muduo网络库源码学习————线程类
muduo库里面的线程类是使用基于对象的编程思想,源码目录为muduo/base,如下所示:
线程类头文件:
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.
//
// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
//线程类
#ifndef MUDUO_BASE_THREAD_H
#define MUDUO_BASE_THREAD_H
#include <muduo/base/Atomic.h>
#include <muduo/base/Types.h>
#include <boost/function.hpp>
#include <boost/noncopyable.hpp>
#include <pthread.h>
//线程类头文件
namespace muduo
{
class Thread : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
typedef boost::function<void ()> ThreadFunc;//函数适配接收的函数
//线程构造函数,参数为回调函数和线程名称
explicit Thread(const ThreadFunc&, const string& name = string());//名称默认值为空的字符串类
//线程析构函数
~Thread();
void start();//启动线程
int join(); // return pthread_join()
bool started() const { return started_; }//线程是否已经启动
// pthread_t pthreadId() const { return pthreadId_; }
pid_t tid() const { return tid_; }//线程的真实pid
const string& name() const { return name_; }//线程的名称
static int numCreated() { return numCreated_.get(); }//已经启动的线程个数
private:
static void* startThread(void* thread);//现成的入口函数,调用runInThread函数
void runInThread();//调用回调函数func_
bool started_;//线程是否已经启动
pthread_t pthreadId_;//线程的pthread_t
pid_t tid_;//线程真实的 pid
ThreadFunc func_;//线程的回调函数
string name_;//线程的名称
static AtomicInt32 numCreated_;//已经创建的线程的个数,每当创建一个线程,该值就加一(原子整数类)
};
}
#endif
线程类的实现文件:
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.
//
// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
//线程类实现文件
#include <muduo/base/Thread.h>
#include <muduo/base/CurrentThread.h>
#include <muduo/base/Exception.h>
//#include <muduo/base/Logging.h>
//暂时不用日志文件,先注释掉
#include <boost/static_assert.hpp>
#include <boost/type_traits/is_same.hpp>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <linux/unistd.h>
namespace muduo
{
namespace CurrentThread
{//__thread两个下划线是gcc 内置的线程局部存储设施
//每个线程各有一个,并不会去共享他
//缓存获取tid是为了提高获取tid的效率
__thread int t_cachedTid = 0;//线程真实pid的缓存,如果每次都用系统调用去获取pid,效率会低
__thread char t_tidString[32];//tid的字符串表示形式
__thread const char* t_threadName = "unknown";//线程的名称
const bool sameType = boost::is_same<int, pid_t>::value;//如果是相同类型,返回true
BOOST_STATIC_ASSERT(sameType);//编译时断言
}
namespace detail
{
pid_t gettid()//通过系统调用SYS_gettid获得tid
{
return static_cast<pid_t>(::syscall(SYS_gettid));//类型转化为pid_t
}
void afterFork()//子进程调用的
{
muduo::CurrentThread::t_cachedTid = 0;//当前线程pid赋值0
muduo::CurrentThread::t_threadName = "main";//名称赋值name
CurrentThread::tid();//进行缓存
// no need to call pthread_atfork(NULL, NULL, &afterFork);
}
class ThreadNameInitializer
{
public:
ThreadNameInitializer()//构造函数
{
muduo::CurrentThread::t_threadName = "main";//线程名称赋为main,即为主线程名称
CurrentThread::tid();//缓存当前线程的pid
//#include <pthread.h>
//int pthread_atfork(void (*prepare)(void), void (*parent)(void), void (*child)(void));
//调用fork时,内部创建子进程前在父进程中会调用prepare,
//内部创建子进程成功后,父进程会调用parent ,子进程会调用child
pthread_atfork(NULL, NULL, &afterFork);//如果使用fork函数,那么子进程会调用邋afterFork
}
};
ThreadNameInitializer init;
}
}
using namespace muduo;
void CurrentThread::cacheTid()
{
if (t_cachedTid == 0)
{
t_cachedTid = detail::gettid();//调用gettid函数获得tid
int n = snprintf(t_tidString, sizeof t_tidString, "%5d ", t_cachedTid);//将tid格式化保存在t_tidString中
assert(n == 6);//断言长度是6,5d后面还有一个空格,所以是6
(void) n;//这一句主要是预防n没有使用从而产生警告
}
}
bool CurrentThread::isMainThread()
{
return tid() == ::getpid();//查看tid是否等于当前进程id
}
AtomicInt32 Thread::numCreated_;
//构造函数,初始化
Thread::Thread(const ThreadFunc& func, const string& n) : started_(false), pthreadId_(0),tid_(0),func_(func),name_(n)
{
numCreated_.increment();//创建的线程的个数加一,为原子性操作
}
Thread::~Thread()
{
// no join
}
void Thread::start()
{
assert(!started_);
started_ = true;
//创建线程,startThread为线程的入口函数
errno = pthread_create(&pthreadId_, NULL, &startThread, this);
if (errno != 0)
{//日志
// LOG_SYSFATAL << "Failed in pthread_create";
}
}
int Thread::join()
{
assert(started_);
return pthread_join(pthreadId_, NULL);
}
//线程的入口函数
void* Thread::startThread(void* obj)
{//this指针传到obj
Thread* thread = static_cast<Thread*>(obj);//转化为线程基类的指针
thread->runInThread();//调用线程函数runInThread
return NULL;
}
//被线程的入口函数调用
void Thread::runInThread()
{
tid_ = CurrentThread::tid();//获取线程的tid
muduo::CurrentThread::t_threadName = name_.c_str();//缓存该线程的名称
try
{
func_();//调用回调函数
muduo::CurrentThread::t_threadName = "finished";
}
catch (const Exception& ex)//异常捕捉
{
muduo::CurrentThread::t_threadName = "crashed";
fprintf(stderr, "exception caught in Thread %s\n", name_.c_str());
fprintf(stderr, "reason: %s\n", ex.what());
fprintf(stderr, "stack trace: %s\n", ex.stackTrace());
abort();
}
catch (const std::exception& ex)
{
muduo::CurrentThread::t_threadName = "crashed";
fprintf(stderr, "exception caught in Thread %s\n", name_.c_str());
fprintf(stderr, "reason: %s\n", ex.what());
abort();
}
catch (...)
{
muduo::CurrentThread::t_threadName = "crashed";
fprintf(stderr, "unknown exception caught in Thread %s\n", name_.c_str());
throw; // rethrow
}
}
CurrentThread头文件
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.
//
// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
#ifndef MUDUO_BASE_CURRENTTHREAD_H
#define MUDUO_BASE_CURRENTTHREAD_H
namespace muduo
{//CurrentThread的名称空间
namespace CurrentThread
{
// internal
extern __thread int t_cachedTid;
extern __thread char t_tidString[32];
extern __thread const char* t_threadName;
void cacheTid();
inline int tid()
{
if (t_cachedTid == 0)//还没有缓存过
{//t_cachedTid初值 是0
cacheTid();//进行缓存
}
return t_cachedTid;//返回缓存的tid
}
inline const char* tidString() // for logging
{
return t_tidString;//返回tid的字符串表示形式
}
inline const char* name()
{
return t_threadName;//返回线程名称
}
bool isMainThread();//是否是主线程
}
}
#endif
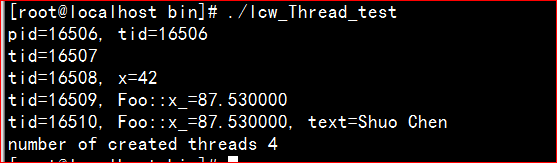
测试代码位于muduo/base/tests
//线程测试程序
#include <muduo/base/Thread.h>
#include <muduo/base/CurrentThread.h>
#include <string>
#include <boost/bind.hpp>
#include <stdio.h>
void threadFunc()
{
printf("tid=%d\n", muduo::CurrentThread::tid());
}
void threadFunc2(int x)
{
printf("tid=%d, x=%d\n", muduo::CurrentThread::tid(), x);
}
class Foo
{
public:
explicit Foo(double x) : x_(x)
{
}
void memberFunc()
{
printf("tid=%d, Foo::x_=%f\n", muduo::CurrentThread::tid(), x_);
}
void memberFunc2(const std::string& text)
{
printf("tid=%d, Foo::x_=%f, text=%s\n", muduo::CurrentThread::tid(), x_, text.c_str());
}
private:
double x_;
};
int main()
{//获取当前线程的pid(进程id 线程pid)
printf("pid=%d, tid=%d\n", ::getpid(), muduo::CurrentThread::tid());
//创建一个线程对象,传递一个函数
muduo::Thread t1(threadFunc);
t1.start();//启动线程
t1.join();
//threadFunc2带了一个参数,用boost::bind函数传递进去,最后是线程的名称,可以不传
muduo::Thread t2(boost::bind(threadFunc2, 42), "thread for free function with argument");
t2.start();
t2.join();
//创建一个对象
Foo foo(87.53);
//创建第三个线程(成员函数的话一定要用&)
muduo::Thread t3(boost::bind(&Foo::memberFunc, &foo), "thread for member function without argument");
t3.start();
t3.join();
//创建第四个线程,这里传进去的函数是带参数的
muduo::Thread t4(boost::bind(&Foo::memberFunc2, boost::ref(foo), std::string("Shuo Chen")));
t4.start();
t4.join();
//打印最后创建的线程总数
printf("number of created threads %d\n", muduo::Thread::numCreated());
}
单独编译后运行结果如下:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号