2022.4.21 常用类 String类
string
特点:
引用类型
字符串是常量;它们的值在创建之后不能更改(在常量池中的字符串不能改变,但是变量指向的地址可以改变)。字符串缓冲区支持可变的字符串。因为 String对象是不可变的,所以可以共享(先检查常量池有没有这个字符串,如果有就不用创建字符串,变量直接指向这个字符串的地址即可)
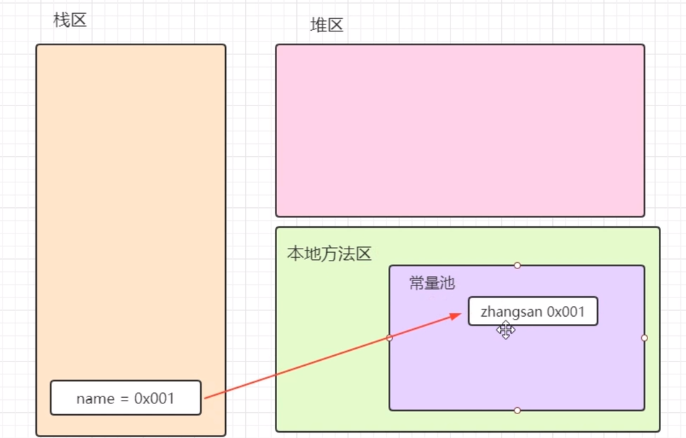
特点:
-
如果发现在方法区中没有对应的字符串,会自动开辞内存存储新的字符串
-
字符串一旦创建了,是不能够被修改的
-
字符串虽然不能够被修改,但是可以共享
-
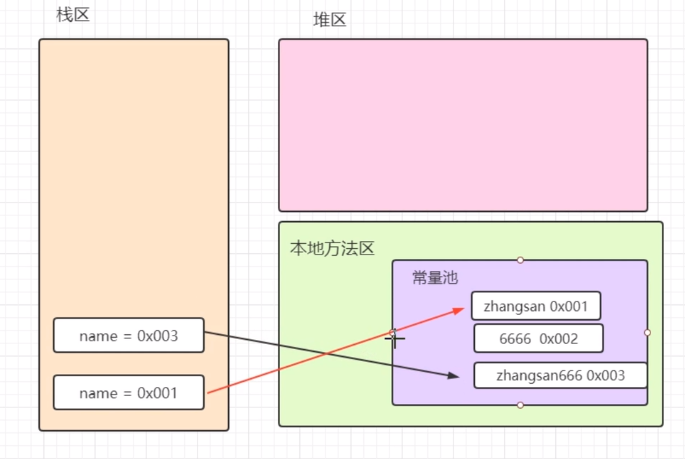
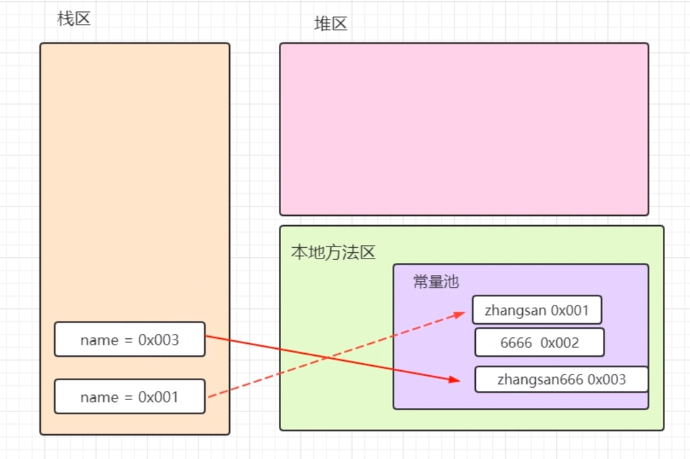
如果字符串频繁的拼接字符串,都会在方法区开辟空间,这样是非常消耗内存空间的,所有如果字符串拼接比较频繁不建议使用String类型,这时我们可以改用StringBuffer或者StringBuilder
1 package com.xing.String; 2 3 public class Test01 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 String name = "zhangsan"; 6 name+="6666"; 7 System.out.println(name);//zhangsan6666 8 9 name="haha"; 10 System.out.println(name);//haha 11 } 12 }
构造方法:
1 package com.xing.String; 2 3 public class Test02 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 //String类型是一个引用类型,那么必然会有对应的构造方法 6 String name1 = new String(); 7 System.out.println(name1);// 8 9 String name2 = new String("zhangsan"); 10 System.out.println(name2);//zhangsan 11 12 char[] c = {'a','b','c'}; 13 String name3 = new String(c); 14 System.out.println(name3);//abc 15 16 //字符数组c从下标1开始的两个字符 17 String name4 = new String(c,1,2); 18 System.out.println(name4);//bc 19 20 } 21 }
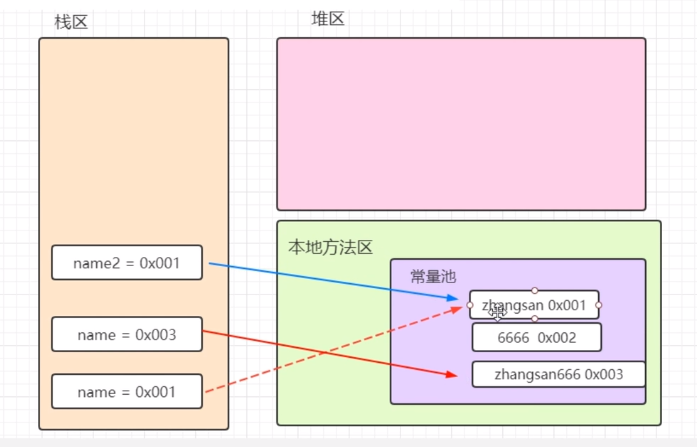
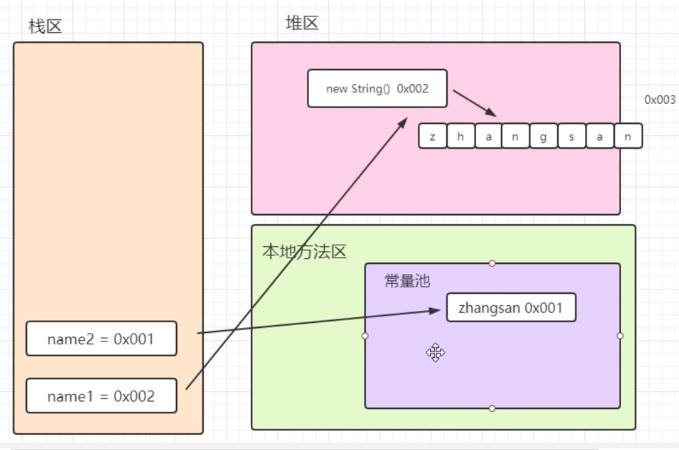
通过构造器获取的String类型和通过字符串字面值获取的字符串的区别
1 package com.xing.String; 2 3 public class Test03 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 String name1 = new String("zhangsan"); 6 String name2 = "zhangsan"; 7 8 System.out.println(name1 == name2);//false 比较的是地址002和001,zhangsan是在name1(形参)时创建的,把形参赋值给了构造器中的char类型数组(也是引用类型,也有地址) 9 System.out.println(name1.equals(name2));//true 比较字符串的值 10 } 11 }
常用方法
1 返回类型 方法名 参数 2 char charAt (int index) //返回指定索引处的char值 3 int indexof (int ch) //返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引 不存在返回-1 4 int indexOf(String str) //返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引 不存在返回-1 5 int indexof (int ch,int fromIndex) //从指定的索引开始搜索,返回在此字符串中第一次出现指定字符处的索引 6 7 int indexof(String str,int fromIndex)//从指定的索引开始搜索,返回在此字符串中第一次出现指定字符串处的索引 8 int lastIndexof(int ch) //返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引 9 int lastIndexOf(int ch,int fromIndex)//从指定的索引处开始进行反向搜索。返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引 10 11 int lastIndexof (String str,int fromIndex) 12 String substring (int start)//返回一个新的字符串,它是此字符串的一个子字符串 13 String substring (int start,int end) 14 int length ()
1 package com.xing.String; 2 3 public class Test04 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 String str = "HelloWorld"; 6 System.out.println(str.charAt(0));//H 7 8 System.out.println(str.indexOf('o'));//4 9 System.out.println(str.indexOf('a'));//-1 10 11 System.out.println(str.indexOf("llo"));//2 12 System.out.println(str.indexOf("lla"));//-1 13 14 //字符串同理 15 System.out.println(str.indexOf('o',5));//6 从下标5开始向后搜索o 返回该字符在字符串的索引 16 System.out.println(str.indexOf('o',4));//4 从下标4开始搜索o 返回该字符在字符串的索引 17 18 System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf('o'));// 6 从后向前找o;但是索引值从前向后数 19 20 //字符串同理 21 System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf('o',5));//4 从下标5开始向前搜索o 返回该字符在字符串的索引 22 System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf('o',6));//6 23 24 System.out.println(str.substring(5));//World 从下标5开始截取字符串(包括下标5) 25 System.out.println(str.substring(5,7));//Wo 从下标5开始截取字符串到第7个(包括下标5,不包括下标7) 26 27 28 } 29 } 30
面试题 :length、length()、size()的区别
-
length:是数组的属性
-
length():是字符串或者其他类的一个方法
-
size():是集合或者其他类的一个长度
课堂案例: 从键盘输入一个字符串,统计这个字符串中的大写字母,小写字母及数字的个数
1 package com.xing.String; 2 import java.util.Scanner; 3 4 public class Test05 { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); 7 8 String s = scanner.nextLine(); 9 int uppercase = 0; 10 int lowercase = 0; 11 int number = 0; 12 for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { 13 char c = s.charAt(i); 14 if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z') { 15 uppercase++; 16 } else if (c > 'a' && c <= 'z') { 17 lowercase++; 18 } else if (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){ 19 number++; 20 } 21 } 22 23 } 24 } 25
返回结果为布尔型的方法
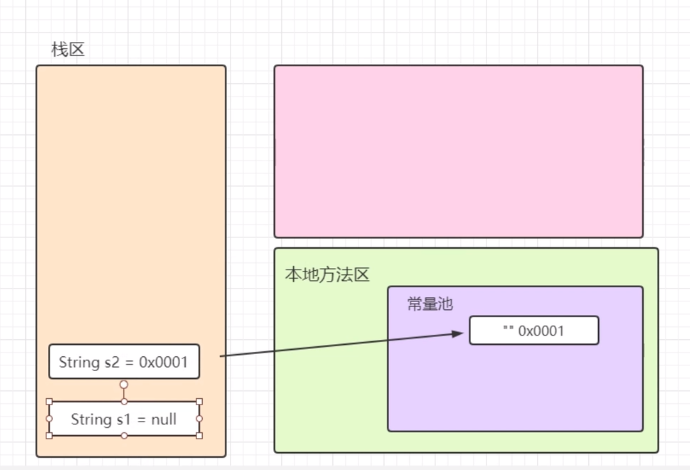
"" 与null
1 boolean isEmpty():判断字符串是否为空。 2 boolean equals(object obj):将此字符串的内容与指定的对象比较,区分大小写。 3 boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str):将此String 与另一个String 比较,忽略大小写。 4 boolean contains(String str):判断字符串中是否包含方法传入的字符串。 5 boolean startswith(String str):判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串开头。 6 boolean endswith(String str):判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串结尾。 7 boolean isEmpty ( ):判断字符串是否为空。
1 package com.xing.String; 2 3 public class Test06 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 String str1 = "HelloWorld123"; 6 String str2 = null; 7 String str3 = ""; 8 9 System.out.println(str1.isEmpty());//false 10 //System.out.println(str2.isEmpty()); 报错 方法有实例调用 可是str2为空 11 System.out.println(str3.isEmpty());//true 12 13 //在实际开发中判断字符串是否为空 14 if("".equals(str1) || str1 == null){ 15 System.out.println("为空"); 16 } 17 18 System.out.println(str1.contains("123"));//true 19 20 System.out.println(str1.startsWith("Hello"));//true 21 System.out.println(str1.endsWith("123"));//true 22 } 23 }
类型转换的相关方法
1 返回值类型 方法名 参数 2 byte[] getBytes () :将字符串转化为字节数组。 3 char[] toCharArray ():将字符串转化为字符数组。 4 static String valueof(char[] chs):将字符数组转换为字符串 5 static String valueof(int i) :将整型转换为字符串 6 valueOf(char c) 7 valueOf(long l) 8 valueOf(float f) 9 valueOf(double d) 10 valueOf(boolean b) 11 valueOf(char[] data) 12 13 String toLowerCase():将此string中的所有字符都转换为小写。 14 String toUpperCase () :将此string 中的所有字符都转换为大写。 15 String concat(String str):将指定字符串连接到此字符串的结尾。
1 package com.xing.String; 2 3 public class Test07 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 String str = "aaBBccDDeeFF"; 6 byte[] b = str.getBytes(); 7 for (byte b1 : b) { 8 System.out.println(b1);//打印的是ASCLL码值 9 System.out.println((char) b1);//打印每个字符 10 } 11 12 char[] c = str.toCharArray(); 13 for (char c1 : c) { 14 System.out.println(c1);//打印每个字符 15 } 16 17 System.out.println(String.valueOf(c));//将字符数组转换为字符串 18 19 System.out.println(String.valueOf(97));//将int型97 转换为String型97 20 System.out.println("" + 97);//与上面同理 21 22 System.out.println(str.toLowerCase()); 23 System.out.println(str.toUpperCase()); 24 25 System.out.println(str.concat("abc"));//aaBBccDDeeFFabc 26 System.out.println(str + "abc");//与上面同理 27 } 28 }
练习
将一个字符串的首字母转换为大写,其他字母转换为小写,同时将每个字符使用__下划线分割开分析: 原字符串: helloworldHahahaA 转换后的字符串:H_e_l_l_o_w_o_r_l_d_h_a_h_a_h_a_a
第一种思路:
-
将字符串转换为字符数组
-
遍历字符数组
-
判断如果i=0将字符转换为大写然后拼接 _
-
如果i!=0将字符转换为小写如果i != length-1拼接
1 package com.xing.String; 2 3 public class Test08 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 String str = "helloworld"; 6 String result = "";//保存结果 7 8 char[] ch1 = str.toCharArray(); 9 for (int i = 0; i < ch1.length; i++) { 10 char c = ch1[i]; 11 String s = String.valueOf(c);//将字符转换为字符串 12 if (i == 0) { 13 result += s.toUpperCase(); 14 result += "_"; 15 } else if (i == ch1.length - 1) { 16 result += s.toLowerCase(); 17 }else{ 18 result += s.toLowerCase(); 19 result += "_"; 20 } 21 } 22 System.out.println(result); 23 24 System.out.println("法二"); 25 26 String first = str.substring(0,1).toUpperCase();//截取首字母变为大写 27 String other = str.substring(1).toUpperCase();//出首字母外都变为小写 28 first.concat(other);//拼接 29 } 30 }
其他方法
1 String replace (char old, char new) :替换功能。 2 String replace (String old,String new) :替换功能。 3 String trim ():去除字符串两空格。 4 int compareTo(String str) :按字典顺序比较两个字符串。 5 int compareToIgnoreCase(String str):按字典顺序比较两个字符串,忽略大小写。 6 public String[] split(String regex):分隔字符串成字符数组。
1 package com.xing.String; 2 3 public class Test09 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 String str = "HelloWorld"; 6 System.out.println(str.replace('o','Z'));//HellZWZrld 替换所有符合字符 7 System.out.println(str.replace("World","111"));//Hello111 替换字符串 8 System.out.println(str.replace("abc","aaa"));//HelloWorld 不存在返回原来字符串 9 10 String str1 = " asd a 1 "; 11 System.out.println(str1.trim());//asd a 1 去除字符串两端空格 12 13 14 String s1 = "abc"; 15 String s2 = "adf"; 16 System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2));//-2 s1的字符与s2的字符相比 大于正数,小于负数,相等为0 字母越靠后越大 17 18 String s3 = "abc,herk,89,a0a8,h"; 19 String[] s4= s3.split(",");//通过,分割字符串 20 for (String s : s4) { 21 System.out.print(s+" "); 22 }//abc herk 89 a0a8 h 23 } 24 }
1 package com.xing.String; 2 3 public class Test10 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 String s1 = "abcdefg"; 6 String result="";//接收结果 7 8 char[] c = s1.toCharArray(); 9 for (int i = c.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { 10 String s = String.valueOf(c[i]); 11 result += s; 12 13 //result+=c[i] 相当于上面两步; 14 } 15 System.out.println(result); 16 } 17 }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号