[技术总结][AUTOSAR][CP][MCAL] Port Driver
[Ref#1] AUTOSAR_CP_RS_PortDriver.pdf
https://www.autosar.org/fileadmin/standards/R24-11/CP/AUTOSAR_CP_RS_PortDriver.pdf
[Ref#2] AUTOSAR_CP_SWS_PortDriver.pdf
https://www.autosar.org/fileadmin/standards/R24-11/CP/AUTOSAR_CP_SWS_PortDriver.pdf
RS_PortDriver, Requirements on Port Driver
1 Scope
specifies requirements on the module PORT Driver.
Constraints: First scope for specification of requirements on basic software modules is systems, which are not safety relevant. For this reason safety requirements are assigned to medium priority.
2 How to Read this Document
2.1 Conventions used
MUST: an absolute requirement of the specification due to legal issues.
MUST NOT: an absolute prohibition of the specification due to legal issues.
SHALL: an absolute requirement of the specification.
SHALL NOT: is an absolute prohibition of the specification.
SHOULD: there may exist valid reasons in particular circumstances to ignore a particular item, but the full implications must be understood and carefully weighed before choosing a different course.
SHOULD NOT: ...
MAY: is truly optional.
2.2 Requirements structure
Functional Requirements
- Configuration (which elements of the module need to be configurable)
- Initialisation
- Normal Operation
- Shutdown Operation
- Fault Operation
- ...
Non-Functional Requirements
- Timing Requirements
- Resource Usage
- Usability
- Output for other WPs (e.g. Description Templates, Tooling,...)
- ...
3 Acronyms and abbreviations
DIO: Digital Input Output
ICU: Input Capture Unit
MCAL: Microconroller Abstraction Layer
SPAL: The name of this working group (Standard Peripheral Abstraction Layer)
STD: Standard
REQ: Requirement
UNINIT: Uninitialized (= not initialized)
4 Requirement Specification
4.1 Functional Overview
This module initializes the whole port structure of the microcontroller.
Many ports and port pins can be assigned to various functionalities like e.g.
- General purpose I/O
- ADC
- SPI
- SCI
- PWM
an overall configuration and initialization of this port structure
The following expressions are used within the Port driver:
| Expression: | Explanation: |
|---|---|
| Physical Level (Input): | Two states possible: LOW/HIGH |
| Physical Level (Output): | Three stats possible: LOW/HIGH/HIGH Impedance |
| Logical level: | This level is seen within the software: TRUE/FALSE |
4.2 Functional Requirements
4.2.1 Configuration
[SRS_Port_12001]The Port driver shall allow the static configuration of the following options for each port.
Upstream requirements:RS_BRF_01864
[SRS_Port_12302] The port driver shall allow the static configuration of the port pin names.
Upstream requirements: RS_BRF_01864

SWS_PortDriver, Specification of Port Driver
2 Introduction and functional overview
(1) specifies the functionality, API and the configuration of the AUTOSAR Basic Software module PORT Driver.
(2) applicable for on-chip ports and port pins.
(3) This module shall provide the service for initializing the whole PORT structure of the microcontroller. Many ports and port pins can be assigned to various functionalities,
e.g.
- General purpose I/O
- ADC
- SPI
- SCI
- PWM
- CAN
- LIN
- etc
For this reason, there shall be an overall configuration and initialization of this port structure. The configuration and mode of these port pins is microcontroller and ECU dependent.
Port initialisation data shall be written to each port as efficiently as possible.
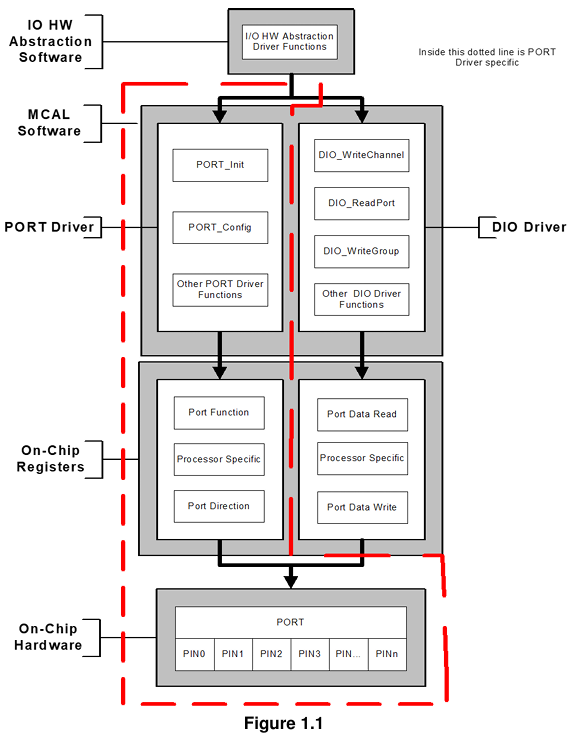
This PORT driver module shall complete the overall configuration and initialisation of the port structure which is used in the DIO driver module. Therefore, the DIO driver works on pins and ports which are configured by the PORT driver.
The PORT driver shall be initialised prior to use of the DIO functions. Otherwise DIO functions will exhibit undefined behaviour.
The diagram below identifies the PORT driver functions, and the structure of the PORT driver and DIO driver within the MCAL software layer [1].




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号