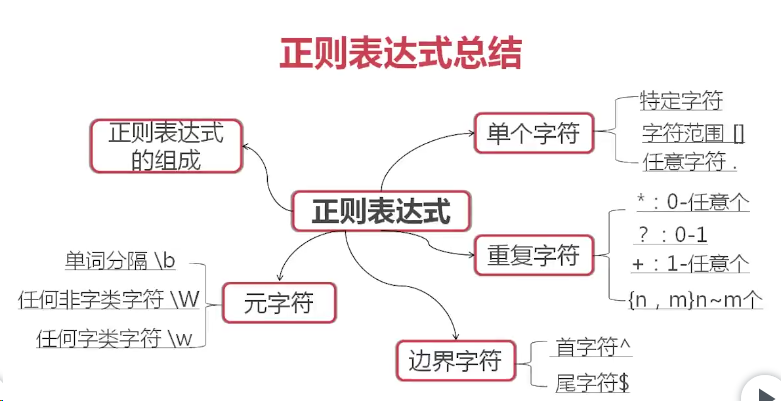
正则表达式
一. 简述
正则表达式与通配符的区别:
正则表达式:
用来在文件中匹配符合条件的字符串
通配符:
用来匹配符合条件的文件名
这种区别只在Shell当中适用,因为用来在文件当中搜索字符串的命令,如grep、awk、sed等命令可以支持正则表达式,而在系统当中搜索文件的命令,如ls、find、cp这些命令不支持
正则表达式,所以只能使用shell自己的通配符来进行匹配了。
正则表达式是一个字符或和元字符组合成的字符集,它们匹配(或指定)一个模式。字符即普通字符(例如字符 a 到 z),元字符即特殊字符(例如前面提到的字符 ^ $ *)。正则表达式作为一个模板,将某个字符模式与所搜索的字符串进行匹配
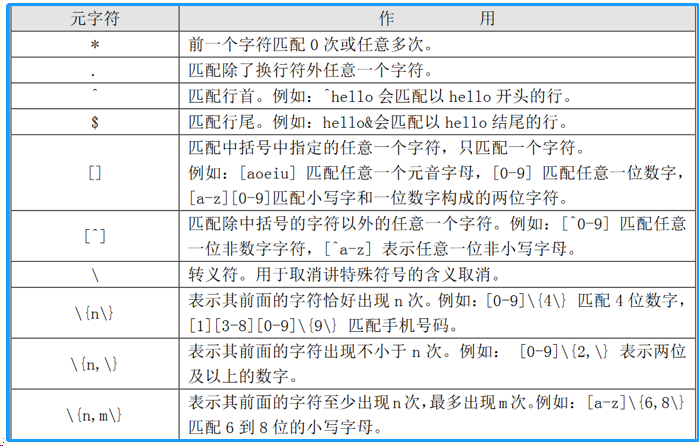
二. 基础正则表达式
三. 扩展正则表达式
在正则表达式中应该还可以支持一些元字符,如: + ? | () 这些。其实Linux是支持这些元字符,只是grep命令默认不支持而已。如果要想支持这些元字符,需要使用 grep -E 选项,所以又把这些元字符称作 扩展元字符。
egrep与grep -E 相同。若man grep:egrep is the same as grep -E。
Shell支持的扩展元字符:
扩展元字符 作用 + 前一个字符匹配1次或任意多次
? 前一个字符匹配0次或1次
| 匹配两个或多个分支选择
() 匹配器整体为一个字符,即模式单元。可理解为由多个单子字符组成的大字符。

\b 匹配一个单词边界,也就是指单词和空格间的位置。 \B 匹配非单词边界。 \w 匹配包括下划线的任何单词字符。等价于''[A-Za-z0-9_]''。 \W 匹配任何非单词字符。等价于''[^A-Za-z0-9_]''。 \d 匹配一个数字字符。等价于[0-9]。 \D 匹配一个非数字字符。等价于[^0-9]。 \f 匹配一个换页符。等价于\x0c和\cL。 \n 匹配一个换行符。等价于\x0a和\cJ。 \r 匹配一个回车符。等价于\x0d和\cM。 \s 匹配任何空白字符,包括空格、制表符、换页符等等。等价于[\f\n\r\t\v]。 \S 匹配任何非空白字符。等价于[^\f\n\r\t\v]。 \t 匹配一个制表符。等价于\x09 和 \cI。 \v 匹配一个垂直制表符。等价于\x0b和\cK。
四. 示例
1.列出当前目录下的所有目录

1.根据属性:drwxr-xr-x,使用grep和正则表达式 [root@host ~]# ls -l |grep "^d" 2. 基于ls 命令,使用 -F 选项,能列出文件类型的指示符号 [root@host ~]# ls -F A.txt B.sh* t1.dir/ t2.dir/ test/ 提示:目录后会有"/",可执行文件会有"*" [root@host ~]# ls -F | grep "/$" t1.dir/ t2.dir/ test/ 延伸: [root@host ~]# ls A.txt B.sh t1.dir t2.dir test [root@host ~]# ls -l |grep "^d" |wc -l 3 [root@host ~]# ls -l |grep "^-" |wc -l 2
2.
内容:[root@host test]# cat a.txt
tom
123
food

1.匹配两个 "o" [root@host test]# cat a.txt |egrep "o{2,}" food 2.匹配 "o{3,5}",最少3个"o",最多5个"o" [root@host test]# cat a.txt |egrep "o{3,5}" tooom 3.匹配 最少0个,最多1个。将会匹配tooom和food的第一个"o" [root@host test]# cat a.txt |egrep "o{0,1}" tooom 123 food 4. \b 匹配一个单词边界,就是指单词和空格间的位置 \B 匹配非单词边界 [root@host test]# cat a.txt TomW from [root@host test]# cat a.txt |grep "om\b" from #"om\b",可匹配"from"中的"om",不能匹配"TomW" 中的 "om" [root@host test]# cat a.txt |egrep "om\B" TomW
3. (多句)

[root@host test]# vim t.sh # vim t.sh ------------------------------- "Open Source" is a good mechanism to develop programs. apple is my favorite food. Football game is not use feet only. this dress doesn't fit me. However, this dress is about $ 3183 dollars. GNU is free air not free beer. Her hair is very beauty. I can't finish the test. Oh! The soup taste good. motorcycle is cheap than car. This window is clear. the symbol '*' is represented as start. Oh!My god! The gd software is a library for drafting programs. You are the best is mean you are the no. 1. The world <Happy> is the same with "glad". I like dog. google is the best tools for search keyword. goooooogle yes! go! go! Let's go. # I am Toom # I am toom123 1.搜寻特定字符串"the" #grep -n "the" t.sh 2.忽略大小写"the" # grep -in "the" t.sh 3.利用括号 [] 来搜寻集合字符 搜索test或taste这两个单词,相似的't?st' # grep -n "t[ae]st" t.sh 搜索有 "oo" 字符 # grep -n 'oo' t.sh 搜索oo时不想搜到 oo 前面有 g,可利用反向选择[^ ] # grep -n "[^g]oo" t.sh 搜索oo前面不想有小写字符 grep -n '[^a-z]oo' t.sh 取得有数字的行 # grep -n '[0-9]' t.sh 补充:考虑到语系对编码顺序的影响,因此除了连续编码使用减号[-]外, 也可以用[:lower:]代替a-z 以及 [:digit:] 代替0-9 使用 # grep -n '[^[:lower:]]oo' t.sh # grep -n '[[:digit:]]' t.sh 4.显示行首为 "the" 的字符串 #grep -n '^the' t.sh 显示行首是小写字符 #grep -n '^[a-z]' t.sh 5.显示行尾为 点. 的那一行 #grep -n '\.$' t.sh 6.显示5-10行数据 # cat -An t.sh |head -n 10|tail -n 6 7.显示空白行 #grep -n '^$' t.sh 8.找出g??d字符串,起头g结束d的四个字符串 # grep -n 'g..d' t.sh 9. o*代表空字符(就是有没有字符都可以)或者一个到N个o字符 #grep -n 'o*' t.sh #会把所有行全部打印出来 10.oo*代表o+空字符或者一个到N个o字符 #grep -n 'oo*' t.sh #会把 o,oo,ooo等 的行全部打印出来 11."goo*g"代表gog,goog,gooog... #grep -n 'goo*g' t.sh 12.找出含g...g字符串的行 # grep -n 'g.*' t.sh #提示 .代表任意字符, .*代表空字符或者一个到N个任意字符 13.找出含两个o的字符串 注:{}因为在shell里有特殊意义,所以需要加转义\ 来让其失去意义 # grep -n 'o\{2\}' t.sh 找出g后含2到5个o然后以g结尾的字符串 # grep -n 'go\{2,5\}' t.sh 找出g后含2以上的o然后以g结尾的字符串 # grep -n 'go\{2,\}' t.sh
4. 任意字符串 .*
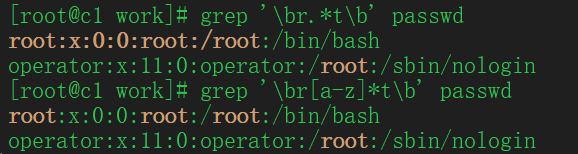
5.逻辑 |

[root@c1 work]# grep 'bin/\(false\|true\)' passwd [root@c1 work]# grep 'bin/\(login\|nologin\)' passwd bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
6.匹配4-10的QQ号

[root@c1 work]# cat qq.txt dfasdfsd 12345678 4423412342435 1234321sdeeee 6789 ^&&**SKKJFD 718273 hellworld [root@c1 work]# grep '^[0-9]\{4,10\}$' qq.txt 12345678 6789 718273
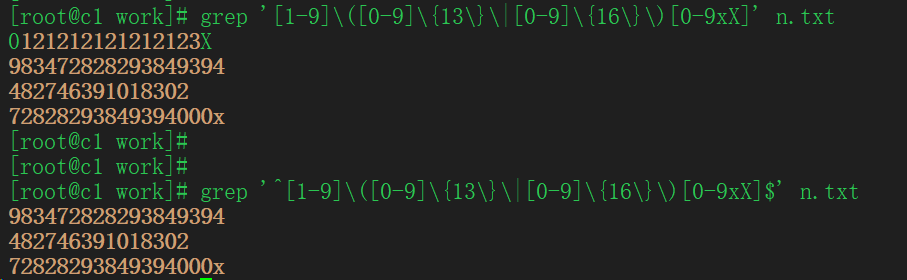
7.匹配15位或18位身份证号(支持带X的)

[root@c1 work]# cat n.txt 0121212121212123X fajdflaldfasd 983472828293849394 482746391018302 72828293849394000x [root@c1 work]# grep '[1-9]\([0-9]\{13\}\|[0-9]\{16\}\)[0-9xX]' n.txt 0121212121212123X 983472828293849394 482746391018302 72828293849394000x [root@c1 work]# [root@c1 work]# [root@c1 work]# grep '^[1-9]\([0-9]\{13\}\|[0-9]\{16\}\)[0-9xX]$' n.txt 983472828293849394 482746391018302 72828293849394000x
8.匹配密码(有数字,26个字母和下划线组成)

[root@c1 work]# cat pwd.txt dfaee 2344355 kk12432ka ss_23_12 02323_a &&&#(!@#@# [root@c1 work]# grep '^\w\+$' pwd.txt dfaee 2344355 kk12432ka ss_23_12 02323_a
重复:
* 零次或多次
+ 一次或多次
? 零次或一次
重复特定次数: {n,m}
* {0,}
+ {1,}
? {0,1}
1.

[root@C1 test]# cat a.txt sesesese se seeeeese eeeeeeee sooooooo +se+se+ ekkkkkk [root@c1 work]# grep 'se*' a.txt sesesese se seeeeese sooooooo +se+se+ [root@c1 work]# grep 'se\+' a.txt sesesese se seeeeese +se+se+ [root@c1 work]# grep 'se\?' a.txt sesesese se seeeeese sooooooo +se+se+ ------------------------- [root@c1 work]# grep '\(se\)*' a.txt sesesese se seeeeese eeeeeeee sooooooo +se+se+ ekkkkkk [root@c1 work]# grep '\(se\)\+' a.txt sesesese se seeeeese +se+se+ [root@c1 work]# grep '\(se\)\?' a.txt sesesese se seeeeese eeeeeeee sooooooo +se+se+ ekkkkkk







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号