10.<tag-二叉树和BST基础>lt.700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索 + lt.98. 验证二叉搜索树 + lt.530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差(同lt.783)
lt.700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
[案例需求]
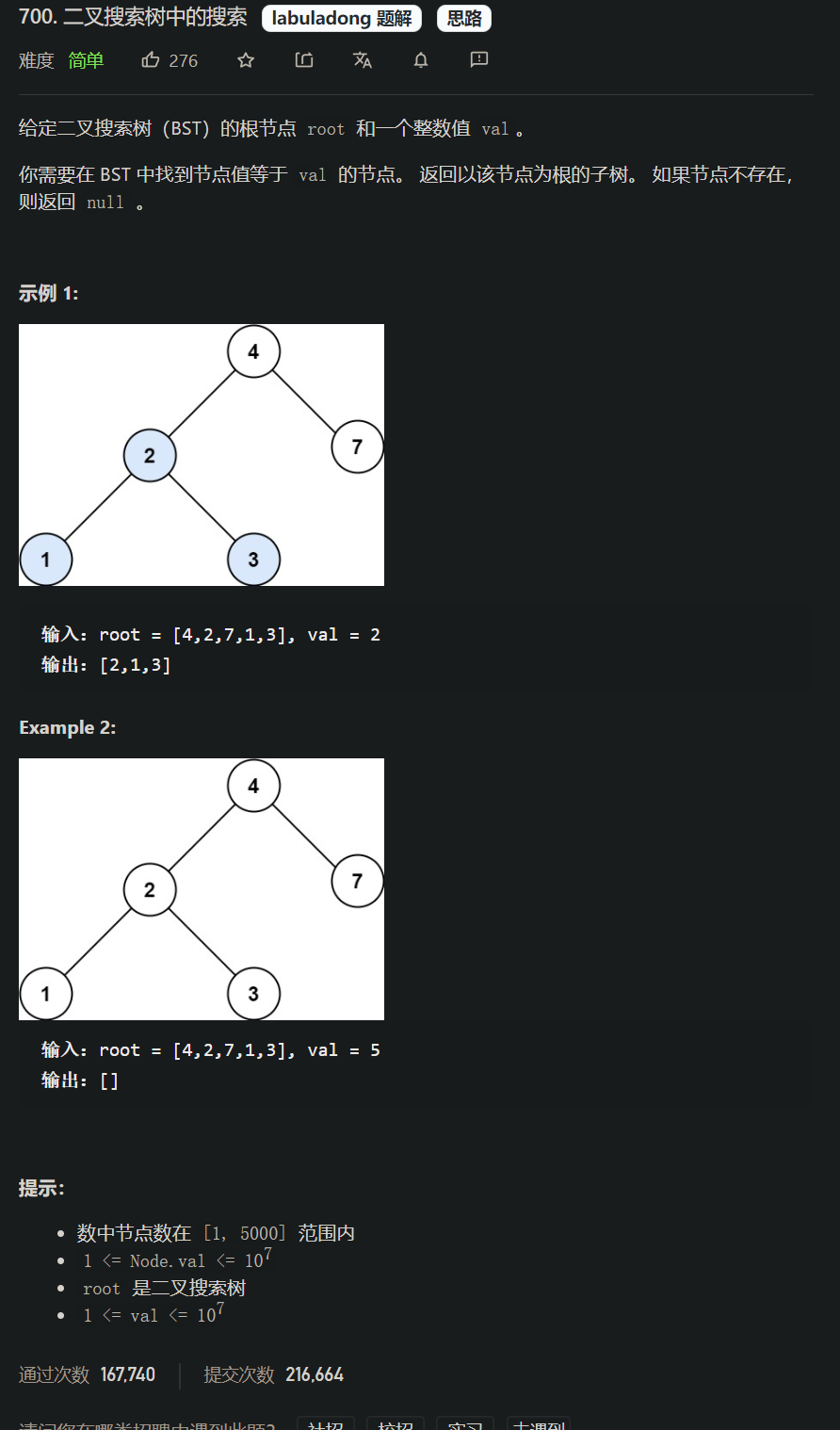
[思路分析]
- 这才是名副其实的简单题嘛
- BST: 二叉搜索树, 对于树中的每个节点,
-
- 她的左节点的值都小于这个节点,
-
- 她的右节点的值都大于这个节点;

- 她的右节点的值都大于这个节点;
[代码实现一, 递归法]
class Solution {
//1. 递归函数, 查找BST, 返回值找到的节点
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
//2. 递归结束条件
if(root == null || root.val == val)return root;
//3. 单层递归逻辑
// if(root.val == val){
// return root;
// }else
if(root.val > val){
return searchBST(root.left, val);
}else{
return searchBST(root.right, val);
}
}
}
简化版
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null || root.val == val) return root;
return root.val > val ? searchBST(root.left, val) : searchBST(root.right, val);
}

[代码实现二, 迭代法]

public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
while (root != null && root.val != val) {
root = root.val > val ? root.left : root.right;
}
return root;
}
lt.98. 验证二叉搜索树
[案例需求]
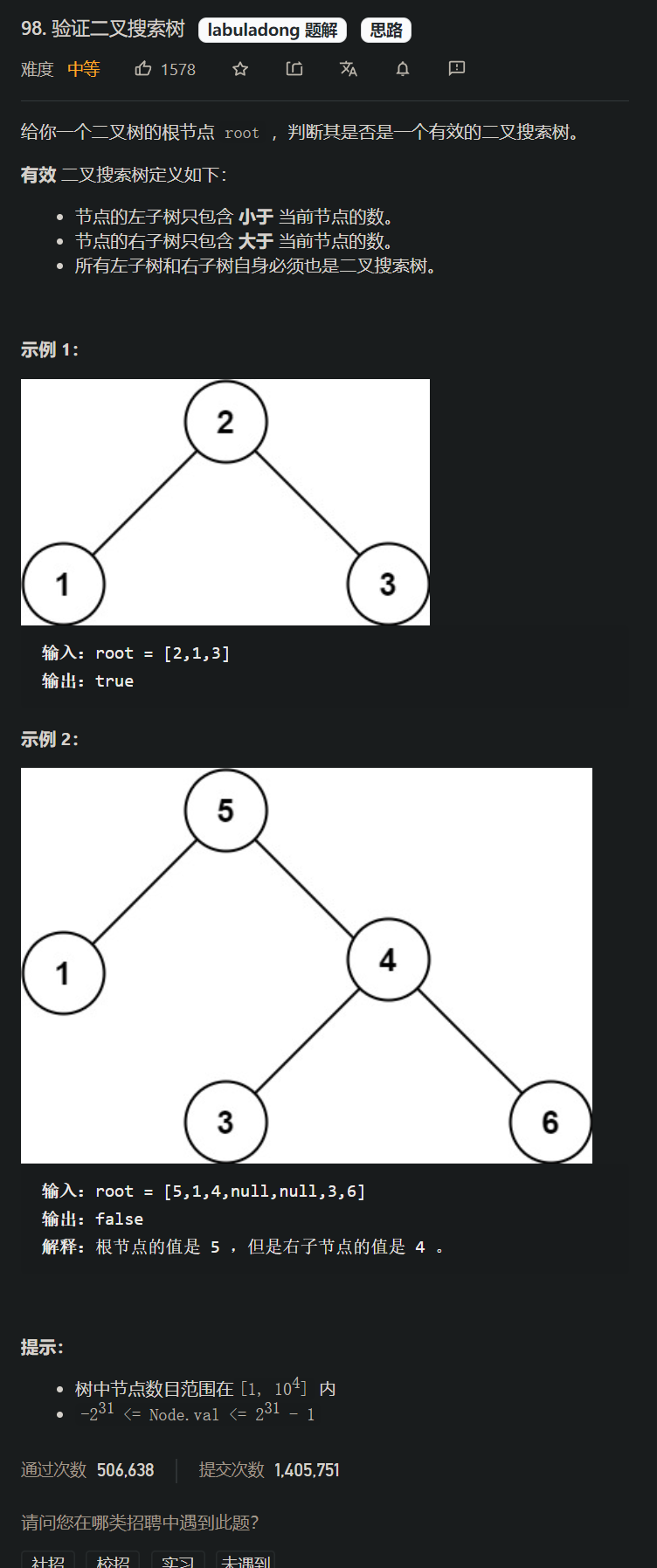
[思路分析一, 递归]
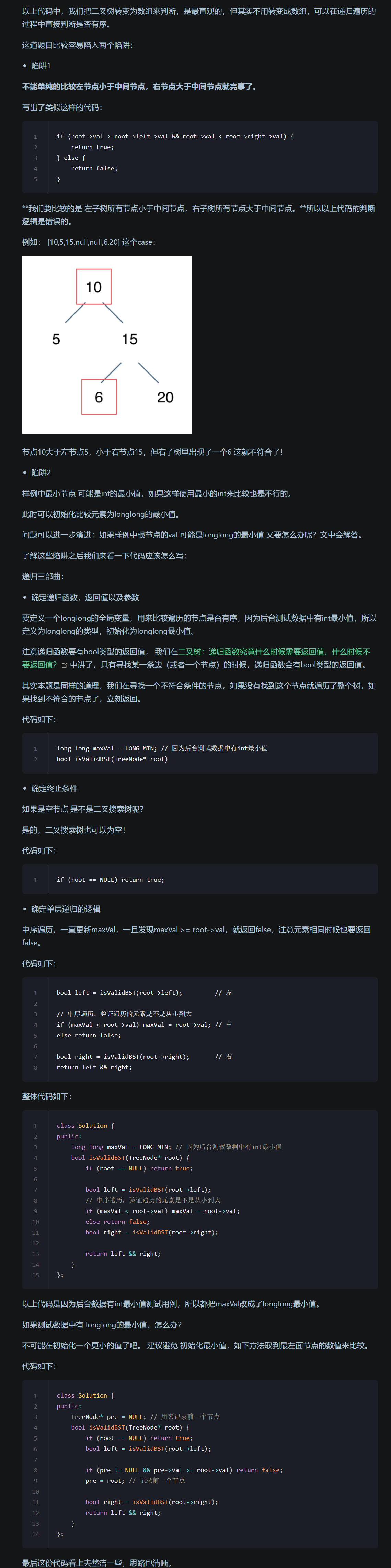
[代码实现]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
//1. 递归函数, 验证每个节点是不是BST,
//参数: 被看做是根节点的当前节点
// 返回: 时还是不是
//long maxVal = Integer.MIN_VALUE; ---> -long, 绝了
TreeNode pre = null;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
//2. 递归出口
if(root == null)return true;
//3. 单层递归逻辑
// BST中的中序遍历是一个递增序列
boolean left = isValidBST(root.left); //左子树
if(pre != null && pre.val >= root.val){
return false;
}else{
pre = root;
}
boolean right = isValidBST(root.right); //右子树
return left && right;
}
}
[思路分析二, 集合 + 递归的方法]
- 记住这句话, 对二叉搜索树(BST)进行中序遍历, 得到的是一个升序排列的序列
- 所以我们可以对BST进行中序遍历, 一边遍历一边把遇到的数放入到集合中(因为长度未知, 不可用数组), 同时比较集合的最后一个数与将要存入的这个数是否是升序的.
[代码实现]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
//1. 放入集合
return dfs(root);
}
public boolean dfs(TreeNode root){
//
if(root == null)return true;
//单层递归逻辑
boolean left = dfs(root.left);
// 1. 集合不为空, 且要存入的root.val > list的最后一个元素, 升序的, 这是正确的
if(!list.isEmpty() && list.get(list.size() - 1) < root.val){
list.add(root.val);
// 2. 集合不为空, 且要存入的root.val <= list的最后一个元素, 非升序的, 这是不正确的
}else if(!list.isEmpty() && list.get(list.size() - 1) >= root.val){
return false;
}else{
//3. 集合为空的时候, 直接存入元素
list.add(root.val);
}
boolean right = dfs(root.right);
return left && right;
}
}
lt.530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差(同lt.783)
[案例需求]
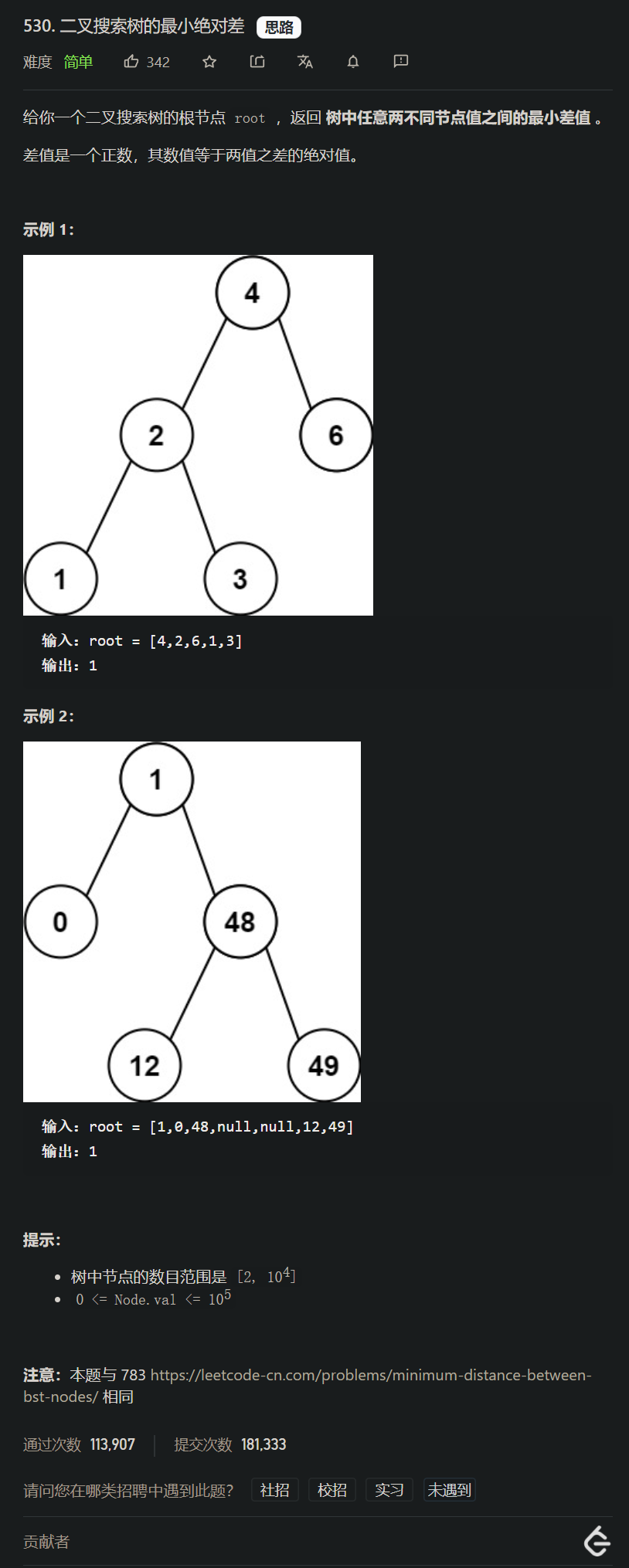
[思路分析一, 集合 + 递归]

[代码实现]
class Solution {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)return 0;
getMinimumDifference(root.left);
if(list.size() > 0){
res = Math.min(res, root.val - list.get(list.size() - 1));
}
list.add(root.val);
getMinimumDifference(root.right);
return res;
}
}
[思路分析二, 递归 + pre记录上一个遍历节点]
[代码实现]
//1. 递归 + 记录前一个节点
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
//1. 递归函数
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
TreeNode pre = null;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
//2. 递归出口
if(root == null)return 0;
//3. 单层递归逻辑(中序遍历)
getMinimumDifference(root.left);
if(pre != null){
res = Math.min(res, root.val - pre.val);
}
pre = root;
getMinimumDifference(root.right);
return res;
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号