【视频笔记】3小时超快速入门Python | 动画教学【2025新版】 林粒粒呀
# 安装python解释器

python的执行过程就是,翻译一行,执行一行
https://www.python.org/


# 安装代码编辑器
Pycharm
https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/download/?section=windows
下载社区版
界面及语言设置
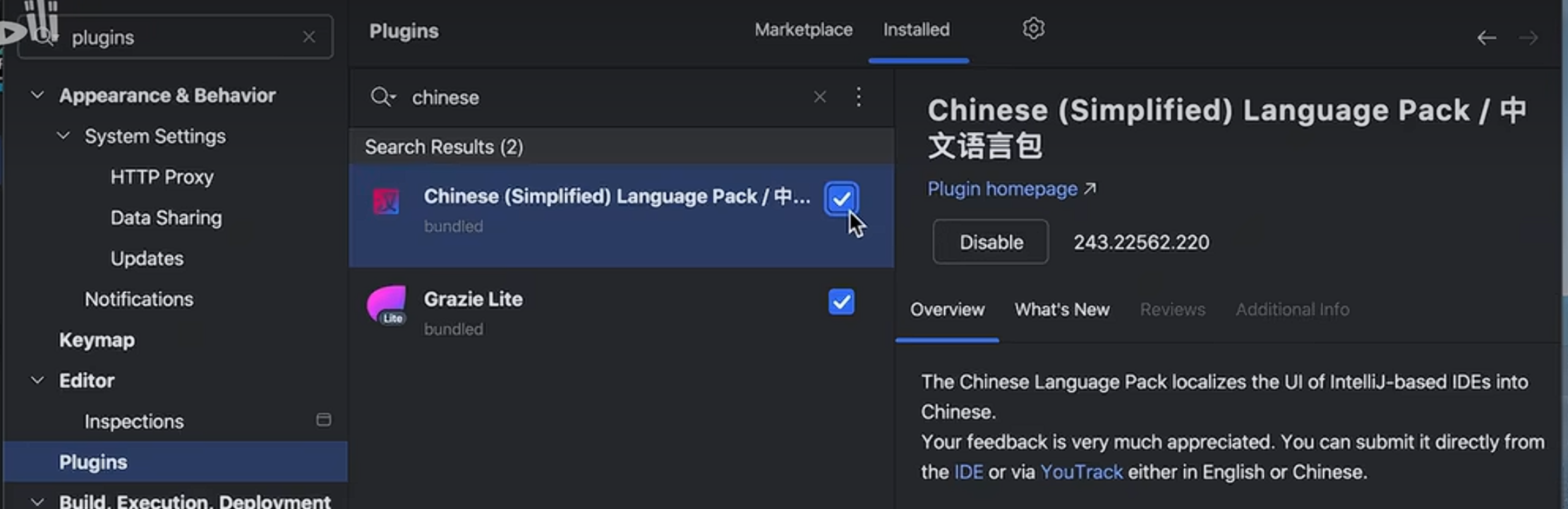
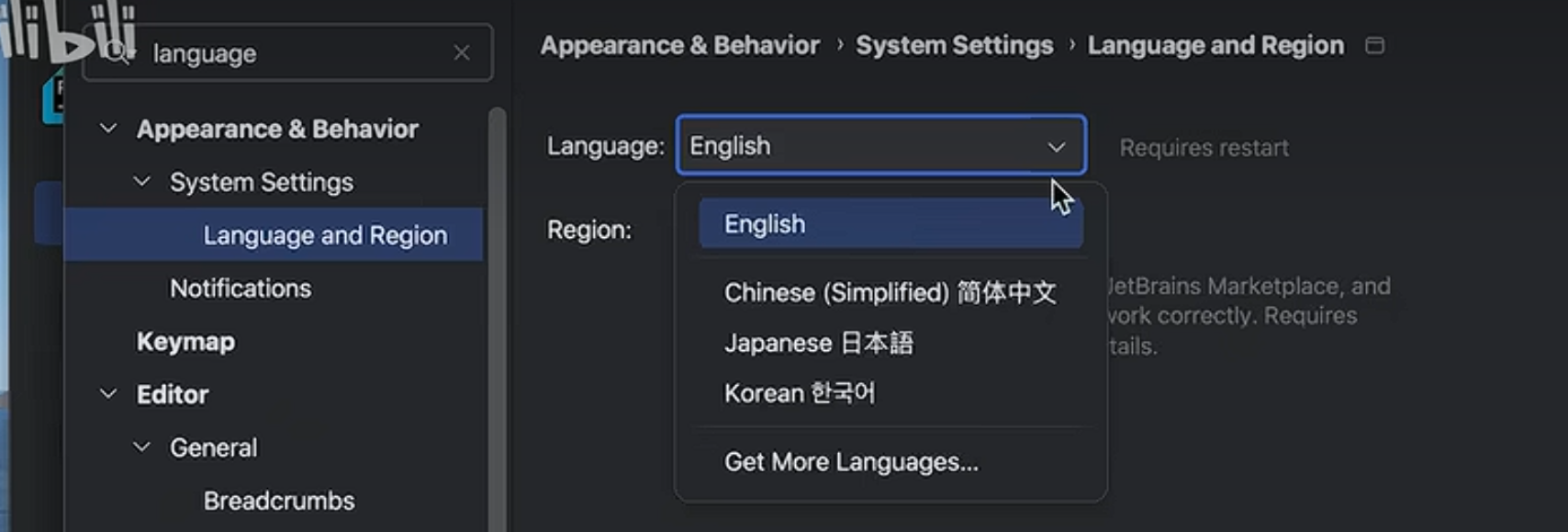
1_print_demo.py
单引号或双引号都可以
print("hello")
字符串拼接,用加号
print("a" +" b" + " c")
单双引号转义,使用反斜杠
print('Let\'s go')
\n表示换行
print("第一行\n第二行")
print默认另起一行
三个单引号或双引号,包裹的内容,python会把新的一行当成内容的换行
print("""
床前明月光
疑是地上霜
""")
变量赋值
great = "您好,吃了么" print(great + ",张三") print(great + ",李四")
变量命名规则
只能由文字、数字、下划线组成。不能有下划线之外的符号,不能有空格,不能数字开头
下划线命名法:
字母全部小写
不同单词用下划线分隔,user_age
python一般不用驼峰
变量名大小写敏感 user_age != user_Age
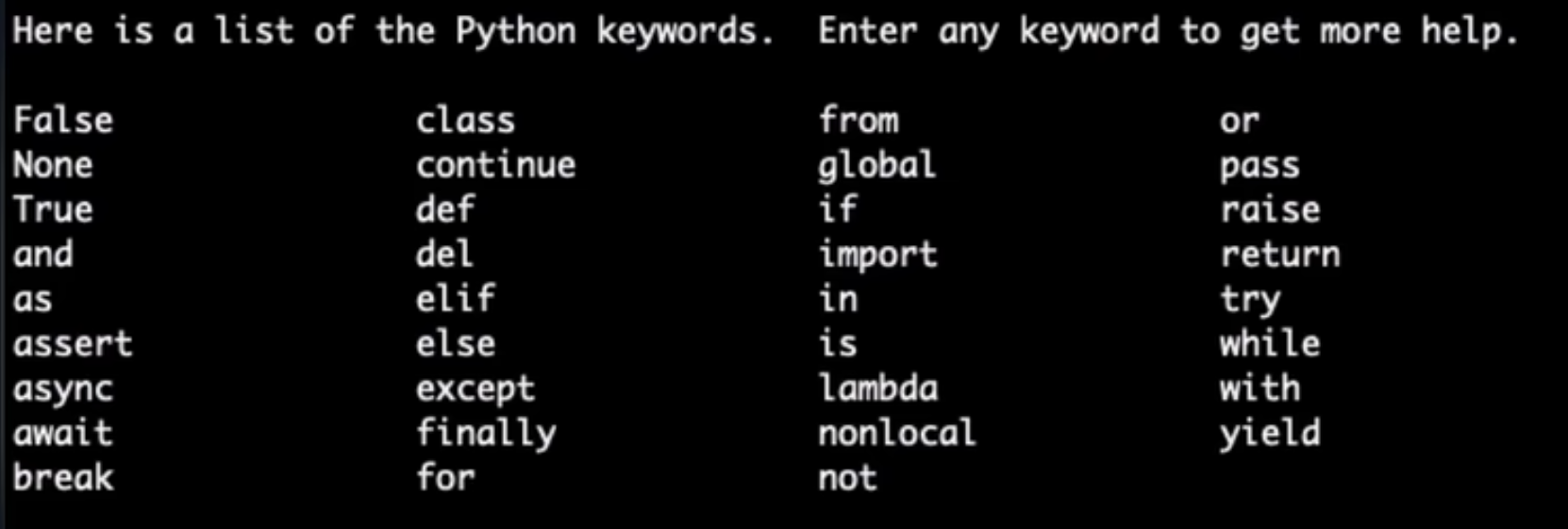
变量名不要占用python关键字,如print
关键字列表
乘方用2个星号表示 **
math函数库
导入库 import math
然后用math.函数名(...),如math.sin(1)
默认就有的函数叫内置函数

10_math.py
import math """ 计算-x**2 - 2*x + 3 == 0 的两个实数根 """ a = -1 b = -2 c = 3 print((-b + math.sqrt(b ** 2 - 4 * a * c)) / (2 * a)) print((-b - math.sqrt(b ** 2 - 4 * a * c)) / (2 * a))
# 后面书写注释内容,井号只管单行
idea给选中的多行,快捷加上注释,ctrl + / ,反过来取消注释也是这组快捷键
三引号表示多行注释
数据类型
包括字符串、整数、浮点数、布尔类型、空值类型、列表、字典
字符串使用len('str')得到长度
\n这种情况下,完整的转义符才占一个长度
使用中括号提取字符,索引。 索引从0开始
print("hello"[2]) 打印l
整数int 浮点数float
布尔类型 bool, True(T要大写)真,False(F大写)假
空值类型 NoneType,只有一个值 None (不是空字符串,不是0,不是False)表示完全没有值
# 对字符串求长度
s = "hello world!"
print(s)
#通过索引获取单个字符
print(s[0])
print(s[11])
print(s[len(s)-1])
print(type(None))
print(type(True))
print(type("str"))
# 打印如下 <class 'NoneType'> <class 'bool'> <class 'str'>
python有2种模式,命令行模式和交互模式
交互模式,退出quit() 或者ctrl+d
user_age = input("请输入年龄:") print(user_age) print(int(user_age)) # BMI = 体重 / (身高 ** 2) weight = float(input("请输入体重:")) height = float(input("请输入身高:")) bmi = weight / (height ** 2) print("您的BMI:" + str(bmi))
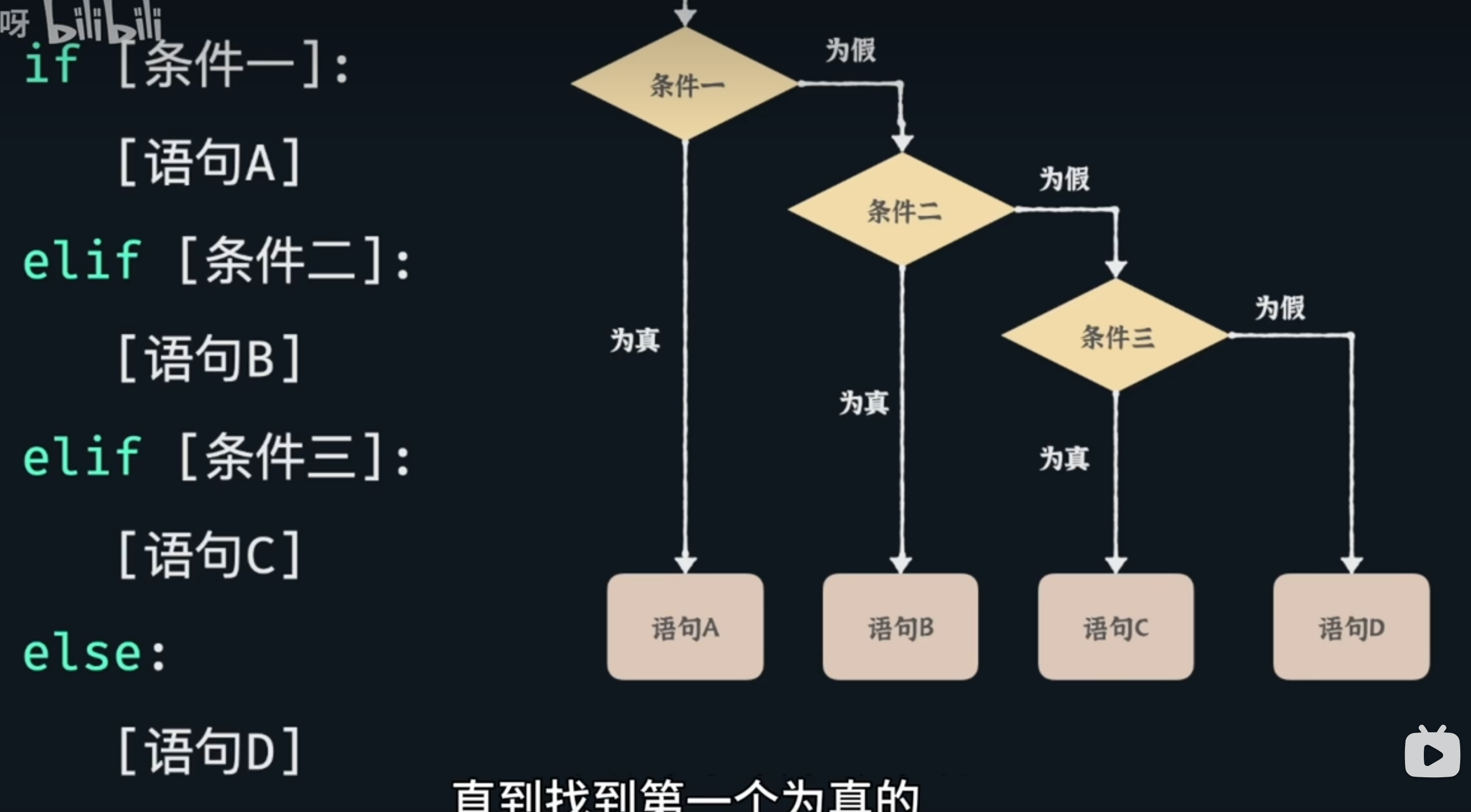
if [条件]: # 条件后面跟冒号
[执行语句] #缩进四个空格
else:
[条件为假执行语句]
cond = int(input("输入值为:")) if cond > 60: print("win") else: print("lose")
嵌套条件语句

多个条件,用elif
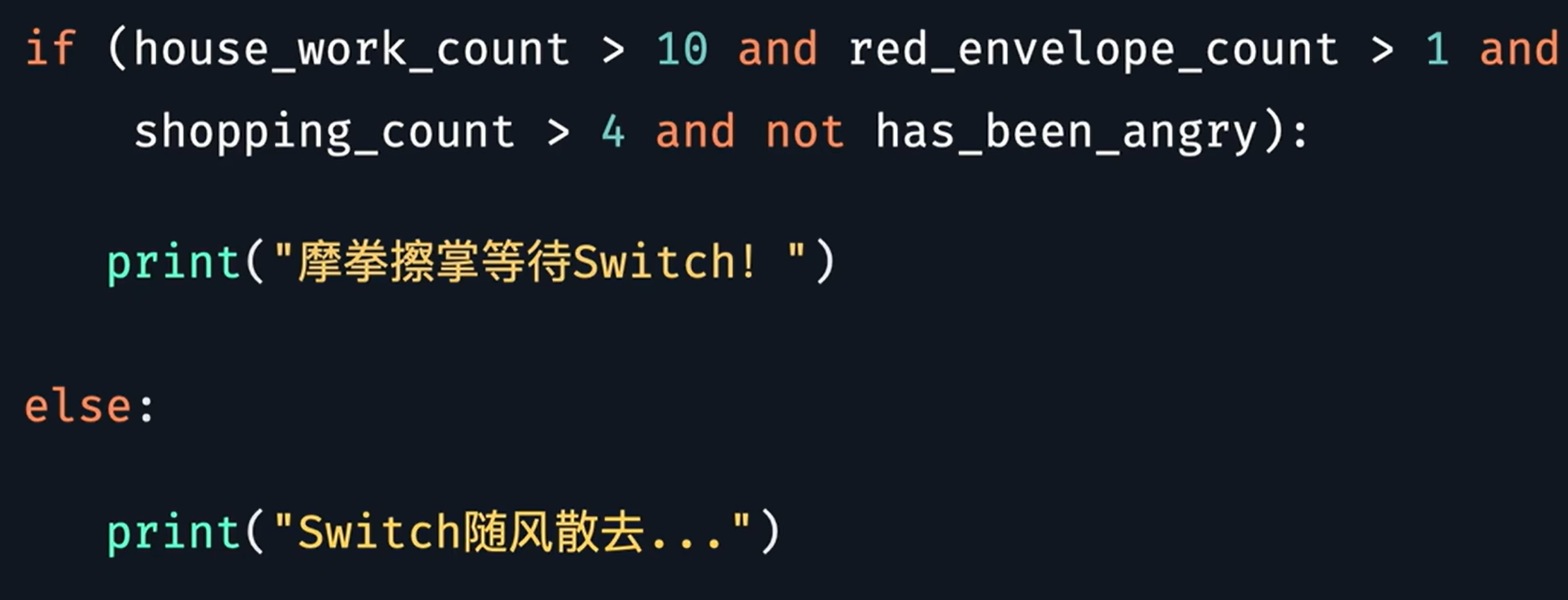
逻辑优先级 not > and > or
python列表
空的列表用空的方括号表示,shopping_list = []
shopping_list = ["a", "b"]
shopping_list.append("c")
len(shopping_list) 返回列表元素数量
列表里的内容会变,而基础类型bool, str等调用方法操作后,原来的值不会变
shopping_list.remove("c") 该元素需在列表中,否则报错
列表中可以放不同类型的数据
shopping_list.append(True)
shopping_list.append(None)
通过索引返回某个位置的元素 shopping_list[0]
sorted(num_list) 返回排好序的列表,不改变原来列表顺序
shopping_list = [] shopping_list.append("a") shopping_list.append("b") print(shopping_list) shopping_list.remove("b") shopping_list.append("c") print(len(shopping_list)) print(shopping_list[0]) shopping_list[1] = "xx" print(shopping_list) price_list = [1, 5, 2, 4] max_price = max(price_list) min_price = min(price_list) sorted_price = sorted(price_list) print(min_price) print(max_price) print(sorted_price)
数据结构 字典 dictionary
空的字典用一对花括号表示, contacts = {}
contacts = {"key1":"val1", "key2","val2"}
获取某键的值, contacts["key1"]
键的类型是不可变的,列表是可变数据类型,不能作为键;而布尔,整数,字符串等不可变类型就可以
python准备了一种不可变但又很像列表的数据结构,元组
example_tuple = ("键盘", "键帽")
contacts = {("张伟1", 10): "1312345", ("张伟1", 10):"1312345"} 把整个元组作为键
设置字典值 contacts["key3"] = "val3"
判断键是否在字典中 "key1" in contacts 返回布尔值
删除键值对,用del, del contacts["key1"] 键不存在则报错
tmp_dict = {"key1": "val1", "key2": "val2"}
tmp_dict["key3"] = "val3"
input_key = input("please input the key:")
if input_key in tmp_dict:
print("yes," + input_key + " it exist")
print("the value is:" + tmp_dict[input_key])
else:
print("not exist")
print("the current len of dict is:" + str(len(tmp_dict)))
for循环进行迭代
迭代的对象可以是列表,字典,字符串等
对列表,就是按顺序对列表的元素做一些事情
对字典,就是按顺序对里面的各个键或值做一些事情
对字符串,就是按顺序对里面的各个字符做一些事情
for 变量名 in 可迭代对象:
# 对每个变量做一些事情
字典
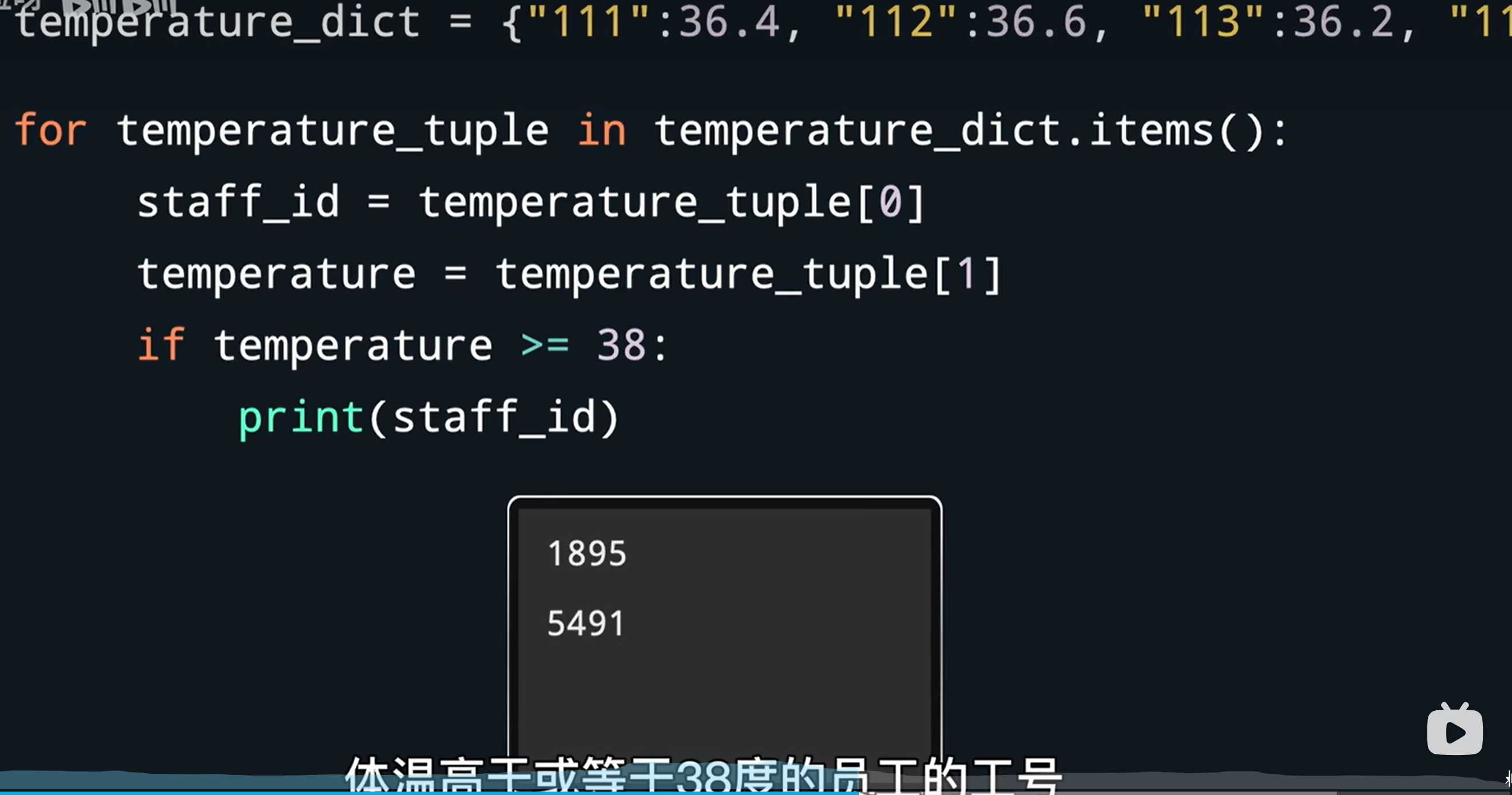
temp_dict = {"111":36.4, "112":36.6}
temp_dict.keys() # 所有键
temp_dict.values() # 所有值
temp_dict.items() # 所有键值对
# 变量会被赋值为键和值组成的元组
for staff_id, temp in temp_dict.items():
if temp >= 38:
print(staff_id)
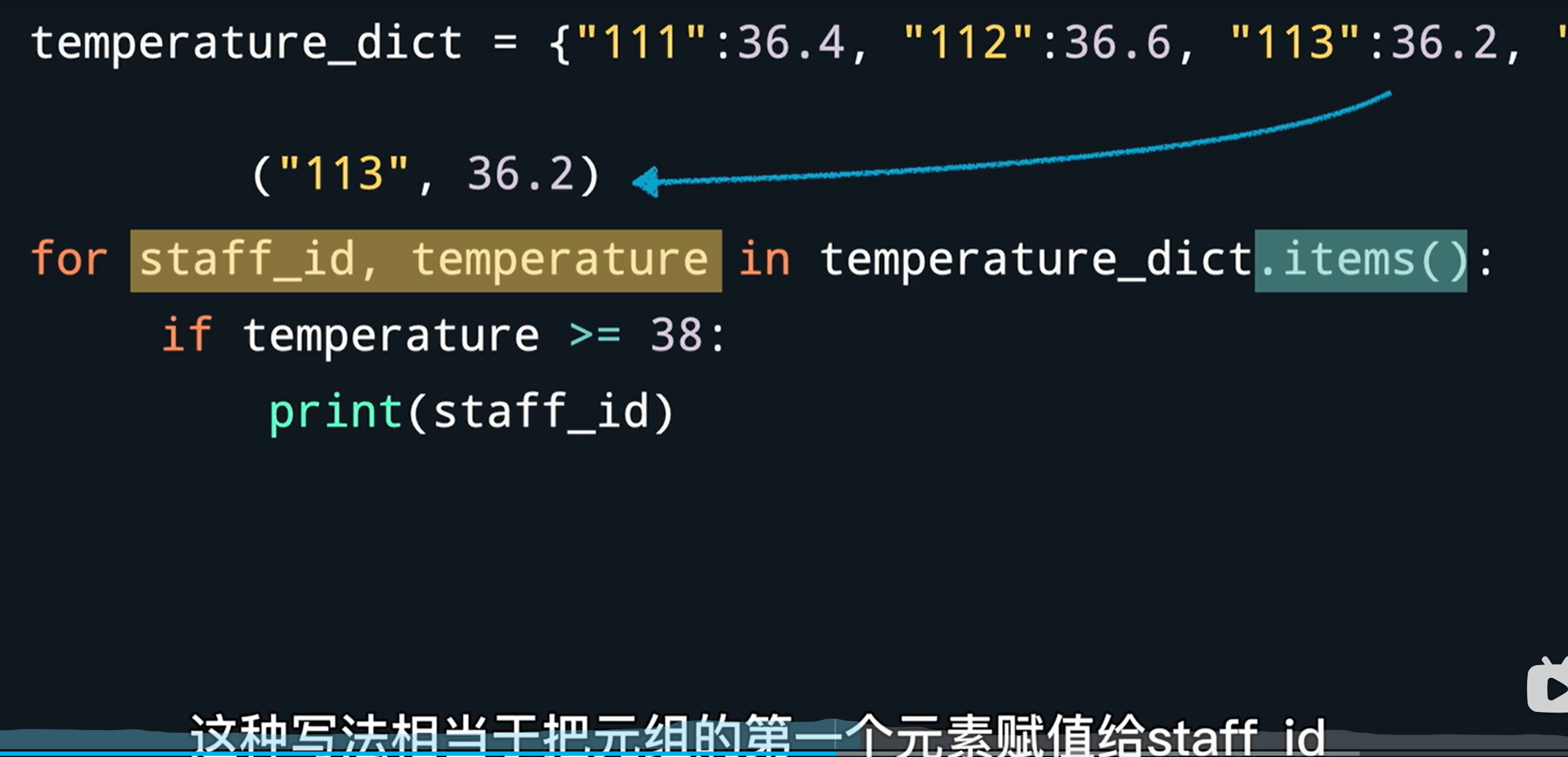
等价于
range用来表示整数序列,
range(5,10) 括号第一个数字表示起始值,最后一个数字表示结束值,结束值不在序列范围内
range(5,10,2) 第三个数字表示步长,不指名默认为1
range(len(list1)) 第一个起始值默认为0,结束值为列表长度
total = 0 for i in range(1, 101): total += i print(total)
求平均值
user_input = input("please input num, if you input q then end: ")
total = 0
num = 0
while user_input != "q":
total += float(user_input)
num += 1
user_input = input("please input num, if you input q then end: ")
if num == 0:
avg_num = 0
else:
avg_num = total / num
print("平均值:"+ str(avg_num))
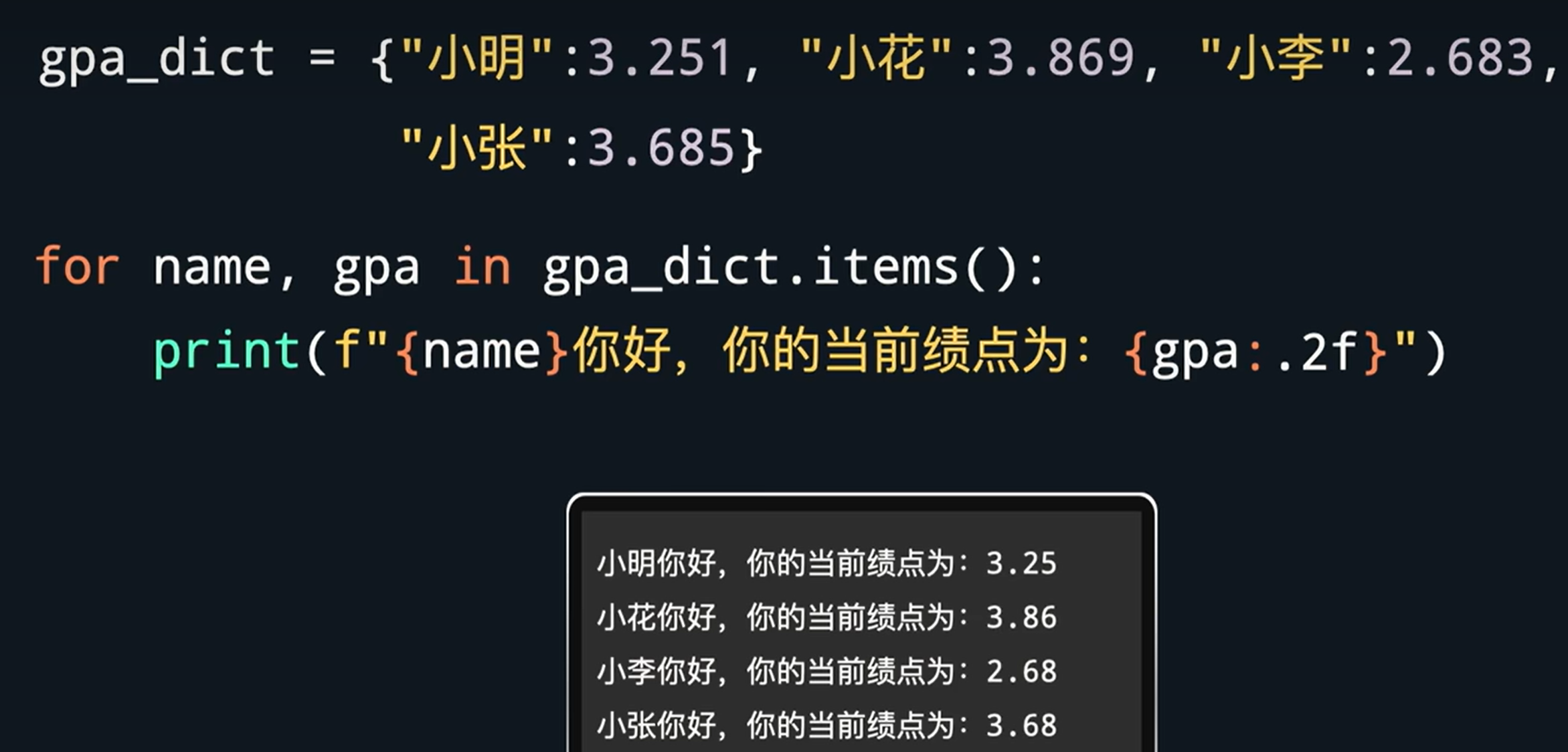
format方法
"""aa {0}bb{1}cc """.format(year, name)
花括号表示会被替换的位置,数字表示会用format里面的第几个参数进行替换
还可以用关键词而不是位置来指定进行替换的对象
"""aa {current_year}bb{receiver_name}cc """.format(current_year = year, receiver_name = name)
name = "aa"
year = "bb"
f字符串,在字符串前加前缀"f"
f"""aa {year}bb{name}cc """
浮点数替换{1:.2f} 表示2位小数
扇形面积
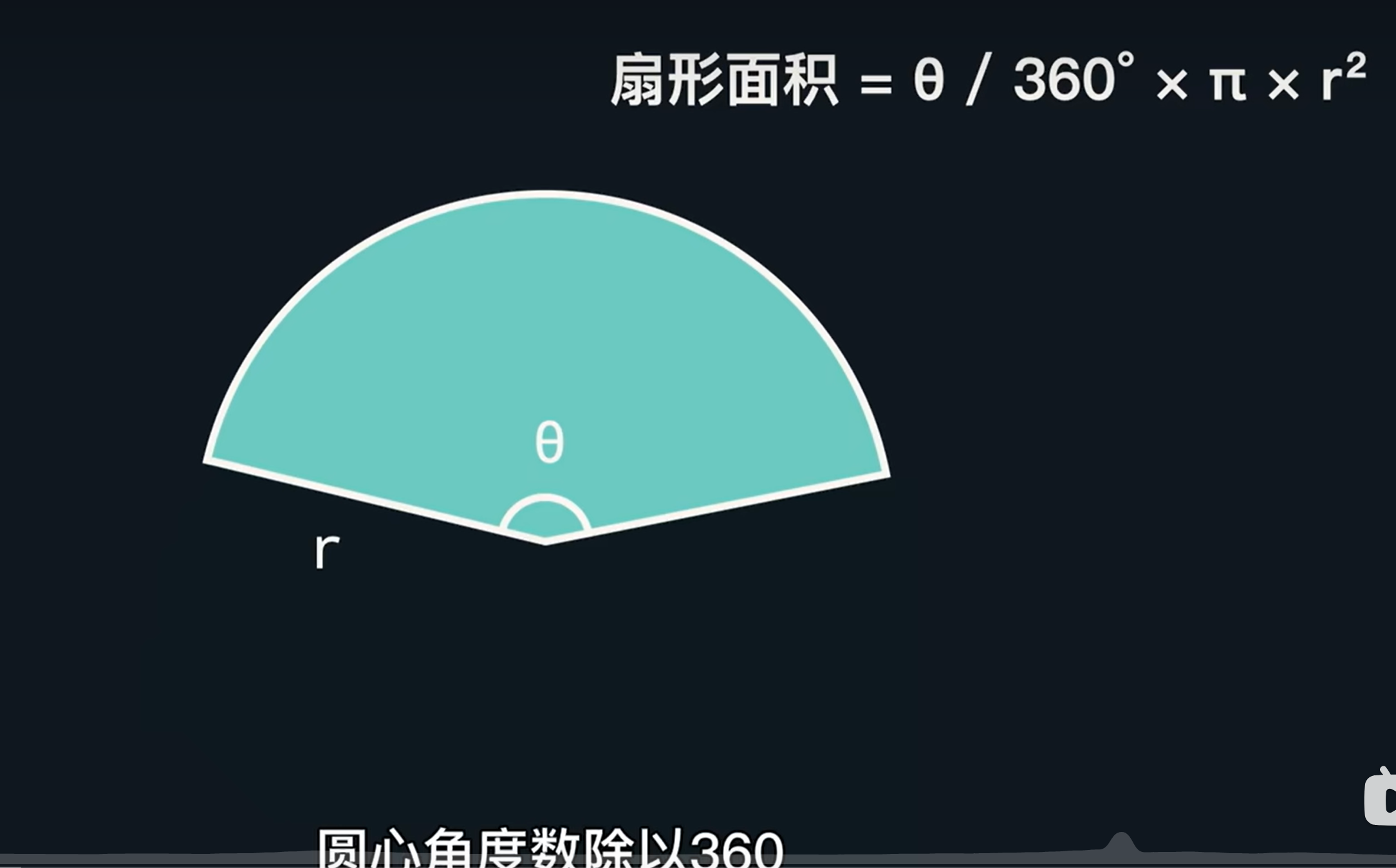
定义函数
def calculate_sector(central_angle, radius): # 接下来是一些定义函数的代码 sector_area = central_angle / 260 * 3.14 * radius ** 2 print(f"此扇形面积为:{sector_area}") calculate_sector(160, 30)
函数内,通过return返回函数结果
默认返回None
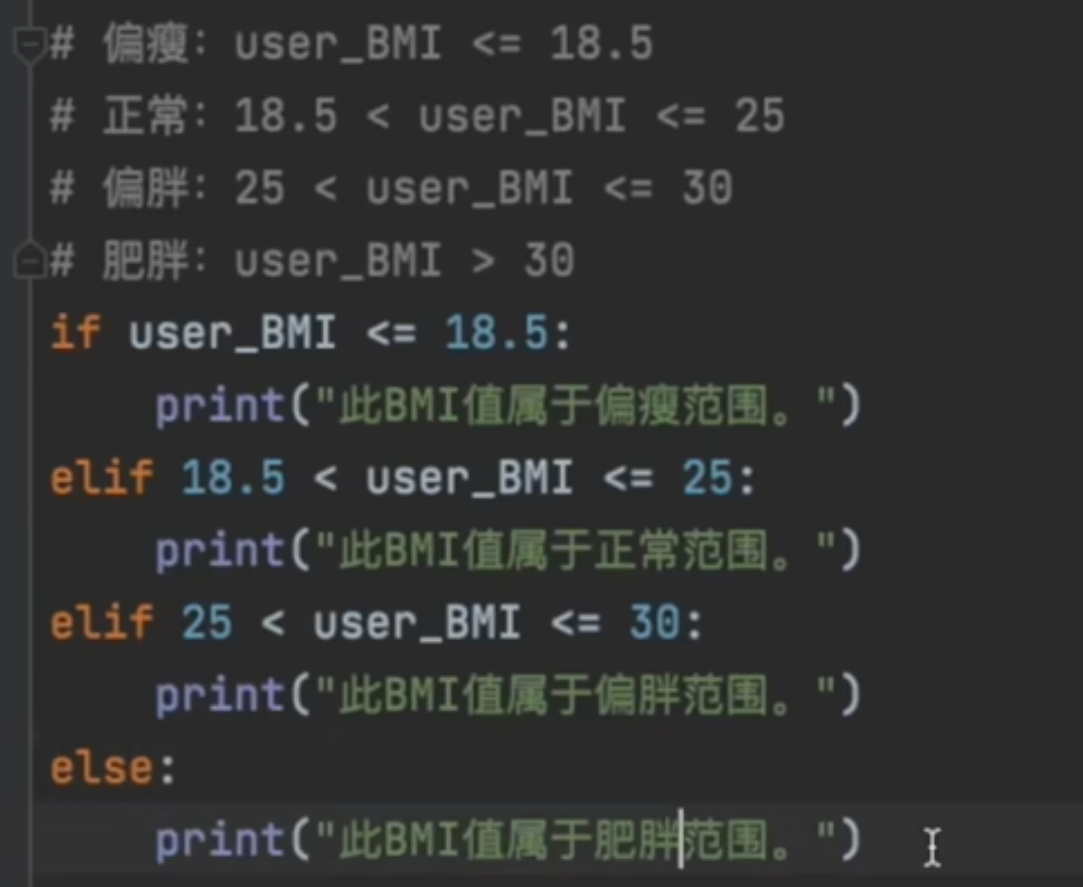
def cal_BMI(weight, height): BMI = weight / height ** 2 if BMI <= 18.5: cat = "偏瘦" elif BMI <= 25: cat = "正常" elif BMI <= 30: cat = "偏胖" else: cat = "肥胖" print("您的BMI类型"+cat) return BMI result = cal_BMI(1.8, 70) print(result)
3//2 两个除号是除完后向下取整的意思,结果为1
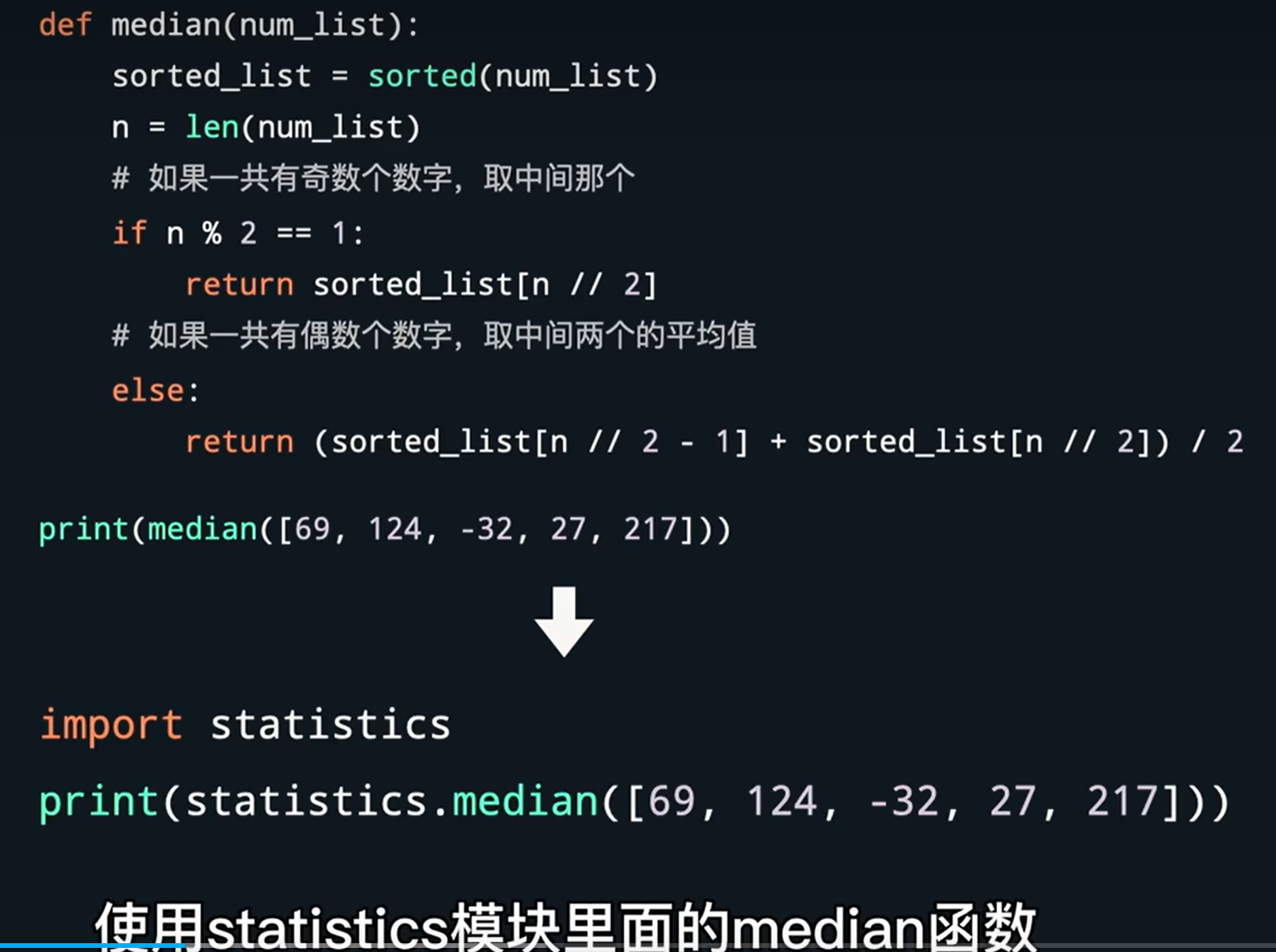
取中位数
import statistics print(statistics.median([69, 124, -32, 27, 217]))
引入模块的方式有三种:
1、import语句, import后面跟上模块的名字,如import statistics
使用时,模块名.函数名或者模块名.变量名来使用
2、from...import...语句,from跟上模块的名字,import后面跟上你在那个模块里要使用的函数或变量
如 from statistics import median, mean
3、from ... import * 语句,from statistics import *,会把模块里的所有内容都进行引入
这种还可能发生冲突,当from A import * 和from B import *都包含abc()函数时
引入之前需要先安装,即从互联网下载别人写好的模块
pip install akshare 安装akshare,pypi.org这个网站可以对第三方库进行搜索
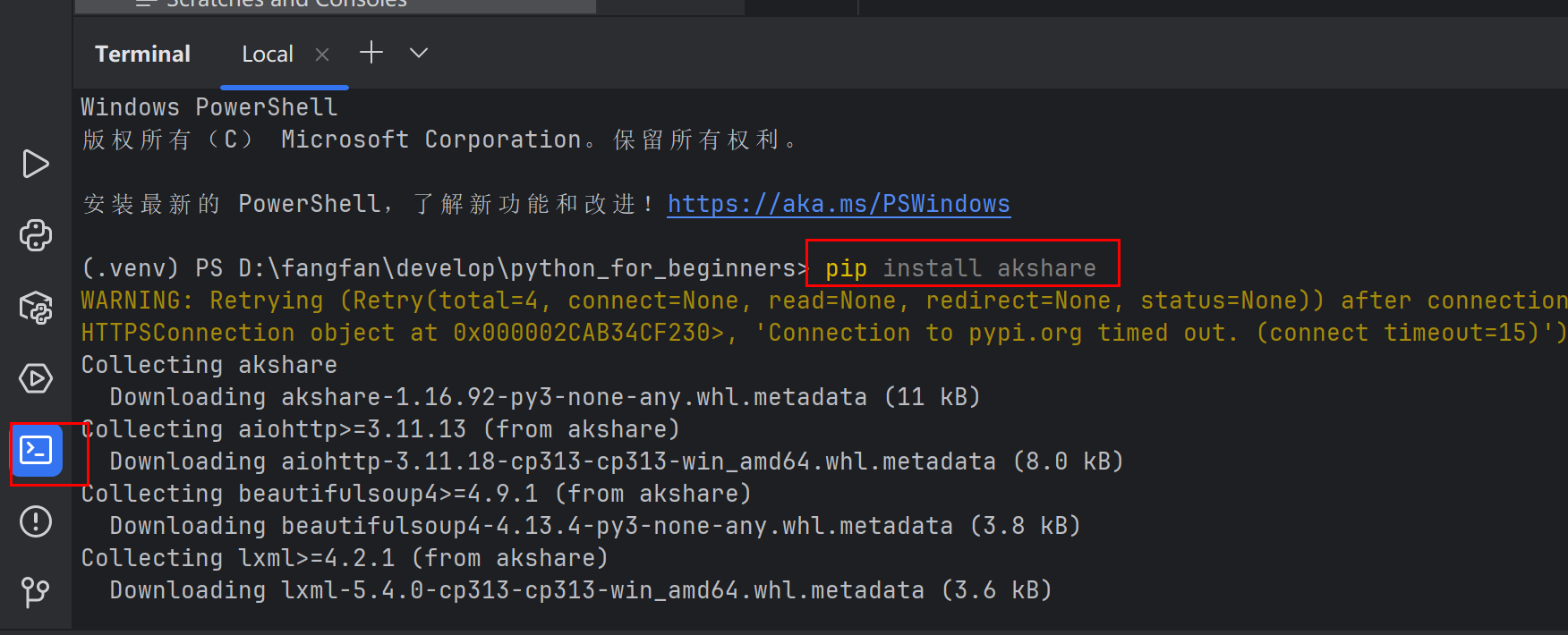
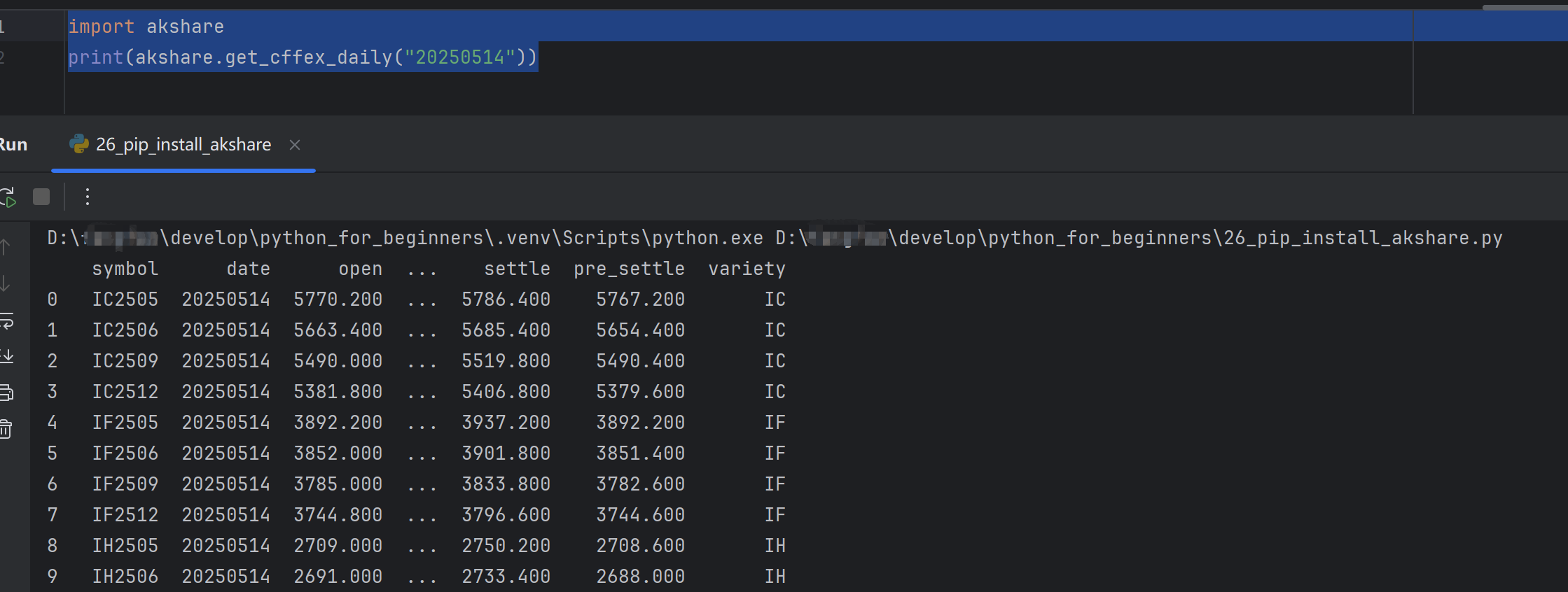
import akshare print(akshare.get_cffex_daily("20250514"))
获取指定日期的金融期货交易所的交易数据
[notice] A new release of pip is available: 25.0.1 -> 25.1.1
[notice] To update, run: python.exe -m pip install --upgrade pip
(.venv) PS D:\xx\develop\python_for_beginners> python.exe -m pip install --upgrade pip
面向对象编程 oop (Ojbect Oriented Programming)
定义类 类是创建对象的模板
# 定义ATM类 class ATM: def __init__(self, 编号, 银行, 支行): #self不需要手动传入 self.编号 = 编号 self.银行 = 银行 self.支行 = 支行 # 创建两个ATM对象 atm1 = ATM("001", "招商银行", "南园支行") atm2 = ATM("002", "中国银行", "北园支行")
下划线命名法
适用于变量名,例子 user_name 、total_distance、list_count
Pascal命名法
适用于类名,例子 UserAccount、CustomerOrder、PaymentData
class CuteCat: def __init__(self, cat_name): self.name = cat_name cat1 = CuteCat("mimi") print(cat1.name)
构造函数,多个参数
class CuteCat: def __init__(self, cat_name, cat_age, cat_color): self.name = cat_name self.age = cat_age self.color = cat_color cat1 = CuteCat("mimi", 2, "黄色") print(cat1.name + "," + str(cat1.age) + "," + cat1.color)
定义方法
class CuteCat: def __init__(self, cat_name, cat_age, cat_color): self.name = cat_name self.age = cat_age self.color = cat_color def speck(self): print("喵" * self.age) # 字符的次数 def think(self, content): print(f"小猫{self.name}在思考{content}...") cat1 = CuteCat("mimi", 2, "黄色") print(cat1.name + "," + str(cat1.age) + "," + cat1.color) cat1.speck() cat1.think("现在是抓老鼠还是睡觉")
Student类及方法
class Student: def __init__(self, name, student_id): self.name = name self.student_id = student_id self.grades = {"语文":0,"数学":0,"英语":0} def set_grade(self, course, grade): if course in self.grades: self.grades[course] = grade def print_grades(self): print(f"学生{self.name}(学号为:{self.student_id})的成绩为:") for course in self.grades: print(f"{course}:{self.grades[course]}分") chen = Student("chen", "1001") chen.set_grade("语文", 90) chen.set_grade("数学", 90) chen.print_grades()
子类没有自己的构造函数就会调用到父类的构造函数,子类有自己的构造函数就会优先调用子类的构造函数

但是上面这种,会导致子类只有has_tail属性,没有其他name等属性
super()会返回当前类的父类,所以在子类的__init__()里调用父类的init方法,super().__init__(name, sex)

什么时候使用继承

全职兼职雇员类
class Employee: def __init__(self, name, id): self.name = name self.id = id def print_info(self): print(f"员工名字:{self.name},员工编号:{self.id}") class FullTimeEmployee(Employee): def __init__(self, name, id, monthly_salary): super().__init__(name, id) self.monthly_salary = monthly_salary def calculate_monthly_pay(self): return self.monthly_salary class PartTimeEmployee(Employee): def __init__(self, name, id, daily_salary, work_days): super().__init__(name, id) self.daily_salary = daily_salary self.work_days = work_days def calculate_monthly_pay(self): return self.daily_salary * self.work_days zhangsan = FullTimeEmployee("zhangsan", "1001", 6000) lisi = PartTimeEmployee("lisi", "1002", 200, 20) zhangsan.print_info() lisi.print_info() print(zhangsan.calculate_monthly_pay()) print(lisi.calculate_monthly_pay())
用python读文件的第一步是,先打开目标文件,用open函数
f = open("./data.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8")
第一个参数是路径,可以是相对路径,也可以是绝对路径
第二个参数是模式,"r"读取模式(只读) "w"写入模式(只写),不写时默认为读取模式
第三个参数(可选),表示编码方式
返回文件对象, 文件对象有个read()方法,调用后,会一次性读取文件里的所有内容,并以字符串方式返回
再次调用read方法会返回空,因为read读取的位置已经到了末尾了
文件特别大的时候,不要用read,会占用很大内存
可以给read传一个数字,表示读取多少字节
readline()方法读文件,一次只会读取一行,根据换行符来判断什么时候算本行的结尾
只要返回的不是空字符串,就继续读下一行,否则就退出循环
line = f.readline() #读第一行
while line != "": 判断当前行是否为空
print(line) # 不为空则打印当前行
line = f.readline() #读取下一行
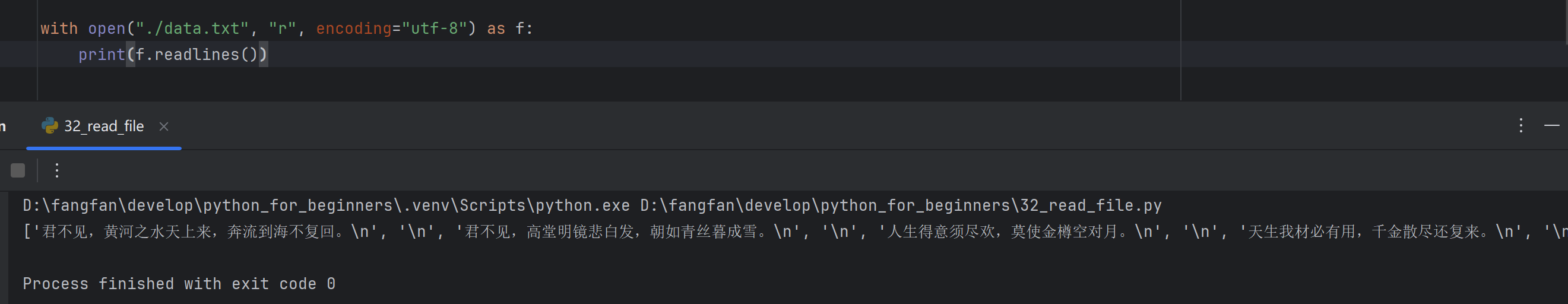
readlines()方法会读取所有行内容,再使用for循环处理每一行
读完之后要关闭文件
f.close()
有时候会忘记关闭,使用with方式,不需要单独调用close了
with open("./data.txt") as f:
f.read() #对文件的操作
f = open("./data.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") print(f.read()) f.close()
with方式
with open("./data.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f: print(f.read())
readlines返回列表
with open("./data.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f: lines = f.readlines() for line in lines: print(line)

写模式下,文件不存在时,程序会自动创建;
如果文件存在,会把文件内容清空,再写入。
如果不想清空,需要用附加模式"a"
"r+"表示读写
f.write()方法,会在文件内容后面添加新的内容
with open("./poem.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write("aaaa,\n")
f.write("Bbbb,\n")
f.write("cccc")
with open("./poem.txt", "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write("\ndddd,\n")
f.write("eeee\n")
异常捕获
try: expression1 except ValueError: expression2 except: #不跟错误类型,可以捕捉所有类型的错误 expression3 try/except语句,捕捉错误时,从上往下运行,如果第一个except语句捕捉了错误,那后面的语句都不会执行了 还可以跟else语句 else: expression4 #try语句没有任何错误时,要执行的语句 finally语句, finally: expression5 #最终都会被执行的语句
unittest就是一个很常用的python单元测试库,python自带不用安装,import unittest引入
对软件中的最小可测试单元进行验证
测试代码放到独立文件里
把test_开头的当做用例
unittest.TestCase类里的assertEqual方法
my_calculate.py
def my_adder(x, y): return x + y
test_my_calculate.py
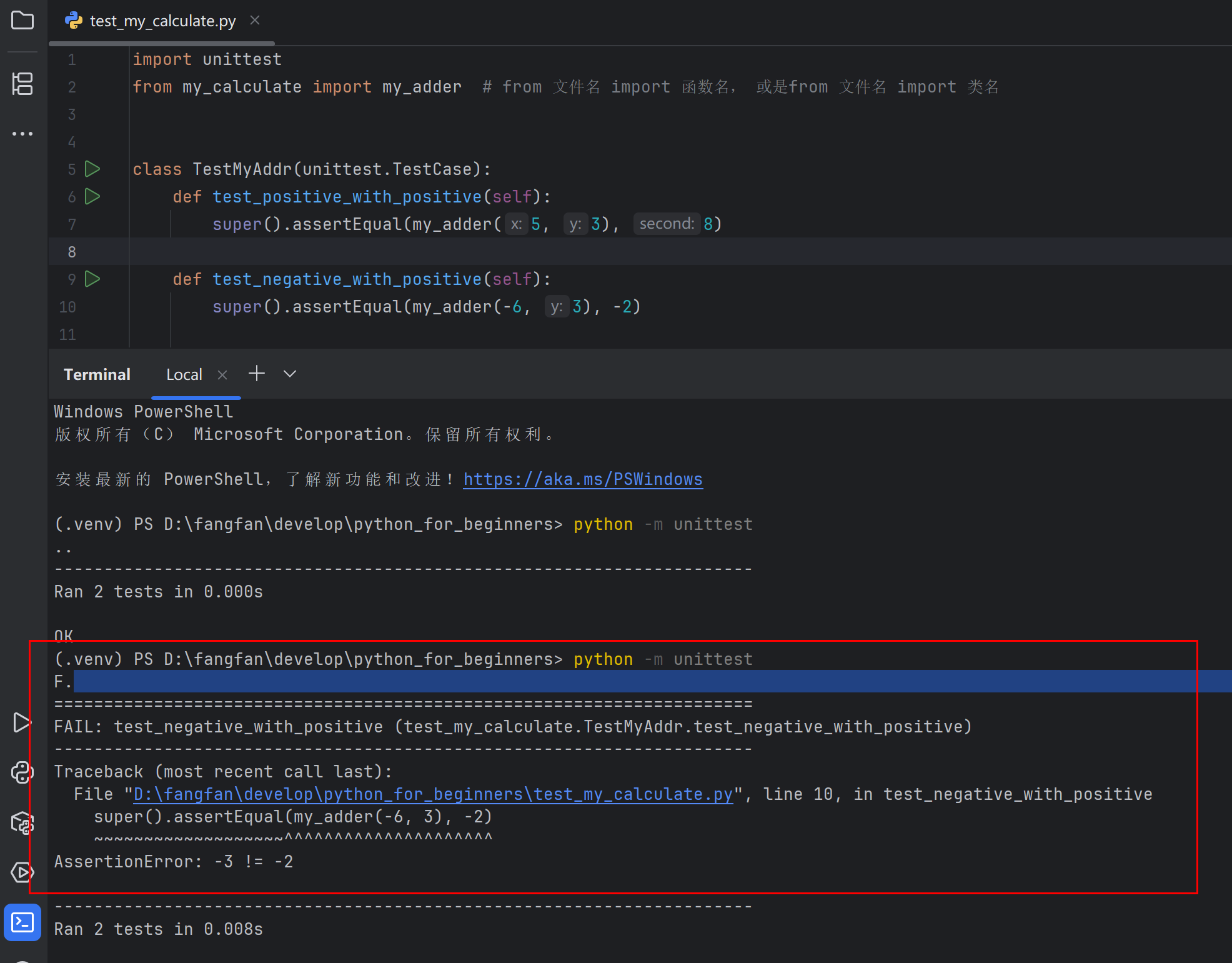
import unittest from my_calculate import my_adder # from 文件名 import 函数名, 或是from 文件名 import 类名 class TestMyAddr(unittest.TestCase): def test_positive_with_positive(self): super().assertEqual(my_adder(5, 3), 8) def test_negative_with_positive(self): super().assertEqual(my_adder(-6, 3), -3)
执行 python -m unittest
表示运行unittest,这个库就会自动搜索所有继承了unittest库里TestCase类的子类,运行他们所有以test_开头的方法
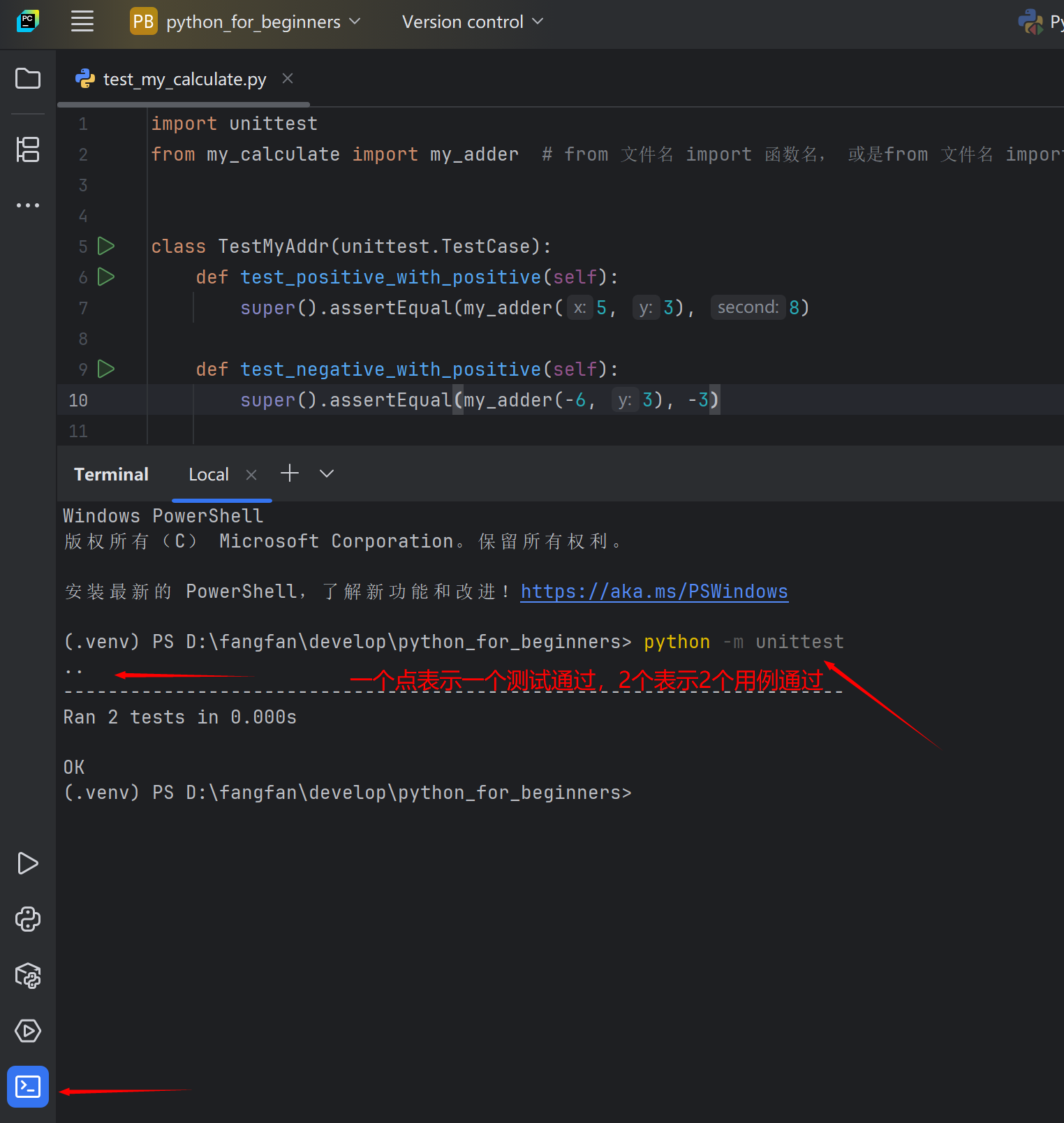
如果一个用例没有通过,其中一个点就会变成F,unittest还会告诉你是那个文件下的哪个方法,造成了失败,以及为什么失败
其他assert方法,及相关含义


更针对的方法,会给出更详细的错误原因

避免每个测试方法里的重复定义,可以使用setUp方法,运行其他测试方法(也就是test_开头的方法前)之前,setUp方法都会先被运行一次

购物清单程序
shopping_list.py
class ShoppingList: """ 初始化购物清单,shopping_list是字典类型,包含商品名和对应价格 例子: {"牙刷":5, "沐浴露":15, "电池":7} """ def __init__(self, shopping_list): self.shopping_list = shopping_list """ 返回购物清单上有多少项商品 """ def get_item_count(self): return len(self.shopping_list) """ 返回购物清单商品价格总额数字 """ def get_total_price(self): total_price = 0 for price in self.shopping_list.values(): total_price += price return total_price
test_shopping_list.py
import unittest from shopping_list import ShoppingList # from 文件名 import 类名 class TestShoppingList(unittest.TestCase): def setUp(self): #初始化方法 self.shopping_list = ShoppingList({"肥皂":10, "牙膏":15, "纸巾":8}) def test_get_item_count(self): self.assertEqual(self.shopping_list.get_item_count(), 3) def test_get_total_price(self): self.assertEqual(self.shopping_list.get_total_price(), 33)
calculate_and_print.py
计算平方
def calculate_and_print(num): result = num * num print(f""" | 数字参数 | {num} | | 计算结果 | {result} | """) calculate_and_print(3)
增加三次方和其他次方
def calculate_and_print(num, power): if power == 2: result = num * num elif power == 3: result = num * num * num else: print("只支持二次方或三次方") return print(f""" | 数字参数 | {num} | | 计算结果 | {result} | """) calculate_and_print(3,2) calculate_and_print(3,3) calculate_and_print(3,4)
calculate_and_print(3, calculate_square) 这种把函数作为参数的函数,被叫做高阶函数
函数名直接传入,后面不要带括号和参数
def calculate_and_print(num, calculate): result = calculate(num) print(f""" | 数字参数 | {num} | | 计算结果 | {result} | """) def calculate_square(num): return num * num def calculate_cube(num): return num * num * num def calculate_plus_10(num): return num + 10 calculate_and_print(4, calculate_square) calculate_and_print(4, calculate_cube) calculate_and_print(4, calculate_plus_10)
还能把格式化的函数作为参数传入,扩展出不同的打印格式
匿名函数 lambda
可以直接在高阶函数的括号里,放入关键字lambda,calculate_and_print(7, lambda num: num * 5, print_with_vertical_bar)

定义后,直接调用
(lambda num1, num2: num1 + num2)(num1, num2)
局限性,冒号后面,没法有多个语句或表达式
推荐书籍
《Python编程:从入门到实践》

进度(36/37)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号