ansible-playbook
yaml格式参数解释

基础用法
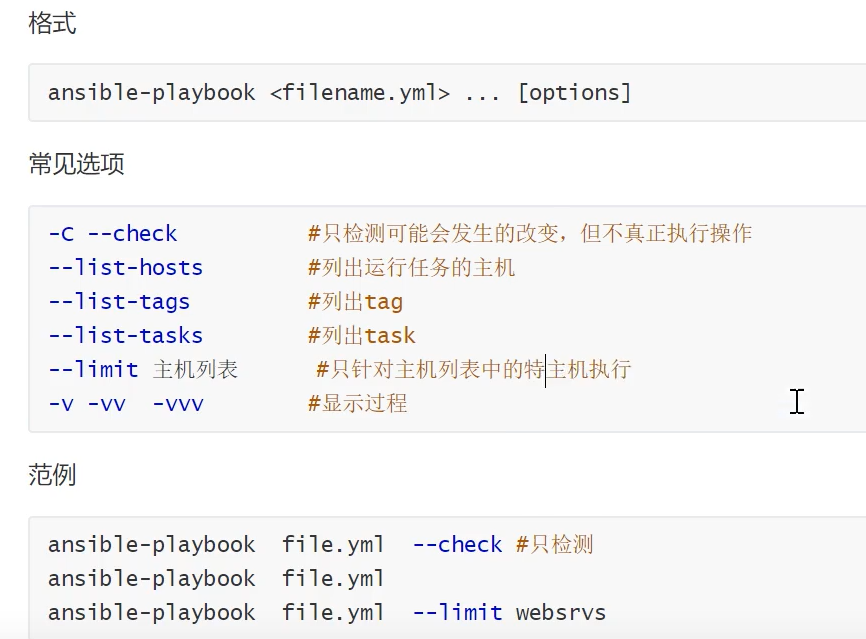
playbook 常见选项
测试
语法检测
[root@master-1 playbook]# ansible-playbook redis.yaml --syntax-check playbook: redis.yaml
-C 模拟运行
ansible-playbook -C(即 --check 模式)用于执行干跑(dry-run),检查 playbook 会执行哪些更改,而不真正执行变更。
ansible-playbook -C 会跳过 unarchive,因为它涉及文件操作,无法模拟
列出主机
[root@master-1 roles]# ansible-playbook -i roles/es_cluster/hosts/inventory.yaml main_nginx_all.yml --list-hosts playbook: main_nginx_all.yml play #1 (elasticsearch): elasticsearch TAGS: [] pattern: [u'elasticsearch'] hosts (3): es-node3 es-node2 es-node1
模拟运行
[root@master-1 roles]# ansible-playbook -i roles/es_cluster/hosts/inventory.yaml main_nginx_all.yml -C
列出任务和hosts
[root@master-1 playbook]# ansible-playbook --list-hosts redis.yaml playbook: redis.yaml play #1 (nginx): nginx TAGS: [] pattern: [u'nginx'] hosts (2): 192.168.43.130 192.168.43.131 [root@master-1 playbook]# ansible-playbook --list-tasks redis.yaml playbook: redis.yaml play #1 (nginx): nginx TAGS: [] tasks: install reddis TAGS: [] copy cfg TAGS: [] start service TAGS: []
playbook高级用法
[root@master-1 playbook]# cat redis.yaml - hosts: nginx remote_user: root # ansible执行的时候默认会收集目标主机的信息,禁用能提高效率 gather_facts: no tasks: - name: install reddis yum: name=redis state=present - name: copy cfg copy: src=/opt/ansible/test.sh dest=/tmp/ansible/test3.sh - name: start service systemd: name=redis state=started enabled=yes
新版本语法
ansible.builtin.lineinfile 是 Ansible 2.10 及以上版本推荐的写法,它明确指定了 lineinfile 模块是 **官方自带(builtin)**的模块。
其他模块如 copy、yum 也建议使用 ansible.builtin.xxx 形式,以确保兼容性和可读性。
- hosts: nginx remote_user: root gather_facts: no tasks: - name: install reddis # yum: name=redis state=present ansible.builtin.yum: name: redis state: present - name: copy cfg #copy: src=/opt/ansible/test.sh dest=/tmp/ansible/test3.sh #notify: restart rediis ansible.builtin.copy: src: /opt/ansible/test.sh dest: /tmp/ansible/test6.sh notify: restart redis - name: start service #systemd: name=redis state=started enabled=yes ansible.builtin.systemd: name: redis state: started enabled: yes handlers: - name: restart redis #systemd: name=redis state=restarted ansible.builtin.systemd: name: redis state: restarted
运行
[root@master-1 playbook]# ansible-playbook redis.yaml
如果文件未发生改变,则不会触发notify
[root@master-1 playbook]# ansible-playbook redis.yaml PLAY [nginx] ******************************************************************************************************************************************************************************* TASK [install reddis] ********************************************************************************************************************************************************************** ok: [192.168.43.130] ok: [192.168.43.131] TASK [copy cfg] **************************************************************************************************************************************************************************** ok: [192.168.43.131] ok: [192.168.43.130] TASK [start service] *********************************************************************************************************************************************************************** ok: [192.168.43.131] ok: [192.168.43.130] PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************************************************************************************************************************* 192.168.43.130 : ok=3 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0 192.168.43.131 : ok=3 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
notify与handlers
在Ansible中,notify 和 handlers 是用于在任务执行过程中触发特定操作的机制。它们通常用于在任务完成后执行一些清理工作、重启服务或应用配置更改等操作。以下是对这两个概念的详细解释:
notify
notify 关键字用于在任务(task)中指定当任务成功执行后要触发的 handler。当某个任务成功执行时,Ansible 会查找与该任务关联的 notify,并执行相应的 handler。
- name: Update a configuration file copy: src: /path/to/new/config.conf dest: /etc/config.conf notify: - Restart the service
handlers
handlers 是在 Ansible playbook 中定义的一组任务,它们不会直接执行,而是由 notify 关键字触发。Handlers 通常用于执行仅在特定条件下需要运行的任务,例如服务重启或配置重新加载。
- 避免重复触发:如果多个任务通知同一个 handler,并且这些任务在同一个 Ansible 运行中成功执行,那么该 handler 只会执行一次。
- 条件性触发:虽然
notify通常用于任务成功后的触发,但也可以结合 Ansible 的条件语句(如when)来实现更复杂的触发逻辑。 - Handler 顺序:Handlers 的执行顺序是按照它们在 playbook 中定义的顺序进行的。如果需要特定的执行顺序,可以调整 handlers 的定义顺序。
- name: start service #systemd: name=redis state=started enabled=yes ansible.builtin.systemd: name: redis state: started enabled: yes
而无论是否触发handlers,都会执行这一步骤,对于service和systemd来说,可以检测服务状态,如果没发生改变,则不做任何改变。
如果是二进制启动,则无法检测
- name: start nginx ansible.builtin.shell: | pkill nginx "{{ nginx_install_dir }}/sbin/nginx"
那么对于nginx来说,无论是kill进程(服务中断)或者启动(端口占用),都是不希望看到的。
解决方式:
1. 进行进程和端口访问测试
使用uri模块和shell模块
- name: start nginx ansible.builtin.systemd: name: nginx daemon_reload: yes state: started - name: check nginx pidfile ansible.builtin.stat: path: "{{ nginx_install_dir }}/logs/nginx.pid" register: nginx_pid - name: output mesage ansible.builtin.debug: msg: "nginx pid文件存在,nginx启动完成..." when: nginx_pid.stat.exists - name: check nginx port ansible.builtin.uri: url: http://localhost:{{ listen_port }} #status_code: 404 status_code: 200 register: result until: result.status == 200 retries: 5 delay: 3 when: nginx_pid.stat.exists handlers: - name: reload nginx #ansible.builtin.systemd: # name: redis # state: restarted #ansible.builtin.shell: | # #pkill nginx # "{{ nginx_install_dir }}/sbin/nginx" -s reload ansible.builtin.systemd: name: nginx state: reloaded when: nginx_pid.stat.exists
2. 使用systemd管理nginx
2.1 创建nginx.conf.j2文件
[root@master-1 playbook]# cat nginx/templates/nginx.service.j2 [Unit] Description=Nginx Web Server After=network.target [Service] Type=forking ExecStartPre={{ nginx_install_dir }}/sbin/nginx -t ExecStart={{ nginx_install_dir }}/sbin/nginx ExecReload={{ nginx_install_dir }}/sbin/nginx -s reload ExecStop={{ nginx_install_dir }}/sbin/nginx -s quit Restart=always User=root LimitNOFILE=100000 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
2.2 playbook
- name: 使用 template 渲染并验证 Nginx 启动文件 ansible.builtin.template: src: nginx.service.j2 dest: "/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service" tags: template_nginx_service
tags
对任务做标签,在执行playbook的时候,可以-t tagname,tagname进行选择性执行。
- name: 使用 template 渲染并验证 Nginx 配置 ansible.builtin.template: src: templates/nginx.conf.j2 dest: "{{ nginx_install_dir }}/conf/nginx.conf" validate: "'{{ nginx_install_dir }}/sbin/nginx' -t -c %s" tags: template_nginx_conf notify: reload nginx handlers: - name: reload nginx #ansible.builtin.systemd: # name: redis # state: restarted ansible.builtin.shell: | #pkill nginx "{{ nginx_install_dir }}/sbin/nginx" -s reload
执行
可以看到只执行了渲染这个模块步骤,并且触发了handlers任务。
[root@master-1 nginx]# ansible-playbook -t template_nginx_conf template-deploy-nginx.yaml PLAY [nginx] **************************************************************************************************************************************************************************** TASK [Gathering Facts] ****************************************************************************************************************************************************************** ok: [192.168.43.131] ok: [192.168.43.130] TASK [使用 template 渲染并验证 Nginx 配置] ******************************************************************************************************************************************************* changed: [192.168.43.130] changed: [192.168.43.131] RUNNING HANDLER [reload nginx] ********************************************************************************************************************************************************** changed: [192.168.43.130] changed: [192.168.43.131] PLAY RECAP ****************************************************************************************************************************************************************************** 192.168.43.130 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0 192.168.43.131 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
案例
1. 二进制部署nginx
在 Playbook 中使用template模块动态生成配置文件
不需要 roles 目录,直接在 playbook.yml 里定义 template 任务,例如:
1. 文件结构
/opt/ansible/playbook/ │── playbook.yml # Ansible Playbook │── vars.yml # 变量文件 │── templates/ │ ├── nginx.conf.j2 # Jinja2 模板文件
2. 变量文件 vars.yml
[root@master-1 nginx]# cat vars.yaml nginx_version: "1.22.1" nginx_src_dir: "/tmp/nginx/" nginx_install_dir: "/usr/local/nginx" server_name: localhost listen_port: 81
3. Playbook (playbook.yml)
- hosts: nginx remote_user: root # 收集远程主机信息 gather_facts: yes #vars: # nginx_version: "1.22.1" # nginx_src_dir: "/tmp/nginx/" # nginx_install_dir: "/usr/local/nginx" vars_files: - vars.yaml tasks: - name: install gcc openssl ansible.builtin.yum: name: - openssl - openssl-devel - make- libxslt-devel - perl - perl-ExtUtils-Embed state: present update_cache: yes when: ansible_distribution == "CentOS" - name: ubuntu install gcc openssl ansible.builtin.apt: name: - build-essential - libpcre3 - libpcre3-dev - openssl - libssl-dev - zlib1g-dev zlib1g state: present update_cache: yes when: ansible_distribution == "Ubuntu" # 使用unarchive 将本地包解压到远程主机 #- name: copy nginx package # ansible.builtin.copy: # src: /opt/ansible/playbook/nginx/nginx-{{ nginx_version }}.tar.gz # dest: "{{ nginx_src_dir }}" #- name: ls nginx # ansible.builtin.shell: | # ls -l /tmp/nginx/ # 如果是将本地文件解压到远程服务器,则目标路径必须存在 - name: unarchive nginx ansible.builtin.file: path: "{{ nginx_src_dir }}" state: directory - name: unarchive nginx ansible.builtin.unarchive: #src: "{{ nginx_src_dir }}nginx-{{ nginx_version }}.tar.gz" src: /opt/ansible/playbook/nginx/nginx-1.22.1.tar.gz dest: "{{ nginx_src_dir }}" # 可以直接将本地包直接解压到目标主机目录下,不用 remote_src: yes #remote_src: yes - name: configuure nginx ansible.builtin.shell: | #{{ nginx_src_dir }}/nginx-{{ nginx_version }}/configure ./configure \ --prefix={{ nginx_install_dir }} \ --user=nginx \ --group=nginx \ --with-http_ssl_module \ --with-http_v2_module \ --with-http_realip_module \ --with-http_stub_status_module \ --with-http_gzip_static_module \ --with-pcre \ --with-stream \ --with-stream_ssl_module \ --with-stream_realip_module args: # Change into this directory before running the command. chdir: "{{ nginx_src_dir }}/nginx-{{ nginx_version }}" # A filename, when it already exists, this step will *not* be run. creates: "{{ nginx_src_dir }}/nginx-{{ nginx_version }}/objs/Makefile" - name: make nginx ansible.builtin.shell: | make args: chdir: "{{ nginx_src_dir }}/nginx-{{ nginx_version }}" creates: "{{ nginx_src_dir }}/nginx-{{ nginx_version }}/objs/nginx" - name: make install ansible.builtin.shell: | make install args: chdir: "{{ nginx_src_dir }}/nginx-{{ nginx_version }}" creates: "{{ nginx_install_dir }}/sbin/nginx" - name: create nginx user ansible.builtin.user: name: nginx shell: /sbin/nologin create_home: false #- name: copy nginx config # ansible.builtin.copy: # src: /opt/ansible/playbook/nginx/nginx.conf # dest: "{{ nginx_install_dir }}/conf/" # 检查nginx配置格式 # 如果 validate 失败,Ansible 会报错并停止 Playbook,后续任务不会执行。 # %s 代表临时文件路径,Ansible 会把新文件存到临时位置进行测试。 # validate: "'{{ nginx_install_dir }}/sbin/nginx' -t -c %s" # 忽略错误,失败后继续执行下面的task # ignore_errors: yes - name: 使用 template 渲染并验证 Nginx 配置 ansible.builtin.template: src: templates/nginx.conf.j2 dest: "{{ nginx_install_dir }}/conf/nginx.conf" validate: "'{{ nginx_install_dir }}/sbin/nginx' -t -c %s" tags: template_nginx_conf notify: reload nginx - name: 使用 template 渲染并验证 Nginx 启动文件 ansible.builtin.template: src: nginx.service.j2 dest: "/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service" tags: template_nginx_service - name: chown nginx_install_dir ansible.builtin.file: path: "{{ nginx_install_dir }}" owner: nginx group: nginx # 递归修改目录权限,仅当state=directory有效 # 相当于 chown -R recurse: yes state: directory - name: start nginx ansible.builtin.systemd: name: nginx daemon_reload: yes state: started - name: check nginx pidfile ansible.builtin.stat: path: "{{ nginx_install_dir }}/logs/nginx.pid" register: nginx_pid - name: output mesage ansible.builtin.debug: msg: "nginx pid文件存在,nginx启动完成..." when: nginx_pid.stat.exists - name: check nginx port ansible.builtin.uri: url: http://localhost:{{ listen_port }} #status_code: 404 status_code: 200 register: result until: result.status == 200 retries: 5 delay: 3 when: nginx_pid.stat.exists handlers: - name: reload nginx #ansible.builtin.systemd: # name: redis # state: restarted #ansible.builtin.shell: | # #pkill nginx # "{{ nginx_install_dir }}/sbin/nginx" -s reload ansible.builtin.systemd: name: nginx state: reloaded when: nginx_pid.stat.exists # 添加了判断条件,nginx特性:只有nginx启动时,pid文件存在。
4. Jinja2 模板 (templates/nginx.conf.j2)
[root@master-1 nginx]# cat templates/nginx.conf.j2 user nginx nginx; worker_processes auto; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { #include mime.types; include {{ nginx_install_dir }}/conf/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; server { listen {{ listen_port }}; server_name {{ server_name }}; location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } } #mail { # } #stream { # ... # } #include /apps/nginx/conf.d/*.conf }
5. 运行 Playbook
ansible-playbook playbook.yml
6. 遇到的问题:
1. include mime.types; validate 无法检查成功
[root@master-1 nginx]# cat templates/nginx.conf.j2 user nginx nginx; worker_processes auto; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; server { listen {{ listen_port }}; server_name {{ server_name }}; location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } } #mail { # } #stream { # ... # } #include /apps/nginx/conf.d/*.conf }
这个include在ansible有什么特殊意义吗,为什么会报错fatal: [192.168.43.130]: FAILED! => {"changed": false, "checksum": "1bbcd856439212a903d0eccf4885c544741c012f", "exit_status": 1, "msg": "failed to validate", "stderr": "nginx: [emerg] open() \"/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1739344206.81-34410-165624038437658/mime.types\" failed (2: No such file or directory) in /root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1739344206.81-34410-165624038437658/source:8\nnginx: configuration file /root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1739344206.81-34410-165624038437658/source test failed\n", "stderr_lines": ["nginx: [emerg] open() \"/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1739344206.81-34410-165624038437658/mime.types\" failed (2: No such file or directory) in /root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1739344206.81-34410-165624038437658/source:8", "nginx: configuration file /root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1739344206.81-34410-165624038437658/source test failed"], "stdout": "", "stdout_lines": []}
而当我注释掉
# include mime.types; 就可以成功
原因:
这个 validate 选项的作用是:
- Ansible 生成一个临时的 Nginx 配置文件,存放在
/root/.ansible/tmp/.../source目录。 - Ansible 让 Nginx 在这个临时路径检查配置文件的正确性:
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t -c /root/.ansible/tmp/.../source
Nginx 解析配置文件,当它执行到:
include mime.types;
这条配置时,它会去查找 mime.types 文件,但默认情况下,它认为 mime.types 文件应该在与 nginx.conf 相同的路径,即:
/root/.ansible/tmp/.../mime.types
但是 mime.types 文件并不在这个临时目录里,所以 Nginx 报错找不到文件
解决:
使用绝对路径
修改 nginx.conf.j2,指定 mime.types 的完整路径:
http {
include {{ nginx_install_dir }}/conf/mime.types;
这样,即使 Nginx 在临时目录检查配置,也会去 正确的路径 查找 mime.types,避免报错。
2. 二进制部署es分布式集群
需求分析:如何动态生成配置文件,比如node.name,discovery.seed_hosts,cluster.initial_master_nodes等。
1. 目录解构
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 231 2月 16 21:49 vars.yaml [root@master-1 es]# tree . . ├── certs │ ├── elastic-certificates.p12 │ └── elastic-stack-ca.p12 ├── config ├── deploy.yaml ├── elasticsearch-7.16.3-linux-x86_64.tar.gz ├── elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.16.3.zip ├── inventory.yaml ├── jdk-8u341-linux-x64.tar.gz ├── templates │ └── elasticsearch.yml.j2 └── vars.yaml
2. 主机清单inventory.yaml
[root@master-1 es]# cat inventory.yaml all: # Ansible 习惯使用 children 来定义组,而 all.hosts 一般只包含独立主机,所以这里设置为空 {} 让结构更清晰。 hosts: {} # 这里将下面hosts定义的单独主机用children权保部写到elasticsearch组。 children: elasticsearch: hosts: es-node1: ansible_host: 192.168.43.129 node_name: es-node1 # 用于when条件控制,生成证书 is_ca: true es-node2: ansible_host: 192.168.43.130 node_name: es-node2 es-node3: ansible_host: 192.168.43.131 node_name: es-node3
3. 变量vars.yml
[root@master-1 es]# cat vars.yaml JAVA_HOME: "/opt/jdk1.8.0_341" cluster_name: cluster listen_port: 9200 es_version: 7.16.3 es_install_dir: "/opt/elasticsearch-{{ es_version }}" password: "$1$6NXikaln$64e67B6Q2C0xK0fuNkVw30" es_ca_pass: 123456 es_cert_pass: 123456
4. elasticsearch.yml.j2配置文件
[root@master-1 es]# egrep -v "^#|^$" templates/elasticsearch.yml.j2 cluster.name: {{ cluster_name }} node.name: {{ node_name }} path.data: {{ es_install_dir }}/data path.logs: {{ es_install_dir }}/logs network.host: {{ ansible_host }} http.port: {{ listen_port }} discovery.seed_hosts: {% for host in groups['elasticsearch'] %} - "{{ hostvars[host]['ansible_host'] }}" {% endfor %} cluster.initial_master_nodes: {% for host in groups['elasticsearch'] %} - "{{ hostvars[host]['node_name'] }}" {% endfor %} transport.tcp.port: 9300 xpack.security.enabled: true xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled: true xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode: certificate xpack.security.transport.ssl.keystore.path: {{ es_install_dir }}/config/elastic-certificates.p12 xpack.security.transport.ssl.truststore.path: {{ es_install_dir }}/config/elastic-certificates.p12 xpack.monitoring.collection.cluster.stats.timeout: '30s' ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false
5. playbook
- hosts: elasticsearch remote_user: root # 收集远程主机信息 gather_facts: yes #vars: # nginx_version: "1.22.1" # nginx_src_dir: "/tmp/nginx/" # nginx_install_dir: "/usr/local/nginx" vars_files: - vars.yaml tasks: - name: unarchive java ansible.builtin.unarchive: src: jdk-8u341-linux-x64.tar.gz dest: /opt/ # blockinfile可以避免重复写入 - name: Configure Java environment variables blockinfile: path: /etc/profile block: | export JAVA_HOME={{ JAVA_HOME }} export CLASSPATH=.:{{ JAVA_HOME }}/jre/lib/rt.jar:{{ JAVA_HOME }}/lib/dt.jar:{{ JAVA_HOME }}/lib/tools.jar export PATH={{ JAVA_HOME }}/bin:$PATH marker: "# {mark} ANSIBLE MANAGED BLOCK - JAVA" ############################################################################ #- name: source # ansible.builtin.shell: | # source /etc/profile # 报错,java命令找不到,所以需要执行时,再source一次 #- name: check java # ansible.builtin.shell: | # java -version # register: java_version # #ignore_errors: yes # 避免 playbook 因错误中断 #- debug: # msg: "{{ java_version.stderr }}" ############################################################################ #- name: 修改内核参数 # ansible.builtin.lineinfile: # path: /etc/sysctl.conf # regexp: '^vm\.max_map_count' # line: "vm.max_map_count= 262144" #- name: 使内核参数生效 # ansible.builtin.shell: # sysctl -p #############################################################################
############################# 优化后 ######################################### - name: 修改并应用内核参数 ansible.builtin.sysctl: name: vm.max_map_count # 只能用'', ""语法报错 value: '262144' state: present reload: yes #- name: 获取主机信息 # setup: # # 将setup收集到信息保存到变量register。 # register: system_info - name: 解压es到远程服务器 ansible.builtin.unarchive: src: elasticsearch-7.16.3-linux-x86_64.tar.gz dest: /opt # 需要开启收集远程主机信息 when: ansible_machine == "x86_64" - name: 创建数据目录 ansible.builtin.file: path: "{{ es_install_dir}}/data" state: directory - name: 修改JVM内存 ansible.builtin.lineinfile: path: "{{ es_install_dir }}/config/jvm.options" regexp: "^## -Xms" #line: "-Xms{{ (system_info.ansible_facts.ansible_memtotal_mb / 2)|int }}m" line: "-Xms{{ (ansible_memtotal_mb / 3)|int }}m" - name: 修改JVM最大使用内存 ansible.builtin.lineinfile: path: "{{ es_install_dir }}/config/jvm.options" regexp: "^## -Xmx" #line: "-Xmx{{ (system_info.ansible_facts.ansible_memtotal_mb / 2)|int }}m" line: "-Xmx{{ (ansible_memtotal_mb / 3)|int }}m" - name: 渲染配置文件 ansible.builtin.template: src: elasticsearch.yml.j2 dest: "{{ es_install_dir }}/config/elasticsearch.yml" notify: restart elasticsearch - name: 生成CA证书 ansible.builtin.shell: | cd "{{ es_install_dir }}/bin" ./elasticsearch-certutil ca --pass "{{ es_ca_pass }}" -out "{{ es_install_dir }}/config/elastic-stack-ca.p12" args: creates: "{{ es_install_dir }}/config/elastic-stack-ca.p12" when: inventory_hostname in groups['elasticsearch'] and hostvars[inventory_hostname].is_ca is defined and hostvars[inventory_hostname].is_ca - name: 生成节点证书 ansible.builtin.shell: | cd "{{ es_install_dir }}/bin" echo "{{ es_cert_pass}}" |./elasticsearch-certutil cert --ca "{{ es_install_dir }}/config/elastic-stack-ca.p12" --ca-pass "{{ es_ca_pass }}" -out "{{ es_install_dir }}/config/elastic-certificates.p12" args: creates: "{{ es_install_dir }}/config/elastic-certificates.p12" when: inventory_hostname in groups['elasticsearch'] and hostvars[inventory_hostname].is_ca is defined and hostvars[inventory_hostname].is_ca - name: 拉取CA证书 ansible.builtin.fetch: src: "{{ es_install_dir }}/config/elastic-stack-ca.p12" dest: "./certs/" # 如果dest以/结尾,则复制到目录下,否则为文件名 flat: yes when: inventory_hostname in groups['elasticsearch'] and hostvars[inventory_hostname].is_ca is defined and hostvars[inventory_hostname].is_ca - name: 拉取服务证书 ansible.builtin.fetch: src: "{{ es_install_dir }}/config/elastic-certificates.p12" dest: "./certs/" # 如果dest以/结尾,则复制到目录下,否则为文件名 flat: yes when: inventory_hostname in groups['elasticsearch'] and hostvars[inventory_hostname].is_ca is defined and hostvars[inventory_hostname].is_ca - name: 拷贝CA证书 ansible.builtin.copy: src: "./certs/elastic-stack-ca.p12" dest: "{{ es_install_dir }}/config/elastic-stack-ca.p12" - name: 拷贝服务证书 ansible.builtin.copy: src: "./certs/elastic-certificates.p12" dest: "{{ es_install_dir }}/config/" - name: 创建keystore ansible.builtin.shell: | cd "{{ es_install_dir }}/bin" ./elasticsearch-keystore create args: creates: "{{ es_install_dir }}/config/elasticsearch.keystore"- name: 导入证书 ansible.builtin.shell: | cd "{{ es_install_dir }}/bin" echo "123456" |./elasticsearch-keystore add xpack.security.transport.ssl.keystore.secure_password echo "123456" |./elasticsearch-keystore add xpack.security.transport.ssl.truststore.secure_password - name: 创建ik分词器目录 ansible.builtin.file: path: "{{ es_install_dir }}/plugins/ik" state: directory - name: 导入ik分词器 ansible.builtin.unarchive: src: elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.16.3.zip dest: "{{ es_install_dir }}/plugins/ik" - name: 创建系统es登录用户 ansible.builtin.user: name: es shell: /bin/bash password: "{{ password}}" - name: 修改目录权限 ansible.builtin.file: path: "{{ es_install_dir }}" owner: es group: es recurse: yes state: directory - name: 切换用户es,并启动es程序 ansible.builtin.shell: | source /etc/profile #cd "{{ es_install_dir }}/bin" && "./elasticsearch -d" nohup "{{ es_install_dir }}/bin/elasticsearch" & become: true become_user: es #- name: 确保 Elasticsearch 进程存在 # ansible.builtin.shell: | # echo "正在启动es服务,请等待..." # sleep 30 # pgrep -f "elasticsearch" # register: es_process # # 判断命令是否执行成功 # # return code 0:正常 1:错误 # failed_when: es_process.rc != 0 - name: 等待 Elasticsearch 端口 9200 可用 ansible.builtin.wait_for: host: "{{ ansible_default_ipv4.address }}" port: "{{ listen_port }}" # 每 5 秒检查一次端口状态 delay: 5 # 总的等待超时时间(秒)。如果在这个时间内端口没有变得可用,任务将失败。 timeout: 60 register: es_ready changed_when: false #- name: 创建es应用登录用户 # ansible.builtin.shell: | # cd {{ es_install_dir }}/bin # ./elasticsearch-setup-passwords interactive #- name: 等待 Elasticsearch HTTP 服务响应 # ansible.builtin.shell: | # until curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" http://{{ ansible_facts.ansible_default_ipv4.address }}:9200 | grep -q "200"; do # sleep 5 # done # register: es_http # # 即使执行成功,让ansible也不认为发生了变化 # changed_when: false handlers: - name: restart elasticsearch ansible.builtin.shell: | kill `ps -ef |grep elasticsearch --no-header |awk '{print $2}'` source /etc/profile #cd "{{ es_install_dir }}/bin" #"./elasticsearch" -d nohup "{{ es_install_dir }}/bin/elasticsearch" &
6. 遇到的问题
6.1.
本文来自博客园,作者:不会跳舞的胖子,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/rtnb/p/18257920


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号