mystat
学习使用stat(1),并用C语言实现
- 提交学习stat(1)的截图
- man -k ,grep -r的使用
- 伪代码
- 产品代码 mystate.c,提交码云链接
- 测试代码,mystat 与stat(1)对比,提交截图
学习截图
stat査看文件的详细信息。
文件名
文件大小 占用的block数 IO块大小 文件类型
设备编号 i节点号 链接数
权限 所有者 所属组
Access Time:简写为atime,表示文件的访问时间。当文件内容被访问时,更新这个时间
Modify Time:简写为mtime,表示文件内容的修改时间,当文件的数据内容被修改时,更新这个时间。
Change Time:简写为ctime,表示文件的状态时间,当文件的状态被修改时,更新这个时间,例如文件的链接数,大小,权限,Blocks数。
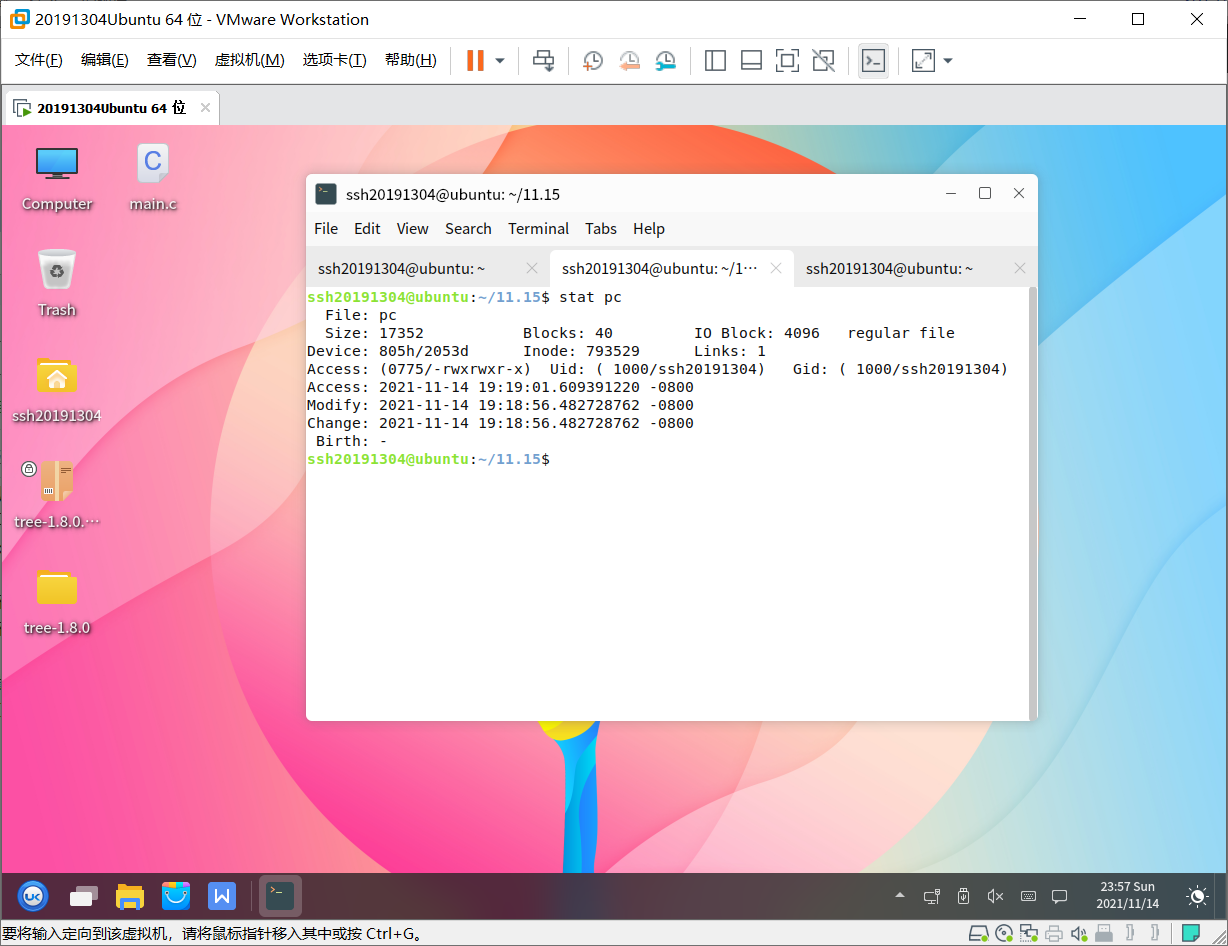
stat -f 査看这个文件所在文件系统的信息
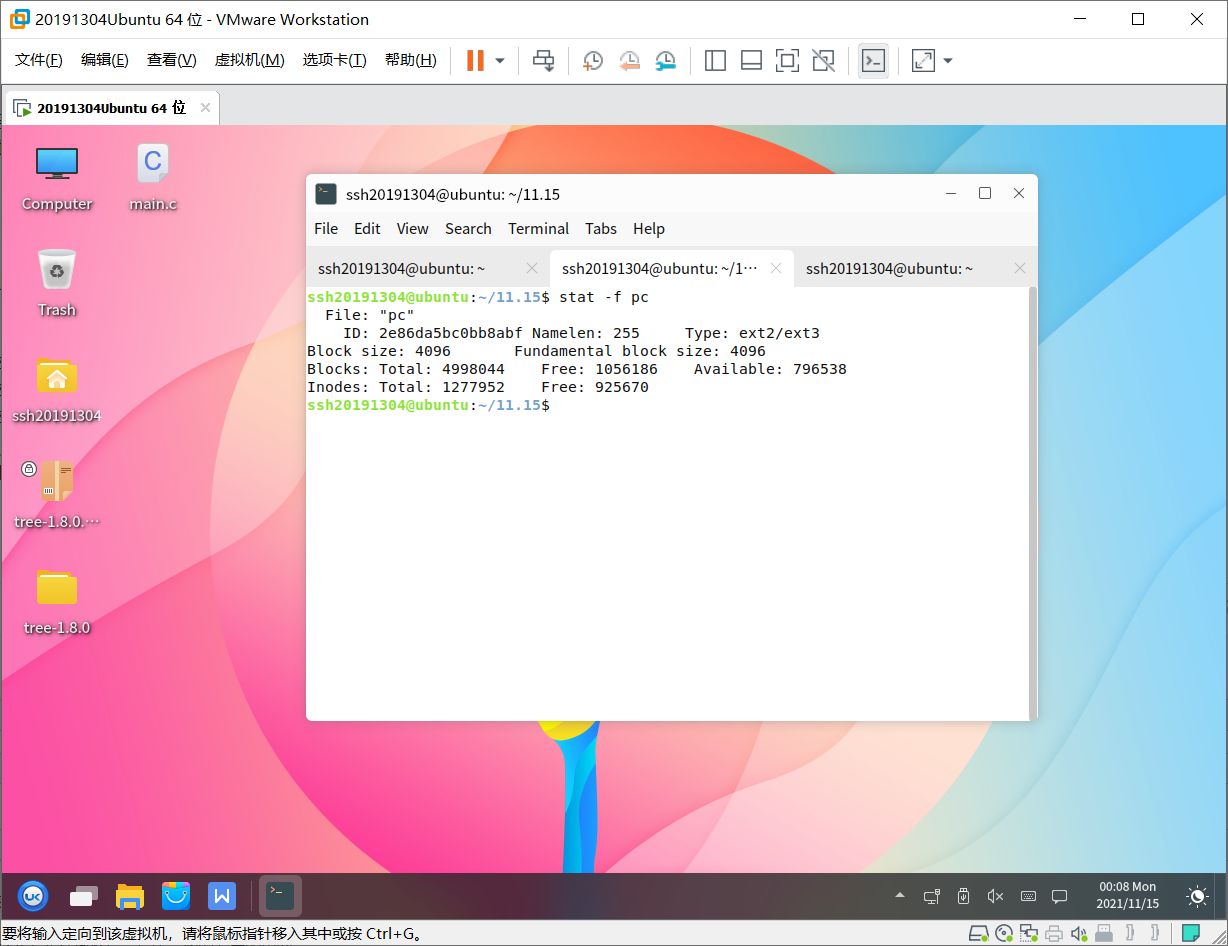
man -k
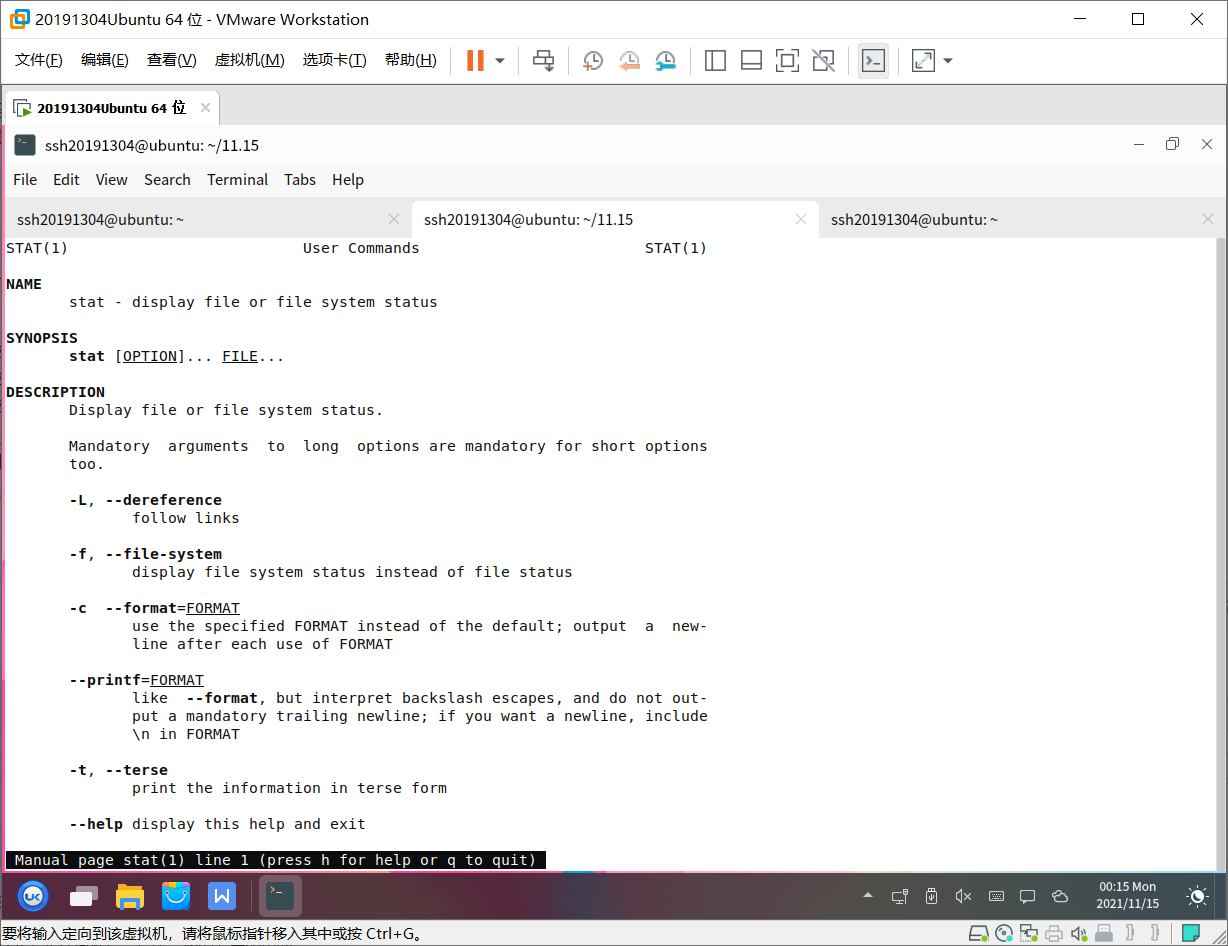
-L, --dereference
follow links //跟随链接
-f, --file-system
display file system status instead of file status //显示文件系统属性而不是文件属性
-c --format=FORMAT
use the specified FORMAT instead of the default; output a new‐
line after each use of FORMAT //使用指定的格式而不是默认格式;每次使用格式后,输出一个新行
--printf=FORMAT
like --format, but interpret backslash escapes, and do not out‐
put a mandatory trailing newline; if you want a newline, include
\n in FORMAT //类似于--format,但解释反斜杠转义,并且不输出强制的尾随换行符;如果需要换行符,请在格式中包含\n
-t, --terse
print the information in terse form //以简洁的形式打印信息
--help display this help and exit
--version
output version information and exit
stat结构体
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* Inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* File type and mode */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* Number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* User ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* Group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* Device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* Total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* Block size for filesystem I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* Number of 512B blocks allocated */
}
伪代码
main:
从argv[]获取文件名
从stat结构体中获取文件大小、占用的block数、IO块大小。文件类型调用type()
从stat结构体中获取device并用(十六进制/十进制)表示。继续获取i节点号和链接数。
权限调用myaccess()。从stat获取uid和gid。
获取atime、mtime、ctime并调用stime()进行时间转换。
type:
根据每个文件类型相关的宏进行打印。
myaccess:
获取st_mode,转换成2进制,取后9位,依次“1”则打印“r/w/x”,"0"则打印“-”。将后9位2进制数转换成8进制,并形成(0775/-rwxrwxr-x)形式。
stime:
调用strftime()进行时间转换。
产品代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <pwd.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pwd.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void type(struct stat buf);
void stime(struct tm *lt);
void myaccess(struct stat buf,char myname[24]);
void showr(int a,int show [8]);
void showw(int a,int show [8]);
void showx(int a,int show [8]);
struct stat buf;
struct tm *lt;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int hex[5]={0};
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
stat(argv[1],&buf);
unsigned long g = buf.st_dev;
printf(" File: %s\n", argv[1]);
printf(" Size: %ld Blocks: %ld IO Block: %ld ", buf.st_size,buf.st_blocks,buf.st_blksize);
type(buf);
struct passwd *pwd = getpwuid(getuid());
char Iname[24];
strcpy(Iname,pwd->pw_name);
printf("Device: ");
while(g>0)
{
hex[i] = (g%16);
g = g/16;
i++;
}
for(j =2;j>=0;j--)
{
printf("%d",hex[j]);
}
printf("h/");
printf("%lu",buf.st_dev);
printf("d Inode: %lu Links: %lu\n",buf.st_ino,buf.st_nlink);
myaccess(buf,Iname);
printf("Access: ");
stime(localtime(&buf.st_atime));
printf("Modify: ");
stime(localtime(&buf.st_mtime));
printf("Change: ");
stime(localtime(&buf.st_ctime));
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
void myaccess(struct stat buf,char myname[24])
{
int m1=0;
int m2=0;
int m3=1;
int m4=2;
int n1=8;
int n2=7;
int n3=6;
int show1[8]={0};
int show2[4]={0};
unsigned a1 = buf.st_mode%1024;
unsigned a2 = buf.st_mode%8192;
while (a1>0)
{
show1[m1] = (a1%2);
a1 = a1/2;
m1++;
}
while (a2>0)
{
show2[m2] = (a2%8);
a2 = a2/8;
m2++;
}
printf("Access: (");
for (m4=3;m4>=0;m4--)
{
printf("%d",show2[m4]);
}
printf("/-");
for (m3=1;m3<=3;m3++)
{
showr(n1,show1);
n1 =n1 -3;
showw(n2,show1);
n2 =n2 -3;
showx(n3,show1);
n3 =n3 -3;
}
printf(")");
printf(" Uid: ( %d/%s)",buf.st_uid,myname);
printf(" Gid: ( %d/%s)\n",buf.st_gid,myname);
}
void showr(int a,int show[8])
{
if(show[a]==1)
{
printf("r");
}else
{
printf("-");
}
}
void showw(int a,int show[8])
{
if(show[a]==1)
{
printf("w");
}else
{
printf("-");
}
}
void showx(int a,int show[8])
{
if(show[a]==1)
{
printf("x");
}else
{
printf("-");
}
}
void stime(struct tm *lt)
{
char t[24];
memset(t,0,sizeof(t));
strftime(t,24,"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",lt);
printf("%s\n",t);
}
void type(struct stat buf)
{
if(S_ISREG(buf.st_mode))
printf("regular file\n");
else if (S_ISDIR(buf.st_mode))
printf("directory file\n");
else if (S_ISCHR(buf.st_mode))
printf("character special file\n");
else if (S_ISBLK(buf.st_mode))
printf("block special file\n");
else if (S_ISFIFO(buf.st_mode))
printf("fifo file\n");
else if (S_ISLNK(buf.st_mode))
printf("symbolic link\n");
else if (S_ISSOCK(buf.st_mode))
printf("socaket\n");
else
printf("** unknown mode **\n");
}
测试结果
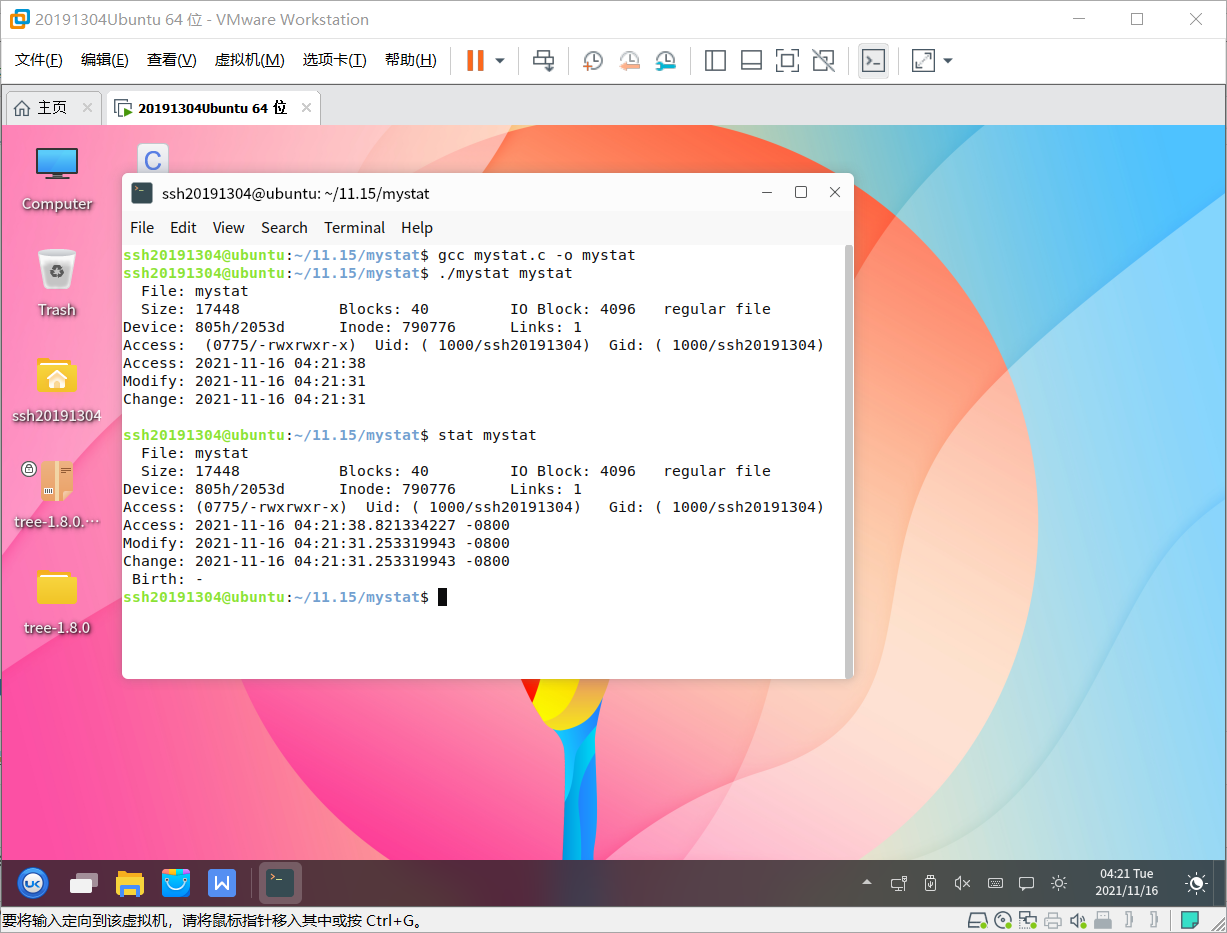
体会
自己写stat,只是实现了最基本的stat。首先是利用grep -nr "struct stat" /usr/include 查找了stat.h在其中寻找struct stat查看结构体内的信息。大部分是直接使用,个别信息需要进制转换,时间转换之类的。感觉最复杂的是access(权限)需要寻找相关宏或者是利用st_mode进行一步步操作,其中更多的是对2进制10进制8进制之间的转换。需要了解其意义。相应的打印r/w/x。中间很多信息需要小幅度的修改,需要获取用户名之类的。每次解决问题都或多或少有些收获。报错最多的是段错误,经常忘记初始化数组之类。因为stat结构体中很多类型不一样,有unsigned long之类的,用错参数的话,打印的时候可能会有一些警告


