烂翻译系列之生成式人工智能初学者入门——第一章 : 生成式人工智能和 LLMs 介绍
(Click the image above to view video of this lesson)
(点击上面的图片查看本课的视频)
Generative AI is artificial intelligence capable of generating text, images and other types of content. What makes it a fantastic technology is that it democratizes AI, anyone can use it with as little as a text prompt, a sentence written in a natural language. There's no need for you to learn a language like Java or SQL to accomplish something worthwhile, all you need is to use your language, state what you want and out comes a suggestion from an AI model. The applications and impact for this is huge, you write or understand reports, write applications and much more, all in seconds.
生成式人工智能(Generative AI)是一种能够生成文本、图像和其他类型内容的人工智能。它之所以是一项了不起的技术,是因为它让AI变得普及化,任何人只需使用文本提示,即使用自然语言写出的句子,就可以使用它。你无需学习如Java或SQL这样的语言来达成有价值的事情,你只需要使用你的语言,说明你想要的内容,然后就会从AI模型中收到一个建议。这项技术的应用和影响力是巨大的,你可以在几秒钟内编写或理解报告、编写应用程序等等。
In this curriculum, we’ll explore how our startup leverages generative AI to unlock new scenarios in the education world and how we address the inevitable challenges associated with the social implications of its application and the technology limitations.
在本课程中,我们将探讨我们的初创公司如何利用生成式人工智能(Generative AI)解锁教育领域的新场景,以及我们如何应对其应用带来的不可避免的社会影响挑战和技术限制。
Introduction 本章概述
This lesson will cover: 本课程将包含以下内容:
- Introduction to the business scenario: our startup idea and mission. 业务场景介绍:我们的创业理念和使命。
- Generative AI and how we landed on the current technology landscape. 生成式人工智能(Generative AI)以及我们如何达到当前的技术前景。
- Inner working of a large language model. 大语言模型(LLMs)的内部工作原理。
- Main capabilities and practical use cases of Large Language Models. 大语言模型(LLMs)的主要功能和实际用例。
Learning Goals 学习目标
After completing this lesson, you will understand: 学习完本课程后,您将会了解到:
- What generative AI is and how Large Language Models work. 什么是生成式人工智能以及大语言模型(LLMs)如何工作。
- How you can leverage large language models for different use cases, with a focus on education scenarios. 您如何利用大语言模型(LLMs)来应对不同的用例,特别关注教育场景。
Scenario: our educational startup 场景: our educational startup(我们的教育初创公司)
Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) represents the pinnacle of AI technology, pushing the boundaries of what was once thought impossible. Generative AI models have several capabilities and applications, but for this curriculum we'll explore how it's revolutionizing education through a fictional startup. We'll refer to this startup as our startup. Our startup works in the education domain with the ambitious mission statement of
生成式人工智能(AI)代表着AI技术的巅峰,它突破了曾经认为的不可能。生成式AI模型具有多种能力和应用,但在这个课程中,我们将探讨它如何通过一家虚构的初创公司来改革教育。我们将这家初创公司称为“Our startup”。Our startup致力于教育领域,其宏伟的使命宣言是
improving accessibility in learning, on a global scale, ensuring equitable access to education and providing personalized learning experiences to every learner, according to their needs.
在全球范围内提高学习的普及性,确保教育机会的公平分配,并根据每位学习者的需求为他们提供个性化的学习体验。
Our startup team is aware we’ll not be able to achieve this goal without leveraging one of the most powerful tools of modern times – Large Language Models (LLMs).
我们的初创团队深知,如果不利用现代最强大的工具之一——大型语言模型(LLMs),我们将无法实现这一目标。
Generative AI is expected to revolutionize the way we learn and teach today, with students having at their disposal virtual teachers 24 hours a day who provide vast amounts of information and examples, and teachers able to leverage innovative tools to assess their students and give feedback.
生成式人工智能预计将彻底改变我们当前的学习和教学方式,学生将能够全天候地获得虚拟教师的帮助,这些虚拟教师会提供大量的信息和示例,而教师则能够利用创新的工具来评估学生并给予反馈。

To start, let’s define some basic concepts and terminology we’ll be using throughout the curriculum.
首先,让我们了解一些在整个课程中将要使用的基本概念和术语。
How did we get Generative AI? 我们是如何获得生成式人工智能的?
Despite the extraordinary hype created lately by the announcement of generative AI models, this technology is decades in the making, with the first research efforts dating back to 60s. We're now at a point with AI having human cognitive capabilities, like conversation as shown by for example OpenAI ChatGPT or Bing Chat, which also uses a GPT model for the web search Bing conversations.
尽管最近生成式AI模型的宣布引发了极大的轰动,但这项技术已经发展了数十年,最早的研究工作可以追溯到上世纪 60 年代。 我们现在正处于 AI 具有人类认知能力的阶段,例如 OpenAI ChatGPT 或 Bing Chat 也在用 GPT 模型进行对话。
Backing up a bit, the very first prototypes of AI consisted of typewritten chatbots, relying on a knowledge base extracted from a group of experts and represented into a computer. The answers in the knowledge base were triggered by keywords appearing in the input text. However, it soon became clear that such approach, using typewritten chatbots, did not scale well.
稍微回顾一下,最初的人工智能原型是由打字机式的聊天机器人组成的,它们依赖于从专家组中提取的知识库,并将这些知识库输入到计算机中。知识库中的回答由输入文本中出现的关键字触发。然而,很快人们就意识到,使用打字机式的聊天机器人这种方法并不具有很好的扩展性。
A statistical approach to AI: Machine Learning 人工智能的统计学方法:机器学习
A turning point arrived during the 90s, with the application of a statistical approach to text analysis. This led to the development of new algorithms – known with the name of machine learning - able to learn patterns from data, without being explicitly programmed. This approach allows a machine to simulate human language understanding: a statistical model is trained on text-label pairings, enabling the model to classify unknown input text with a pre-defined label representing the intention of the message.
20世纪90年代,随着统计方法被应用于文本分析,一个转折点出现了。这促使了新算法的发展——即众所周知的机器学习——能够从数据中学习模式,而无需明确编程。这种方法使得机器能够模拟人类语言理解:在文本-标签配对上训练统计模型,使模型能够用预定义的标签对未知输入文本进行分类,以表示消息的意图。
Neural networks and modern virtual assistants 神经网络和现代虚拟助手
In more recent times, the technological evolution of the hardware, capable of handling larger amounts of data and more complex computations, encouraged research in the AI fields, leading to the development of advanced machine learning algorithms – called neural networks or deep learning algorithms.
在最近的一段时间里,硬件技术的演变,使其能够处理更大量的数据和更复杂的计算,推动了人工智能领域的研究,进而发展了先进的机器学习算法——被称为神经网络或深度学习算法。
Neural networks (and in particular Recurrent Neural Networks – RNNs) significantly enhanced natural language processing, enabling the representation of the meaning of text in a more meaningful way, valuing the context of a word in a sentence.
神经网络(特别是循环神经网络——RNNs)极大地增强了自然语言处理,能够以更有意义的方式表示文本含义,并重视句子中单词的上下文之间的联系。
This is the technology that powered the virtual assistants born in the first decade of the new century, very proficient in interpreting the human language, identifying a need, and performing an action to satisfy it – like answering with a pre-defined script or consuming a 3rd party service.
神经网络是新世纪头十年诞生的虚拟助手所使用的技术,它非常擅长解读人类语言,识别需求,并执行满足该需求的操作——比如用预定义的脚本回答或调用第三方服务。
Present day, Generative AI 今天 - 生成式人工智能
So that’s how we came to Generative AI today, which can be seen as a subset of deep learning.
这就是我们今天提出生成式人工智能的原因,它可以被视为深度学习的一个子集。
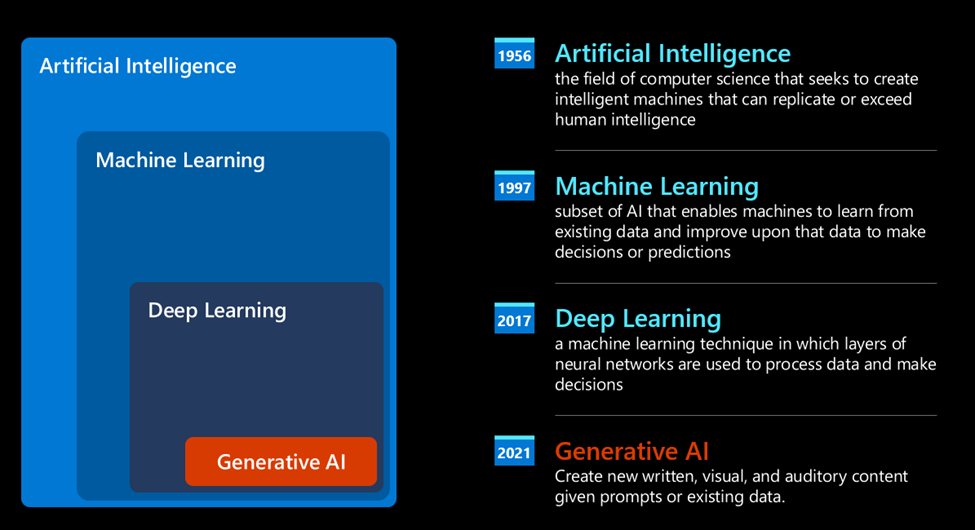
After decades of research in the AI field, a new model architecture – called Transformer – overcame the limits of RNNs, being able to get much longer sequences of text as input. Transformers are based on the attention mechanism, enabling the model to give different weights to the inputs it receives, ‘paying more attention’ where the most relevant information is concentrated, regardless of their order in the text sequence.
经过人工智能领域数十年的研究,一种新的模型架构——称为“转换器(Transformer)”——突破了RNNs的局限性,能够获取更长的文本序列作为输入。转换器基于注意力机制,使模型能够为其接收到的输入赋予不同的权重,在最重要的信息集中的地方“给予更多关注”,而不管这些信息在文本序列中的顺序如何。
Most of the recent generative AI models – also known as Large Language Models (LLMs), since they work with textual inputs and outputs – are indeed based on this architecture. What’s interesting about these models – trained on a huge amount of unlabeled data from diverse sources like books, articles and websites – is that they can be adapted to a wide variety of tasks and generate grammatically correct text with a semblance of creativity. So, not only did they incredibly enhance the capacity of a machine to ‘understand’ an input text, but they enabled their capacity to generate an original response in human language.
最近的大多数生成式人工智能模型——也称为大型语言模型(LLMs),因为它们使用文本输入和输出——确实基于这种架构。这些模型的有趣之处在于——它们是在大量来自书籍、文章和网站等多样化来源的未标记数据上进行训练的——它们可以适应各种各样的任务,并生成语法正确、看似具有创造力的文本。因此,它们不仅极大地提高了机器“理解”输入文本的能力,还使它们能够用人类语言生成原创的回应。
How do large language models work? 大语言模型(LLMs)如何工作?
In the next chapter we are going to explore different types of Generative AI models, but for now let’s have a look at how large language models work, with a focus on OpenAI GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) models.
在下一章中,我们将探索不同类型的生成式 AI 模型,但现在让我们看看大型语言模型是如何工作的,重点是 OpenAI GPT(生成式预训练 Transformer)模型。
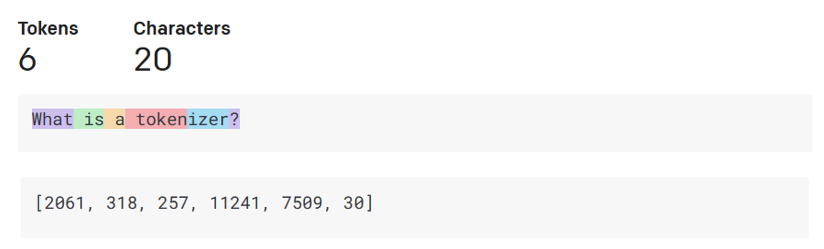
- Tokenizer, text to numbers: Large Language Models receive a text as input and generate a text as output. However, being statistical models, they work much better with numbers than text sequences. That’s why every input to the model is processed by a tokenizer, before being used by the core model. A token is a chunk of text – consisting of a variable number of characters, so the tokenizer's main task is splitting the input into an array of tokens. Then, each token is mapped with a token index, which is the integer encoding of the original text chunk. 分词器(Tokenizer),文本到数字:大型语言模型接收文本作为输入并生成文本作为输出。然而,作为统计模型,它们处理数字比处理文本序列更有效。这就是为什么模型的每个输入在被核心模型使用之前都要经过分词器的处理。一个分词(token)是一段文本——由可变数量的字符组成,因此分词器的主要任务是将输入分割成一组分词。然后,每个分词都映射到一个分词索引,这是原始文本块的整数编码。
-
Predicting output tokens: Given n tokens as input (with max n varying from one model to another), the model is able to predict one token as output. This token is then incorporated into the input of the next iteration, in an expanding window pattern, enabling a better user experience of getting one (or multiple) sentence as an answer. This explains why, if you ever played with ChatGPT, you might have noticed that sometimes it looks like it stops in the middle of a sentence. 预测输出分词:给定n个分词作为输入(每个模型的最大n值各不相同),模型能够预测一个分词作为输出。然后,这个分词被纳入下一次迭代的输入中,以扩展窗口模式进行,从而为用户提供了一个更好的体验,即获得一个(或多个)句子作为回答。这解释了为什么,如果你曾经使用过ChatGPT,您可能会注意到有时它在生成结果时在句子中间出现停顿。
-
Selection process, probability distribution: The output token is chosen by the model according to its probability of occurring after the current text sequence. This is because the model predicts a probability distribution over all possible ‘next tokens’, calculated based on its training. However, not always the token with the highest probability is chosen from the resulting distribution. A degree of randomness is added to this choice, in a way that the model acts in a non-deterministic fashion - we do not get the exact same output for the same input. This degree of randomness is added to simulate the process of creative thinking and it can be tuned using a model parameter called temperature. 选择过程,概率分布:模型根据当前文本序列后该分词出现的概率来选择输出分词。这是因为模型基于其训练预测了所有可能的“下一个分词”的概率分布。然而,并非总是从结果分布中选择概率最高的分词。在选择过程中加入了一定程度的随机性,使得模型以非确定性的方式运行——相同的输入不会得到完全相同的输出。这种随机性的程度是为了模拟人类创造性思维过程,并且可以通过一个称为“温度”的模型参数进行调整。
How can our startup leverage Large Language Models? “Our startup” 如何利用大语言模型(LLMs )?
Now that we have a better understanding of the inner working of a large language model, let’s see some practical examples of the most common tasks they can perform pretty well, with an eye to our business scenario. We said that the main capability of a Large Language Model is generating a text from scratch, starting from a textual input, written in natural language.
现在我们对大型语言模型的内部工作原理有了更好的理解,让我们来看看它们能够出色完成的一些最常见任务的实际例子,同时关注我们的业务场景。我们之前说过,大型语言模型的主要能力是从自然语言的文本输入开始,从头开始生成文本。
But what kind of textual input and output? The input of a large language model is known as prompt, while the output is known as completion, term that refers to the model mechanism of generating the next token to complete the current input. We are going to dive deep into what is a prompt and how to design it in a way to get the most out of our model. But for now, let’s just say that a prompt may include:
但是是什么样的文本输入和输出呢?大型语言模型的输入被称为提示(prompt),而输出被称为补全(completion),这个术语指的是模型生成下一个分词以完成当前输入的机制。我们将深入探讨什么是提示以及如何设计它以充分利用我们的模型。但现在,我们只需说提示可能包括:
-
An instruction specifying the type of output we expect from the model. This instruction sometimes might embed some examples or some additional data. 通过一条指令,指定我们期望模型输出的类型。 该指令有时可能会包含一些示例或一些附加数据。
-
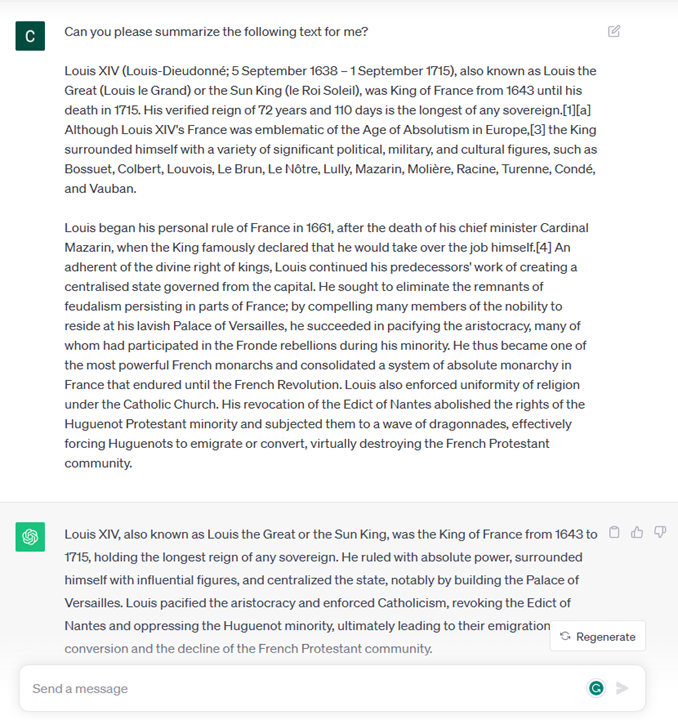
Summarization of an article, book, product reviews and more, along with extraction of insights from unstructured data. 文章、书籍、产品评论等的摘要,以及从非结构化数据中提取见解。
-
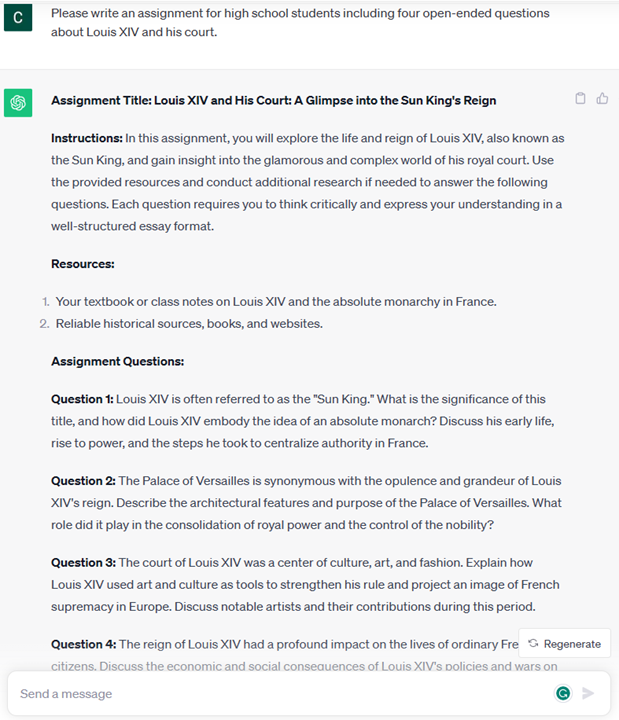
Creative ideation and design of an article, an essay, an assignment or more. 文章、论文、作业等的创意构思和设计。
-
-
A question, asked in the form of a conversation with an agent. 问题,以与代理对话的形式提出。
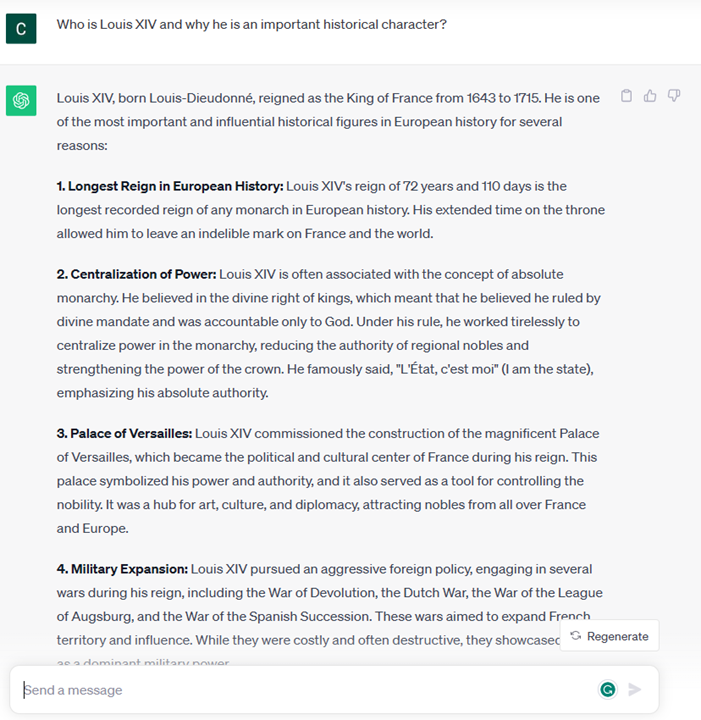
- A chunk of text to complete, which implicitly is an ask for writing assistance. 文本补全,这隐含着对写作帮助的请求。

- A chunk of code together with the ask of explaining and documenting it, or a comment asking to generate a piece of code performing a specific task. 一段代码,连同解释和记录它的要求,或者要求生成一段执行特定任务的代码的注释。
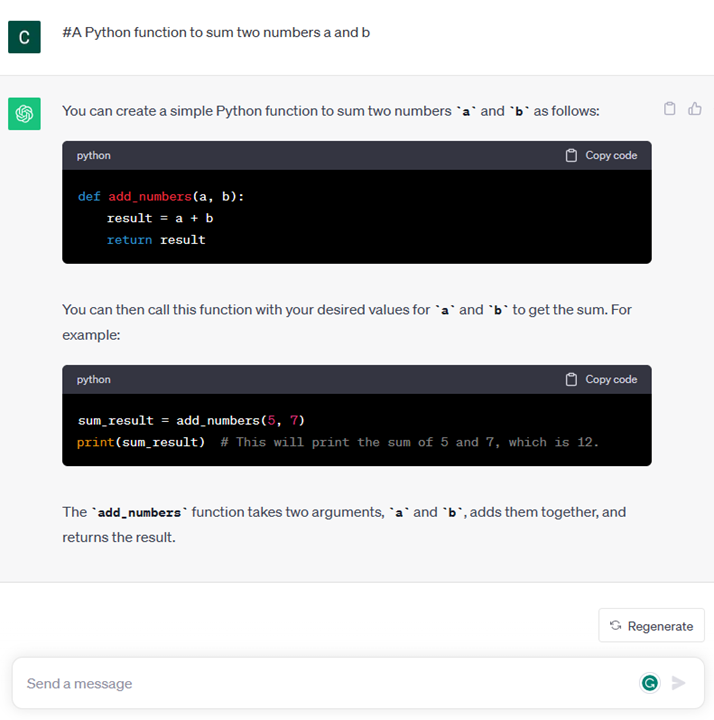
The examples above are quite simple and don’t want to be an exhaustive demonstration of Large Language Models capabilities. They just want to show the potential of using generative AI, in particular but not limited to educational context.
以上的例子非常简单,并不是对生成式人工智能功能的详尽演示。 只是想展示使用生成式人工智能的潜力,并不局限于教育领域。
Also, the output of a generative AI model is not perfect and sometimes the creativity of the model can work against it, resulting in an output which is a combination of words that the human user can interpret as a mystification of reality, or it can be offensive. Generative AI is not intelligent - at least in the more comprehensive definition of intelligence, including critical and creative reasoning or emotional intelligence; it is not deterministic, and it is not trustworthy, since fabrications, such as erroneous references, content, and statements, may be combined with correct information, and presented in a persuasive and confident manner. In the following lessons, we’ll be dealing with all these limitations and we’ll see what we can do to mitigate them.
此外,生成式AI模型的输出并不完美,有时模型的创造力可能会适得其反,导致输出结果成为一系列词汇的组合,人类用户可能会将其解读为对现实的迷惑,或者它可能是冒犯性的。生成式AI并不智能——至少从更全面的智能定义来看,包括批判性和创造性推理或情感智能;它不是确定性的,也不是可信的,因为错误的引用、内容和声明等捏造内容可能与正确的信息混合在一起,并以具有说服力和自信的方式呈现。在以下课程中,我们将处理所有这些限制,并探讨我们可以采取哪些措施来降低影响。
Assignment 任务
Your assignment is to read up more on generative AI and try to identify an area where you would add generative AI today that doesn't have it. How would the impact be different from doing it the "old way", can you do something you couldn't before, or are you faster? Write a 300 word summary on what your dream AI startup would look like and include headers like "Problem", "How I would use AI", "Impact" and optionally a business plan.
你的任务是深入了解生成式AI,并尝试确定一个目前没有使用生成式AI的领域,但你会在今天加入生成式AI。使用生成式AI与“旧方法”相比,其影响有何不同?你能做一些以前不能做的事情吗?或者你的速度更快了吗?写一篇300字的摘要,描述你梦想中的AI初创公司会是什么样子,包括“问题”、“我将如何使用AI”、“影响”等标题,还可以选择做一份商业计划。
If you did this task, you might even be ready to apply to Microsoft's incubator, Microsoft for Startups Founders Hub we offer credits for both Azure, OpenAI, mentoring and much more, check it out!
如果您完成了此任务,您甚至可以准备好申请 Microsoft 的创业孵化器Microsoft for Startups Founders Hub,我们为您提供 Azure 和 OpenAIc redits 以及相关指导等等
Knowledge check 知识检查
What's true about large language models? 大语言模型的真实情况是什么?
- You get the exact same response every time. 你每次都会得到完全相同的回应。
- It does things perfectly, great at adding numbers, produce working code etc. 它能够完美地完成任务,擅长加法运算,生成可运行的代码等等。
- The response may vary despite using the same prompt. It's also great at giving you a first draft of something, be it text or code. But you need to improve on the results. 尽管使用相同的提示,但回应可能会有所不同。它也很擅长为你提供某事物的初稿,无论是文本还是代码。但你需要对结果进行改进。
A: 3, an LLM is non-deterministic, the response vary, however, you can control its variance via a temperature setting. You also shouldn't expect it to do things perfectly, it's here to do the heavy-lifting for you which often means you get a good first attempt at something that you need to gradually improve.
正确答案:3, 大语言模型(LLM)是非确定性的,其回应会有所不同,但你可以通过温度设置来控制其变化。同时,你也不应该期待它能完美地完成任务,它的作用是为你完成繁重的工作,这通常意味着你会得到一个不错的初步尝试,然后你需要逐渐改进。
Great Work! Continue the Journey 继续您的学习旅程
After completing this lesson, check out our Generative AI Learning collection to continue leveling up your Generative AI knowledge!
完成本课程后,请查看我们的生成式AI学习系列,继续提升您的生成式AI知识!
Head over to Lesson 2 where we will look at how to explore and compare different LLM types!前往第二章,我们将了解如何探索和比较不同类型的 LLM !



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号