Java修炼——面向对象的内存分析和构造方法
面向对象的内存分析
Java虚拟机的内存可以分为三个区域:
栈stack、堆heap、方法区method area。
栈的特点如下:
1. 栈描述的是方法执行的内存模型。每个方法被调用 都会创建一个栈帧(存储局部变量、操作数、方法出 口等)
2. JVM为每个线程创建一个栈,用于存放该线程执行方 法的信息(实际参数、局部变量等)
3. 栈属于线程私有,不能实现线程间的共享!
4. 栈的存储特性是“先进后出,后进先出”
5. 栈是由系统自动分配,速度快!栈是一个连续的内存 空间!
堆的特点如下:
1. 堆用于存储创建好的对象和数组(数组也是对象)
2. JVM只有一个堆,被所有线程共享
3. 堆是一个不连续的内存空间,分配灵活,速度慢!
方法区(又叫静态区)特点如下:
1. JVM只有一个方法区,被所有线程共享!
2. 方法区实际也是堆,只是用于存储类、常量相关的 信息!
3. 用来存放程序中永远是不变或唯一的内容。(类信息 【Class对象】、静态变量、字符串常量等)
内存分配图:
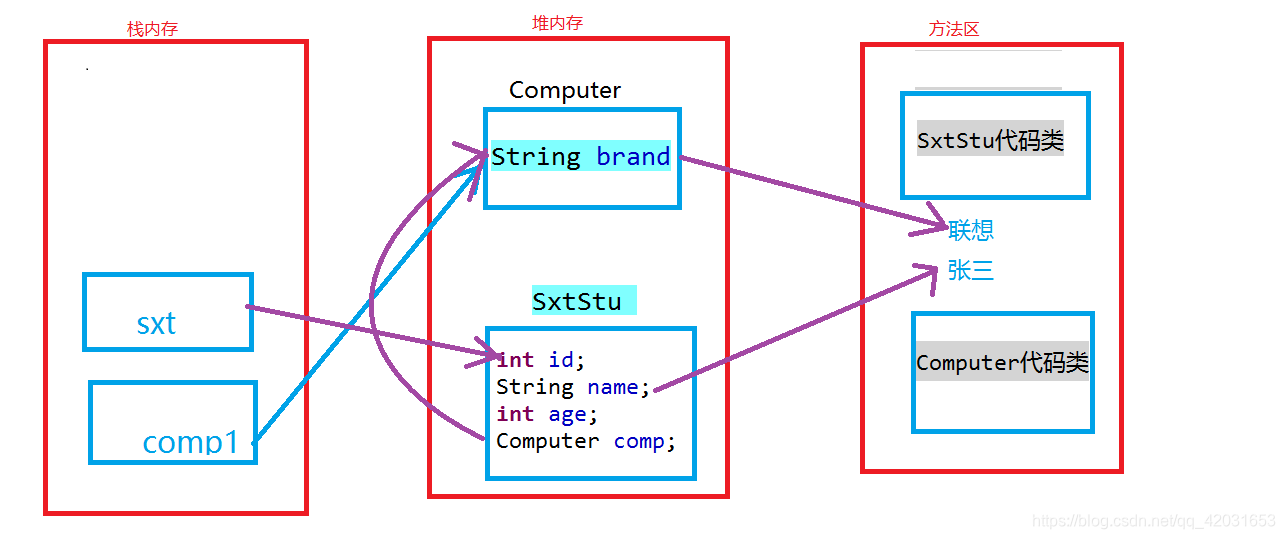
package com.bjsxt.test;
class Computer{
String brand;
}
public class SxtStu {
int id;
String name;
int age;
Computer comp;
public SxtStu(int id, String name, int age) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public SxtStu() {
}
public void study(){
System.out.println(name+"正在学习!使用我的电脑"+comp.brand);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SxtStu sxt=new SxtStu();
sxt.name="张三";
SxtStu sxt1=new SxtStu(1001, "历史", 45);
System.out.println(sxt1.getName());
Computer comp1=new Computer();
comp1.brand="联想";
sxt.comp=comp1;
sxt.study();
}
}
构造方法详解_构造方法重载
构造器也叫构造方法,用于对象的初始化。
要点:
1.通过new关键字调用。
2.构造器虽然有返回值,但是不能定义返回值类型(返回值类型肯定是本类),不能再构造器里面使用return返回某个值
3.如果没有定义构造器,则编译器会自动定义一个无参的构造函数。如果已定义则编译器不会自动添加
4.构造器的方法名必须个类名一致。
class Point {
double x, y;
public Point(double _x, double _y) {
x = _x;
y = _y;
}
public double getDistance(Point p) {
return Math.sqrt((x - p.x) * (x - p.x) + (y - p.y) * (y - p.y));
}
}
public class TestConstructor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point p = new Point(3.0, 4.0);
Point origin = new Point(0.0, 0.0);
System.out.println(p.getDistance(origin));
}
}
如果方法构造中形参名与属性名相同时,需要使用this关键字区分属性与形参。
public class User {
int id; // id
String name; // 账户名
String pwd; // 密码
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public User(int id, String name, String pwd) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.pwd = pwd;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
User u1 = new User();
User u2 = new User(101, "高小七");
User u3 = new User(100, "高淇", "123456");




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号