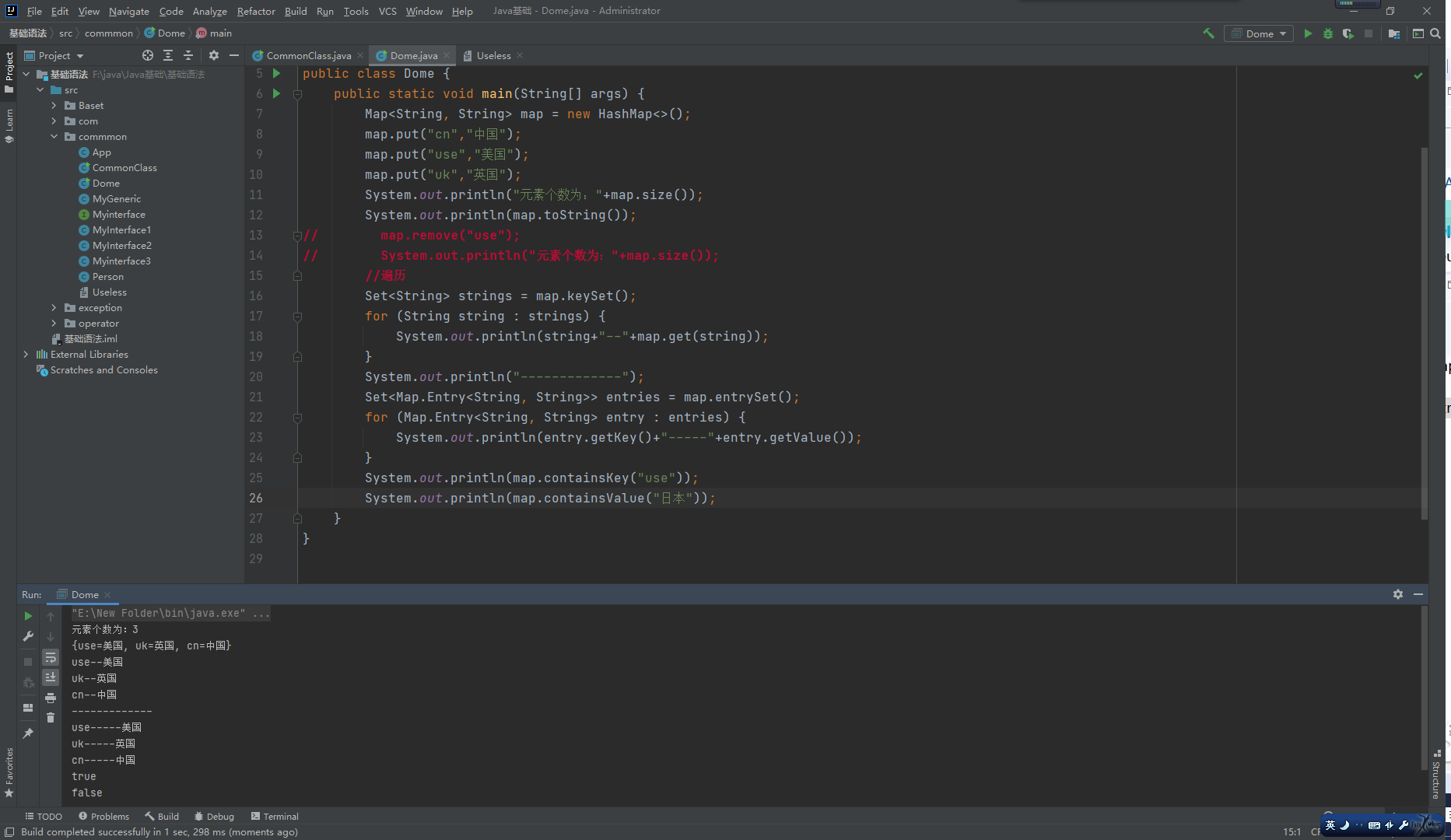
Map父接口:
-
特点:存储一对数据(Key-Value),无序、无下标,键不可重复,值可重复。
-
方法:
-
v put(K key,v value)//将对象存入到集合中,关联键值。key重复则覆盖原值。
-
0bject get(Object key)//根据键获取对应的值。
-
Set<K>//返回所有key。
-
Collection<V> values()//返回包含所有值的Collection集合。
-
Set<Map. Entry<K, V>>//键值匹配的Set集合。
-
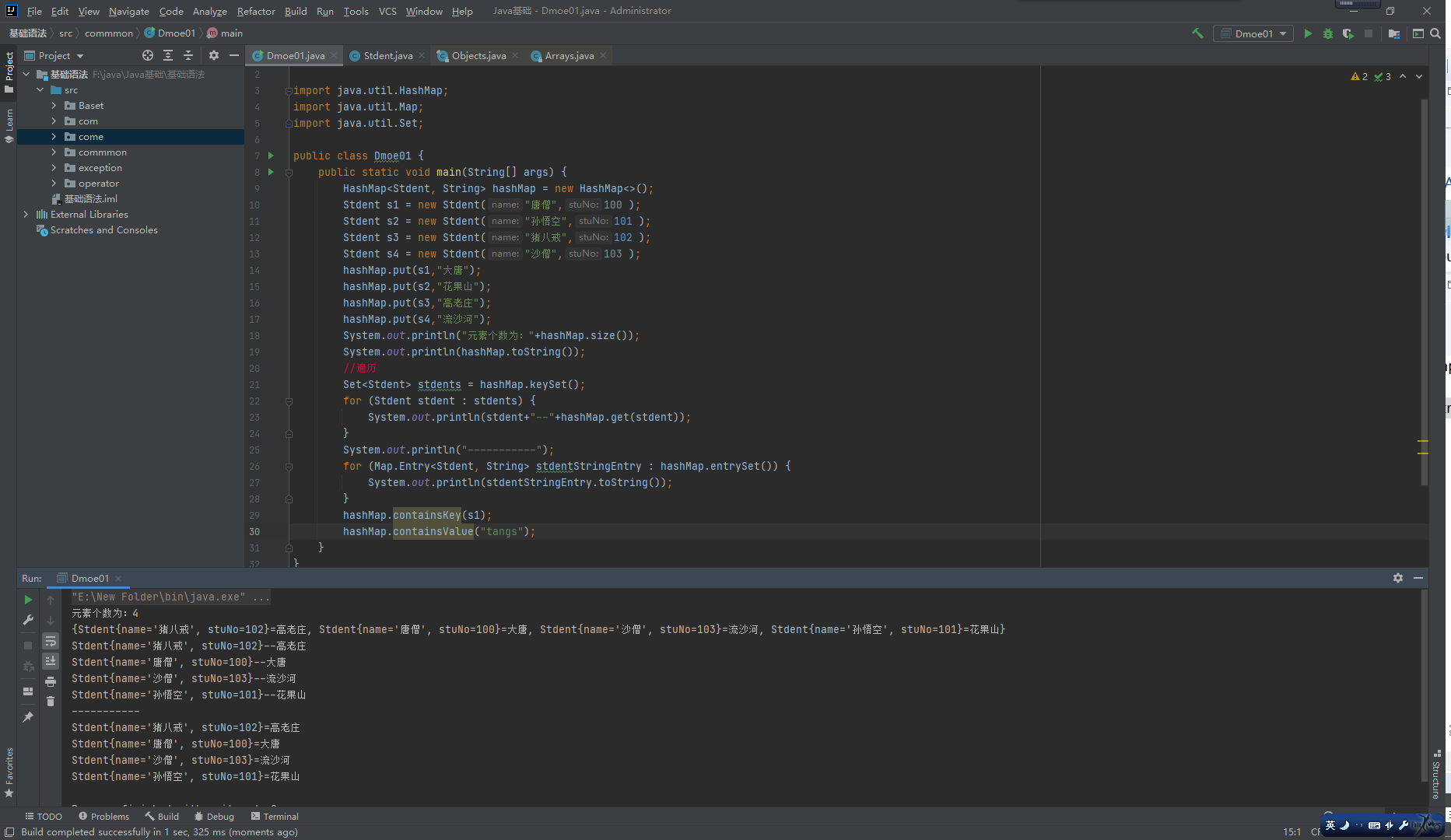
HashMap
-
HashMap源码分析
-
默认初始化容量:
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16-
数组最大容量:
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
-
-
默认加载因子:
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; -
链表调整为红黑树的链表长度阈值(JDK1.8):
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; -
红黑树调整为链表的链表长度阈值(JDK1.8):
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; -
链表调整为红黑树的数组最小阈值(JDK1.8):
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; -
HashMap存储的数组:
transient Node<K,V>[] table; -
HashMap存储的元素个数:
transient int size; -
默认加载因子是什么?
-
就是判断数组是否扩容的一个因子。假如数组容量为100,如果HashMap的存储元素个数超过了100*0.75=75,那么就会进行扩容。
-
链表调整为红黑树的链表长度阈值是什么?
-
假设在数组中下标为3的位置已经存储了数据,当新增数据时通过哈希码得到的存储位置又是3,那么就会在该位置形成一个链表,当链表过长时就会转换成红黑树以提高执行效率,这个阈值就是链表转换成红黑树的最短链表长度;
-
红黑树调整为链表的链表长度阈值是什么?
-
当红黑树的元素个数小于该阈值时就会转换成链表。
-
链表调整为红黑树的数组最小阈值是什么?
-
并不是只要链表长度大于8就可以转换成红黑树,在前者条件成立的情况下,数组的容量必须大于等于64才会进行转换。
-
-
TreeMap
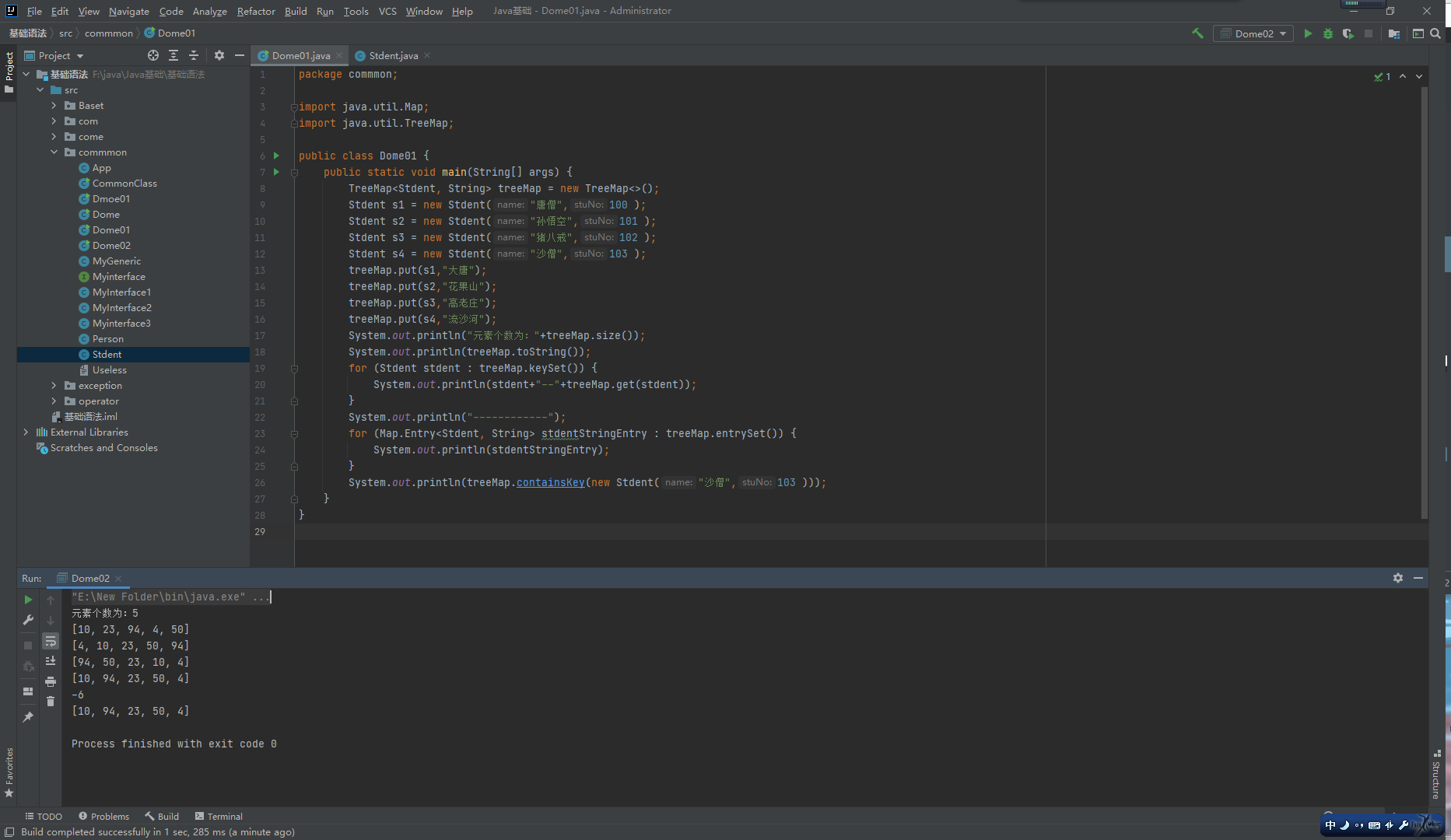
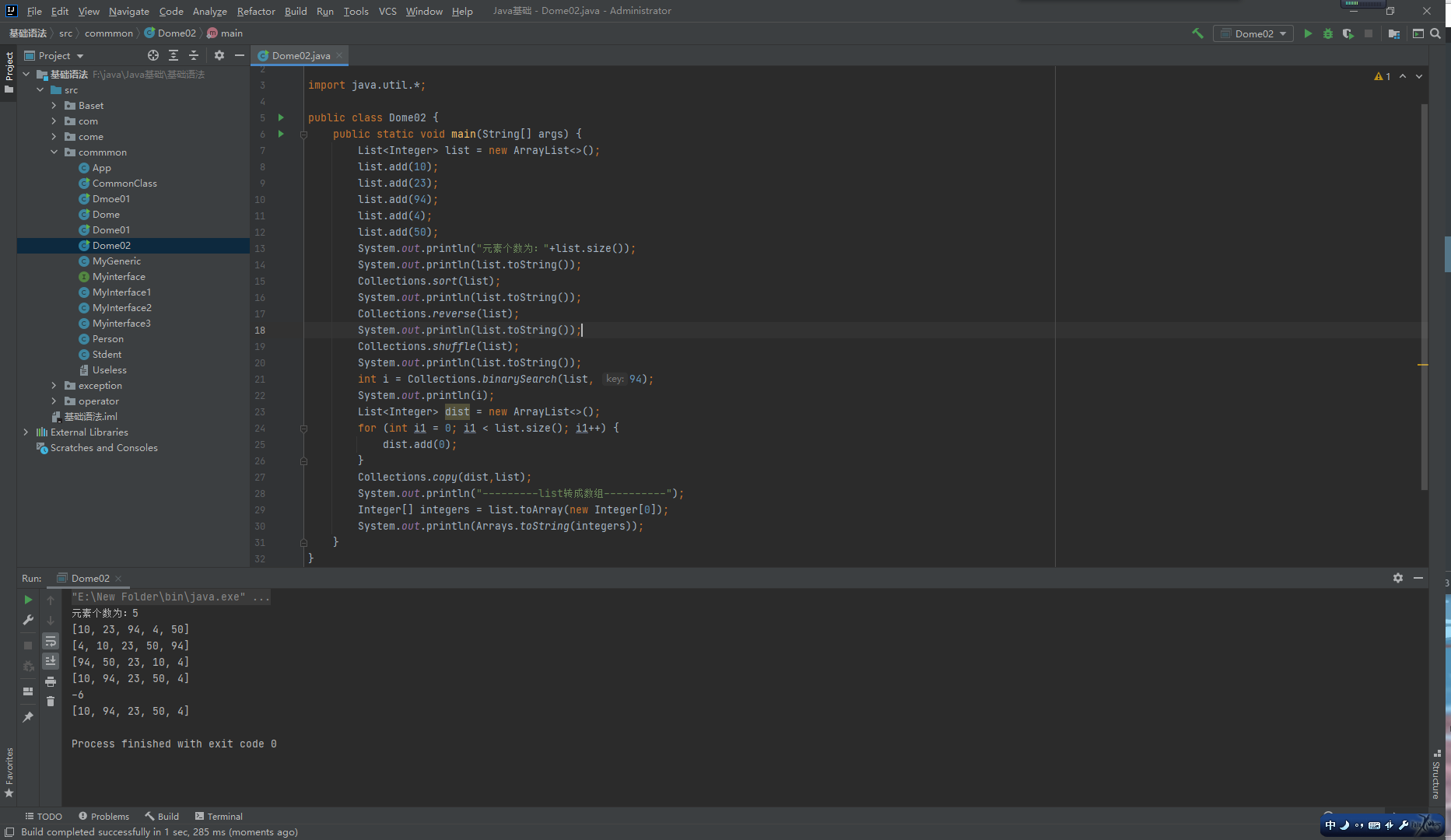
Colletions工具类
-
概念:集合工具类,定义了除了存取以外的集合常用方法。
-
方法:
-
public static void reverse(List<?> list)//反转集合中元素的顺序
-
public static void shuffle(List<?> list)//随机重置集合元素的顺序
-
public static void sort(List<T> list)//升序排序(元素类型必须实现Comparable接口)
-


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号