集合(2):顶层接口Collection
集合(2):顶层接口Collection
一、Collection的概述
1、Collection的含义
是集合中的顶层接口,它存在由它扩展开来的继承体系,为什么要分出很多不同的集合?
因为我们需要根据元素是否唯一,是否有序来区分这么多集合
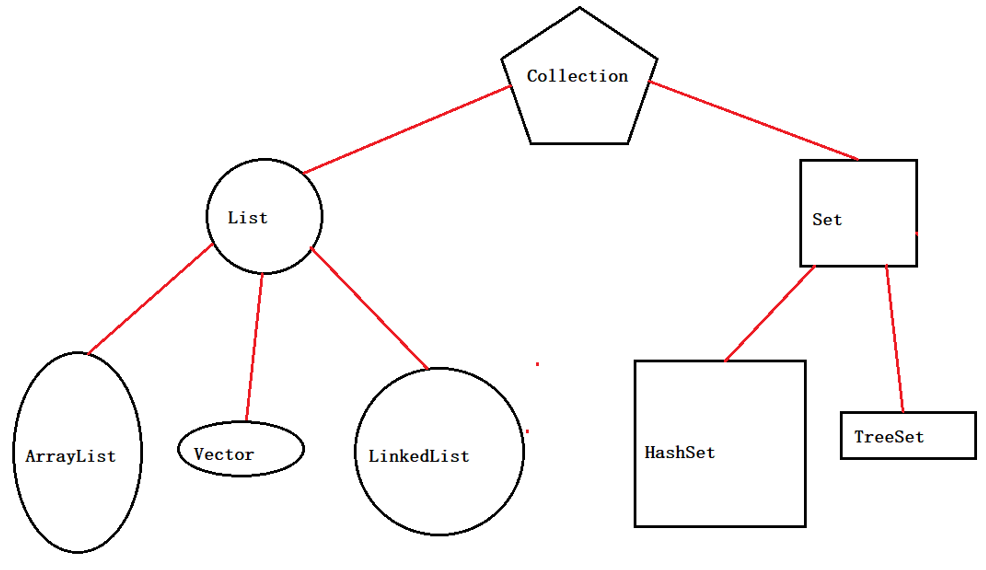
2、如何创建Collection对象
因为Collection是一个接口,接口不能实例化,想要创建Collection对象,必须使用它的子类来创建对象,
通过API查找List也是一个接口,也不能创建对象,继续向下寻找;
通过API查找到ArrayList是一个类,可以创建对象,属于接口多态创建对象
3、通过API查找Collection的方法
1、添加功能
(1)boolean add(Object obj)//来确认指定的元素是否成功加入到集合,返回boolean类型
(2)boolean addAll(Collection c)//将指定集合中的所有元素添加到此集合
2、删除功能
(1)boolean remove(Object o)
//输入一个集合中的元素,调用该方法来删除它,一次只能删除一个
//如果该方法有机会来删除它,返回true;如果没有机会,返回false
(2)boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)//删除指定集合中包含的所有此集合的元素(可选操作)
(3)void clear()//删除集合中的所有元素
3、获取功能
Iterator<E> iterator() //返回此集合中的元素的迭代器
4、判断功能
(1)boolean contains(Object o)//判断此集合包含指定的元素
(2)boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c)//如果此集合包含指定 集合中的所有元素,则返回true
(3)boolean isEmpty()//判断此集合还有没有元素,没有,则返回 true
5、获取长度功能
int size()//返回此集合中的元素数
6、求交集功能
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c)//从该集合中删除所有不包含在指定集合中的元素
7、将集合转换成数组
Object[] toArray()//返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组
案例1:运用到 了以下功能
集合的添加功能(1):boolean add(Object obj)
集合的删除功能(1):boolean remove(Object o)
集合的删除功能(3):void clear()
判断功能(1):boolean contains(Object o)
判断功能(3):boolean isEmpty()
获取长度功能:int size()
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class CollectionDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//通过Collection的子类ArrayList来创建对象
//这叫接口多态
Collection c = new ArrayList();
//集合的添加功能(1):boolean add(Object obj)
//来确认指定的元素是否成功加入到集合,返回boolean类型
//将元素添加到集合里面
System.out.println(c.add("hello"));//返回true,说明元素添加成功
System.out.println(c.add("hello"));//返回true,说明元素添加成功
//上面说明集合中的元素可以重复
c.add(20);//可以添加整型
c.add(12.34);//可以添加double型
//集合的删除功能(3):void clear()
//删除集合中的所有元素
// c.clear();
//此方法调用之后,集合元素已被清空
//集合的删除功能(1):boolean remove(Object o)
//输入一个集合中的元素,调用该方法来删除它,一次只能删除一个
//如果该方法有机会来删除它,返回true;如果没有机会,返回false
System.out.println(c.remove("hello"));//true
//如果上一个功能c.clear();执行的话,此结果将会返回false
//上一个功能删除了hello,但是不知道删了几个
//判断功能(1):boolean contains(Object o)
//如果此集合包含指定的元素,则返回true
System.out.println(c.contains("hello"));//true
//返回的是true,说明上一个功能只删除了一个,集合中还有hello
//判断功能(3):boolean isEmpty()
//如果此集合不包含元素,则返回true
System.out.println(c.isEmpty());//false
//获取长度功能:int size()
//返回此集合中的元素数
System.out.println(c.size());//3
System.out.println(c);//[hello, 20, 12.34]
//此结果可以说明ArrayList重写了toString()方法
/**
* java.lang.Object
* java.util.AbstractCollection<E>
* java.util.AbstractList<E>
* java.util.ArrayList<E>
*/
//实际上ArrayList是重写了AbstractList的toString()方法
}
}
案例2:运用到了以下功能
添加功能(2):boolean addAll(Collection c)
删除功能(2):boolean removeAll(Collection c)
判断功能(2):boolean containsAll(Collection c)
求交集功能:boolean retainAll(Collection c)
public class CollectionDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个集合对象
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
//向集合中添加元素
c1.add("hello");
c1.add("world");
c1.add("java");
c1.add("hadoop");
c1.add("hive");
// c1.add("spark");
//定义另一个集合
Collection c2 = new ArrayList();
c2.add("hello");
c2.add("world");
c2.add("hive");
c2.add("spark");
System.out.println("c1: "+c1);//c1: [hello, world, java, hadoop, hive]
System.out.println("c2: "+c2);//c2: [hello, world, hive, spark]
//添加功能(2):boolean addAll(Collection c)
//将c2中的所有元素添加到从c1中
System.out.println(c1.addAll(c2));//true
System.out.println("c1: "+c1);
//c1: [hello, world, java, hadoop, hive, hello, world, hive, spark]
System.out.println("c2: "+c2);
//c2: [hello, world, hive, spark]
//删除功能(2):boolean removeAll(Collection c) 删除指定集合中包含的所有此集合的元素
//此调用返回后,此集合将不包含与指定集合相同的元素。
System.out.println(c1.removeAll(c2));//true
System.out.println("c1: "+c1);//c1: [java, hadoop]
System.out.println("c2: "+c2);//c2: [hello, world, hive, spark]
//判断功能(2):boolean containsAll(Collection c)
//如果此集合包含指定集合中的所有元素,则返回true
System.out.println(c1.containsAll(c2));//false,c1包含c2的所有元素
//boolean retainAll(Collection c)
//从该集合中删除所有不包含在指定集合中的元素。
//假设有两个集合 c1,c2
//c1对c2做交集,最终的结果保存在c1中,c2不变
//删除c1中与c2不相同的元素
System.out.println(c1.retainAll(c2));//true
System.out.println("c1: "+c1);//c1: []
System.out.println("c2: "+c2);//c2: [hello, world, hive, spark]
}
}
4、把集合转成数组,可以实现集合的遍历
1、集合的遍历:目的就是将集合中的元素依次取出来
2、Object[] toArray():把集合转成数组,可以实现集合的遍历
案例1
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class CollectionDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
//添加String类型元素
c1.add("hello");
c1.add("world");
c1.add("java");
c1.add("20");
// c1.add(10);
//将集合转换成数组
Object[] array = c1.toArray();
//遍历数组获取数组中每一个元素
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
System.out.println(array[i]);
//如果想遍历的同时,也想输出元素的长度,怎么办?
/*
System.out.println(array[i].length());会报错
获取到的元素类型是父类Object类型,父类中没有length()方法
但是String类有length()方法
想调用字符串中的方法,就需要进行向下转型
*/
//向下转型,转成字符的类型,就可以调用length()方法了
String s = (String) array[i];
System.out.println("长度为:" + s.length());
}
}
}
执行结果如下:
hello
长度为:5
world
长度为:5
java
长度为:4
20
长度为:2
Process finished with exit code 0
案例2
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
/*
需求:向集合中添加3个学生对象,并遍历学生信息
*/
public class CollectionDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
//创建3个学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("李玉伟", 18);
Student s2 = new Student("刘生发", 17);
Student s3 = new Student("朱佳乐", 16);
//将学生对象添加到集合中
c1.add(s1);
c1.add(s2);
c1.add(s3);
//将学生对象集合转成数组
Object[] array = c1.toArray();
//遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
//向下转型,可以转成Student类型,可以调用getXxx()方法来接收
Student s = (Student) array[i];
System.out.println(s.getName() + "--" + s.getAge());
/*
System.out.println(array[i]);
//直接输出,输出的类型是Object类型,并不是Student类型
执行结果如下:
Student{name='李玉伟', age=18}
Student{name='刘生发', age=17}
Student{name='朱佳乐', age=16}
Process finished with exit code 0
*/
}
}
}
执行结果为:
李玉伟--18
刘生发--17
朱佳乐--16
Process finished with exit code 0
小结
(1)如果集合中添加的是字符串,调用集合以外的方法,需要向下转型,转型要转成字符类型
//String s = (String) array[i];
(2)如果集合中添加的是对象,调用集合以外的方法,需要向下转型,转型要转成对象类型
//Student s = (Student) array[i];
向下转型的目的:(1)为了调用集合以外的方法 (2)使输出的类型和添加的类型一致
5、迭代器:集合的专用遍历方式
1、迭代器的概述
(1)遍历数组的时候,之前我们用的都是for()循环;但是在集合中,提供了一个专门遍历集合的东西,叫做迭代器
迭代器只能在集合中使用
(2)迭代器有自己的类型,叫做Iterator类型,Iterator类有很多方法,其中就包含了遍历集合的方法
(3)通过查找API,发现Iterator类属于一个接口类型
2、迭代器的使用
(1)迭代器的方法
①Iterator iterator()
//迭代器,集合的专用遍历方式。使用的时候需要用集合的对象名调用,调用的时候需要接收
②boolean hasNext()
//判断下一位置是否还有元素,如果有,返回true
③Object next():
//调用该方法,依次获取迭代器中的元素,调用一次,就获取一个元素
(2)迭代器的使用
案例1:使用迭代器遍历集合中的元素(元素是String类)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class CollectionDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
//向集合中添加元素
c1.add("hello");
c1.add("world");
c1.add("java");
c1.add("hadoop");
//调用迭代器,获取添加的元素到迭代器里,返回的是Iterator对象
Iterator i = c1.iterator();
/*
调用迭代器之后,i里面就存放了集合的元素
System.out.println(i);
直接打印输出的是地址值java.util.ArrayList$Itr@4554617c
java.util.ArrayList表示ArrayList对象的迭代器
Itr说明底层调用的是Itr对象
@4554617c是Itr的地址值
总体意思是:返回的是ArrayList特有的Itr迭代器
*/
//需要调用迭代器的Object next()方法,依次输出迭代器中的元素
//调用方法的次数不能超过集合中元素的个数,否则会报错
//调用依次只能获得一个元素
//System.out.println(i.next());//hello
//System.out.println(i.next());//world
//System.out.println(i.next());//java
//System.out.println(i.next());//hadoop
/*
当集合的元素有很多的时候,我们不确定要调用next()方法多少次,
实际应该在获取之前加入判断功能:boolean hasNext();
判断一下下一个位置上是否有元素,如果有,就next()获取;如果没有,就不获取
if(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
....
加入判断的时候,如果元素很多,依旧不知道到底要判断多少次
这时候就需要使用循环结构
*/
//由于不确定什么时候结束循环,因此使用while循环
while (i.hasNext()) {//判断下一位置是否还有元素,如果是true,就执行循环语句
Object next = i.next();//调用Object next()方法来获取元素
//向下转型,并调用length()方法来获取长度
String s = (String) next;
System.out.println(s + ",长度为:" + s.length());
}
}
}
执行结果如下:
hello,长度为:5
world,长度为:5
java,长度为:4
hadoop,长度为:6
Process finished with exit code 0
案例2:使用迭代器遍历集合中的元素(元素是对象信息)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class CollectionDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建学生集合对象
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
//创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("张咪", 16);
Student s2 = new Student("张梦云", 17);
Student s3 = new Student("刘梦云", 18);
//将学生对象添加到集合中
c1.add(s1);
c1.add(s2);
c1.add(s3);
//获取迭代器对象
Iterator i = c1.iterator();
//遍历迭代器对象,获取迭代器中的每个元素
while (i.hasNext()) {
Object next = i.next();
//向下转型,调用getXxx()来接收
Student s = (Student) next;
System.out.println(s.getName() + "--" + s.getAge());
}
}
}
执行结果如下:
张咪--16
张梦云--17
刘梦云--18
Process finished with exit code 0
1、能否将while循环改成普通for循环呢?能,但是不推荐,推荐使用whil循环
2、为什么将Iterator一个接口呢?而不是一个类呢?
将来你需要根据不同的数据创建不同的集合进行存储,每个集合都有自身独有特点,很有可能每一个
集合遍历的顺序特点不一样,所以取值的方式也很有可能不一样,所以不应该直接实现,而是通过一个接口
将来特有的集合要去使用迭代器时候,就实现一下这个接口,添加自己特有的遍历元素逻辑代码
二、 Collection集合编写代码,完整代码1.0版本
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/*
需求:将5个学生对象添加到集合中并遍历
*/
public class CollectionDemo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建学生集合对象
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
//创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("张咪", 16);
Student s2 = new Student("张梦云", 17);
Student s3 = new Student("刘梦云", 18);
Student s4 = new Student("贝贝", 20);
Student s5 = new Student("姜水旺", 21);
//将学生对象添加到集合中
c1.add(s1);
c1.add(s2);
c1.add(s3);
c1.add(s4);
c1.add(s5);
//获取集合中的迭代器对象
Iterator iterator = c1.iterator();
//遍历迭代器元素
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
//向下转型
Student s = (Student) next;
System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge());
}
}
}
执行结果如下:
张咪---16
张梦云---17
刘梦云---18
贝贝---20
姜水旺---21
Process finished with exit code 0




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号