CS231N Assignment3 入门笔记(Q4 GANs)
斯坦福2023年春季CS231N课程第三次作业(最后一次)解析、笔记与代码,作为初学者入门学习。
在这项作业中,将实现语言网络,并将其应用于 COCO 数据集上的图像标题。然后将训练生成对抗网络,生成与训练数据集相似的图像。最后,将学习自我监督学习,自动学习无标签数据集的视觉表示。
本作业的目标如下:
1.理解并实现 RNN 和 Transformer 网络。将它们与 CNN 网络相结合,为图像添加标题。
2.了解如何训练和实现生成对抗网络(GAN),以生成与数据集中的样本相似的图像。
3.了解如何利用自我监督学习技术来帮助完成图像分类任务。
Q4: Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
In the notebook Generative_Adversarial_Networks.ipynb you will learn how to generate images that match a training dataset and use these models to improve classifier performance when training on a large amount of unlabeled data and a small amount of labeled data. When first opening the notebook, go to Runtime > Change runtime type and set Hardware accelerator to GPU.
到目前为止,在CS231N中,我们所探索的所有神经网络的应用都是**discriminative models**,它们接受输入并被训练产生标记的输出。这包括从图像类别的直接分类到句子生成(这仍然是一个分类问题,我们在词汇空间中重复捕获多个单词标签)。在这个notebook中,我们将进行扩展,使用神经网络建立**生成性模型**。具体地说,我们将学习如何构建模型,以生成类似于一组训练图像的新图像。
### What is a GAN?
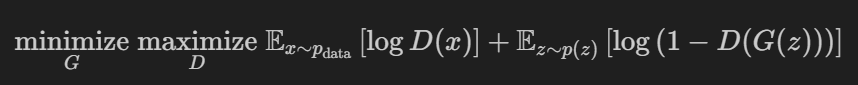
为了优化这个Minimax博弈,我们将交替在G的目标上采用梯度*下降*和在D的目标上采用梯度*上升*:
![]()
2. Update the discriminator (D), to maximize the probability of the discriminator making the correct choice on real and generated data:
![]()
sample noise函数
def sample_noise(batch_size, dim, seed=None): """ Generate a PyTorch Tensor of uniform random noise. Input: - batch_size: Integer giving the batch size of noise to generate. - dim: Integer giving the dimension of noise to generate. Output: - A PyTorch Tensor of shape (batch_size, dim) containing uniform random noise in the range (-1, 1). """ if seed is not None: torch.manual_seed(seed) # *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** noise = 2 * torch.rand(batch_size, dim) - 1 return noise # *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
# Discriminator
def discriminator(seed=None): """ Build and return a PyTorch model implementing the architecture above. """ if seed is not None: torch.manual_seed(seed) model = None # TODO: Implement architecture # # HINT: nn.Sequential might be helpful. You'll start by calling Flatten(). # model = nn.Sequential( nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(784, 256, bias=True), nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01), nn.Linear(256, 256, bias=True), nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01), nn.Linear(256, 1, bias=True), ) return model
# Generator
def generator(noise_dim=NOISE_DIM, seed=None): """ Build and return a PyTorch model implementing the architecture above. """ if seed is not None: torch.manual_seed(seed) model = None # TODO: Implement architecture # # HINT: nn.Sequential might be helpful. # model = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(noise_dim, 1024, bias=True), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(1024, 1024, bias=True), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(1024, 784, bias=True), nn.Tanh() ) return model
# GAN Loss
def bce_loss(input, target): """ Numerically stable version of the binary cross-entropy loss function in PyTorch. Inputs: - input: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N, ) giving scores. - target: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N,) containing 0 and 1 giving targets. Returns: - A PyTorch Tensor containing the mean BCE loss over the minibatch of input data. """ bce = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss() return bce(input.squeeze(), target) def discriminator_loss(logits_real, logits_fake): """ Computes the discriminator loss described above. Inputs: - logits_real: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N,) giving scores for the real data. - logits_fake: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N,) giving scores for the fake data. Returns: - loss: PyTorch Tensor containing (scalar) the loss for the discriminator. """ loss = None # *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** # true张量全0,false张量全1 true_labels = torch.ones(logits_real.shape[0]).type(dtype) false_labels = torch.zeros(logits_fake.shape[0]).type(dtype) # 将真实数据和生成数据的分数张量连接在一起,得到形状为(2N,)的张量 targets = torch.cat([true_labels, false_labels], dim=0) logits = torch.cat([logits_real, logits_fake], dim=0) loss = bce_loss(logits, targets) * 2 # *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** return loss def generator_loss(logits_fake): """ Computes the generator loss described above. Inputs: - logits_fake: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N,) giving scores for the fake data. Returns: - loss: PyTorch Tensor containing the (scalar) loss for the generator. """ loss = None # *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** targets = torch.ones(logits_fake.shape[0]).type(dtype) loss = bce_loss(logits_fake, targets) # *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** return loss
# Optimizing our Loss
optimizer = optim.Adam(params=model.parameters(), lr=1e-3, betas=(0.5, 0.99))
建议看一看run_a_gan函数,解析如下:
def run_a_gan(D, G, D_solver, G_solver, discriminator_loss, generator_loss, loader_train, show_every=250, batch_size=128, noise_size=96, num_epochs=10): """ Train a GAN! Inputs: - D, G: PyTorch models for the discriminator and generator - D_solver, G_solver: torch.optim Optimizers to use for training the discriminator and generator. - discriminator_loss, generator_loss: Functions to use for computing the generator and discriminator loss, respectively. - show_every: Show samples after every show_every iterations. - batch_size: Batch size to use for training. - noise_size: Dimension of the noise to use as input to the generator. - num_epochs: Number of epochs over the training dataset to use for training. """ images = [] iter_count = 0 # 外层循环控制迭代次数 # 内层循环遍历训练数据加载器loader_train中的批量数据 for epoch in range(num_epochs): for x, _ in loader_train: if len(x) != batch_size: continue D_solver.zero_grad() # 判别器的梯度清零 real_data = x.type(dtype) # 通过判别器D计算真实数据的分数logits_real logits_real = D(2* (real_data - 0.5)).type(dtype) # 生成一个噪声种子g_fake_seed,并通过生成器G生成假图像fake_images # 并将其从计算图中分离(detach) # 通过判别器D计算假图像的分数logits_fake g_fake_seed = sample_noise(batch_size, noise_size).type(dtype) fake_images = G(g_fake_seed).detach() logits_fake = D(fake_images.view(batch_size, 1, 28, 28)) # D_solver进行参数更新 d_total_error = discriminator_loss(logits_real, logits_fake) d_total_error.backward() D_solver.step() G_solver.zero_grad() g_fake_seed = sample_noise(batch_size, noise_size).type(dtype) fake_images = G(g_fake_seed) # 将生成器的梯度清零,并再次生成噪声种子g_fake_seed # 通过生成器G生成假图像fake_images。 # 通过判别器D计算生成的假图像的分数gen_logits_fake。计算生成器的损失g_error gen_logits_fake = D(fake_images.view(batch_size, 1, 28, 28)) g_error = generator_loss(gen_logits_fake) g_error.backward() # G_solver进行参数更新 G_solver.step() if (iter_count % show_every == 0): print('Iter: {}, D: {:.4}, G:{:.4}'.format(iter_count,d_total_error.item(),g_error.item())) imgs_numpy = fake_images.data.cpu().numpy() images.append(imgs_numpy[0:16]) iter_count += 1 return images
# Least Squares GAN 最小二乘GAN
def ls_discriminator_loss(scores_real, scores_fake): """ Compute the Least-Squares GAN loss for the discriminator. Inputs: - scores_real: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N,) giving scores for the real data. - scores_fake: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N,) giving scores for the fake data. Outputs: - loss: A PyTorch Tensor containing the loss. """ loss = None # *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** loss = 0.5 * ((scores_real-1)**2).mean(axis=0) + 0.5 * (scores_fake**2).mean(axis=0) # *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** return loss def ls_generator_loss(scores_fake): """ Computes the Least-Squares GAN loss for the generator. Inputs: - scores_fake: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N,) giving scores for the fake data. Outputs: - loss: A PyTorch Tensor containing the loss. """ loss = None # *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** loss = 0.5 * ((scores_fake-1)**2).mean(axis=0) # *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** return loss
# Deeply Convolutional GANs
def build_dc_classifier(batch_size): """ Build and return a PyTorch model for the DCGAN discriminator implementing the architecture above. """ model = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=32, kernel_size=5, stride=1, bias=True), nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01), nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=5, stride=1, bias=True), nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01), nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(in_features=4*4*64, out_features=4*4*64, bias=True), nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01), nn.Linear(in_features=4*4*64, out_features=1, bias=True), ) return model def build_dc_generator(noise_dim=NOISE_DIM): """ Build and return a PyTorch model implementing the DCGAN generator using the architecture described above. """ model = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(in_features=noise_dim, out_features=1024, bias=True), nn.ReLU(), nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features=1024), nn.Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=7*7*128, bias=True), nn.ReLU(), nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features=7*7*128), nn.Unflatten(dim=1, unflattened_size=(128, 7, 7)), nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=64, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1), nn.ReLU(), nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=64), nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=1, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1), nn.Tanh(), nn.Flatten(), ) return model
注意最后一个batchnorm是2d的
|
vanilla GAN |
LS GAN | Deeply Convolutional GANs |
|
|

|
|




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号