CS Course Learning
【李宏毅】2024大语言模型课程
课程学习
课程链接:https://speech.ee.ntu.edu.tw/~hylee/genai/2024-spring.php
Bilibili相关视频链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1XS411w7qr
GPT: Autoregressive model
In-context Learning
- Chain of Thoughts (CoT)
- Tree of Thoughts (ToT)
- Algorithm of Thoughts (AoT)
- ....
使用工具:
- 搜寻引擎 Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
- 写程序 Program of Thought (PoT)
- 文字生图 DALL-E
Explainable ML:
- Local Explanation
- Saliency Map
- SmoothGrad (improved Saliency Map)
- Integrated Gradient(IG)
- Global Explanation
Three steps of LLM training:
- Pre-train -> Foundation model
- Instruction Fine-tuning (Supervised Learning)
- Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF)
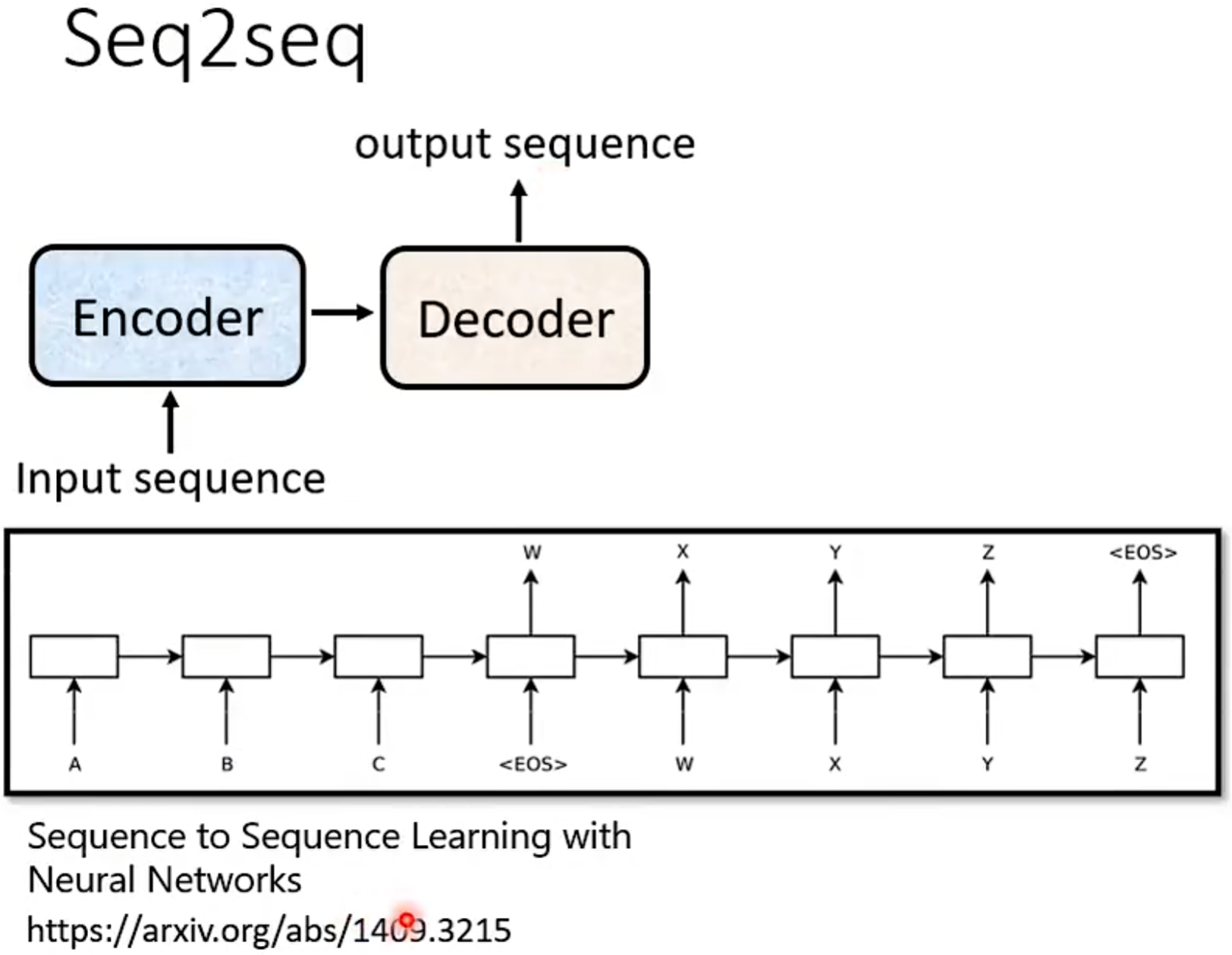
Seq2seq:
-
Syntactic Parsing (文法分析)
-
Multi-label Classification (区别于 Multi-class Classification)
An object can belong to multiple classes
-
Object Detection
Tranformer:
- Self-attention
- Cross-attention
Copy Mechanism => Summarization
- Pointer Network
Attention Decoder
- Greedy Decoding (每次都选择输出概率最大的token)
- Bean Search
- Sampling (more creative, randomness is needed for decoder when generating)
Prompt Hacking
- Jailbeaking
- Prompt Injection
Generative model:
- Autoregressive (AR)
按部就班,逐个token生成、生成速度较慢 - Non-autoregressive (NAR)
一次性生成、生成速度较快
Sepeculative Decoding
作业总结
seed
import random
import numpy as np
def set_random_seed(seed):
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
torch.manual_seed(seed)
if torch.cuda.is_available():s
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
random.seed(seed)
np.random.seed(seed)
transformers
pipeline
from transformers import pipeline
# 1. task
pipe = pipeline(task="automatic-speech-recognition") # ASR
output = pipe("https://huggingface.co/datasets/Narsil/asr_dummy/resolve/main/mlk.flac")
print(output)
# 2. model
pipe = pipeline(model="FacebookAI/roberta-large-mnli")
pipe("This restaurant is awesome")
print(output)
# 3. multi-input
pipe = pipeline(model="FacebookAI/roberta-large-mnli")
output = pipe(["This restaurant is awesome", "It is ugly"])
print(output)
# 4. with gradio
import gradio as gr
pipe = pipeline(task="sentiment-analysis", model="FacebookAI/roberta-large-mnli")
gr.Interface.from_pipeline(pipe).launch()
"""
task: str = None
`image-classification`
`image-segmentation`
`object-detection`
`text-generation`
...
"""
AutoClass
# load model and tokenizer
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(<model_path>)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(<model_path>)
openai
from openai import OpenAI
# use deepseek API as an example
client = OpenAI(api_key="<DeepSeek API Key>", base_url="https://api.deepseek.com")
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-chat",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant"},
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello"},
],
stream=False
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
【李宏毅】2023机器学习系列课程
课程学习
能够使用工具的AI:
- WebGPT
- Toolformer
作业总结
Pytorch
trainer
# trainer
n_epochs = config['n_epochs']
criterion = nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean') # define loss function
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=config['learning_rate'], momentum=0.7) # define optimizer
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
# train
model.train()
loss_record = []
for X, y in train_loader:
optimizer.zero_grad()
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
pred = model(X)
loss = criterion(pred, y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
loss_record.append(loss.detach().item()) # loss value of a batch : loss.detach().item()
mean_train_loss = sum(loss_record) / len(loss_record)
# evaluate
model.eval()
loss_record = []
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in valid_loader:
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
pred = model(X)
loss = criterion(pred, y)
loss_record.append(loss.detach().item()) # loss value of a batch : loss.detach().item()
mean_eval_loss = sum(loss_record) / len(loss_record)
tensorboard
.
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
writer = SummaryWriter() # Writer of tensoboard.
writer.add_scalar('Loss/train', mean_train_loss, step)
"""
def add_scalar(
tag: Any, # 图表的名称
scalar_value: Any, # 纵坐标取值
global_step: Any | None = None, # 横坐标取值
walltime: Any | None = None,
new_style: bool = False,
double_precision: bool = False
)
"""
BLUE
Bilingual Evaluation Understudy,是一种用于评估机器翻译质量的自动指标,核心思想是计算翻译与参考译文之间的 n-gram重叠程度 ,并结合一些调整因子(如长度惩罚)得出一个综合得分。
- \(p_n\):第n-gram的精度。
- \(w_n\):每个n-gram的权重,通常均匀分布(如1/4)。
- \(BP\):长度惩罚因子。
【ETH】2020 Digital Design and Computer Architecture
课程链接:https://safari.ethz.ch/digitaltechnik/spring2020/doku.php?id=start
课程视频链接:https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL5Q2soXY2Zi_FRrloMa2fUYWPGiZUBQo2
课程学习
DRAM:动态存储器(需要每隔一段时间刷新一次数据才能保存数据),断电数据丢失
SRAM:静态存储器(不需要刷新电路),断电数据丢失
作业总结
【UCB】2020 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs
课程链接:https://web.archive.org/web/20210104105406/https://cs61a.org/


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号