蚂蚁通讯框架SOFABolt之私有通讯协议设计

前言
SOFABolt 是蚂蚁金融服务集团开发的一套基于 Netty 实现的网络通信框架。
-
为了让 Java 程序员能将更多的精力放在基于网络通信的业务逻辑实现上,而不是过多的纠结于网络底层 NIO 的实现以及处理难以调试的网络问题,Netty 应运而生。
-
为了让中间件开发者能将更多的精力放在产品功能特性实现上,而不是重复地一遍遍制造通信框架的轮子,SOFABolt 应运而生。
Bolt 名字取自迪士尼动画-闪电狗,是一个基于 Netty 最佳实践的轻量、易用、高性能、易扩展的通信框架。 这些年蚂蚁金融服务集团在微服务与消息中间件在网络通信上解决过很多问题,积累了很多经验,并持续的进行着优化和完善,希望能把总结出的解决方案沉淀到 SOFABolt 这个基础组件里,让更多的使用网络通信的场景能够统一受益。 目前该产品已经运用在了蚂蚁中间件的微服务 (SOFARPC)、消息中心、分布式事务、分布式开关、以及配置中心等众多产品上。
调试环境搭建
依赖工具
-
Maven
-
Git
-
JDK
-
IntelliJ IDEA
源码拉取
从官方仓库https://github.com/alipay/sofa-bolt Fork 出属于自己的仓库,为什么要Fork ? 既然开始阅读、调试源码,我们可能会写一些注释,有了自己的仓库,可以进行自由的提交。😈
使用 IntelliJ IDEA 从 Fork 出来的仓库拉取代码。
example 模块
在test模块里,官网提供了多个Bolt的使用示例。
我们提供了一个 RpcClient 与 RpcServer,经过简单的必要功能初始化,或者功能开关,即可使用。
RpcServer
执行 com.alipay.remoting.demo.RpcServerDemoByMain 的 #main(args) 方法,启动服务端。输出日志如下:
Sofa-Middleware-Log SLF4J : Actual binding is of type [ com.alipay.remoting Log4j2 ] server start ok!
RpcClient
执行 com.alipay.remoting.demo.RpcClientDemoByMain 的 #main(args) 方法,启动服务端。输出日志如下:
Sofa-Middleware-Log SLF4J : Actual binding is of type [ com.alipay.remoting Log4j2 ] invoke sync result = [HELLO WORLD! I'm server return]
如此,我们就可以愉快的进行 Netty 调试啦。读源码,一定要多多调试源码。非常重要!!!👿
私有通讯协议设计
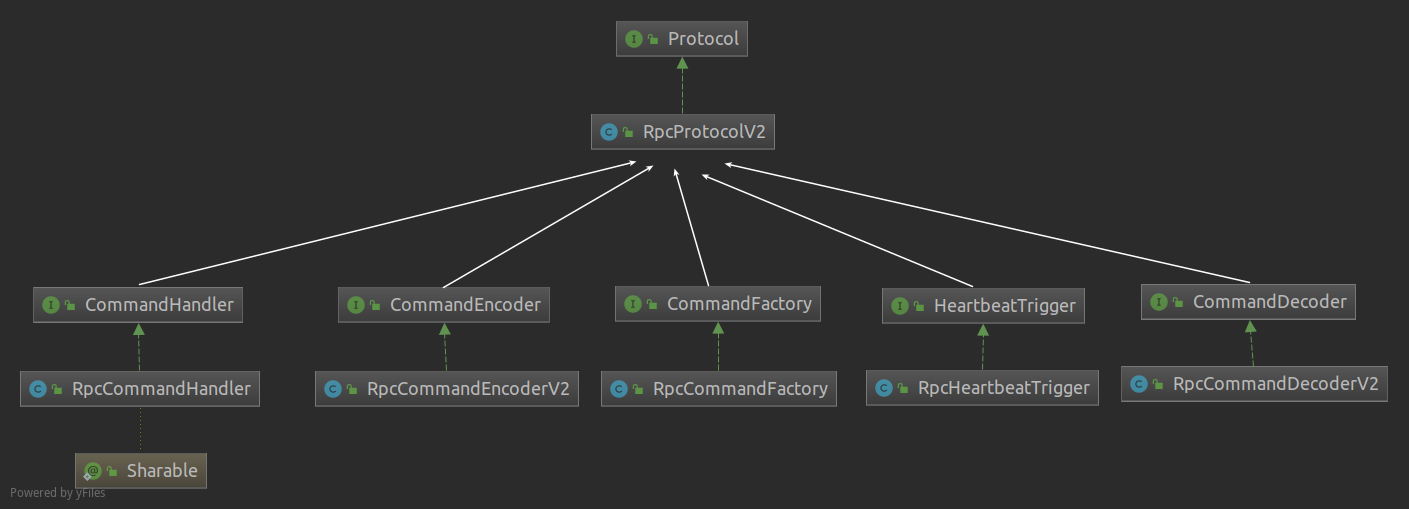
图1 - 私有协议与必要功能模块
Protocol
| 字段名 | 字节范围 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| proto | 1字节 | 协议的魔数 |
| ver1 | 1字节 | 协议版本 |
| type | 1字节 | (1)request (2)response (3) request oneway |
| cmdcode | 2字节 | 远程命令代码 |
| ver2 | 1字节 | 远程命令版本 |
| requestId | 4字节 | 请求ID |
| codec | 1字节 | 序列化代码 |
| switch | 1字节 | 协议功能开关 |
| timeout或者respstatus | 4字节或者2字节 | 请求超时或者回复状态 |
| classLen | 2字节 | 请求或响应类名称的长度 |
| headerLen | 2字节 | 协议头长度 |
| contentLen | 4字节 | 协议内容长度 |
| content | N字节 | 内容 |
| CRC32(optional) | 4字节 | 帧的CRC32(当ver1> 1时存在) |
在Bolt通讯框架中,有2个协议规范。因为设计误差,其中RpcProtocol这个协议版本被废弃,以下的解读为RpcProtocolV2版本。
-
首先,第一个字段是魔数,通常情况下为固定的几个字节(我们这边规定为1个字节)。 为什么需要这个字段,而且还是一个固定的数?假设我们在服务器上开了一个端口,比如 80 端口,如果没有这个魔数,任何数据包传递到服务器,服务器都会根据自定义协议来进行处理。 例如,我们直接通过
http://服务器ip来访问服务器(默认为 80 端口), 服务端收到的是一个标准的 HTTP 协议数据包,但是它仍然会按照事先约定好的协议来处理 HTTP 协议,显然,这是会解析出错的。而有了这个魔数之后,服务端首先取出前面四个字节进行比对,能够在第一时间识别出这个数据包并非是遵循自定义协议的,也就是无效数据包,为了安全考虑可以直接关闭连接以节省资源。 在 Java 的字节码的二进制文件中,开头的 1 个字节为(byte)2用来标识这是个字节码文件,亦是异曲同工之妙。 -
接下来一个字节为版本号,通常情况下是预留字段,用于协议升级的时候用到,有点类似 TCP 协议中的一个字段标识是 IPV4 协议还是 IPV6 协议,其中第一个版本为(byte) 1,第二个版本为(byte) 2。
-
第三部分,type表示Rpc类型是请求命令还是回复命令。其中请求命令分为request_oneway和request,其中request_oneway代表单工,即只请求,不用回复。而request就是常规的请求回复模型。
-
第四部分是远程命令代码,远程命令代码代表一种特定的远程命令,每种命令有自己的编号。其中在Bolt,(short) 0被心跳所占用,不能被其他命令所使用。
-
第五部分是远程命令代码版本,其作用和协议版本作用相同,为预留字段,用于远程命令版本升级的时候用到。
-
第六部分为请求编号,
-
第七部分为序列化代码,虽然字段标示是codec,但是实际的意思为Serializer,二者是不同的意思。Serializer主要用于将字节反序列化为对象,或将对象序列化为字节。我们可以使用hessian,json,protocol buff等。默认序列化为Hessian2。
-
第八部分为功能开关,这个可以对通讯协议部分功能的开启还是关闭来决定是否编解码此位置,例如通过判断协议crc功能是否开启,判断是否对内容进行循环冗余校验。
-
第九部分为timeout或respstatus,在Rpc请求命令中此位置为timout(超时时间),在Rpc回复命令中此位置为respstatus(回复状态)。回复状态有SUCCESS,ERROR,SERVER_EXCEPTION,TIMEOUT等。
-
第十部分为classLen,headerLen,contentLen。这些字段表示在负载内容中,类,头部以及内容所占的长度。
-
CRC32(optional),最后这个字段是可选择的,通过协议开关来决定是否对内容进行循环冗余校验。
Encoder 与 Decoder
协议相关的编解码方式: 私有协议需要有核心的encode与decode过程,并且针对业务负载能支持不同的序列化与反序列化机制。这部分,不同的私有协议,由于字段的差异,核心encode和decode过程是不一样的,因此需要分开考虑。
Encoder
首先我们来看编码实现,源代码路径 com.alipay.remoting.rpc.protocol.RpcCommandEncoderV2, 代码如下:
1 /** 2 * Encode remoting command into ByteBuf v2. 3 * 编码远程命令成ByteBuf 第二版本 4 * 5 * @author jiangping 6 * @version $Id: RpcCommandEncoderV2.java, v 0.1 2017-05-27 PM8:11:27 tao Exp $ 7 */ 8 public class RpcCommandEncoderV2 implements CommandEncoder { 9 /** logger 日志 */ 10 private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger("RpcRemoting"); 11 12 /** 13 * @see CommandEncoder#encode(ChannelHandlerContext, Serializable, ByteBuf) 14 */ 15 @Override 16 public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Serializable msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception { 17 try { 18 if (msg instanceof RpcCommand) { 19 /* 20 * proto: magic code for protocol 协议的魔数 21 * ver: version for protocol 协议版本 22 * type: request/response/request oneway Rpc命令类型 23 * cmdcode: code for remoting command 远程命令代码 24 * ver2:version for remoting command 远程命令版本 25 * requestId: id of request 请求编号 26 * codec: code for codec 序列化代码 27 * switch: function switch 协议功能开关 28 * (req)timeout: request timeout. 当命令类型是请求时,此位置为超时时间,4个字节 29 * (resp)respStatus: response status 当命令类型是回复时,此位置为回复状态,2个字节 30 * classLen: length of request or response class name 请求类和回复类的长度 31 * headerLen: length of header 头部长度 32 * cotentLen: length of content 内容长度 33 * className 类名 34 * header 协议 35 * content 内容 36 * crc (optional) 帧的CRC32(当ver1 > 1时存在) 37 */ 38 int index = out.writerIndex(); //写指针 39 RpcCommand cmd = (RpcCommand) msg; 40 //写入版本魔数 (byte) 2 41 out.writeByte(RpcProtocolV2.PROTOCOL_CODE); 42 //从连接属性中获取协议版本 43 Attribute<Byte> version = ctx.channel().attr(Connection.VERSION); 44 byte ver = RpcProtocolV2.PROTOCOL_VERSION_1; 45 if (version != null && version.get() != null) { 46 ver = version.get(); 47 } 48 //写入协议版本 49 out.writeByte(ver); 50 //写入RPC类型代码 51 out.writeByte(cmd.getType()); 52 //写入RPC远程命令代码值 53 out.writeShort(((RpcCommand) msg).getCmdCode().value()); 54 //写入远程命令版本 55 out.writeByte(cmd.getVersion()); 56 //写入Rpc编号 57 out.writeInt(cmd.getId()); 58 //写入协议序列化值 59 out.writeByte(cmd.getSerializer()); 60 //写入协议功能开关 61 out.writeByte(cmd.getProtocolSwitch().toByte()); 62 // 判断命令是RequestCommand还是ResponseCommand来写入超时还是回复状态值 63 if (cmd instanceof RequestCommand) { 64 //timeout 65 out.writeInt(((RequestCommand) cmd).getTimeout()); 66 } 67 if (cmd instanceof ResponseCommand) { 68 //response status 69 ResponseCommand response = (ResponseCommand) cmd; 70 out.writeShort(response.getResponseStatus().getValue()); 71 } 72 //写入类长度 73 out.writeShort(cmd.getClazzLength()); 74 //写入头部长度 75 out.writeShort(cmd.getHeaderLength()); 76 //写入内容长度 77 out.writeInt(cmd.getContentLength()); 78 //写入类 79 if (cmd.getClazzLength() > 0) { 80 out.writeBytes(cmd.getClazz()); 81 } 82 //写入头部 83 if (cmd.getHeaderLength() > 0) { 84 out.writeBytes(cmd.getHeader()); 85 } 86 //写入内容 87 if (cmd.getContentLength() > 0) { 88 out.writeBytes(cmd.getContent()); 89 } 90 //通过判断协议是v2且crc功能是开启的,对内容进行循环冗余校验 91 if (ver == RpcProtocolV2.PROTOCOL_VERSION_2 92 && cmd.getProtocolSwitch().isOn(ProtocolSwitch.CRC_SWITCH_INDEX)) { 93 // compute the crc32 and write to out 94 byte[] frame = new byte[out.readableBytes()]; 95 out.getBytes(index, frame); 96 out.writeInt(CrcUtil.crc32(frame)); 97 } 98 } else { 99 // 抛出异常 100 String warnMsg = "msg type [" + msg.getClass() + "] is not subclass of RpcCommand"; 101 logger.warn(warnMsg); 102 } 103 } catch (Exception e) { 104 logger.error("Exception caught!", e); 105 throw e; 106 } 107 } 108 }
从代码中,我们可以看到Netty里面的数据读写是以ByteBuf为单位进行交互的,我们就来简要了解一下ByteBuf。
ByteBuf结构
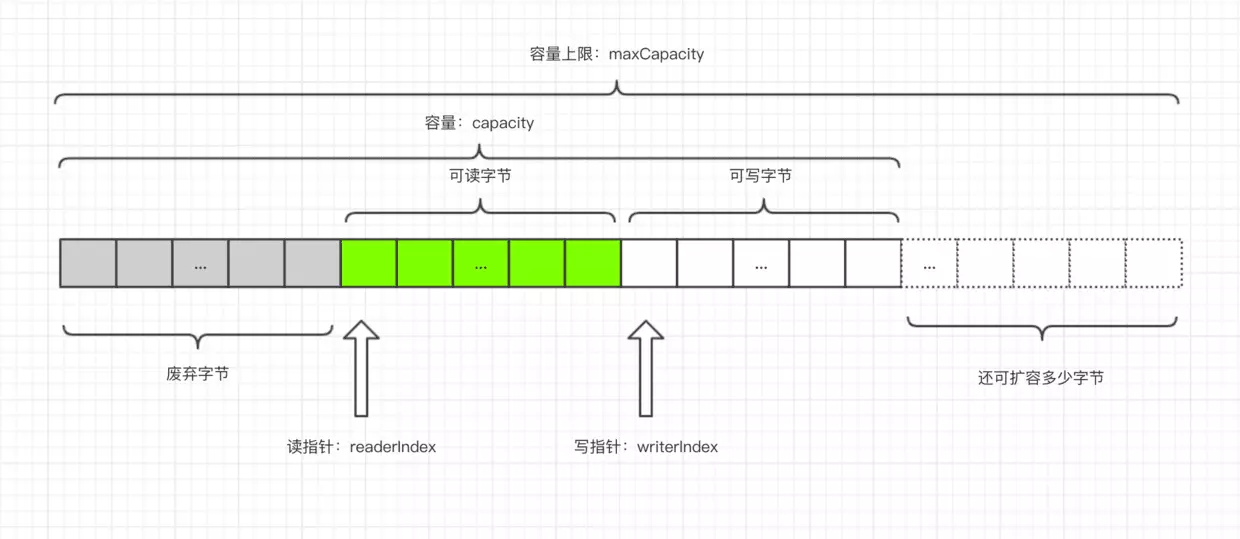
以上就是一个 ByteBuf 的结构图,从上面这幅图可以看到
-
ByteBuf 是一个字节容器,容器里面的的数据分为三个部分,第一个部分是已经丢弃的字节,这部分数据是无效的;第二部分是可读字节,这部分数据是 ByteBuf 的主体数据, 从 ByteBuf 里面读取的数据都来自这一部分;最后一部分的数据是可写字节,所有写到 ByteBuf 的数据都会写到这一段。最后一部分虚线表示的是该 ByteBuf 最多还能扩容多少容量
-
以上三段内容是被两个指针给划分出来的,从左到右,依次是读指针(readerIndex)、写指针(writerIndex),然后还有一个变量 capacity,表示 ByteBuf 底层内存的总容量
-
从 ByteBuf 中每读取一个字节,readerIndex 自增1,ByteBuf 里面总共有 writerIndex-readerIndex 个字节可读, 由此可以推论出当 readerIndex 与 writerIndex 相等的时候,ByteBuf 不可读
-
写数据是从 writerIndex 指向的部分开始写,每写一个字节,writerIndex 自增1,直到增到 capacity,这个时候,表示 ByteBuf 已经不可写了
-
ByteBuf 里面其实还有一个参数 maxCapacity,当向 ByteBuf 写数据的时候,如果容量不足,那么这个时候可以进行扩容,直到 capacity 扩容到 maxCapacity,超过 maxCapacity 就会报错
Netty 使用 ByteBuf 这个数据结构可以有效地区分可读数据和可写数据,读写之间相互没有冲突,当然,ByteBuf 只是对二进制数据的抽象,具体底层的实现我们在下面的小节会讲到,在这一小节,我们 只需要知道 Netty 关于数据读写只认 ByteBuf。
容量 API
capacity()
表示 ByteBuf 底层占用了多少字节的内存(包括丢弃的字节、可读字节、可写字节),不同的底层实现机制有不同的计算方式,后面我们讲 ByteBuf 的分类的时候会讲到
maxCapacity()
表示 ByteBuf 底层最大能够占用多少字节的内存,当向 ByteBuf 中写数据的时候,如果发现容量不足,则进行扩容,直到扩容到 maxCapacity,超过这个数,就抛异常
readableBytes() 与 isReadable()
readableBytes() 表示 ByteBuf 当前可读的字节数,它的值等于 writerIndex-readerIndex,如果两者相等,则不可读,isReadable() 方法返回 false
writableBytes()、 isWritable() 与 maxWritableBytes()
writableBytes() 表示 ByteBuf 当前可写的字节数,它的值等于 capacity-writerIndex,如果两者相等,则表示不可写,isWritable() 返回 false,但是这个时候,并不代表不能往 ByteBuf 中写数据了, 如果发现往 ByteBuf 中写数据写不进去的话,Netty 会自动扩容 ByteBuf,直到扩容到底层的内存大小为 maxCapacity,而 maxWritableBytes() 就表示可写的最大字节数,它的值等于 maxCapacity-writerIndex
读写API
本质上,关于 ByteBuf 的读写都可以看作从指针开始的地方开始读写数据
writeBytes(byte[] src) 与 buffer.readBytes(byte[] dst)
writeBytes() 表示把字节数组 src 里面的数据全部写到 ByteBuf,而 readBytes() 指的是把 ByteBuf 里面的数据全部读取到 dst,这里 dst 字节数组的大小通常等于 readableBytes(),而 src 字节数组大小的长度通常小于等于 writableBytes()
writeByte(byte b) 与 buffer.readByte()
writeByte() 表示往 ByteBuf 中写一个字节,而 buffer.readByte() 表示从 ByteBuf 中读取一个字节,类似的 API 还有 writeBoolean()、writeChar()、writeShort()、writeInt()、writeLong()、writeFloat()、writeDouble() 与 readBoolean()、readChar()、readShort()、readInt()、readLong()、readFloat()、readDouble() 这里就不一一赘述了,相信读者应该很容易理解这些 API
与读写 API 类似的 API 还有 getBytes、getByte() 与 setBytes()、setByte() 系列,唯一的区别就是 get/set 不会改变读写指针,而 read/write 会改变读写指针。
Decoder
接下来我们来看解码实现过程,源代码路径 com.alipay.remoting.rpc.protocol.RpcCommandDecoderV2。
首先需要可读数据进行长度判断,是否大于请求报文头部和回复报文头部的最小长度。以及对ByteBuf进行魔数的验证,当不是可识别的协议,即抛出异常。
代码如下:
private int lessLen; { lessLen = RpcProtocolV2.getResponseHeaderLength() < RpcProtocolV2.getRequestHeaderLength() ? RpcProtocolV2 .getResponseHeaderLength() : RpcProtocolV2.getRequestHeaderLength(); } // 请求报文头部和回复报文头部的最小长度 // the less length between response header and request header if (in.readableBytes() >= lessLen) { //保存当前的读指针 in.markReaderIndex(); //读取协议魔数 byte protocol = in.readByte(); //恢复读指针到原来的位置,即 in.mark..位置 in.resetReaderIndex(); if (protocol == RpcProtocolV2.PROTOCOL_CODE) { ...... } else { //发现魔数异常,抛出不知道的协议错误! String emsg = "Unknown protocol: " + protocol; logger.error(emsg); throw new RuntimeException(emsg); } }
读写指针相关的 API
readerIndex() 与 readerIndex(int)
前者表示返回当前的读指针 readerIndex, 后者表示设置读指针
writeIndex() 与 writeIndex(int)
前者表示返回当前的写指针 writerIndex, 后者表示设置写指针
markReaderIndex() 与 resetReaderIndex()
前者表示把当前的读指针保存起来,后者表示把当前的读指针恢复到之前保存的值,下面两段代码是等价的
// 代码片段1
int readerIndex = buffer.readerIndex();
// .. 其他操作
buffer.readerIndex(readerIndex);
// 代码片段二
buffer.markReaderIndex();
// .. 其他操作
buffer.resetReaderIndex();
希望大家多多使用代码片段二这种方式,不需要自己定义变量,无论 buffer 当作参数传递到哪里,调用 resetReaderIndex() 都可以恢复到之前的状态,在解析自定义协议的数据包的时候非常常见,推荐大家使用这一对 API
markWriterIndex() 与 resetWriterIndex()
RPC请求命令解码和回复命令解码是相似的,以下我以请求解码为例进行解读:
1 if (type == RpcCommandType.REQUEST || type == RpcCommandType.REQUEST_ONEWAY) { 2 //decode request 因已经读取三个byte了,所以需要减3 3 if (in.readableBytes() >= RpcProtocolV2.getRequestHeaderLength() - 3) { 4 short cmdCode = in.readShort(); 5 byte ver2 = in.readByte(); 6 int requestId = in.readInt(); 7 byte serializer = in.readByte(); 8 byte protocolSwitchValue = in.readByte(); 9 int timeout = in.readInt(); 10 short classLen = in.readShort(); 11 short headerLen = in.readShort(); 12 int contentLen = in.readInt(); 13 byte[] clazz = null; 14 byte[] header = null; 15 byte[] content = null; 16 17 // decide the at-least bytes length for each version 18 int lengthAtLeastForV1 = classLen + headerLen + contentLen; 19 //判断协议是否开启CRC,如有,最小bytes长度加4 20 boolean crcSwitchOn = ProtocolSwitch.isOn( 21 ProtocolSwitch.CRC_SWITCH_INDEX, protocolSwitchValue); 22 int lengthAtLeastForV2 = classLen + headerLen + contentLen; 23 if (crcSwitchOn) { 24 lengthAtLeastForV2 += 4;// crc int 25 } 26 27 // 如果满足V1协议且长度大于最小V1协议长度 或 满足V2协议且长度大于最小V2协议长度,则继续读取 28 // continue read 29 if ((version == RpcProtocolV2.PROTOCOL_VERSION_1 && in.readableBytes() >= lengthAtLeastForV1) 30 || (version == RpcProtocolV2.PROTOCOL_VERSION_2 && in 31 .readableBytes() >= lengthAtLeastForV2)) { 32 // 读取类 33 if (classLen > 0) { 34 clazz = new byte[classLen]; 35 in.readBytes(clazz); 36 } 37 // 读取头部 38 if (headerLen > 0) { 39 header = new byte[headerLen]; 40 in.readBytes(header); 41 } 42 // 读取内容 43 if (contentLen > 0) { 44 content = new byte[contentLen]; 45 in.readBytes(content); 46 } 47 if (version == RpcProtocolV2.PROTOCOL_VERSION_2 && crcSwitchOn) { 48 //校验内容 49 checkCRC(in, startIndex); 50 } 51 } else {// not enough data 不足够的数据,重置读指针 52 in.resetReaderIndex(); 53 return; 54 } 55 56 RequestCommand command; 57 //判断是心跳命令还是请求命令 58 if (cmdCode == CommandCode.HEARTBEAT_VALUE) { 59 command = new HeartbeatCommand(); 60 } else { 61 command = createRequestCommand(cmdCode); 62 } 63 //封装实体 64 command.setType(type); 65 command.setVersion(ver2); 66 command.setId(requestId); 67 command.setSerializer(serializer); 68 command.setProtocolSwitch(ProtocolSwitch.create(protocolSwitchValue)); 69 command.setTimeout(timeout); 70 command.setClazz(clazz); 71 command.setHeader(header); 72 command.setContent(content); 73 74 out.add(command); 75 } else { 76 in.resetReaderIndex(); 77 } 78
Heartbeat
协议相关的心跳触发与处理:不同的协议对心跳的需求,处理逻辑也可能是不同的。因此心跳的触发逻辑,心跳的处理逻辑,也都需要单独考虑。源代码路径为:com.alipay.remoting.rpc.protocol.RpcHeartbeatTrigger。
/** max trigger times 最大触发次数,默认为3次 */ public static final Integer maxCount = ConfigManager.tcp_idle_maxtimes(); private static final long heartbeatTimeoutMillis = 1000; @Override public void heartbeatTriggered(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { //获得连接心跳次数 Integer heartbeatTimes = ctx.channel().attr(Connection.HEARTBEAT_COUNT).get(); final Connection conn = ctx.channel().attr(Connection.CONNECTION).get(); //如果心跳次数触发大于3次,则关闭连接 if (heartbeatTimes >= maxCount) { try { conn.close(); //抛出异常 logger.error( "Heartbeat failed for {} times, close the connection from client side: {} ", heartbeatTimes, RemotingUtil.parseRemoteAddress(ctx.channel())); } catch (Exception e) { logger.warn("Exception caught when closing connection in SharableHandler.", e); } } else { boolean heartbeatSwitch = ctx.channel().attr(Connection.HEARTBEAT_SWITCH).get(); if (!heartbeatSwitch) { return; } final HeartbeatCommand heartbeat = new HeartbeatCommand(); final InvokeFuture future = new DefaultInvokeFuture(heartbeat.getId(), new InvokeCallbackListener() { @Override public void onResponse(InvokeFuture future) { ResponseCommand response; ...... // 触发次数加一 Integer times = ctx.channel().attr(Connection.HEARTBEAT_COUNT).get(); ctx.channel().attr(Connection.HEARTBEAT_COUNT).set(times + 1); } } @Override public String getRemoteAddress() { return ctx.channel().remoteAddress().toString(); } }, null, heartbeat.getProtocolCode().getFirstByte(), this.commandFactory); final int heartbeatId = heartbeat.getId(); conn.addInvokeFuture(future); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Send heartbeat, successive count={}, Id={}, to remoteAddr={}", heartbeatTimes, heartbeatId, RemotingUtil.parseRemoteAddress(ctx.channel())); } //异步回调结果 ctx.writeAndFlush(heartbeat).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { ...... } }); //TimerHolder为Netty工具类时间轮算法实现 TimerHolder.getTimer().newTimeout(new TimerTask() { @Override public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception { InvokeFuture future = conn.removeInvokeFuture(heartbeatId); if (future != null) { future.putResponse(commandFactory.createTimeoutResponse(conn .getRemoteAddress())); future.tryAsyncExecuteInvokeCallbackAbnormally(); } } }, heartbeatTimeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } }
对HashedWheelTimer感兴趣的人,可以了解一下以下文章。
Command 与 Command Handler
-
可扩展的命令与命令处理器管理
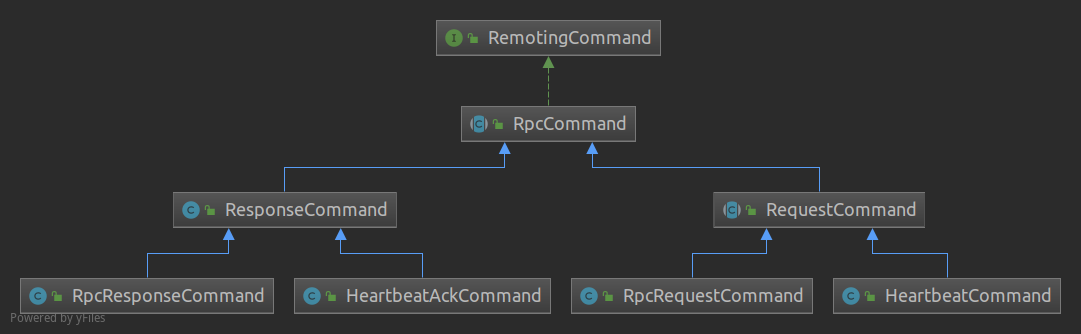
图2 - 通信命令设计举例
-
负载命令:一般传输的业务的具体数据,比如带着请求参数,响应结果的命令;
-
控制命令:一些功能管理命令,心跳命令等,它们通常完成一些复杂的分布式跨节点的协调功能,以此来保证负载命令通信过程的稳定,是必不可少的一部分。
-
协议的通信过程,会有各种命令定义,逻辑上,我们把传输业务具体负载的请求对象,叫做负载命令(Payload Command),另一种叫做控制命令(Control Command),比如一些功能管理命令,或者心跳命令。
-
定义了通信命令,我们还需要定义命令处理器,用来编写各个命令对应的业务处理逻辑。同时,我们需要保存命令与命令处理器的映射关系,以便在处理阶段,走到正确的处理器。
commandFactory与其RpcCommandFactory
这2个类的主要作用为命令工厂的作用,用请求实体生成请求命令,以及生成一些带着请求参数,响应结果的命令。回复状态有SUCCESS,ERROR,SERVER_EXCEPTION,TIMEOUT等。
RpcCommandHandler和CommandHandler
1 /** 2 * Command handler. 3 * 命令处理类 4 * @author jiangping 5 * @version $Id: CommandHandler.java, v 0.1 2015-12-14 PM4:03:55 tao Exp $ 6 */ 7 public interface CommandHandler { 8 /** 9 * Handle the command. 10 * 处理命令 11 * @param ctx 12 * @param msg 13 * @throws Exception 14 */ 15 void handleCommand(RemotingContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception; 16 17 /** 18 * Register processor for command with specified code. 19 * 注册命令特定代码的处理器 20 * @param cmd 21 * @param processor 22 */ 23 void registerProcessor(CommandCode cmd, RemotingProcessor<?> processor); 24 25 /** 26 * Register default executor for the handler. 27 * 注册处理类的默认执行者 28 * @param executor 29 */ 30 void registerDefaultExecutor(ExecutorService executor); 31 32 /** 33 * Get default executor for the handler. 34 * 得到处理类的默认执行者 35 */ 36 ExecutorService getDefaultExecutor(); 37 38 }
通过创建ExecutorService线程池,将命令的处理提交给线程池来实现。如果没有为此处理类设置线程池,Bolt默认创建一个以下参数的线程池:
-
corePoolSize(线程池的基本大小) : 20
-
-
keepAliveTime(线程活动保持时间): 60s
-
runnableTaskQueue(任务队列): ArrayBlockingQueue,队列大小为6000
-
ThreadFactory: 一个创建前缀为"Bolt-default-executor"的命名工厂。
如若对线程池了解不多的选手,可以阅读以下文章,认知一下。
-
其他
关于蚂蚁通讯框架SOFABolt之私有通讯协议设计详解到这里就结束了。当然以上所有注释,我已在我的github上上传了我的Bolt注释库。
链接:https://github.com/sanshengshui/bolt
原创不易,如果感觉不错,希望给个推荐!您的支持是我写作的最大动力!
版权声明:
作者:穆书伟
github出处:https://github.com/sanshengshui
个人博客出处:https://sanshengshui.github.io/




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号