Java SPI机制使用
1. Service Provider Interface SPI描述
接口提供者优先规定接口要求,然后交由具体的实现者对接口进行内容的实现;
2. 实现
//1. 定义接口
public Interface Demo_interface{
//具体实现者必须要实现的内容
void doexcute();
}
//2.实现接口
public class Demo_Impl implements Demo_interface{
void doexcute(){
//pass
}
}
//3. 使用ServiceLoader读取文件加载对象(ServiceLoader是主进程模块调用的)
ServiceLoader<Demo_interface> demoServiceLoader = ServiceLoader.load(Demo_interface.class);
3 举例说明
以 JDBC 的 PostgreSQL 实现为例(Mysql同理)
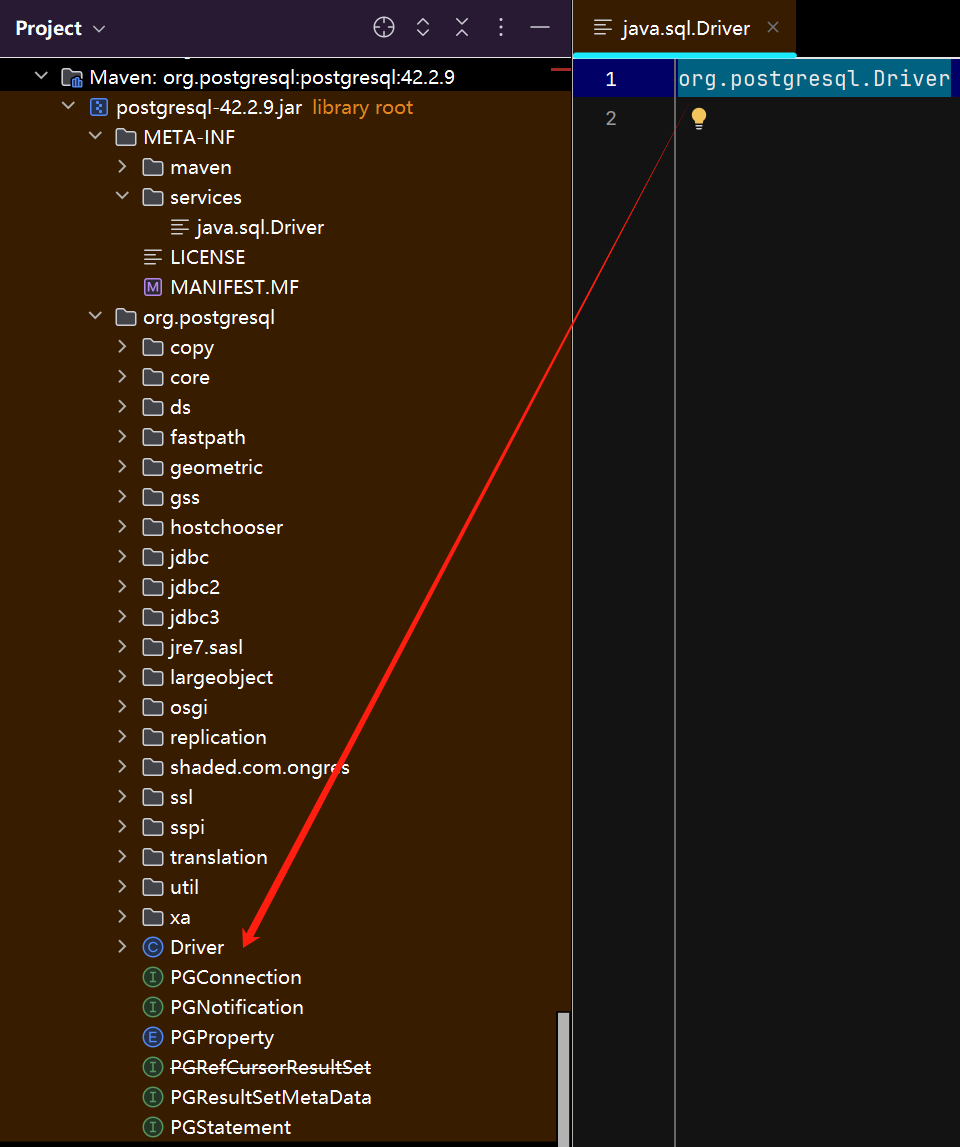
- 一 : 实现类模块文件结构需要保持下图所示,其中文件名称
java.sql.Drive就是JDBC定义需要被实现的接口,内容org.postgresql.Driver表明的是实现类的路径
- 二 :JDBC步骤说明;注册驱动 ==> 创建连接 ==> 构建执行器 ==> 获取结果集 ==> 关闭连接
//注册驱动,这里的DriverManager将会调用ServiceLoader将实现类注入
public static void register() throws SQLException {
if (isRegistered()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Driver is already registered. It can only be registered once.");
} else {
Driver registeredDriver = new Driver();
DriverManager.registerDriver(registeredDriver);
Driver.registeredDriver = registeredDriver;
}
}
// 驱动初始化,DriverManager调用ServiceLoader(DriverManager属于java.sql包下)
//调取时机,此方法是写在static块中,所以和class一起,故class.forName("")即可注册驱动
private static void loadInitialDrivers() {
String drivers;
try {
drivers = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<String>() {
public String run() {
return System.getProperty("jdbc.drivers");
}
});
} catch (Exception ex) {
drivers = null;
}
// If the driver is packaged as a Service Provider, load it.
// Get all the drivers through the classloader
// exposed as a java.sql.Driver.class service.
// ServiceLoader.load() replaces the sun.misc.Providers()
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
ServiceLoader<Driver> loadedDrivers = ServiceLoader.load(Driver.class);
Iterator<Driver> driversIterator = loadedDrivers.iterator();
/* Load these drivers, so that they can be instantiated.
* It may be the case that the driver class may not be there
* i.e. there may be a packaged driver with the service class
* as implementation of java.sql.Driver but the actual class
* may be missing. In that case a java.util.ServiceConfigurationError
* will be thrown at runtime by the VM trying to locate
* and load the service.
*
* Adding a try catch block to catch those runtime errors
* if driver not available in classpath but it's
* packaged as service and that service is there in classpath.
*/
try{
while(driversIterator.hasNext()) {
driversIterator.next();
}
} catch(Throwable t) {
// Do nothing
}
return null;
}
});
println("DriverManager.initialize: jdbc.drivers = " + drivers);
if (drivers == null || drivers.equals("")) {
return;
}
String[] driversList = drivers.split(":");
println("number of Drivers:" + driversList.length);
for (String aDriver : driversList) {
try {
println("DriverManager.Initialize: loading " + aDriver);
Class.forName(aDriver, true,
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
} catch (Exception ex) {
println("DriverManager.Initialize: load failed: " + ex);
}
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号