![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import xlsxwriter
2 # Create an new Excel file and add a worksheet.
3 workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook('demo.xlsx')
4 worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet()
5 # Widen the first column to make the text clearer.
6 worksheet.set_column('A:A', 20)
7 # Add a bold format to use to highlight cells.
8 bold = workbook.add_format({'bold': True})
9 # Write some simple text.
10 worksheet.write('A1', 'Hello')
11 # Text with formatting.
12 worksheet.write('A2', 'World', bold)
13 # Write some numbers, with row/column notation.
14 worksheet.write(2, 0, 123) # 第二3行第1列
15 worksheet.write(3, 0, 123.456) # 第四行第1列
16 # Insert an image.
17 worksheet.insert_image('B5', 'logo.png')
18 workbook.close()
![]()
1 import xlwt
2 from datetime import datetime
3 style0 = xlwt.easyxf('font: name Times New Roman, color-index red, bold on',
4 num_format_str='#,##0.00')
5 style1 = xlwt.easyxf(num_format_str='D-MMM-YY')
6 wb = xlwt.Workbook()
7 ws = wb.add_sheet('A Test Sheet')
8 ws.write(0, 0, 1234.56, style0)
9 ws.write(1, 0, datetime.now(), style1)
10 ws.write(2, 0, "hello world")
11 ws.write(3, 0, 1)
12 ws.write(3, 1, 3)
13 ws.write(3, 2, xlwt.Formula("A4+B4"))
14 wb.save('example.xls')
![]()
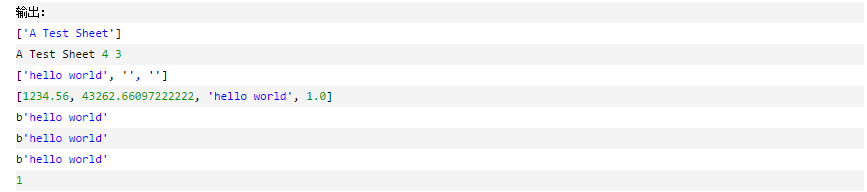
1 import xlrd
2 # 打开文件
3 workbook = xlrd.open_workbook('example.xls')
4 sheet2_name = workbook.sheet_names() # 获取所有sheet名称
5 print(sheet2_name)
6 # 根据sheet索引或者名称获取sheet内容
7 sheet1 = workbook.sheet_by_index(0) # sheet索引从0开始
8 # sheet1 = workbook.sheet_by_name('sheet2')
9 # sheet1的名称,行数,列数
10 print(sheet1.name, sheet1.nrows, sheet1.ncols)
11 # 获取整行和整列的值(数组)
12 rows = sheet1.row_values(2) # 获取第三行内容
13 cols = sheet1.col_values(0) # 获取第1列内容
14 print(rows)
15 print(cols)
16 # 获取单元格内容
17 print(sheet1.cell(2, 0).value.encode('utf-8'))
18 print(sheet1.cell_value(2, 0).encode('utf-8'))
19 print(sheet1.row(2)[0].value.encode('utf-8'))
20 # 获取单元格内容的数据类型
21 print(sheet1.cell(2, 0).ctype)
![]()
![]()
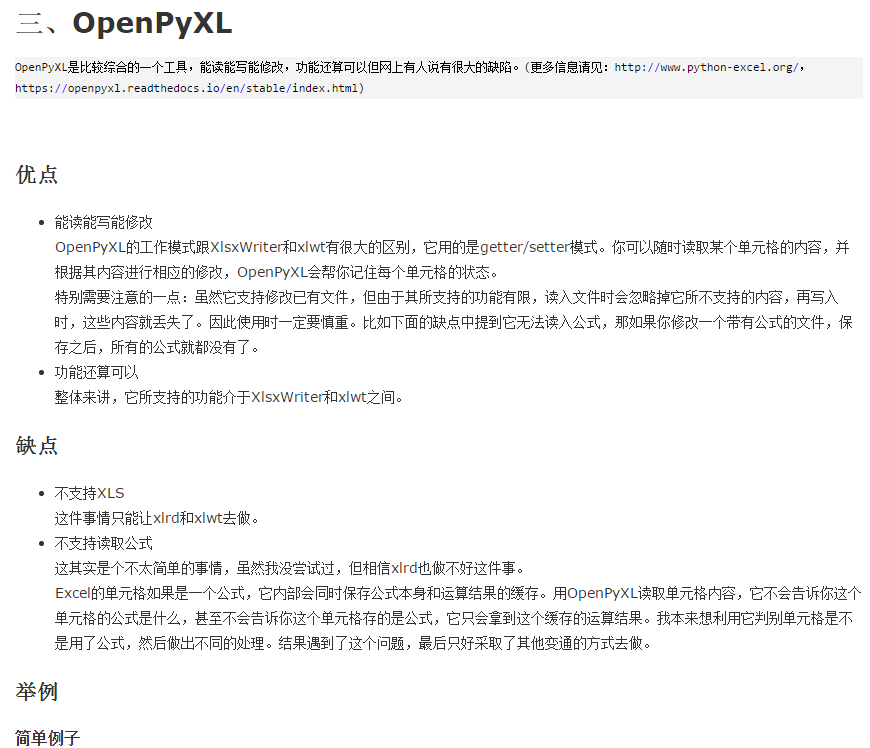
from openpyxl import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
# grab the active worksheet
ws = wb.active
# Data can be assigned directly to cells
ws['A1'] = 42
# Rows can also be appended
ws.append([1, 2, 3])
# Python types will automatically be converted
import datetime
ws['A2'] = datetime.datetime.now()
# Save the file
wb.save("sample.xlsx")
![]()
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.compat import range
from openpyxl.utils import get_column_letter
wb = Workbook()
dest_filename = 'book.xlsx'
ws1 = wb.active
ws1.title = "range names"
for row in range(1, 5):
ws1.append(range(0, 10))
ws2 = wb.create_sheet(title="Pi")
ws2['F5'] = 3.14
ws3 = wb.create_sheet(title="Data")
for row in range(2, 10):
for col in range(27, 40):
_ = ws3.cell(column=col, row=row, value="{0}".format(get_column_letter(col)))
wb.save(filename=dest_filename)
![]()
1 from openpyxl import load_workbook
2 wb = load_workbook(filename='book.xlsx')
3 sheet_ranges = wb['range names']
4 print(sheet_ranges['D2'].value)
![]()
![]()
1 import pyexcel as p # make sure you had pyexcel-xls installed
2 a_list_of_dictionaries = [
3 {
4 "Name": 'Adam',
5 "Age": 28
6 },
7 {
8 "Name": 'Beatrice',
9 "Age": 29
10 },
11 {
12 "Name": 'Ceri',
13 "Age": 30
14 },
15 {
16 "Name": 'Dean',
17 "Age": 26
18 }
19 ]
20 pyexcel.save_as(records=a_list_of_dictionaries, dest_file_name="your_file.xls")
![]()
1 import pyexcel as p # make sure you had pyexcel-xls installed
2 records = p.iget_records(file_name="your_file.xls")
3 for record in records:
4 print("%s is aged at %d" % (record['Name'], record['Age']))
5 p.free_resources()
![]()
















 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号