2022.4.26 集合 Map接口
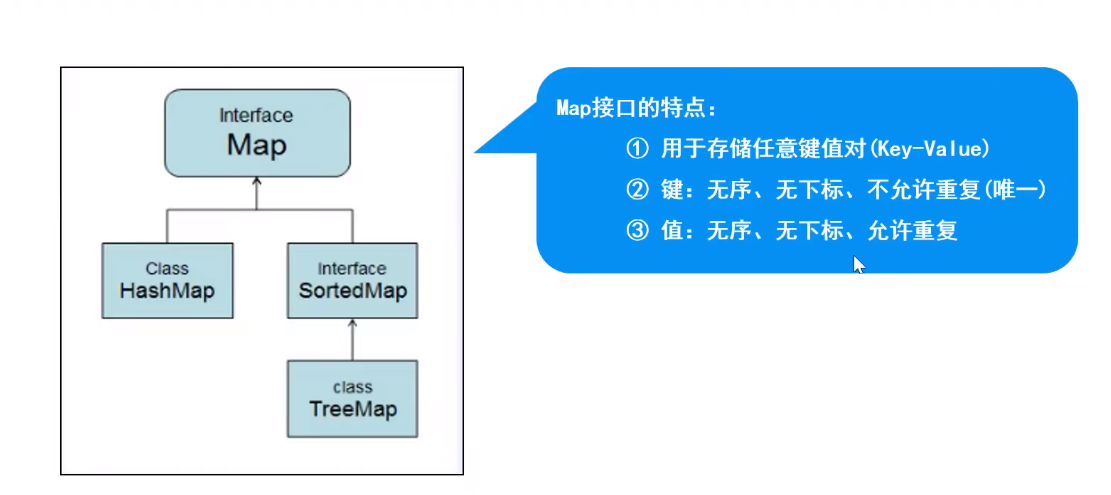
Map接口的特点
1. 用于存储任意键值对(key - value)
2. 键:无序、无下标、不允许重复(唯一)
3. 值:无序、无下标、允许重复
方法:
1 V put(K key, V value) 将对象存到集合中,关联键值,key重复则覆盖原值 2 Object get(Object key) 根据键获得对应的值 3 Set<K> 返回所有的Key 4 Collection<V> values() 返回包含所有值的Collection集合 5 Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> 键值匹配的Set集合
Map接口的使用
1 package com.xing.map; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.Map; 5 import java.util.Set; 6 7 public class Demo01 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 //Map接口 Map<K,Y> 键:key 值:value 确定键值类型 使用下面的实现类 10 Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(); 11 12 // 添加元素 13 map.put("cn", "中国"); 14 map.put("uk", "英国"); 15 map.put("cn", "zhongguo"); // 会替换第一个 16 17 System.out.println(map.size());//2 18 System.out.println(map.toString());//{uk=英国, cn=zhongguo} 19 20 //删除 参数为键 21 // map.remove("uk"); 22 23 //判断 24 System.out.println(map.containsKey("cn")); 25 System.out.println(map.containsValue("zhongguo")); 26 27 //遍历 1.使用KeySet() 返回值为所有Key的Set集合 Set<键的类型> 28 Set<String> keyset = map.keySet(); 29 for (String key : keyset) { 30 // get(key)方法:通过key值获得value 31 System.out.println(key+":"+map.get(key));//打印key值 32 } 33 34 //2 使用entrySet()方法 Entry将键值封装成了一个对象,一个Entry包含一个键和一个值 35 Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = map.entrySet();//返回值为Set集合 但是集合元素类型为Map.Entry<String, String> 36 for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : entries) { 37 //getKey() getValue() 38 System.out.println(entry.getKey()+":"+entry.getValue()); 39 } 40 } 41 } 42
HashMap实现类 【重点】
JDK1.2版本,线程不安全,运行效率快;允许用null 作为key或是value。
无参构造方法默认初始容量为16
存储结构:哈希表(数组+链表+红黑树) 无序
增、删、遍历、判断与上述一致
1 package com.xing.map; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 5 //重复依据:使用key的hashcode和equals作为重复依据判断 set接口时讲过 6 public class Demo02 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Student s1 = new Student("小明", 20); 9 Student s2 = new Student("小红", 22); 10 Student s3 = new Student("小蓝", 23); 11 12 HashMap<Student, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); 13 hashMap.put(s1, "你好"); 14 hashMap.put(s2, "您好"); 15 hashMap.put(s3, "不好"); 16 ////不重写方法能插入进去,因为重写了hashCode()与equals()方法 所以插入不进去 17 hashMap.put(new Student("小明", 20),"haha"); 18 19 System.out.println(hashMap.size()); 20 System.out.println(hashMap.toString()); 21 //{Student{name='小蓝', age=23}=不好, Student{name='小红', age=22}=您好, Student{name='小明', age=20}=你好} 22 23 } 24 } 25 class Student{ 26 private String name; 27 private int age; 28 29 public Student() { 30 } 31 32 public Student(String name, int age) { 33 this.name = name; 34 this.age = age; 35 } 36 37 public String getName() { 38 return name; 39 } 40 41 public void setName(String name) { 42 this.name = name; 43 } 44 45 public int getAge() { 46 return age; 47 } 48 49 public void setAge(int age) { 50 this.age = age; 51 } 52 53 @Override 54 public String toString() { 55 return "Student{" + 56 "name='" + name + '\'' + 57 ", age=" + age + 58 '}'; 59 } 60 61 @Override 62 public int hashCode() { 63 int n1 = this.name.hashCode(); 64 int n2 = this.age; 65 return n1+n2; 66 } 67 68 @Override 69 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 70 //1 判断是不是同一个对象 71 if(this == obj){ 72 return true; 73 } 74 //2 判断是否为空 75 if(obj == null){ 76 return false; 77 } 78 //3 判断是否是Student类型 79 if(obj instanceof Student){ 80 Student s = (Student) obj; 81 //4 比较属性 82 if(this.name.equals(s.getName()) && this.age == s.getAge()){ 83 return true; 84 } 85 } 86 //5 不满足条件返回false 87 return false; 88 } 89 } 90
原码分析总结:
-
HashMap刚创建时,table是null,size是0,节省空间,当添加第一个元素时,table容量调整为16
-
当元素个数大于阈值(16*0.75 = 12)时,会进行扩容,扩容后的大小为原来的两倍,目的是减少调整元素的个数
-
jdk1.8 当每个链表长度 >8 ,并且数组元素个数 ≥64时,会调整成红黑树,目的是提高效率
-
jdk1.8 当链表长度 <6 时 调整成链表
-
jdk1.8 以前,链表时头插入,之后为尾插入
1 static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4 ; //hashMap初始容量大小 2的4次方 16 2 static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 <<30;//hashmap的数组最大容量 2的30次方 3 static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR =0.75f;//默认加载因子 4 static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;//jdk1.8当链表长度大于8时,调整成红黑数 5 static final int UNTREETFY_THRESHOLD = 6;//jdk1.8当链表长度小于6时,调整成链表 6 static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;// jdk1.8 当链表长度大于8时,并且集合元素个数大于等于64调整成红黑数 7 transient Node<K,V>[] table ; //哈希表中的数组 8 size;//元紊个数
Hashtable实现类(几乎不用 )
线程安全,运行效率慢;不允许null作为key或是value
Properties属性集合
hashtable的子类,要求key和value都是string,通常用于配置文件的读取
特点
-
存储属性名和属性值(键值对)
-
属性名和属性值都是字符串类型
-
没有泛型
-
和流有关
1 package com.xing.properties; 2 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.PrintWriter; 5 import java.util.Properties; 6 import java.util.Set; 7 8 public class Demo01 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { 10 //创建集合 11 Properties properties = new Properties(); 12 //添加元素 键 值 13 properties.setProperty("username", "zhangsan"); 14 properties.setProperty("age", "20"); 15 System.out.println(properties.toString());//{age=20, username=zhangsan} 16 17 //遍历 keySet entrySet 18 19 //遍历stringPropertyNames() 键值必须是字符串类型 20 Set<String> s = properties.stringPropertyNames();//返回一个字符串类型的set集合 21 for (String s1 : s) { 22 // 打印 键 键所对应的值 23 System.out.println(s1+":"+properties.getProperty(s1));//打印 键 24 } 25 } 26 }

list()列表
1 package com.xing.properties; 2 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.PrintWriter; 5 import java.util.Properties; 6 import java.util.Set; 7 8 public class Demo01 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { 10 //创建集合 11 Properties properties = new Properties(); 12 //添加元素 键 值 13 properties.setProperty("username", "zhangsan"); 14 properties.setProperty("age", "20"); 15 16 //和流有关的方法 list() 17 //将Properties的键值写入磁盘 18 PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("d:\\print.txt"); 19 properties.list(pw); 20 pw.close(); 21 } 22 } 23

store方法 保存
1 package com.xing.properties; 2 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.FileWriter; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.io.PrintWriter; 7 import java.util.Properties; 8 import java.util.Set; 9 10 public class Demo01 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 12 //创建集合 13 Properties properties = new Properties(); 14 //添加元素 键 值 15 properties.setProperty("姓名", "zhangsan"); 16 properties.setProperty("年龄", "20"); 17 18 //store方法 保存 属性集合的拓展名一般为properties 19 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("d:\\print.properties"); 20 // 字符流或字节流 注释中文可能乱码 21 properties.store(fw,"zhushi"); 22 fw.close(); 23 24 } 25 }

load() 加载
1 package com.xing.properties; 2 3 import java.io.*; 4 import java.util.Properties; 5 import java.util.Set; 6 7 public class Demo01 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 9 //load加载 10 Properties properties = new Properties(); 11 //字符输入流 12 FileReader fr = new FileReader("d:print.properties"); 13 properties.load(fr);//加载流 14 fr.close(); 15 System.out.println(properties.toString()); 16 17 } 18 }

TreeMap实现类
存储结构:红黑树 有顺序
实现了SortedMap接口(是map的子接口),可以对key自动排序
与hashmap语句几乎一样
1 package com.xing.treemap; 2 3 import java.util.TreeMap; 4 5 public class Demo01 { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 8 Student s1 = new Student("小明", 20); 9 Student s2 = new Student("小红", 22); 10 Student s3 = new Student("小蓝", 23); 11 12 // key value 13 TreeMap<Student,String> treeMap = new TreeMap<>(); 14 treeMap.put(s1, "haha"); 15 treeMap.put(s2, "haha"); 16 treeMap.put(s3, "haha"); 17 treeMap.put(new Student("小huang",20), "haha");//没加入 重写了Comparable 年龄一样不能加入 18 19 //treeMap会对元素进行排序 但是Student对象有两个参数 不知以哪个为标准进行比较 20 //所以元素必须实现Comparable接口 compareTo()方法返回值为0,认为是重复元素 21 System.out.println(treeMap.size()); 22 System.out.println(treeMap.toString()); 23 24 25 } 26 } 27 // 继承Comparable接口 28 class Student implements Comparable<Student>{ 29 private String name; 30 private int age; 31 32 public Student() { 33 } 34 35 public Student(String name, int age) { 36 this.name = name; 37 this.age = age; 38 } 39 40 public String getName() { 41 return name; 42 } 43 44 public void setName(String name) { 45 this.name = name; 46 } 47 48 public int getAge() { 49 return age; 50 } 51 52 public void setAge(int age) { 53 this.age = age; 54 } 55 56 @Override 57 public String toString() { 58 return "Student{" + 59 "name='" + name + '\'' + 60 ", age=" + age + 61 '}'; 62 } 63 64 65 // @Override 66 // public int hashCode() { 67 // int n1 = this.name.hashCode(); 68 // int n2 = this.age; 69 // return n1+n2; 70 // } 71 // 72 // @Override 73 // public boolean equals(Object obj) { 74 // //1 判断是不是同一个对象 75 // if(this == obj){ 76 // return true; 77 // } 78 // //2 判断是否为空 79 // if(obj == null){ 80 // return false; 81 // } 82 // //3 判断是否是Student类型 83 // if(obj instanceof Student){ 84 // Student s = (Student) obj; 85 // //4 比较属性 86 // if(this.name.equals(s.getName()) && this.age == s.getAge()){ 87 // return true; 88 // } 89 // } 90 // //5 不满足条件返回false 91 // return false; 92 // } 93 94 //重写接口中的方法 按年龄比 95 @Override 96 public int compareTo(Student o) { 97 int n2 = this.age - o.getAge();//年龄比较 98 return n2; 99 } 100 } 101




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号