52、Java JUC
1、java高级语法、java集合类 、Java多线程 、java IO
一、Lamda 表达式口诀:复制小括号,写死箭头号,落地大括号
接口还可以这样写
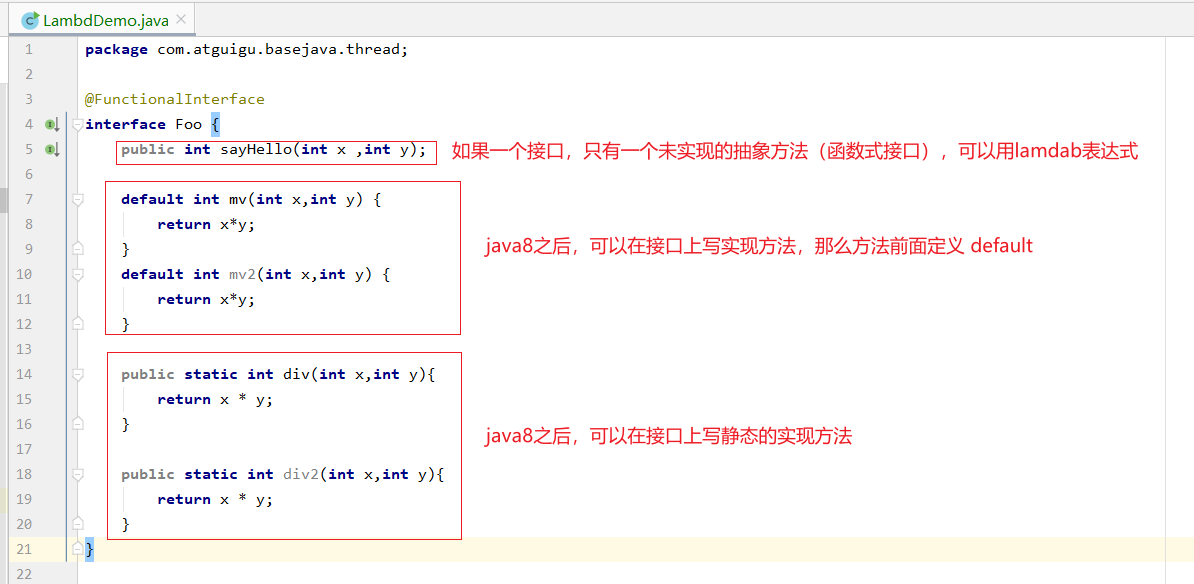
测试Lambda表达式,接口的默认方法,接口的静态方法
public class LambdDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Foo foo = (int x ,int y) -> { System.out.println(" ++++++come in here "); return x+y; }; System.out.println(foo.sayHello(3, 4)); System.out.println(foo.mv(3, 5)); System.out.println(Foo.div(4, 5)); } }
二、JUC的 Lock 锁的使用 实现高并发、多线程访问资源类
声明资源类
class Ticket { int number = 30; private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public void saleTicket() { try{ lock.lock(); if (number >0 ){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程\t买出的票"+(number--)+"还剩下的票:"+ number); } }finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
测试多线程访问资源类
public static void main(String[] args) { Ticket ticket = new Ticket(); new Thread(()->{ for(int i=1;i<40;i++) { ticket.saleTicket(); } },"A").start(); new Thread(()->{ for(int i=1;i<40;i++) { ticket.saleTicket(); } },"B").start(); new Thread(()->{ for(int i=1;i<40;i++) { ticket.saleTicket(); } },"C").start(); }
3、线程之间的通信
使用:synchronized、notifyAll,wait 实现线程之间的通信
编写资源类
class Air { int number = 0; public synchronized void increment () throws InterruptedException { while (number != 0) { this.wait(); } //干活 number++; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+ number); //唤醒其他线程 this.notifyAll(); } public synchronized void decrement() throws InterruptedException { while (number == 0) { this.wait(); } //干活 number--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+ number); //唤醒其他线程 this.notifyAll(); } }
测试多线程调用资源类
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ Air air = new Air(); new Thread(()->{ try { for (int i =1;i<=10;i++){ air.increment(); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"A").start(); new Thread(()->{ try { for (int i =1;i<=10;i++){ air.increment(); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"B").start(); }
使用:Lock、condition.await();,condition.signalAll();实现线程之间的通信
编写资源类
class AirMode { private int number = 0; private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); public void increment() { try { lock.lock(); while (number != 0) { condition.await();//this.wait } number ++; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t: "+ number); condition.signalAll();//this.notifyAll }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void decrement() { try { lock.lock(); while (number == 0) { condition.await();//this.wait } number --; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t: "+ number); condition.signalAll();//this.notifyAll }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
测试JUC多线程调用资源类
public static void main(String[] args) { AirMode airMode = new AirMode(); new Thread(()->{ for(int i = 1;i<=10; i++) { airMode.increment(); } },"A").start(); new Thread(()->{ for(int i = 1;i<=10; i++) { airMode.decrement(); } },"B").start(); new Thread(()->{ for(int i = 1;i<=10; i++) { airMode.increment(); } },"C").start(); new Thread(()->{ for(int i = 1;i<=10; i++) { airMode.decrement(); } },"D").start(); }
使用:Lock、condition.await();,condition.signal();实现线程之间的通信并且精准通知
编写资源类
class ShareResource { //标志位 private int number = 1; //A->1 B->2 C->3 private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition(); private Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition(); private Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition(); public void print5() { lock.lock(); try { while (number != 1){ condition1.await(); } for (int i =1;i<=5;i++){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程"+"第"+i+"次"); } number = 2; condition2.signal(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void print10() { lock.lock(); try { while (number != 2){ condition2.await(); } for (int i =1;i<=10;i++){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程"+"第"+i+"次"); } number = 3; condition3.signal(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void print15() { lock.lock(); try { while (number != 3){ condition3.await(); } for (int i =1;i<=15;i++){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程"+"第"+i+"次"); } number = 1; condition1.signal(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
测试线程之间的精准通知
public static void main(String[] args) { ShareResource shareResource = new ShareResource(); for (int i=1;i<3;i++){ new Thread(()->{ shareResource.print5(); },"A").start(); new Thread(()->{ shareResource.print10(); },"B").start(); new Thread(()->{ shareResource.print15(); },"C").start(); } }
4、多线程8锁 详解
编写资源类
class Phone { public synchronized void sendEmail() { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("============sendEmail============="); } public synchronized void sendSMS() { System.out.println("============sendSMS============="); } public void hello () { System.out.println("============hello============="); } }
测试运行结果
/** * 1、 同一部手机,先打印发邮件还是发短信 * 2、两部部手机,先打印发邮件还是发短信 * 3、同一部手机,A调用同步方法,B调用普通方法,先打印发邮件还是发短信 * 4、同一部手机,A调用静态同步方法,B调用静态同步方法,先打印发邮件还是发短信 * 5、两部手机,A调用静态同步方法,B调用静态同步方法,先打印发邮件还是发短信 * 6、同一部手机,A调用静态同步方法,B调用普通同步方法,先打印发邮件还是发短信 * 7、两部部手机,A调用静态同步方法,B调用普通同步方法,先打印发邮件还是发短信 */ public class Lock8 { public static void main(String[] args) { Phone phone1 = new Phone(); Phone phone2 = new Phone(); new Thread(() ->{ phone1.sendEmail(); },"A").start(); new Thread(() ->{ phone2.sendSMS(); //phone2.sendSMS(); //phone1.hello(); },"B").start(); } }
总结:要搞清楚锁的是哪里
1、普通同步方法锁的是当前对象
2、静态同步方法锁的是当前模板类,Class
3、普通方法锁不参与多线程竞争
5、多线程的创建方式,继承Thread,实现Runable,实现Callable
以实现Callable
class MyThread implements Callable<Integer>{ @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); System.out.println("============= come in ==============="); return 1024; } }
测试调用
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask(new MyThread()); new Thread(futureTask,"A").start(); System.out.println("===============计算完成=============="); System.out.println(futureTask.get()); }
6、控制线程的执行顺序
CountDownLatch 的使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(6); for (int i=1;i<=6;i++){ new Thread(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 离开走人"); countDownLatch.countDown(); },String.valueOf(i)).start(); } countDownLatch.await(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 班长走人"); }
CyclicBarrier 的使用
public static void main(String[] args) { CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(7,()->{ System.out.println("============召唤神龙"); }); for (int i =1;i<=7;i++){ final int tempInt = i; new Thread(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 获得第"+ tempInt+"颗龙珠"); try { cyclicBarrier.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (BrokenBarrierException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },String.valueOf(i)).start(); } }
Semaphore 的使用
public static void main(String[] args) { Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3); for(int i =1;i<=6;i++) { new Thread(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 抢占到车位"); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 离开车位"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { semaphore.release(); } },String.valueOf(i)).start(); } }
ReadWriteLock 的使用,在写的时候要求数据的一致性不能被别的线程打断,在读取数据的时候可以多个线程同时读
编写资源类
class MyCache { private volatile Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); private ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); public void put(String key,Object value) { try{ readWriteLock.writeLock().lock(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t ------写入数据中"); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } map.put(key,value); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t ------写入数据完成"); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock(); } } public void get(String key){ try{ readWriteLock.readLock().lock(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 读取数据中"); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } Object value = map.get(key); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 读取数据完成"); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { readWriteLock.readLock().unlock(); } } }
测试ReadWriteLock
public static void main(String[] args) { MyCache myCache = new MyCache(); for(int i=1;i<=5;i++) { int tempInt = i; new Thread(()->{ myCache.put(Thread.currentThread().getName(),tempInt); },String.valueOf(i)).start(); } for(int i=1;i<=5;i++) { int tempInt = i; new Thread(()->{ myCache.get(Thread.currentThread().getName()); },String.valueOf(i)).start(); } }
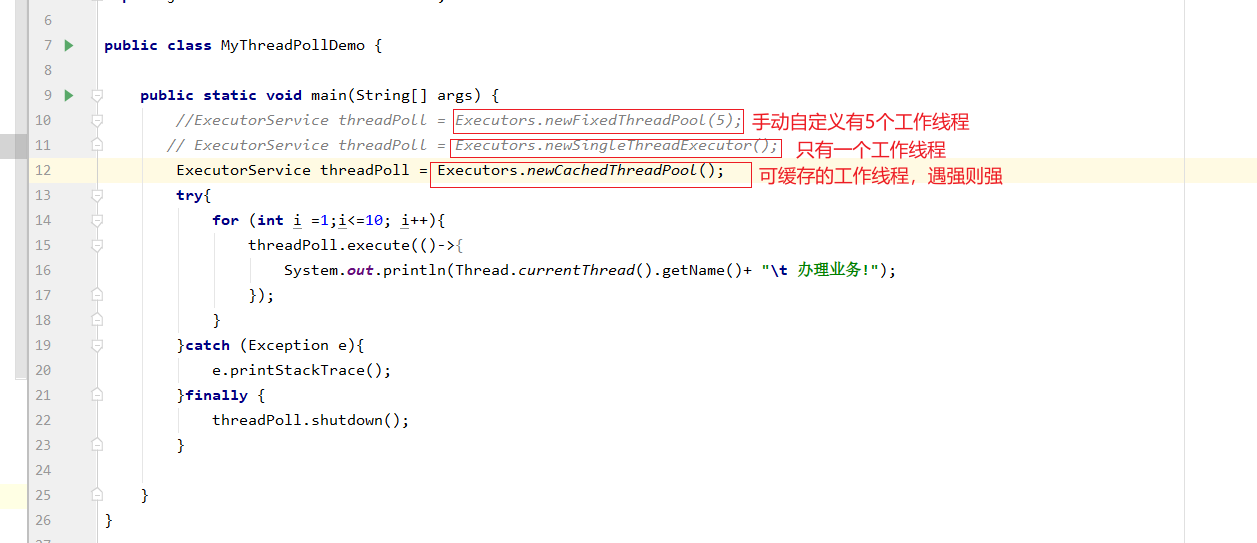
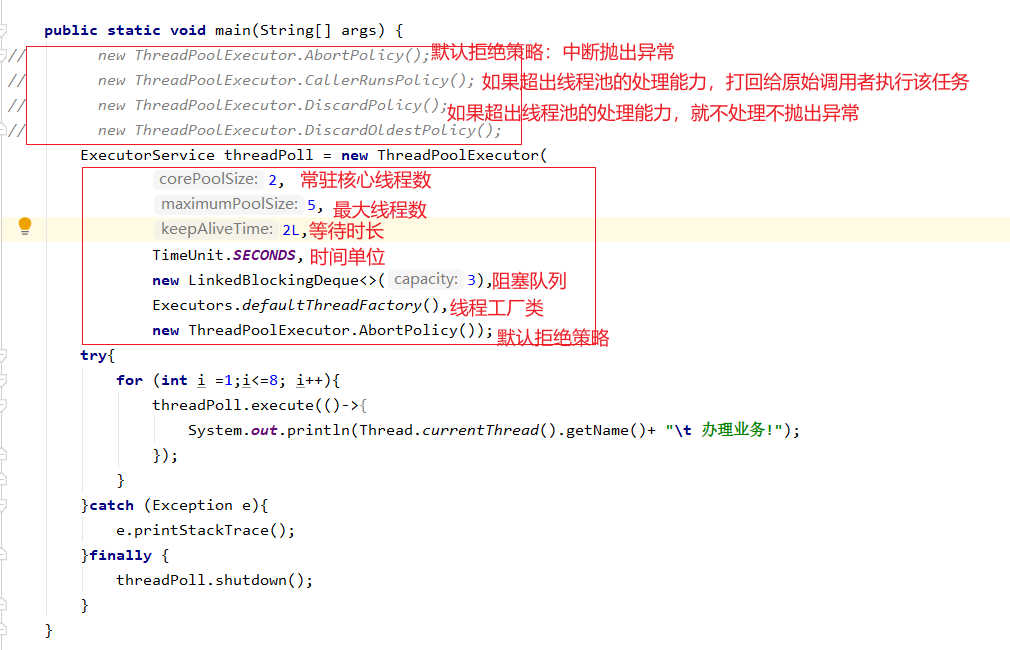
7、线程池的使用
三个常用的线程池
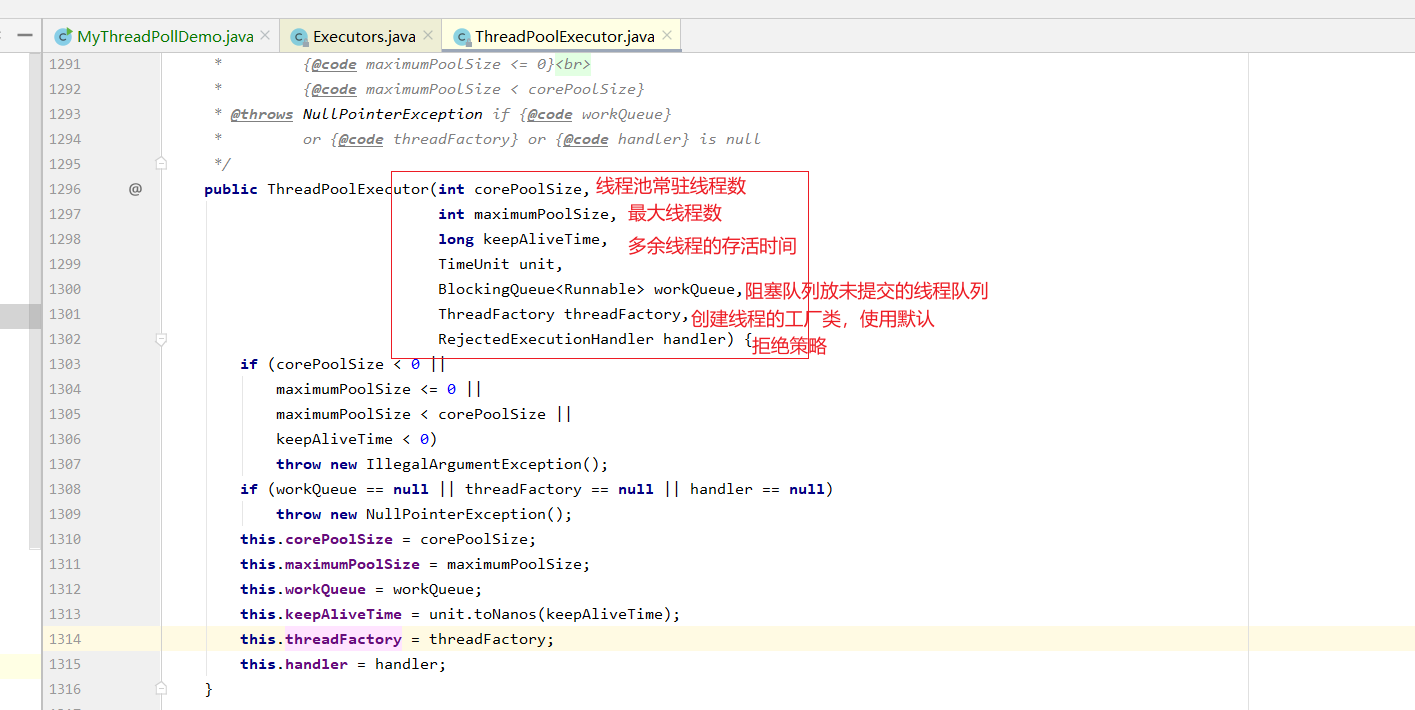
线程池的七个重要参数
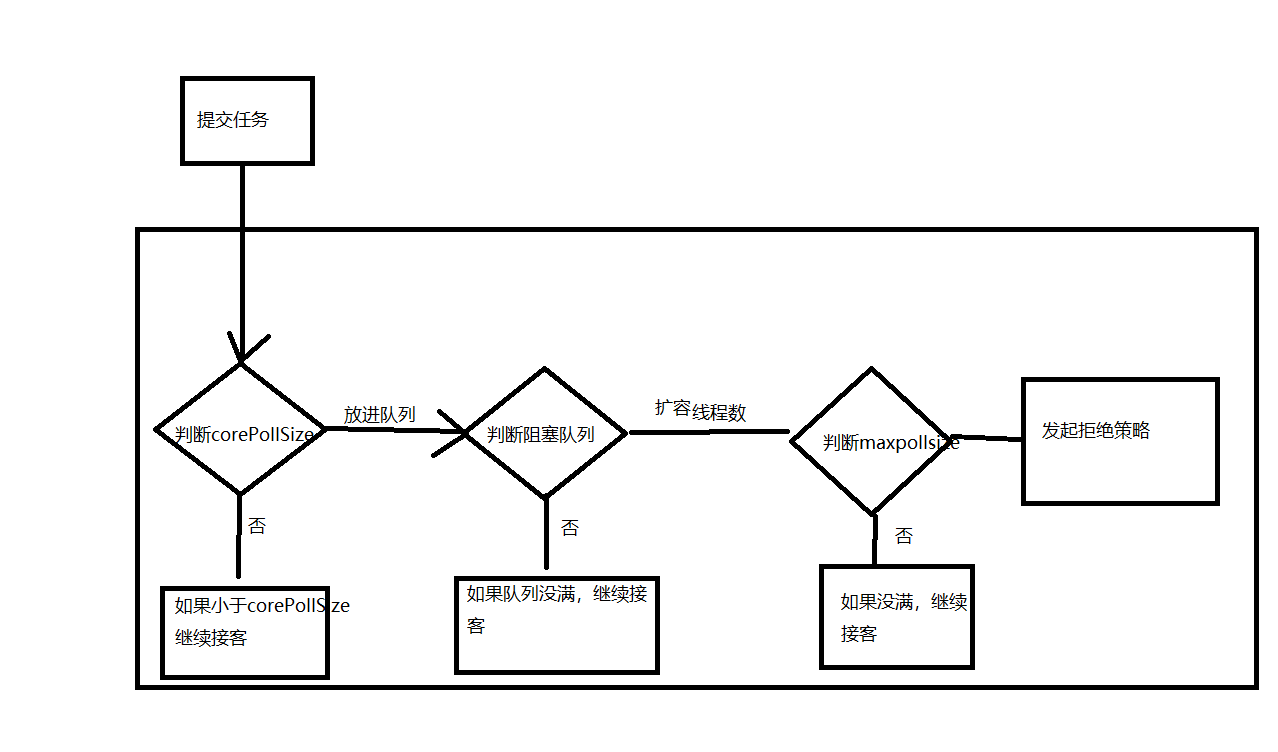
线程池的原理见图
工作中手写线程池
public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService threadPoll = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 2, 5, 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(3), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()); try{ for (int i =1;i<=8; i++){ threadPoll.execute(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "\t 办理业务!"); }); } }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { threadPoll.shutdown(); } }
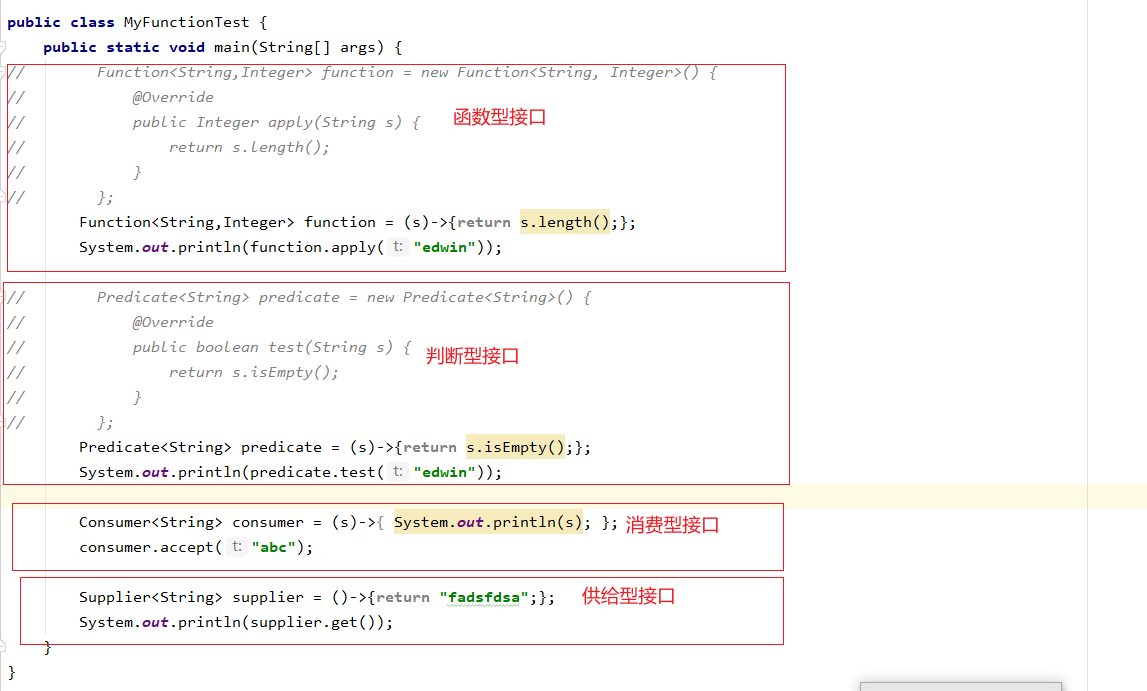
9、 四大函数式接口
链式编程的写法
@AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor @Data @Accessors(chain = true) public class Book { private Integer id; private String bookName; private double price; public static void main(String[] args) { Book book = new Book(); book.setId(1).setBookName("Java").setPrice(30.3d); System.out.println(book.toString()); } }
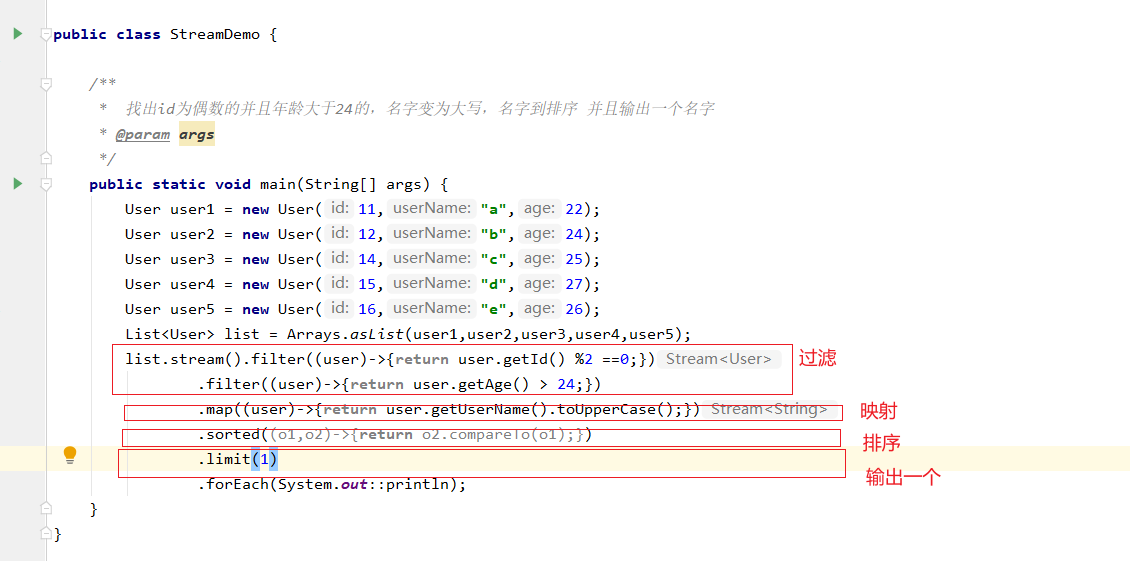
10、Stream 的流式计算
filter、map、sorted、limit 的使用
11、异步回调 CompletableFuture 的使用








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号