Python--day5
unsupported :无支持的、无支援的
operand :操作数、运算数
一、 正则表达式
导入re模块
正则表达式符号含义:

#!/usr/bin/env python
# encoding: utf-8
import re
# string = "192.168.3.101111"
# m = re.match("([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}\d{1,3}",string)
# print(m.group())
#
# string2 = "alex li"
# #string2 = "ALEX"
# m = re.search("[A-Z]",string2,flags=re.I)
# m = re.search("^a.*i$",string2)
# print(m.group())
#查找emal
email = "alex.li@126.com http://www.oldboyedu.com"
m = re.search(r"[0-9.a-z]{0,26}@[0-9.a-z]{1,20}.[0-9a-z]{1,6}",email)
print(m.group())
# 查找ip地址
ip_addr = "inet addr:192.168.1.251 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0"
m = re.search("\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}",ip_addr)
print(m.group())
#查找电话号码
phone_str = "hey my name is shidong,and my phone number is 13691474012,please call me if you are pretty!"
phone_str2 = "hey my name is lilei,and my phone number is 18511028340,please call me if you are pretty!"
m = re.search("[0-9]{1,11}",phone_str)
m1 = re.search("(1)[138]\d{9}",phone_str2)
print(m.group())
print(m1.group())
m = [1,8,25,144,66,358,14,5,7,]
print(sorted(m))
冒泡算法:
冒泡排序原理: 每一趟只能将一个数归位, 如果有n个数进行排序,只需将n-1个数归位, 也就是说要进行n-1趟操作(已经归位的数不用再比较)
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding:utf-8 def bubbleSort(nums):
for i in range(len(nums)-1):
# 这个循环负责设置冒泡排序进行的次数
for j in range(len(nums)-i-1):
# j为列表下标
if nums[j] > nums[j+1]:
nums[j], nums[j+1] = nums[j+1], nums[j]
return nums
nums = [5,2,45,6,8,2,1]
print bubbleSort(nums)
缺点: 冒泡排序解决了桶排序浪费空间的问题, 但是冒泡排序的效率特别低
时间复杂度:
(1)时间频度 一个算法执行所耗费的时间,从理论上是不能算出来的,必须上机运行测试才能知道,但是我们不可能也没有必要对每个算法都上机测试,只需知道哪个算法花费的时间多,
哪个算法花费的时间少就可以了,并且一个算法花费的时间与算法中语句的执行次数成正比例,哪个算法汇总语句执行次数多,它花费的时间就越多,一个算法中的语句执行次数称为语句频度
或时间频度。记为T(n)
二、模块
模块,用一坨代码实现了某个功能的代码集合。
os是系统相关的模块
模块分为三种:
1、自定义模块
2、内置标准模块(又称标准库)
3、开源模块
__init__.py 作用:是把一个文件夹变成包
random模块(返回随机数):
import random
# 返回一个随机小数
print(random.random())
#返回一个随机整数
print(random.randint(1,10))
#效果和randint一样
print(random.randrange(1 ,10 ))
实例:随机生成验证码:
import random
v_code = ""
for i in range(4):
if i != random.randint(0,4):
temp = chr(random.randint(65,90))
v_code += temp
else:
temp = str(random.randint(0,9))
v_code += temp
print(v_code)

OS模块:
os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cdos.curdir 返回当前目录: ('.')os.pardir 获取当前目录的父目录字符串名:('..')os.makedirs('dirname1/dirname2') 可生成多层递归目录os.removedirs('dirname1') 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推os.mkdir('dirname') 生成单级目录;相当于shell中mkdir dirnameos.rmdir('dirname') 删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错;相当于shell中rmdir dirnameos.listdir('dirname') 列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印os.remove() 删除一个文件os.rename("oldname","newname") 重命名文件/目录os.stat('path/filename') 获取文件/目录信息os.sep 输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为"\\",Linux下为"/"os.linesep 输出当前平台使用的行终止符,win下为"\t\n",Linux下为"\n"os.pathsep 输出用于分割文件路径的字符串os.name 输出字符串指示当前使用平台。win->'nt'; Linux->'posix'os.system("bash command") 运行shell命令,直接显示os.environ 获取系统环境变量os.path.abspath(path) 返回path规范化的绝对路径os.path.split(path) 将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回os.path.dirname(path) 返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素os.path.basename(path) 返回path最后的文件名。如何path以/或\结尾,那么就会返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素os.path.exists(path) 如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回Falseos.path.isabs(path) 如果path是绝对路径,返回Trueos.path.isfile(path) 如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回Falseos.path.isdir(path) 如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True。否则返回Falseos.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) 将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略os.path.getatime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后存取时间os.path.getmtime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间sys模块:
sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0)sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息sys.maxint 最大的Int值sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称sys.stdout.write('please:')val = sys.stdin.readline()[:-1]shutil模块:
高级的 文件、文件夹、压缩包 处理模块
shutil.copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst[, length])
将文件内容拷贝到另一个文件中,可以部分内容

def copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst, length=16*1024):
"""copy data from file-like object fsrc to file-like object fdst"""
while 1:
buf = fsrc.read(length)
if not buf:
break
fdst.write(buf)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
拷贝文件

def copyfile(src, dst):
"""Copy data from src to dst"""
if _samefile(src, dst):
raise Error("`%s` and `%s` are the same file" % (src, dst))
for fn in [src, dst]:
try:
st = os.stat(fn)
except OSError:
# File most likely does not exist
pass
else:
# XXX What about other special files? (sockets, devices...)
if stat.S_ISFIFO(st.st_mode):
raise SpecialFileError("`%s` is a named pipe" % fn)
with open(src, 'rb') as fsrc:
with open(dst, 'wb') as fdst:
copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst)
shutil.copymode(src, dst)
仅拷贝权限。内容、组、用户均不变

def copymode(src, dst):
"""Copy mode bits from src to dst"""
if hasattr(os, 'chmod'):
st = os.stat(src)
mode = stat.S_IMODE(st.st_mode)
os.chmod(dst, mode)
shutil.copystat(src, dst)
拷贝状态的信息,包括:mode bits, atime, mtime, flags

def copystat(src, dst):
"""Copy all stat info (mode bits, atime, mtime, flags) from src to dst"""
st = os.stat(src)
mode = stat.S_IMODE(st.st_mode)
if hasattr(os, 'utime'):
os.utime(dst, (st.st_atime, st.st_mtime))
if hasattr(os, 'chmod'):
os.chmod(dst, mode)
if hasattr(os, 'chflags') and hasattr(st, 'st_flags'):
try:
os.chflags(dst, st.st_flags)
except OSError, why:
for err in 'EOPNOTSUPP', 'ENOTSUP':
if hasattr(errno, err) and why.errno == getattr(errno, err):
break
else:
raise
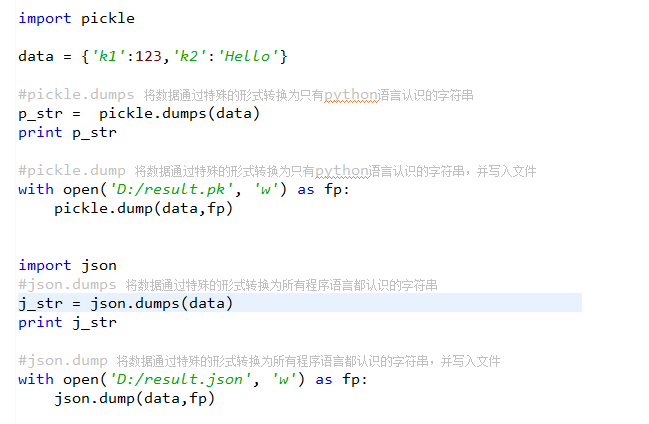
json & pickle 模块
用于序列化的两个模块
- json,用于字符串 和 python数据类型间进行转换
- pickle,用于python特有的类型 和 python的数据类型间进行转换
Json模块提供了四个功能:dumps、dump、loads、load
pickle模块提供了四个功能:dumps、dump、loads、load




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号