基础提升讲解
一、哈希函数与哈希表
1.设计RandomPool结构

public static class Pool<K> {
private HashMap<K, Integer> keyIndexMap;
private HashMap<Integer, K> indexKeyMap;
private int size;
public Pool() {
this.keyIndexMap = new HashMap<K, Integer>();
this.indexKeyMap = new HashMap<Integer, K>();
this.size = 0;
}
public void insert(K key) {
if (!this.keyIndexMap.containsKey(key)) {
this.keyIndexMap.put(key, this.size);
this.indexKeyMap.put(this.size++, key);
}
}
public void delete(K key) {
if (this.keyIndexMap.containsKey(key)) {
int deleteIndex = this.keyIndexMap.get(key);
int lastIndex = --this.size;
K lastKey = this.indexKeyMap.get(lastIndex);
this.keyIndexMap.put(lastKey, deleteIndex);
this.indexKeyMap.put(deleteIndex, lastKey);
this.keyIndexMap.remove(key);
this.indexKeyMap.remove(lastIndex);
}
}
public K getRandom() {
if (this.size == 0) {
return null;
}
int randomIndex = (int) (Math.random() * this.size); // 0 ~ size -1
return this.indexKeyMap.get(randomIndex);
}
}
2.布隆过滤器
(1)什么是布隆过滤器
布隆过滤器是一种空间效率很高的随机数据结构,专门用来检测集合中是否存在特定的元素。布隆过滤器由一个长度为m比特的位数组与k个独立的哈希函数组成的数据结构。位数组初始化均为0,所有的哈希函数都可以分别把输入数据尽量均匀地散列。当要向布隆过滤器中插入一个元素时,该元素经过k个哈希函数计算产生k个哈希值,以哈希值作为位数组中的下标,将所有k个对应的比特值由0置为1。当要查询一个元素时,同样将其经过哈希函数计算产生哈希值,然后检查对应的k个比特值:如果有任意一个比特为0,表明该元素一定不在集合中;如果所有比特均为1,表明该元素有可能性在集合中。
(2)算法实现步骤
- 选取k个哈希函数,记为
- 假设现在有n个元素需要被映射到bit数组中,bit数组的长度是m。初始时,将m位的bit数组的每个位置的元素都置为0。
- 现在,把这个n个元素依次用第1步选取的k个哈希函数映射到bit数组的位置上,bit数组被映射到的位置的元素变为1。显然,一个元素能被映射到k个位置上。
- 最后,需要检查一个元素是否在已有的集合中时,同样用这k个哈希函数把要判断的元素映射到bit数组的位置上,只要bit数组被映射到的位中有一个位不是1,那一定说明了这个元素不在已有的集合内。
(3)优缺点
优点:
- 节省空间:不需要存储数据本身,只需要存储数据对应hash比特位
- 时间复杂度低:插入和查找的时间复杂度都为O(k),k为哈希函数的个数
缺点: - 存在假阳性:布隆过滤器判断存在,但可能出现元素实际上不在集合中的情况;误判率取决于哈希函数的个数,
- 不支持删除元素:如果一个元素被删除,但是却不能从布隆过滤器中删除,这也是存在假阳性的原因之一
(4)参数的选择
假设E表示错误率,n表示要插入的元素个数,m表示bit数组的长度,k表示hash函数的个数。
- 当hash函数个数 k = (ln2) * (m/n)时,错误率E最小(此时bit数组中有一半的值为0)
- 在错误率不大于E的情况下,bit数组的长度m需要满足的条件为:m ≥ n * lg(1/E)。
- 结合上面两个公式,在hash函数个数k取到最优时,要求错误率不大于E,这时我们对bit数组长度m的要求是:m>=nlg(1/E) * lg(e) ,也就是 m ≥ 1.44n*lg(1/E)(lg表示以2为底的对数)
3.一致性哈希原理
(1)普通hash算法的缺陷
如果服务器已经不能满足缓存需求,就需要增加服务器数量,假设我们增加了一台缓存服务器,此时如果仍然使用普通hash算法对同一张图片进行缓存,那么这张图片所在的服务器编号必定与原来3台服务器时所在的服务器编号不同,因为除数由3变为了4,最终导致所有缓存的位置都要发生改变,也就是说,当服务器数量发生改变时,所有缓存在一定时间内是失效的,当应用无法从缓存中获取数据时,则会向后端服务器请求数据;同理,假设突然有一台缓存服务器出现了故障,那么我们则需要将故障机器移除,那么缓存服务器数量从3台变为2台,同样会导致大量缓存在同一时间失效,造成了缓存的雪崩,后端服务器将会承受巨大的压力,整个系统很有可能被压垮。为了解决这种情况,就有了一致性哈希算法。
(2)什么是一致性hash算法:
一致性哈希算法也是使用取模的方法,但是取模算法是对服务器的数量进行取模,而一致性哈希算法是对 2^32 取模,具体步骤如下:
- 步骤一:一致性哈希算法将整个哈希值空间按照顺时针方向组织成一个虚拟的圆环,称为 Hash 环;
- 步骤二:接着将各个服务器使用 Hash 函数进行哈希,具体可以选择服务器的IP或主机名作为关键字进行哈希,从而确定每台机器在哈希环上的位置
- 步骤三:最后使用算法定位数据访问到相应服务器:将数据key使用相同的函数Hash计算出哈希值,并确定此数据在环上的位置,从此位置沿环顺时针寻找,第一台遇到的服务器就是其应该定位到的服务器
(3)一致性hash算法的优点
一致性Hash算法对于节点的增减都只需重定位环空间中的一小部分数据,只有部分缓存会失效,不至于将所有压力都在同一时间集中到后端服务器上,具有较好的容错性和可扩展性。
(4)hash环的倾斜与虚拟节点
一致性哈希算法在服务节点太少的情况下,容易因为节点分部不均匀而造成数据倾斜问题,也就是被缓存的对象大部分集中缓存在某一台服务器上,从而出现数据分布不均匀的情况,这种情况就称为 hash 环的倾斜。
hash 环的倾斜在极端情况下,仍然有可能引起系统的崩溃,为了解决这种数据倾斜问题,一致性哈希算法引入了虚拟节点机制,即对每一个服务节点计算多个哈希,每个计算结果位置都放置一个此服务节点,称为虚拟节点,一个实际物理节点可以对应多个虚拟节点,虚拟节点越多,hash环上的节点就越多,缓存被均匀分布的概率就越大,hash环倾斜所带来的影响就越小,同时数据定位算法不变,只是多了一步虚拟节点到实际节点的映射。
4.岛问题

public static int countIslands(int[][] m) {
if (m == null || m[0] == null) {
return 0;
}
int N = m.length; //二维数组的行数
int M = m[0].length; //二维数组的列数
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (m[i][j] == 1) {
res++;
infect(m, i, j, N, M);
}
}
}
return res;
}
public static void infect(int[][] m, int i, int j, int N, int M) {
if (i < 0 || i >= N || j < 0 || j >= M || m[i][j] != 1) {
return;
}
m[i][j] = 2;
infect(m, i + 1, j, N, M);
infect(m, i - 1, j, N, M);
infect(m, i, j + 1, N, M);
infect(m, i, j - 1, N, M);
}
5.并查集结构
public class Code04_UnionFind {
public static class Element<V> {
public V value;
public Element(V value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public static class UnionFindSet<V> {
public HashMap<V, Element<V>> elementMap;
public HashMap<Element<V>, Element<V>> fatherMap; //key表示某个元素,value表示该元素的父
public HashMap<Element<V>, Integer> rankMap; //key表示某个集合的代表元素,value表示该集合的大小
//初始化所给列表中的每一个元素
public UnionFindSet(List<V> list) {
elementMap = new HashMap<>();
fatherMap = new HashMap<>();
rankMap = new HashMap<>();
for (V value : list) { //初始化
Element<V> element = new Element<V>(value);
elementMap.put(value, element);
fatherMap.put(element, element);
rankMap.put(element, 1);
}
}
//找到给定元素的顶部元素
private Element<V> findHead(Element<V> element) {
Stack<Element<V>> path = new Stack<>();
//找到最顶部的元素,也就是找到父
while (element != fatherMap.get(element)) {
path.push(element);
element = fatherMap.get(element);
}
//扁平化,直接将挂载在父元素下的所有元素的父全部指向父元素
while (!path.isEmpty()) {
fatherMap.put(path.pop(), element);
}
return element;
}
//判断所给的两个元素是否属于同一个集合
public boolean isSameSet(V a, V b) {
if (elementMap.containsKey(a) && elementMap.containsKey(b)) {
return findHead(elementMap.get(a)) == findHead(elementMap.get(b));
}
return false;
}
//将不属于同一个集合的两个元素进行合并
public void union(V a, V b) {
if (elementMap.containsKey(a) && elementMap.containsKey(b)) {
Element<V> aF = findHead(elementMap.get(a));
Element<V> bF = findHead(elementMap.get(b));
if (aF != bF) {
Element<V> big = rankMap.get(aF) >= rankMap.get(bF) ? aF : bF;
Element<V> small = big == aF ? bF : aF;
fatherMap.put(small, big); //把小的集合挂载到大的集合上
rankMap.put(big, rankMap.get(aF) + rankMap.get(bF));
rankMap.remove(small);
}
}
}
}
}
6.并行求解岛问题
并行的关键在于,把一个大图分成几个小图,让各个机器并行处理各个小图。然后再把小图的结果汇总。主要问题在于,一个岛可能在分割过程中被分成两部分,因此每个小图的岛的数量的和可能大于大图的岛的数量。为了能够实现岛的合并过程,我们就可以借助并查集来实现这个过程。
第一步:对于每个独立的小图,并行运算,分别使用感染过程,得到每个小图的岛的数量。同时,使用并查集结构,将每个被感染的点的父节点设置成感染它的源头。
第二步:遍历所有出现在边界两侧的点对,如果两个点都被感染了,且两个点不在一个集合里(查),那么将这两个点所在的集合合并(并),然后总岛数减1。
这样我们就得到了总的岛数。
二、KMP算法
1.KMP算法步骤
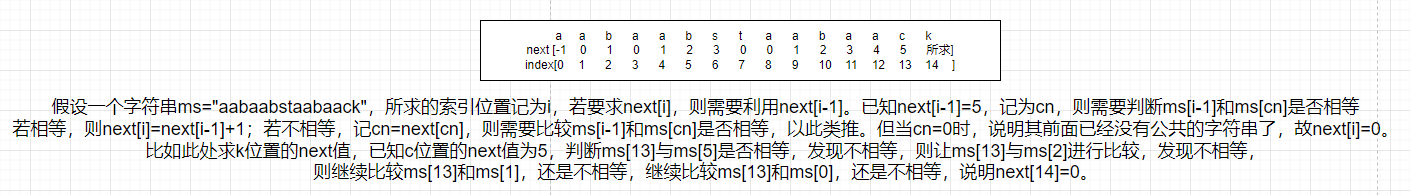
(1)构建next数组,数组中记录的是当前位置前面的字符串中最长公共前缀和后缀字符串的长度
例如:字符串为aabaabsaabaabst,人为规定next[0]=-1,next[1]=0,从第2个位置开始计算。当索引为2的时候,其前面字符串为aa,最长公共的前缀和后缀字符串为a,所以next[2]=1;当索引为3的时候,其前面字符串为aab,无公共的前缀和后缀字符串,所以next[3]为0;当索引为4的时候,其前面字符串为aaba,最长公共前缀和后缀字符串为a,所以next[4]为1;以此类推。最终得到的next数组为:[-1,0,1,0,1,2,3,0,1,2,3,4,5,6,0]
注:next数组是对待匹配字符串进行操作的
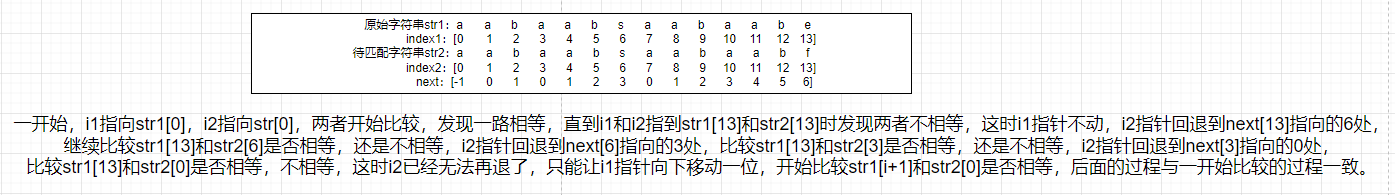
(2)假设字符串x="aaacaaab",要匹配的字符串y="aaab",需要返回y在x中的位置。根据第一步,可得到y的next数组为[-1,0,1,2]。设置两个指针i和j,i指向x[0],j指向y[0],一开始,i和j都从0开始比,当i和j都为3时,发现x[i]≠y[j]。若按照暴力算法,则需要将i置为1,j置为0,再继续一个一个匹配。若用KMP算法,则i=3不用动,j回退到next[3]中的值2处,接下来匹配x[3]和y[2]是否相等,若相等,则继续往下匹配;若不相等,则再将j回退到next[2]中的值1处,接下来匹配x[3]和y[1]是否相等,以此类推。当j回退到0位置的时候,已经不能再退了,这时就需要将i往右移到i+1的位置,从x[i+1]处和y[0]处开始进行匹配。
2.字符串匹配问题

getNextArray函数的比较过程:
getIndexOf函数的比较过程:
public static int getIndexOf(String s, String m) {
if (s == null || m == null || m.length() < 1 || s.length() < m.length()) {
return -1;
}
char[] str1 = s.toCharArray();
char[] str2 = m.toCharArray();
int i1 = 0;
int i2 = 0;
int[] next = getNextArray(str2);
while (i1 < str1.length && i2 < str2.length) { //此处while循环的时间复杂度是O(N)
if (str1[i1] == str2[i2]) { //当前位置两者相等,则两个指针同时向后移
i1++;
i2++;
} else if (next[i2] == -1) { //next[i2] == -1与i2 == 0等价,说明str2中比对的位置不能再往前跳了
i1++;
} else { //若对应位置不相等,则将i2向前跳
i2 = next[i2];
}
}
return i2 == str2.length ? i1 - i2 : -1; //i2越界代表配出了str2,i1越界代表没有配出
}
public static int[] getNextArray(char[] ms) {
if (ms.length == 1) {
return new int[] { -1 };
}
int[] next = new int[ms.length];
next[0] = -1; //next[0]人为规定为-1
next[1] = 0; //next[1]人为规定为0
int i = 2; //next数组的位置
int cn = 0; //拿cn位置的字符跟i-1位置的字符比,也代表当前使用的信息是多少
while (i < next.length) { //此处while循环的时间复杂度是O(N)
if (ms[i - 1] == ms[cn]) { //求i位置的next数组值,需要利用i-1位置的next数组值,若ms[i-1]==ms[cn],则next[i]=next[i-1]+1=cn+1
next[i++] = ++cn;
} else if (cn > 0) { //当前跳到cn位置的字符跟i-1位置的字符不匹配,把cn往前跳
cn = next[cn];
} else { //若cn=0时,ms[cn]≠ms[i-1],则说明next[i]=0;
next[i++] = 0;
}
}
return next;
}
三、Manacher算法
1.Manacher算法中的一些概念
回文直径:从对称轴开始向左向右衍生,直到回文区域边界后统计的字符总数。
回文半径:从对称轴开始向左或向右衍生,直到回文区域边界后统计的字符总数。
参数设置:
(1)需要给被辅助字符处理的字符串中的每一个字符计算回文半径,从而构建一个回文半径数组。
(2)设置一个变量 R,记录之前匹配回文区域的所有字符中,回文边界达到的最右下标(初值为-1)。R 永远是只增不减的,只要有字符的回文更靠右,下标就会更新给 R。
(3)设置一个变量 C,和 R 一起用,记录当前取得最右下标的回文区域的中心点的下标(初值为-1,如果最右下标重合,按照原中心点的下标)。C 也是永远只增不减的,R 更新 C 一定更新,R 不更新 C 一定不更新。
2.Manacher算法的流程
首先需要构建回文半径数组,在构建回文半径数组时,会遇到两种大情况:
2.1 情况1:当前匹配的字符的位置不在之前匹配的字符的回文区域的最右边界中
该情况无优化,只能从该中心点开始同时向两边暴力扩展匹配,同时计算出该字符的回文半径。

2.2 情况2:当前匹配的字符的位置在之前匹配的字符的回文区域的最右边界中
当第二种大情况出现的时候,一定存在下图表示的通用拓扑结构:
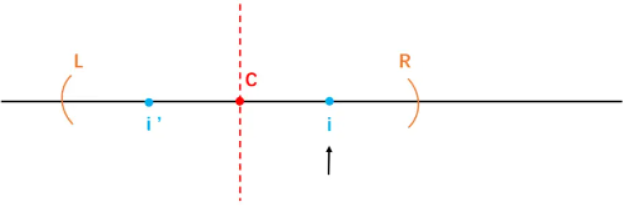
i为当前匹配的字符的位置,i'是以C为对称轴所作的i的对称点。C、L和R一定都存在。
i和C是不可能重合的,因为C表示的是i之前字符构建的最长回文子串的中心点。当遍历到i位置时,C一定已经遍历过了。
按照i'的回文区域的状况可以将第二种大情况划分成三种具体的情况,每一种情况都有单独的优化。
2.2.1 情况2-1:i'的回文区域完全在L~R的内部
此时,i的回文半径就是i'的回文半径。
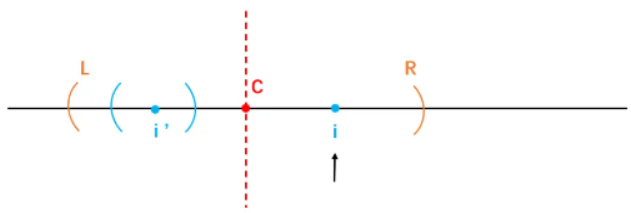
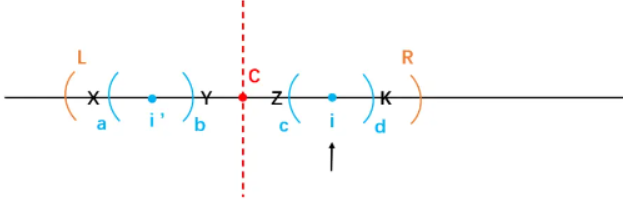
在i位置作与i'等量的回文区域cd。由于整个LR是一个以C为中心的回文串,因此ab和cd一定关于C对称,从而cd一定是ab的逆序。而ab是回文串,且回文串的逆序也是回文串,因此cd最少一定与ab等规模。为什么cd不能更大?需要证明。
设置ab区域前一个字符为X,后一个字符为Y;设置cd区域前一个字符为Z,后一个字符为K。
为什么i'当时没有将自己的回文区域扩的更大?
原因只有一个,就是X!=Y。又因为X和K对称,Y和Z对称,因此XK,YZ,K!=Z,i的回文区域也无法再扩大。
2.2.2 情况2-2:i'的回文区域有一部分在L~R的外部
此时i的回文半径就是i~R。

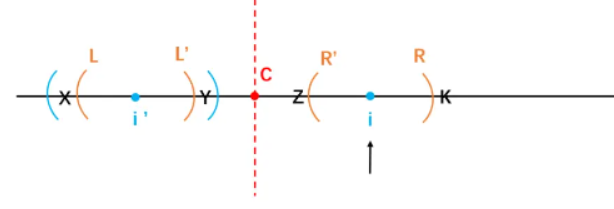
L作i'的对称点L',R作i的对称点R'。
LL'和RR'一定是逆序关系,LL'是回文,因为在LL'在LR的内部,因此RR'一定也是回文,因此i的回文区域至少与LL'等规模。为什么RR'不能更大?需要证明。
设置LL'前一个字符为X,LL'后一个字符为Y;RR'前一个字符为Z,RR'后一个字符为K。
因为X和Y都在i'的回文区域中,且关于i'对称,所以XY。
又因为Y和Z都在C的回文区域中,且关于C对称,所以YZ。
为什么当时C没有将自己的回文区域扩的更大?
原因只有一个,就是X!=K,所以Z!=K,i的回文区域也无法再扩大。
2.2.3 情况2-3:i'的回文区域的左边界正好和L重合
此时不能直接得出i的回文半径,只能确定回文半径最小就是i~R。能不能更大,需要从i位置向外扩展匹配。
但是此时可以设计一个常数加速,因为i~R是确定的最小回文半径,因此可以直接从R开始继续向外扩展匹配。

3.求最长回文子串的长度

//用于对给定字符串加上特殊字符,比如将1221->#1#2#2#1#
public static char[] manacherString(String str) {
char[] charArr = str.toCharArray();
char[] res = new char[str.length() * 2 + 1];
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i != res.length; i++) {
res[i] = (i & 1) == 0 ? '#' : charArr[index++]; //res数组中奇数位放#,偶数位放chars数组中的数
}
return res;
}
public static int maxLcpsLength(String str) {
if (str == null || str.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
char[] charArr = manacherString(str);
int[] pArr = new int[charArr.length]; //回文半径数组
int C = -1; //中心
int R = -1; //回文右边界的再往右一个位置,最右的有效区是R-1位置
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; //扩出来的最大值
for (int i = 0; i != charArr.length; i++) { //每一个位置都求回文半径
// 先确定所有情况中最低回文半径
// 如果i > R,表示第一种大情况,最低回文半径为自身为1
// 如果 i < R,表示第二种大情况:
// 如果是第①种小情况,i'的回文半径会比R-i小,直接可以确定为i'的回文半径
// 如果是第②种小情况,i’的回文半径会比R-i大,直接可以确定为R-i
// 如果是第③种小情况,i’的回文半径和R-i相等,虽然不能确定最终的回文半径,但是可以确定最少就是i'的回文半径或R-i
pArr[i] = R > i ? Math.min(pArr[2 * C - i], R - i) : 1; //判断当前位置是否在右边界的外面,如果当前位置在右边界的外面,则不需要验证的区域为1,如果当前位置在右边界的里面,则不需要验证的区域是pArr[2*C-i]和R-i中的最小值
// 无论是遇到哪一种情况都会尝试着往外扩,因为只有第一种大情况和第二种大情况的第③种小情况需要向外扩,因此如果是第二种大情况的
// 第①种小情况或者第②种小情况虽然也会走向外扩的流程,但是第一次就会失败,从而跳出循环。
// 这是为了省略多个if-else所做的一个统一的流程,优化了代码的长度,并不会影响时间复杂度
while (i + pArr[i] < charArr.length && i - pArr[i] > -1) {
if (charArr[i + pArr[i]] == charArr[i - pArr[i]]) //从不需要验证区域的外面开始比较
pArr[i]++;
else {
break;
}
}
// 判断R和C是否需要更新
if (i + pArr[i] > R) {
R = i + pArr[i];
C = i;
}
max = Math.max(max, pArr[i]);
}
//处理串中i位的回文半径长度 - 1 = 原串中以i为对称轴的回文子串长度
return max - 1;
}
注:所加的特殊字符可以跟原始字符串中的字符一样,不会影响最终的答案
完整介绍可参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/1792c8260333
四、滑动窗口
1.双端队列实现滑动窗口
滑动窗口: 使用双端队列实现,双端队列的作用是保证每次L边界右移时从队列头弹出的都是当前窗口的最大值。队列中存储元素下标即可,因为对于数组结构有索引什么都可以搞定!
实现步骤:
(1)给定一个限制为k的窗口大小 ,L,R分别代表窗口左右边界,L和R只能向右移动,当R触碰到数组长度极限时结束. (2)L和R初始为index 0,R先移动,当R - L == K 时说明此时的窗口已来到规定的窗口大小,那么之后L和R同步移动,L和R的每次同步移动都会导致当前窗口内最大值的变化
(3)为了能在L和R同步移动时知道此时窗口内的最大值,在开始遍历时,如果队列为空,直接放入队尾,如果不为空,比对要存入的值与队列尾部的值,如果队尾的值小于或者等于,那就一直弹出,直到遇到比要插入值大的停,然后插入
(4)当左边界L移动时,就会导致有一个元素被移出窗口,队列也应该有具体的变化.如果L当前的值与队列头比对,如果索引不同那就不操作,如果相同,就从队列头弹出(队列变化的目的就是为了保证当前窗口中的最大值位于队列头部)
图解如下:

2.滑动窗口的应用

public static int[] getMaxWindow(int[] arr, int w) {
if (arr == null || w < 1 || arr.length < w) {
return null;
}
LinkedList<Integer> qmax = new LinkedList<Integer>(); //初始化一个双端队列
int[] res = new int[arr.length - w + 1]; //arr.length - w + 1代表在arr数组中有多少个w大小的窗口
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
while (!qmax.isEmpty() && arr[qmax.peekLast()] <= arr[i]) { //如果双端队列非空并且双端队列尾部元素小于要插入的元素,则需要将双端队列尾部元素弹出,直到双端队列尾部元素大于要插入的元素时,才把要插入的元素加入双端队列
qmax.pollLast();
}
qmax.addLast(i);
if (qmax.peekFirst() == i - w) { //如果双端队列的头部元素与过期的索引号相同,则将头部元素弹出
qmax.pollFirst();
}
if (i >= w - 1) { //从索引w-1处开始,将每个窗口的最大值记录在res数组中
res[index++] = arr[qmax.peekFirst()];
}
}
return res;
}
五、单调栈结构
1.单调栈
在数组中找到一个数,左边和右边比这个数大,且离这个数最近的位置,使用单调栈结构的图解:
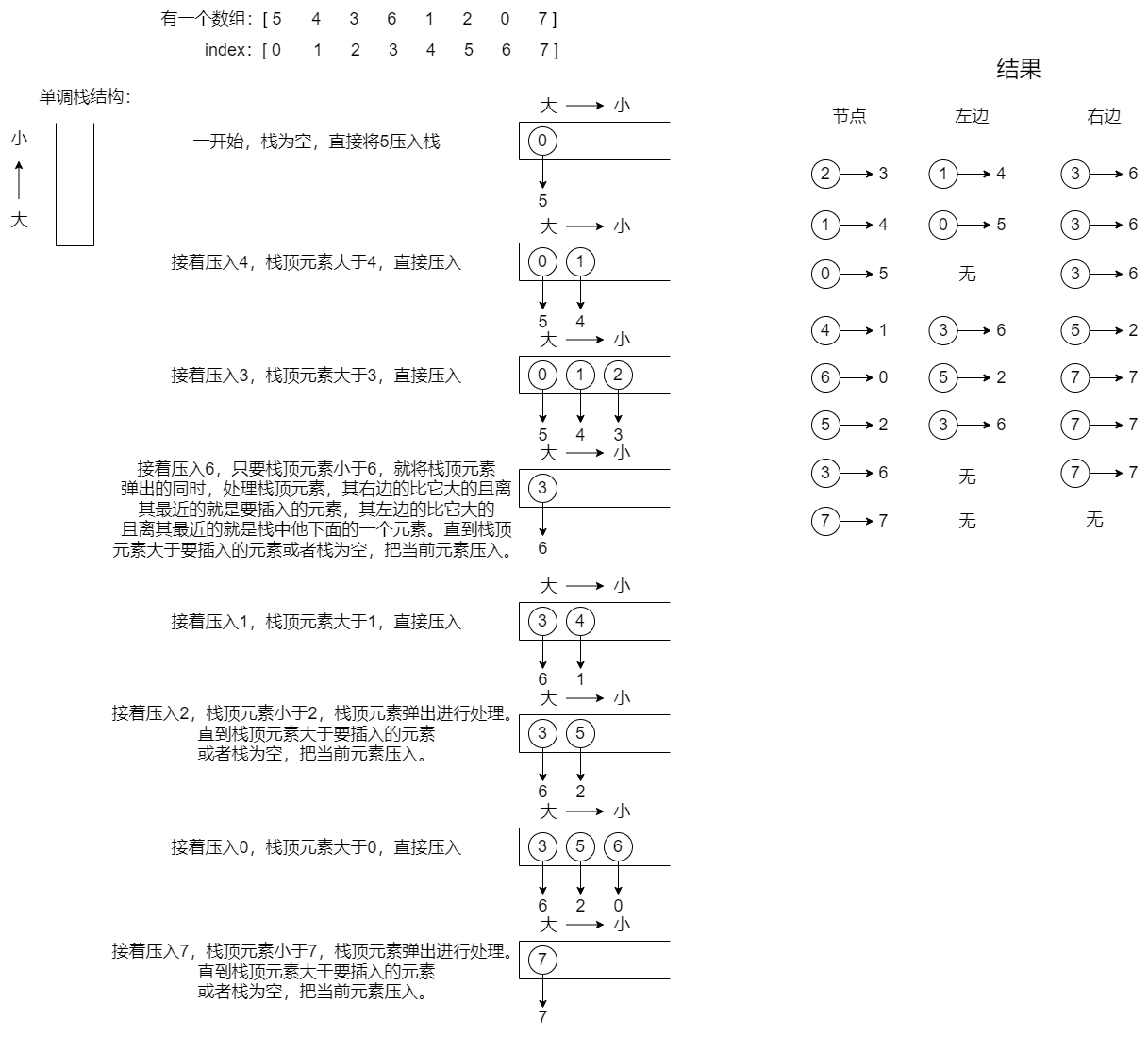
若是相反的情况,只需要将单调栈的单调性改变即可。

//不存在重复值
public static int[][] getNearLessNoRepeat(int[] arr) {
int[][] res = new int[arr.length][2];
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek()] > arr[i]) { //如果栈非空且栈顶元素大于当前数
int popIndex = stack.pop();
int leftLessIndex = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();
res[popIndex][0] = leftLessIndex;
res[popIndex][1] = i;
}
stack.push(i);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int popIndex = stack.pop();
int leftLessIndex = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();
res[popIndex][0] = leftLessIndex;
res[popIndex][1] = -1;
}
return res;
}
//存在重复值
public static int[][] getNearLess(int[] arr) {
int[][] res = new int[arr.length][2];
Stack<List<Integer>> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek().get(0)] > arr[i]) {
List<Integer> popIs = stack.pop();
// 取位于下面位置的列表中,最晚加入的那个
int leftLessIndex = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek().get(
stack.peek().size() - 1);
for (Integer popi : popIs) {
res[popi][0] = leftLessIndex;
res[popi][1] = i;
}
}
if (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek().get(0)] == arr[i]) {
stack.peek().add(Integer.valueOf(i));
} else {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(i);
stack.push(list);
}
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> popIs = stack.pop();
// 取位于下面位置的列表中,最晚加入的那个
int leftLessIndex = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek().get(
stack.peek().size() - 1);
for (Integer popi : popIs) {
res[popi][0] = leftLessIndex;
res[popi][1] = -1;
}
}
return res;
}
2.单调栈的应用

public static int max1(int[] arr) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < arr.length; j++) {
int minNum = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int sum = 0;
for (int k = i; k <= j; k++) {
sum += arr[k];
minNum = Math.min(minNum, arr[k]);
}
max = Math.max(max, minNum * sum);
}
}
return max;
}
public static int max2(int[] arr) {
int size = arr.length;
int[] sums = new int[size];
sums[0] = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
sums[i] = sums[i - 1] + arr[i];
}
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek()] >= arr[i]) {
int j = stack.pop();
max = Math.max(max, (stack.isEmpty() ? sums[i - 1] : (sums[i - 1] - sums[stack.peek()])) * arr[j]);
}
stack.push(i);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int j = stack.pop();
max = Math.max(max, (stack.isEmpty() ? sums[size - 1] : (sums[size - 1] - sums[stack.peek()])) * arr[j]);
}
return max;
}
六、树形dp套路
1.树形dp套路使用前提
如果题目求解目标是S规则,则求解流程可以定成以每一个节点为头节点的子树在S规则下的每一个答案,并且最终答案一定在其中。
2.树形dp套路
第一步:以某个节点X为头节点的子树中,分析答案有哪些可能性,并且这种分析是以X的左子树、X的右子树和X整棵树的角度来考虑可能性的
第二步:根据第一步的可能性分析,列出所有需要的信息
第三步:合并第二步的信息,对左树和右树提出同样的要求,并写出信息结构
第四步:设计递归函数,递归函数是处理以X为头节点的情况下的答案。包括设计递归的basecase,默认直接得到左树和右树的所有信息,以及把可能性做整合,并且要返回第三步的信息结构这四个小步骤
3.求解二叉树节点间的最大距离问题

public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static int maxDistance(Node head) {
int[] record = new int[1];
return posOrder(head, record);
}
public static class ReturnType{
public int maxDistance;
public int h;
public ReturnType(int m, int h) {
this.maxDistance = m;;
this.h = h;
}
}
//返回以head为头节点的整棵树的两个信息
public static ReturnType process(Node head) {
if(head == null) {
return new ReturnType(0,0);
}
ReturnType leftReturnType = process(head.left);
ReturnType rightReturnType = process(head.right);
int includeHeadDistance = leftReturnType.h + 1 + rightReturnType.h;
int p1 = leftReturnType.maxDistance;
int p2 = rightReturnType.maxDistance;
int resultDistance = Math.max(Math.max(p1, p2), includeHeadDistance);
int hitself = Math.max(leftReturnType.h, leftReturnType.h) + 1;
return new ReturnType(resultDistance, hitself);
}
public static int posOrder(Node head, int[] record) {
if (head == null) {
record[0] = 0;
return 0;
}
int lMax = posOrder(head.left, record);
int maxfromLeft = record[0];
int rMax = posOrder(head.right, record);
int maxFromRight = record[0];
int curNodeMax = maxfromLeft + maxFromRight + 1;
record[0] = Math.max(maxfromLeft, maxFromRight) + 1;
return Math.max(Math.max(lMax, rMax), curNodeMax);
}
4.求解派对的最大快乐值

public static class Employee {
public int happy; //这名员工可以带来的快乐值
public List<Employee> nexts; //这名员工有哪些直接下级
}
public static int maxHappy(Employee boss) {
Info headInfo = process(boss);
return Math.max(headInfo.laiMaxHappy, headInfo.buMaxHappy);
}
public static class Info {
public int laiMaxHappy;
public int buMaxHappy;
public Info(int lai, int bu) {
laiMaxHappy = lai;
buMaxHappy = bu;
}
}
public static Info process(Employee x) {
if (x.nexts.isEmpty()) { //x是基层员工的时候
return new Info(x.happy, 0);
}
int lai = x.happy; //x来的情况下,整棵树最大收益
int bu = 0; //x不来的情况下,整棵树最大收益
for (Employee next : x.nexts) {
Info nextInfo = process(next);
lai += nextInfo.buMaxHappy;
bu += Math.max(nextInfo.laiMaxHappy, nextInfo.buMaxHappy);
}
return new Info(lai, bu);
}
public static int maxHappy(int[][] matrix) {
int[][] dp = new int[matrix.length][2];
boolean[] visited = new boolean[matrix.length];
int root = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
if (i == matrix[i][0]) {
root = i;
}
}
process(matrix, dp, visited, root);
return Math.max(dp[root][0], dp[root][1]);
}
public static void process(int[][] matrix, int[][] dp, boolean[] visited, int root) {
visited[root] = true;
dp[root][1] = matrix[root][1];
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
if (matrix[i][0] == root && !visited[i]) {
process(matrix, dp, visited, i);
dp[root][1] += dp[i][0];
dp[root][0] += Math.max(dp[i][1], dp[i][0]);
}
}
}
七、Morris遍历
1.Morris遍历简介
一种遍历二叉树的方式,并且时间复杂度O(N),额外空间复杂度O(1)。
通过利用原树中大量空闲指针的方式,达到节省空间的目的。
2.Morris遍历细节
假设来到当前节点cur,开始时cur来到头节点位置
- 如果cur没有左孩子,cur向右移动(cur = cur.right)
- 如果cur有左孩子,找到左子树上最右的节点mostRight:
a.如果mostRight的右指针指向空,让其指向cur,然后cur向左移动(cur = cur.left)
b.如果mostRight的右指针指向cur,让其指向null,然后cur向右移动(cur = cur.right) - cur为空时遍历停止
3.Morris遍历的实质
建立一种机制,对于没有左子树的节点只到达一次,对于有左子树的节点会到达两次。
先序、中序可以由morris遍历加工得到
后序遍历也可由morris遍历加工得到,但是把处理时机放在,能够达到两次的节点并且是第二次到达的时候
4.Morris遍历代码
public static class Node {
public int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
//Morris中序遍历,如果节点只出现一次,直接打印,如果出现两次,第二次打印
public static void morrisIn(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Node cur1 = head;
Node mostRight = null;
while (cur1 != null) {
mostRight = cur1.left; //mostRight是cur1的左孩子
if (mostRight != null) { //有左子树
//找到左子树中的最右节点
while (mostRight.right != null && mostRight.right != cur1) {
mostRight = mostRight.right;
}
//mostRight变成了cur1左子树上最右的节点
if (mostRight.right == null) { //第一次来到cur1节点
mostRight.right = cur1;
cur1 = cur1.left;
continue;
} else {
mostRight.right = null;
}
}
System.out.print(cur1.value + " ");
cur1 = cur1.right;
}
}
//Morris先序遍历,如果节点只出现一次,直接打印,如果出现两次,第一次打印
public static void morrisPre(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Node cur1 = head;
Node mostRight = null;
while (cur1 != null) {
mostRight = cur1.left;
if (mostRight != null) {
while (mostRight.right != null && mostRight.right != cur1) {
mostRight = mostRight.right;
}
if (mostRight.right == null) {
mostRight.right = cur1;
System.out.print(cur1.value + " ");
cur1 = cur1.left;
continue;
} else {
mostRight.right = null;
}
} else {
System.out.print(cur1.value + " ");
}
cur1 = cur1.right;
}
}
//Morris后序遍历
public static void morrisPos(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Node cur1 = head;
Node cur2 = null;
while (cur1 != null) {
cur2 = cur1.left;
if (cur2 != null) {
while (cur2.right != null && cur2.right != cur1) {
cur2 = cur2.right;
}
if (cur2.right == null) {
cur2.right = cur1;
cur1 = cur1.left;
continue;
} else {
cur2.right = null;
printEdge(cur1.left);
}
}
cur1 = cur1.right;
}
printEdge(head);
}
public static void printEdge(Node head) {
Node tail = reverseEdge(head);
Node cur = tail;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.right;
}
reverseEdge(tail);
}
public static Node reverseEdge(Node from) {
Node pre = null;
Node next = null;
while (from != null) {
next = from.right;
from.right = pre;
pre = from;
from = next;
}
return pre;
}
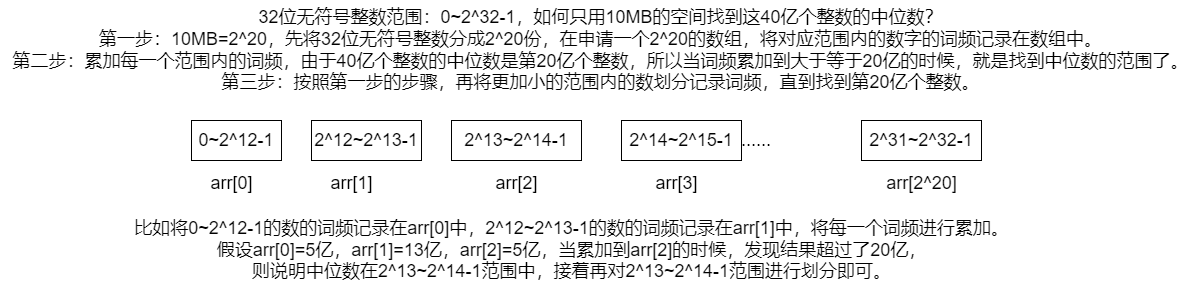
八、大数据题目
1.大数据题目的解题技巧
- 哈希函数可以把数据按照种类均匀分流
- 布隆过滤器用于集合的建立与查询,并可以节省大量空间
- 一致性哈希解决数据服务器的负载管理问题
- 利用并查集结构做岛问题的并行计算
- 位图解决某一范围上数字的出现情况,并可以节省大量空间
- 利用分段统计思想、并进一步节省大量空间
- 利用堆、外排序来做多个处理单元的结果合并
题目一

解法:
题目二

public static int flip(int n) {
return n ^ 1;
}
//n为非负数返回1,n为负数返回0
public static int sign(int n) {
return flip((n >> 31) & 1);
}
public static int getMax1(int a, int b) {
int c = a - b; //当c溢出的时候,该函数会出错
int scA = sign(c);
int scB = flip(scA);
return a * scA + b * scB;
}
public static int getMax2(int a, int b) {
int c = a - b;
int sa = sign(a); //a为非负数返回1,a为负数返回0
int sb = sign(b); //b为非负数返回1,b为负数返回0
int sc = sign(c); //c为非负数返回1,c为负数返回0
int difSab = sa ^ sb; //若sa和sb符号相同,则difSab为0,否则为1
int sameSab = flip(difSab); //若sa和sb符号相同,则sameSab为1,否则为0
int returnA = difSab * sa + sameSab * sc; //当sa和sb符号相同,且sc为1时,说明a>b;当sa和sb符号不同时,若sa为正,sb为负,则a>b返回1,若sa为负,sb为正,则a<b返回0。由于difSab和sameSab是互斥的,所以此处可用+连接两个表达式
int returnB = flip(returnA); //returnA与returnB互斥
return a * returnA + b * returnB; //若returnA为1,返回a;若returnB为1,返回b。
}
题目三

//2的幂说明二进制状态中只有一个1
public static boolean is2Power(int n) {
return (n & (n - 1)) == 0; //假设n为001000,则n-1为000111,两者相与为0则是2的幂,不为0则不是2的幂
}
//第一步:先判断是不是2的幂
//4:00000100 16:00010000 64:01000000
//可以发现4的幂的1的位置从右往左数都是放在奇数位上,所以与0x55555555可以知道奇数位上是不是1,如果是1则为4的幂,反之则不是
public static boolean is4Power(int n) {
return (n & (n - 1)) == 0 && (n & 0x55555555) != 0;
}
题目四

加法的图解:
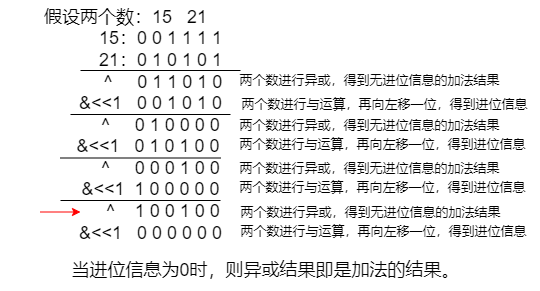
减法则是加法的逆运算,加上一个数的相反数即可,求相反数的做法就是对原数进行取反后加一即可。
乘法图解:

除法图解:

//如果用户传入的参数a+b就是溢出的,不用管
public static int add(int a, int b) {
int sum = a;
while (b != 0) { //当进位信息为空时,跳出循环
sum = a ^ b; //无进位加法的结果
b = (a & b) << 1; //进位信息
a = sum;
}
return sum;
}
public static int negNum(int n) {
return add(~n, 1);
}
public static int minus(int a, int b) {
return add(a, negNum(b));
}
public static int multi(int a, int b) {
int res = 0;
while (b != 0) {
if ((b & 1) != 0) { //判断b的最右边一位数是0还是1,若是1,则+a,若是0,则不加。
res = add(res, a);
}
a <<= 1;
b >>>= 1;
}
return res;
}
public static boolean isNeg(int n) {
return n < 0;
}
public static int div(int a, int b) {
//将x和y变为正数进行计算
int x = isNeg(a) ? negNum(a) : a;
int y = isNeg(b) ? negNum(b) : b;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 31; i > -1; i = minus(i, 1)) {
if ((x >> i) >= y) {
res |= (1 << i);
x = minus(x, y << i);
}
}
return isNeg(a) ^ isNeg(b) ? negNum(res) : res;
}
public static int divide(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("divisor is 0");
}
if (a == Integer.MIN_VALUE && b == Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
return 1;
} else if (a == Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
return 0;
} else if (b == Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
int res = div(add(a, 1), b);
return add(res, div(minus(a, multi(res, b)), b));
} else {
return div(a, b);
}
}
九、暴力递归到动态规划
一、简介
动态规划就是暴力尝试减少重复计算的技巧而已,这种技巧就是一个大型套路。
先写出用尝试的思路解决问题的递归函数,而不用操心时间复杂度。
这个过程是无可替代的,没有套路的,只能依靠个人智慧,或者足够多的经验。
但是怎么把尝试的版本,优化成动态规划,是有固定套路的,大体步骤如下
1)找到什么可变参数可以代表一个递归状态,也就是哪些参数一旦确定,返回值就确定了
2)把可变参数的所有组合映射成一张表,有 1 个可变参数就是一维表,2 个可变参数就是二维表,......
3)最终答案要的是表中的哪个位置,在表中标出
4)根据递归过程的 base case,把这张表的最简单、不需要依赖其他位置的那些位置填好值
5)根据递归过程非base case的部分,也就是分析表中的普遍位置需要怎么计算得到,那么这张表的填写顺序也就确定了
6)填好表,返回最终答案在表中位置的值
二、机器人到达指定位置方法数

public static int ways1(int N, int M, int K, int P) {
// 参数无效直接返回0
if (N < 2 || K < 1 || M < 1 || M > N || P < 1 || P > N) {
return 0;
}
// 总共N个位置,从M点出发,还剩K步,返回最终能达到P的方法数
return walk(N, M, K, P);
}
// N : 位置为1 ~ N,固定参数
// cur : 当前在cur位置,可变参数
// rest : 还剩res步没有走,可变参数
// P : 最终目标位置是P,固定参数
// 该函数的含义:只能在1~N这些位置上移动,当前在cur位置,走完rest步之后,停在P位置的方法数作为返回值返回
public static int walk(int N, int cur, int rest, int P) {
// 如果没有剩余步数了,当前的cur位置就是最后的位置
// 如果最后的位置停在P上,那么之前做的移动是有效的
// 如果最后的位置没在P上,那么之前做的移动是无效的
if (rest == 0) {
return cur == P ? 1 : 0;
}
// 如果还有rest步要走,而当前的cur位置在1位置上,那么当前这步只能从1走向2
// 后续的过程就是,来到2位置上,还剩rest-1步要走
if (cur == 1) {
return walk(N, 2, rest - 1, P);
}
// 如果还有rest步要走,而当前的cur位置在N位置上,那么当前这步只能从N走向N-1
// 后续的过程就是,来到N-1位置上,还剩rest-1步要走
if (cur == N) {
return walk(N, N - 1, rest - 1, P);
}
// 如果还有rest步要走,而当前的cur位置在中间位置上,那么当前这步可以走向左,也可以走向右
// 走向左之后,后续的过程就是,来到cur-1位置上,还剩rest-1步要走
// 走向右之后,后续的过程就是,来到cur+1位置上,还剩rest-1步要走
// 走向左、走向右是截然不同的方法,所以总方法数要都算上
return walk(N, cur + 1, rest - 1, P) + walk(N, cur - 1, rest - 1, P);
}
public static int ways2(int N, int M, int K, int P) {
// 参数无效直接返回0
if (N < 2 || K < 1 || M < 1 || M > N || P < 1 || P > N) {
return 0;
}
int[][] dp = new int[K + 1][N + 1];
dp[0][P] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= K; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
if (j == 1) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][2];
} else if (j == N) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][N - 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j + 1];
}
}
}
return dp[K][M];
}
public static int ways3(int N, int M, int K, int P) {
// 参数无效直接返回0
if (N < 2 || K < 1 || M < 1 || M > N || P < 1 || P > N) {
return 0;
}
int[] dp = new int[N + 1];
dp[P] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= K; i++) {
int leftUp = dp[1];// 左上角的值
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
int tmp = dp[j];
if (j == 1) {
dp[j] = dp[j + 1];
} else if (j == N) {
dp[j] = leftUp;
} else {
dp[j] = leftUp + dp[j + 1];
}
leftUp = tmp;
}
}
return dp[M];
}
三、换钱的最少货币数

public static int minCoins1(int[] arr, int aim) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || aim < 0) {
return -1;
}
return process(arr, 0, aim);
}
// 当前考虑的面值是arr[i],还剩rest的钱需要找零
// 如果返回-1说明自由使用arr[i..N-1]面值的情况下,无论如何也无法找零rest
// 如果返回不是-1,代表自由使用arr[i..N-1]面值的情况下,找零rest需要的最少张数
public static int process(int[] arr, int i, int rest) {
// base case:
// 已经没有面值能够考虑了
// 如果此时剩余的钱为0,返回0张
// 如果此时剩余的钱不是0,返回-1
if (i == arr.length) {
return rest == 0 ? 0 : -1;
}
// 最少张数,初始时为-1,因为还没找到有效解
int res = -1;
// 依次尝试使用当前面值(arr[i])0张、1张、k张,但不能超过rest
for (int k = 0; k * arr[i] <= rest; k++) {
// 使用了k张arr[i],剩下的钱为rest - k * arr[i]
// 交给剩下的面值去搞定(arr[i+1..N-1])
int next = process(arr, i + 1, rest - k * arr[i]);
if (next != -1) { // 说明这个后续过程有效
res = res == -1 ? next + k : Math.min(res, next + k);
}
}
return res;
}
public static int minCoins2(int[] arr, int aim) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || aim < 0) {
return -1;
}
int N = arr.length;
int[][] dp = new int[N + 1][aim + 1];
// 设置最后一排的值,除了dp[N][0]为0之外,其他都是-1
for (int col = 1; col <= aim; col++) {
dp[N][col] = -1;
}
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 从底往上计算每一行
for (int rest = 0; rest <= aim; rest++) { // 每一行都从左往右
dp[i][rest] = -1; // 初始时先设置dp[i][rest]的值无效
if (dp[i + 1][rest] != -1) { // 下面的值如果有效
dp[i][rest] = dp[i + 1][rest]; // dp[i][rest]的值先设置成下面的值
}
// 左边的位置不越界并且有效
if (rest - arr[i] >= 0 && dp[i][rest - arr[i]] != -1) {
if (dp[i][rest] == -1) { // 如果之前下面的值无效
dp[i][rest] = dp[i][rest - arr[i]] + 1;
} else { // 说明下面和左边的值都有效,取最小的
dp[i][rest] = Math.min(dp[i][rest],
dp[i][rest - arr[i]] + 1);
}
}
}
}
return dp[0][aim];
}
四、排成一条线的纸牌博弈问题

public static int win1(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
return Math.max(f(arr, 0, arr.length - 1), s(arr, 0, arr.length - 1));
}
//先手函数
//当前该你拿,自己在arr[i...j]范围上拿
//返回你的最好分数
public static int f(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
if (i == j) {
return arr[i];
}
return Math.max(arr[i] + s(arr, i + 1, j), arr[j] + s(arr, i, j - 1));
}
//后手函数
//当前不该你拿,是对方在arr[i...j]范围上拿
//返回你的最好分数
public static int s(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
if (i == j) {
return 0;
}
return Math.min(f(arr, i + 1, j), f(arr, i, j - 1));
}
public static int win2(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[][] f = new int[arr.length][arr.length];
int[][] s = new int[arr.length][arr.length];
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
f[j][j] = arr[j];
for (int i = j - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
f[i][j] = Math.max(arr[i] + s[i + 1][j], arr[j] + s[i][j - 1]);
s[i][j] = Math.min(f[i + 1][j], f[i][j - 1]);
}
}
return Math.max(f[0][arr.length - 1], s[0][arr.length - 1]);
}
五、象棋中马的跳法

public static int getWays(int x, int y, int step) {
return process(x, y, step);
}
//从(0,0)位置出发,去往(x,y)位置,必须跳step步
//返回方法数
public static int process(int x, int y, int step) {
if (x < 0 || x > 8 || y < 0 || y > 9) {
return 0;
}
if (step == 0) {
return (x == 0 && y == 0) ? 1 : 0;
}
//要到达的位置不越界,也有步数可以跳
return process(x - 1, y + 2, step - 1)
+ process(x + 1, y + 2, step - 1)
+ process(x + 2, y + 1, step - 1)
+ process(x + 2, y - 1, step - 1)
+ process(x + 1, y - 2, step - 1)
+ process(x - 1, y - 2, step - 1)
+ process(x - 2, y - 1, step - 1)
+ process(x - 2, y + 1, step - 1);
}
public static int dpWays(int x, int y, int step) {
if (x < 0 || x > 8 || y < 0 || y > 9 || step < 0) {
return 0;
}
int[][][] dp = new int[9][10][step + 1];
dp[0][0][0] = 1;
for (int h = 1; h <= step; h++) {
for (int r = 0; r < 9; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < 10; c++) {
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r - 1, c + 2, h - 1);
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r + 1, c + 2, h - 1);
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r + 2, c + 1, h - 1);
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r + 2, c - 1, h - 1);
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r + 1, c - 2, h - 1);
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r - 1, c - 2, h - 1);
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r - 2, c - 1, h - 1);
dp[r][c][h] += getValue(dp, r - 2, c + 1, h - 1);
}
}
}
return dp[x][y][step];
}
public static int getValue(int[][][] dp, int row, int col, int step) {
if (row < 0 || row > 8 || col < 0 || col > 9) {
return 0;
}
return dp[row][col][step];
}
六、Bob的生存概率

public static String bob1(int N, int M, int i, int j, int K) {
long all = (long) Math.pow(4, K);
long live = process(N, M, i, j, K);
long gcd = gcd(all, live);
return String.valueOf((live / gcd) + "/" + (all / gcd));
}
//N*M的区域,Bob从(row,col)位置出发,走rest步之后,获得的生存方法数
public static long process(int N, int M, int row, int col, int rest) {
if (row < 0 || row == N || col < 0 || col == M) {
return 0;
}
if (rest == 0) {
return 1;
}
long live = process(N, M, row - 1, col, rest - 1);
live += process(N, M, row + 1, col, rest - 1);
live += process(N, M, row, col - 1, rest - 1);
live += process(N, M, row, col + 1, rest - 1);
return live;
}
public static long gcd(long m, long n) {
return n == 0 ? m : gcd(n, m % n);
}
public static String bob2(int N, int M, int i, int j, int K) {
int[][][] dp = new int[N + 2][M + 2][K + 1];
for (int row = 1; row <= N; row++) {
for (int col = 1; col <= M; col++) {
dp[row][col][0] = 1;
}
}
for (int rest = 1; rest <= K; rest++) {
for (int row = 1; row <= N; row++) {
for (int col = 1; col <= M; col++) {
dp[row][col][rest] = dp[row - 1][col][rest - 1];
dp[row][col][rest] += dp[row + 1][col][rest - 1];
dp[row][col][rest] += dp[row][col - 1][rest - 1];
dp[row][col][rest] += dp[row][col + 1][rest - 1];
}
}
}
long all = (long) Math.pow(4, K);
long live = dp[i + 1][j + 1][K];
long gcd = gcd(all, live);
return String.valueOf((live / gcd) + "/" + (all / gcd));
}
七、矩阵的最小路径和

//记忆搜索法
public static int minPathSum(int[][] m) {
if (m == null || m[0] == null || m[0].length == 0) { //base case
return 0;
}
int row = m.length; //行数
int col = m[0].length; //列数
int[][] dp = new int[row][col];
for (int i = 0; i < dp.length; i++) { //将数组中的值全部初始化为-1,除了最右下角的值
for (int j = 0; j < dp[0].length; j++) {
dp[i][j] = -1;
}
}
return processPath(m, 0, 0, dp);
}
private static int processPath(int[][] m, int i, int j, int[][] dp) {
if (m == null || m[0] == null || m[0].length == 0 || i < 0 || i >= m.length || j < 0 || j >= m[0].length) { //base case
return 0;
}
if (dp[i][j] != -1) {
return dp[i][j];
}
int row = m.length;
int col = m[0].length;
if (i == row - 1 && j == col - 1) { //在右下角,直接返回右下角的数值
dp[i][j] = m[i][j];
} else if (i == row - 1) { //在最后一行,但不是右下角,只能向右走
dp[i][j] = m[i][j] + processPath(m, i, j + 1, dp);
} else if (j == col - 1) { //在最后一列,但不是右下角,只能向下走
dp[i][j] = m[i][j] + processPath(m, i + 1, j, dp);
}else{
dp[i][j] = m[i][j] + Math.min(processPath(m, i, j + 1, dp), processPath(m, i + 1, j, dp));
}
return dp[i][j];
}
//动态规划法
public static int minPathSum(int[][] m) {
if (m == null || m[0] == null || m[0].length == 0) { //base case
return 0;
}
int row = m.length; //行数
int col = m[0].length; //列数
int[][] dp = new int[row][col];
for (int i = 0; i < dp.length; i++) { //将数组中的值全部初始化为-1,除了最右下角的值
for (int j = 0; j < dp[0].length; j++) {
dp[i][j] = -1;
}
}
dp[row - 1][col - 1] = m[row - 1][col - 1];
for (int j = col - 2; j >= 0; j--) { //处理最下面一行
dp[row - 1][j] = dp[row - 1][j + 1] + m[row - 1][j];
}
for (int i = row - 2; i >= 0; i--) { //处理最右边一列
dp[i][col - 1] = dp[i + 1][col - 1] + m[i][col - 1];
}
for (int i = row - 2; i >= 0; i--) { //从下往上
for (int j = col - 2; j >= 0; j--) { //从右往左
dp[i][j] = m[i][j] + Math.min(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j + 1]);
}
}
return dp[0][0];
}





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号