策略模式
1、概述
定义一系列的算法,把每一个算法封装起来,并且使它们可相互替换。本模式使得算法与对象独立开来,算法可独立于使用它的客户而变化。
2、模式分析
当实现一个功能有多种算法或策略时,我们可以将这些算法写到一个类中,在该类中提供多个方法,每一个方法对应一个具体的查找算法,通过if…else…或者case等条件判断语句来进行选择。这两种实现方法我们都可以称之为硬编码,如果需要增加新的算法,或者需要修改已有算法;将修改大量代码。在这个算法类中封装了大量查找算法,该类代码将较复杂,维护较为困难。
我们将这些算法封装成一个一个类,在运行过程中,可以自由切换算法。
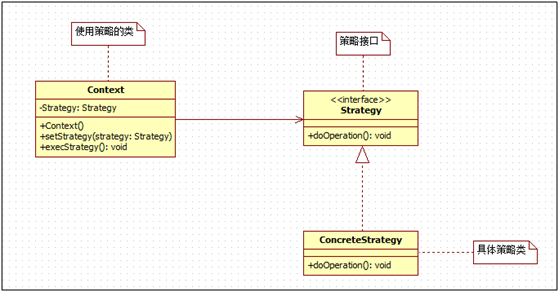
3、模式角色
策略接口(Strategy):策略接口,声明策略算法;
具体策略类(ConcreteStrategy):具体的策略实现类,实现策略接口中的具体算法;
使用某种策略的类(Context):在该类中可以定义多种不同的具体策略类,在运行过程中根据不同的条件使用不同的策略类。
4、优点与缺点
优点:
- 算法可以自由切换;
- 避免了多重条件的判断;
- 扩展性良好
缺点:
具体的策略类较多,增加系统的复杂性。
5、应用示例
假设Context是个含有一个整型数组的类,为了测试不同排序算法的时间复杂度,需要在运行过程中调用不同的排序算法,现采用策略模式实现这一测试过程。简单起见,这里只介绍简单选择排序和冒泡排序。
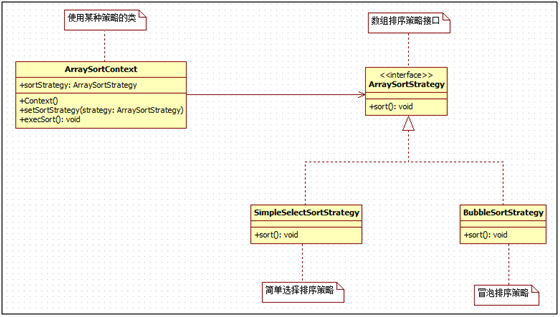
ArraySortStrategy(数组排序策略接口)
1 /** 2 * 数组排序策略接口 3 * @author hjy 4 */ 5 public interface ArraySortStrategy { 6 7 /** 8 * 对数组进行排序,返回比较的次数 9 * @param arr 10 * @return 11 */ 12 public int sort(int[] arr); 13 }
SimpleSelectSortStrategy(简单选择排序策略)
1 /** 2 * 简单选择排序策略 3 * @author hjy 4 */ 5 public class SimpleSelectSortStrategy implements ArraySortStrategy { 6 7 @Override 8 public int sort(int[] arr) { 9 int size = arr.length; 10 int count = 0; 11 12 for(int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++){ 13 int max_index = i; 14 //选择出最大值的索引位置 15 for(int j = i + 1; j < size; j++){ 16 if(arr[j] > arr[max_index]){ 17 count++; 18 max_index = j; 19 } 20 } 21 //交换位置 22 if(max_index != i){ 23 int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[max_index]; arr[max_index] = temp; 24 } 25 } 26 return count; 27 } 28 }
BubbleSortStrategy(冒泡排序策略)
1 /** 2 * 冒泡排序策略 3 * @author hjy 4 */ 5 public class BubbleSortStrategy implements ArraySortStrategy { 6 @Override 7 public int sort(int[] arr) { 8 int size = arr.length; 9 int count= 0; 10 11 for(int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++){ 12 for(int j = 0; j < size - i -1; j++){ 13 if(arr[j] < arr[j+1]){ 14 count++; 15 int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j+1]; arr[j+1] = temp; 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 return count; 20 } 21 }
ArraySortContext(使用不同策略的类)
1 /** 2 * 使用不同排序策略的类 3 * @author hjy 4 */ 5 public class ArraySortContext { 6 //策略成员类 7 private ArraySortStrategy sortStrategy; 8 9 //set方法,指定不同的策略 10 public void setSortStrategy(ArraySortStrategy sortStrategy){ 11 this.sortStrategy = sortStrategy; 12 } 13 14 //执行策略 15 public void execSort(int[] arr){ 16 int count = sortStrategy.sort(arr); 17 System.out.println("比较次数:" + count); 18 } 19 }
ArraySortClient(客户端)
1 public class ArraySortClient { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 int[] arr1 = new int[20]; 4 int[] arr2 = new int[20]; 5 Random random = new Random(); 6 for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++){ 7 int num = random.nextInt(100) + 1; 8 arr1[i] = num; 9 arr2[i] = num; 10 } 11 12 //定义简单选择排序策略 13 ArraySortStrategy simpleSelectSortStrategy = new SimpleSelectSortStrategy(); 14 //定义冒泡排序策略 15 ArraySortStrategy bubbleSortStrategy = new BubbleSortStrategy(); 16 17 //定义使用不同排序策略的类 18 ArraySortContext context = new ArraySortContext(); 19 20 //使用简单排序策略来进行排序 21 context.setSortStrategy(simpleSelectSortStrategy); 22 context.execSort(arr1); 23 print(arr1); 24 25 //使用冒泡排序策略来进行排序 26 context.setSortStrategy(bubbleSortStrategy); 27 context.execSort(arr2); 28 print(arr2); 29 } 30 31 private static void print(int[] arr){ 32 StringBuffer strBuffer = new StringBuffer(); 33 for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){ 34 if(i == arr.length - 1){ 35 strBuffer.append(arr[i]); 36 }else{ 37 strBuffer.append(arr[i]).append(", "); 38 } 39 } 40 System.out.println(strBuffer.toString()); 41 } 42 }
结果:
比较次数:34 100, 95, 93, 86, 83, 82, 80, 80, 74, 62, 60, 58, 56, 53, 46, 44, 29, 17, 14, 7 比较次数:82 100, 95, 93, 86, 83, 82, 80, 80, 74, 62, 60, 58, 56, 53, 46, 44, 29, 17, 14, 7





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号