烂翻译系列之——MCP开发——构建MCP服务
Get started building your own server to use in Claude for Desktop and other clients.
开始构建你自己的服务,用于 Claude Desktop 及其他客户端。
In this tutorial, we’ll build a simple MCP weather server and connect it to a host, Claude for Desktop.
在本教程中,我们将构建一个简单的 MCP 天气服务,并将其连接到主机 Claude for Desktop。
What we’ll be building 我们将要构建的内容
We’ll build a server that exposes two tools: get_alerts and get_forecast. Then we’ll connect the server to an MCP host (in this case, Claude for Desktop):
我们将构建一个提供两个工具的服务:get_alerts 和 get_forecast。然后,我们将该服务连接到一个 MCP 主机(本例中为 Claude for Desktop):

Servers can connect to any client. We’ve chosen Claude for Desktop here for simplicity, but we also have guides on building your own client as well as a list of other clients here.
服务可以连接到任何客户端。我们在此选择 Claude for Desktop 是为了简化说明,但我们也有相关指南介绍如何构建你自己的客户端,以及其他客户端的列表,详见此处。
Core MCP Concepts 核心 MCP 概念
MCP servers can provide three main types of capabilities:
MCP服务可提供三大类功能::
-
Resources: File-like data that can be read by clients (like API responses or file contents) 资源:可供客户端读取的类文件数据(例如API响应或文件内容)
-
Tools: Functions that can be called by the LLM (with user approval) 工具:可由大语言模型(LLM)调用的函数(需用户批准)
-
Prompts: Pre-written templates that help users accomplish specific tasks 提示词:预设的模板,帮助用户完成特定任务
This tutorial will primarily focus on tools.
本教程将主要聚焦于“工具”的实现。
Let’s get started with building our weather server! You can find the complete code for what we’ll be building here.
Prerequisite knowledge 前置知识
This quickstart assumes you have familiarity with:
本快速入门教程假设你已具备以下知识:
-
C#
-
LLMs like Claude 像 Claude 这样的大语言模型
-
.NET 8 or higher .NET 8 或更高版本
Logging in MCP Servers MCP 服务中的日志记录
When implementing MCP servers, be careful about how you handle logging:
在实现 MCP 服务时,需谨慎处理日志记录:
For STDIO-based servers: Never write to standard output (stdout). This includes:
对于基于 STDIO 的服务:切勿向标准输出(stdout)写入内容。这包括:
-
print()statements in Python Python 中的print()语句 -
console.log()in JavaScript JavaScript 中的console.log() -
fmt.Println()in Go Go 中的fmt.Println() -
Similar stdout functions in other languages 其他语言中类似向 stdout 输出的函数
Writing to stdout will corrupt the JSON-RPC messages and break your server.
向 stdout 写入内容会破坏 JSON-RPC 消息,导致服务无法正常工作。
For HTTP-based servers: Standard output logging is fine since it doesn’t interfere with HTTP responses.
对于基于 HTTP 的服务:可以正常使用标准输出进行日志记录,因为它不会干扰 HTTP 响应。
Best Practices 最佳实践
- Use a logging library that writes to stderr or files 使用将日志写入 stderr 或文件的日志记录库
System requirements 系统要求
- .NET 8 SDK or higher installed. 已安装 .NET 8 SDK 或更高版本。
Set up your environment 设置你的环境
First, let’s install dotnet if you haven’t already. You can download dotnet from official Microsoft .NET website. Verify your dotnet installation:
首先,如果尚未安装 dotnet,请先进行安装。你可以从微软官方 .NET 网站下载 dotnet。安装完成后,请验证你的 dotnet 安装:
dotnet --versionNow, let’s create and set up your project:
现在,让我们创建并配置你的项目:
| macOS/Linux | Windows |
|
|
After running dotnet new console, you will be presented with a new C# project. You can open the project in your favorite IDE, such as Visual Studio or Rider. Alternatively, you can create a C# application using the Visual Studio project wizard. After creating the project, add NuGet package for the Model Context Protocol SDK and hosting:
运行 dotnet new console 后,系统将为你创建一个新的 C# 项目。你可以使用你喜爱的集成开发环境(IDE)(例如 Visual Studio 或 Rider)打开该项目。或者,你也可以使用 Visual Studio 的项目向导来创建 C# 应用程序。项目创建完成后,添加 Model Context Protocol SDK 及其宿主功能的 NuGet 包:
# Add the Model Context Protocol SDK NuGet package
dotnet add package ModelContextProtocol --prerelease
# Add the .NET Hosting NuGet package
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.HostingNow let’s dive into building your server.
现在,让我们开始深入构建你的服务。
Building your server 构建你的服务
Open the Program.cs file in your project and replace its contents with the following code:
在项目中打开 Program.cs 文件,并将其内容替换为以下代码:
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using ModelContextProtocol;
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
var builder = Host.CreateEmptyApplicationBuilder(settings: null);
builder.Services.AddMcpServer()
.WithStdioServerTransport()
.WithToolsFromAssembly();
builder.Services.AddSingleton(_ =>
{
var client = new HttpClient() { BaseAddress = new Uri("https://api.weather.gov") };
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.UserAgent.Add(new ProductInfoHeaderValue("weather-tool", "1.0"));
return client;
});
var app = builder.Build();
await app.RunAsync();When creating the
ApplicationHostBuilder, ensure you useCreateEmptyApplicationBuilderinstead ofCreateDefaultBuilder. This ensures that the server does not write any additional messages to the console. This is only necessary for servers using STDIO transport.在创建
ApplicationHostBuilder时,务必使用CreateEmptyApplicationBuilder而不是CreateDefaultBuilder。这可以确保服务不会向控制台写入任何额外消息。此要求仅适用于使用 STDIO 传输的服务。
This code sets up a basic console application that uses the Model Context Protocol SDK to create an MCP server with standard I/O transport.
Weather API helper functions 天气 API 辅助函数
Create an extension class for HttpClient which helps simplify JSON request handling:
创建一个 HttpClient 的扩展类,以简化 JSON 请求的处理:
using System.Text.Json;
internal static class HttpClientExt
{
public static async Task<JsonDocument> ReadJsonDocumentAsync(this HttpClient client, string requestUri)
{
using var response = await client.GetAsync(requestUri);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
return await JsonDocument.ParseAsync(await response.Content.ReadAsStreamAsync());
}
}Next, define a class with the tool execution handlers for querying and converting responses from the National Weather Service API:
接下来,定义一个类,其中包含用于查询和转换美国国家气象局(NWS)API响应的工具执行处理程序:
using ModelContextProtocol.Server;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Globalization;
using System.Text.Json;
namespace QuickstartWeatherServer.Tools;
[McpServerToolType]
public static class WeatherTools
{
[McpServerTool, Description("Get weather alerts for a US state.")]
public static async Task<string> GetAlerts(
HttpClient client,
[Description("The US state to get alerts for.")] string state)
{
using var jsonDocument = await client.ReadJsonDocumentAsync($"/alerts/active/area/{state}");
var jsonElement = jsonDocument.RootElement;
var alerts = jsonElement.GetProperty("features").EnumerateArray();
if (!alerts.Any())
{
return "No active alerts for this state.";
}
return string.Join("\n--\n", alerts.Select(alert =>
{
JsonElement properties = alert.GetProperty("properties");
return $"""
Event: {properties.GetProperty("event").GetString()}
Area: {properties.GetProperty("areaDesc").GetString()}
Severity: {properties.GetProperty("severity").GetString()}
Description: {properties.GetProperty("description").GetString()}
Instruction: {properties.GetProperty("instruction").GetString()}
""";
}));
}
[McpServerTool, Description("Get weather forecast for a location.")]
public static async Task<string> GetForecast(
HttpClient client,
[Description("Latitude of the location.")] double latitude,
[Description("Longitude of the location.")] double longitude)
{
var pointUrl = string.Create(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, $"/points/{latitude},{longitude}");
using var jsonDocument = await client.ReadJsonDocumentAsync(pointUrl);
var forecastUrl = jsonDocument.RootElement.GetProperty("properties").GetProperty("forecast").GetString()
?? throw new Exception($"No forecast URL provided by {client.BaseAddress}points/{latitude},{longitude}");
using var forecastDocument = await client.ReadJsonDocumentAsync(forecastUrl);
var periods = forecastDocument.RootElement.GetProperty("properties").GetProperty("periods").EnumerateArray();
return string.Join("\n---\n", periods.Select(period => $"""
{period.GetProperty("name").GetString()}
Temperature: {period.GetProperty("temperature").GetInt32()}°F
Wind: {period.GetProperty("windSpeed").GetString()} {period.GetProperty("windDirection").GetString()}
Forecast: {period.GetProperty("detailedForecast").GetString()}
"""));
}
}Running the server
Finally, run the server using the following command:
最后,使用以下命令运行服务器:
dotnet runThis will start the server and listen for incoming requests on standard input/output.
Testing your server with Claude for Desktop 使用 Claude for Desktop 测试你的服务
Claude for Desktop is not yet available on Linux. Linux users can proceed to the Building a client tutorial to build an MCP client that connects to the server we just built.
Claude for Desktop 目前尚未在 Linux 系统上提供。Linux 用户可以前往“构建客户端”教程,创建一个 MCP 客户端,连接到我们刚刚构建的服务。
First, make sure you have Claude for Desktop installed. You can install the latest version here. If you already have Claude for Desktop, make sure it’s updated to the latest version. We’ll need to configure Claude for Desktop for whichever MCP servers you want to use. To do this, open your Claude for Desktop App configuration at ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json in a text editor. Make sure to create the file if it doesn’t exist. For example, if you have VS Code installed:
首先,请确保你已安装 Claude for Desktop。你可以在此处安装最新版本。如果你已安装 Claude for Desktop,请确保其已更新至最新版本。我们需要对 Claude for Desktop 进行配置,以使用你希望连接的 MCP 服务。为此,请在文本编辑器中打开 Claude for Desktop 的应用配置文件:~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json。如果该文件不存在,请先创建它。例如,如果你已安装 VS Code:
| macOS/Linux | Windows |
|
|
You’ll then add your servers in the mcpServers key. The MCP UI elements will only show up in Claude for Desktop if at least one server is properly configured. In this case, we’ll add our single weather server like so:
然后,你需要在 mcpServers 键中列出你的服务。只有在正确配置了至少一个服务后,Claude for Desktop 中才会显示 MCP 的用户界面元素。在此示例中,我们将添加刚刚创建的天气服务,如下所示:
| macOS/Linux | Windows |
|
|
-
There’s an MCP server named “weather” 有一个名为“weather”(天气)的 MCP 服务
-
Launch it by running
dotnet run /ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PROJECT通过运行dotnet run /ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PROJECT来启动该服务
Save the file, and restart Claude for Desktop.
保存文件,然后重启 Claude for Desktop。
Test with commands 使用命令进行测试
Let’s make sure Claude for Desktop is picking up the two tools we’ve exposed in our weather server. You can do this by looking for the “Search and tools” icon:
让我们确认 Claude for Desktop 能够识别我们天气服务提供的两个工具。你可以通过查找“搜索和工具” 图标 来验证:

After clicking on the slider icon, you should see two tools listed:
点击 图标后,你应该会看到列出的两个工具:

If your server isn’t being picked up by Claude for Desktop, proceed to the Troubleshooting section for debugging tips.
如果 Claude for Desktop 未能识别你的服务,请前往“故障排除”部分获取调试建议。
If the tool settings icon has shown up, you can now test your server by running the following commands in Claude for Desktop:
如果工具设置图标已成功显示,你现在可以在 Claude for Desktop 中运行以下命令来测试你的服务:
-
What’s the weather in Sacramento? 萨克拉门托的天气如何?
-
What are the active weather alerts in Texas? 得克萨斯州当前有哪些天气预警?

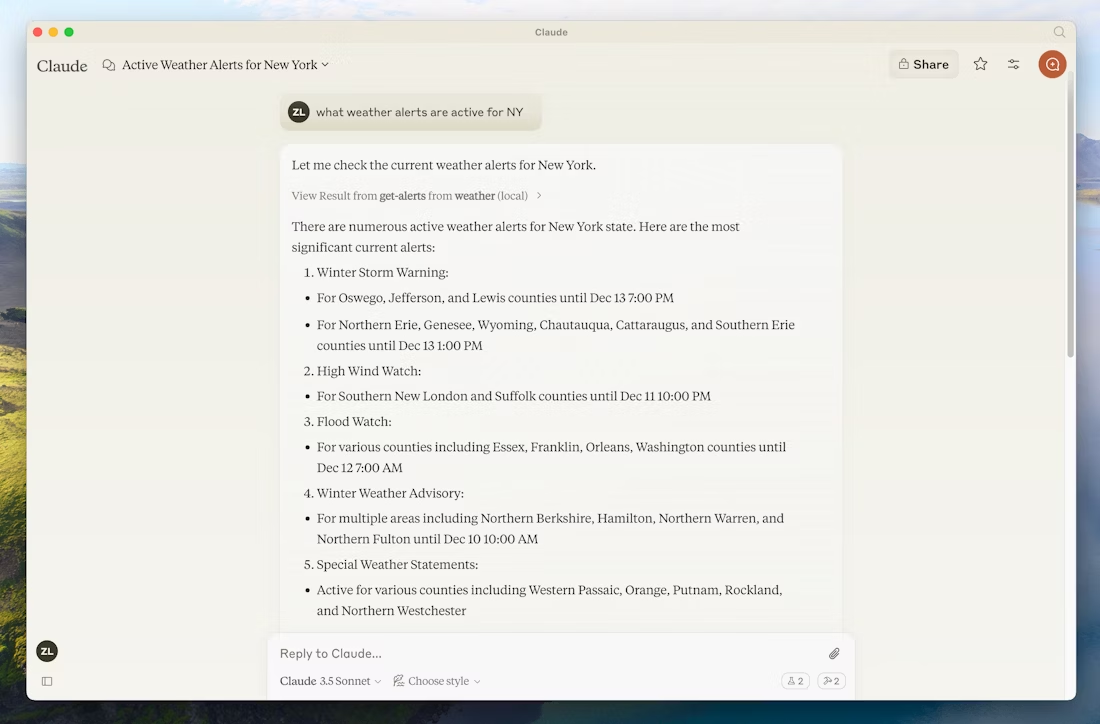
Since this is the US National Weather service, the queries will only work for US locations.
由于这是美国国家气象服务,查询仅对美国境内的地点有效。
What’s happening under the hood 幕后发生了什么
When you ask a question:
当你提出一个问题时,整个流程如下:
-
The client sends your question to Claude 客户端将你的问题发送给 Claude
-
Claude analyzes the available tools and decides which one(s) to use Claude 分析可用的工具,并决定使用哪一个(或多个)
-
The client executes the chosen tool(s) through the MCP server 客户端通过 MCP 服务执行所选的工具
-
The results are sent back to Claude 工具执行结果被发送回 Claude
-
Claude formulates a natural language response Claude 生成自然语言形式的回复
-
The response is displayed to you! 回复内容显示给你!
Troubleshooting 故障排除
| Claude for Desktop Integration Issues Claude for Desktop 集成问题 |
|
Getting logs from Claude for Desktop 从 Claude for Desktop 获取日志 Claude.app logging related to MCP is written to log files in Claude.app 会将与 MCP 相关的日志写入
You can run the following command to list recent logs and follow along with any new ones: 你可以运行以下命令来列出最近的日志,并实时跟踪新生成的日志: Server not showing up in Claude 服务未在 Claude 中显示
Tool calls failing silently 工具调用静默失败 If Claude attempts to use the tools but they fail: 如果 Claude 尝试使用工具但操作失败:
None of this is working. What do I do? 以上方法均无效。我该怎么办? Please refer to our debugging guide for better debugging tools and more detailed guidance. 请参考我们的调试指南,获取更强大的调试工具和更详细的指导。 |
| Weather API Issues 天气API问题 |
|
Error: Failed to retrieve grid point data 错误:无法获取网格点数据 This usually means either: 这通常意味着以下情况之一:
Fix: 解决方法:
Error: No active alerts for [STATE] 错误:[美国的某个州] 无活跃天气预警 This isn’t an error - it just means there are no current weather alerts for that state. Try a different state or check during severe weather. 这并非真正的错误——仅表示该州当前没有天气预警。可以尝试查询其他州,或在恶劣天气期间再次检查。 |
For more advanced troubleshooting, check out our guide on Debugging MCP
如需更高级的故障排除,请查阅我们的《MCP 调试指南》。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号