链表——数据结构与算法学习
链表
为什么需要链表数据结构
与队列和数组相比,链表由于具有指针结构,是最容易进行增删改的数据结构形式。
关于链表结构的几道面试题思考(思考多种方法)
首先定义节点和单链表结构
public class HeroNode {//这里定义一个节点对象,Java里默认没有数据的节点就是Node对象
public int no;
public String name;//此处代表链表的数据,可以补充别的
public HeroNode next;//下一个节点
public HeroNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
}
public class SingleLinkedList {//初始化单链表结构
public static HeroNode head;//初始化一个头节点
//实现单链表的添加
public void add(HeroNode heroNode){
if(head == null){
head = heroNode;
}else{
HeroNode temp = head;//相当于复制一个head指针
//先找到最后一个节点
while(true){
if(temp.next == null){
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = heroNode;
}
}
public static int getNum(HeroNode head){
//首先考虑是否为空
if (head == null){
return 0;
}
int length = 0;
//定义一个辅助节点帮忙遍历
HeroNode temp = head;
while(temp != null){
length ++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return length;
}
}
求单链表中有效节点的个数
public static int getNum(HeroNode head){
//首先考虑是否为空
if (head == null){
return 0;
}
int length = 0;
//定义一个辅助节点帮忙遍历(因为头结点的指针不能随意变动,所以必须要定义辅助节点)
HeroNode temp = head;
while(temp != null){
length ++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return length;
}
查找单链表中的倒数第k个节点
//查找单链表中的倒数第k个结点
public static HeroNode findLastIndexNode(HeroNode head, int index){
//如果链表为空,返回null
if(head == null){
return null;
}
int num = getNum(head);//获取链表总长度
//定义辅助节点
HeroNode temp = head;
//遍历找到位置(这里找到索引就很容易
for (int i = 0; i < num - index ; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
return temp;//时刻记住这是指针,返回的指针指向的节点
}
单链表反转
//单链表反转
public static void ReverseLinkedList(){
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return;
}
//定义辅助节点和中间指针,便于交换
HeroNode temp = head;
HeroNode next;
HeroNode reversehead = new HeroNode(0,"") ;
//开始进行交换
while(temp != null){
next = temp.next;
temp.next = reversehead.next;//用图解法了解较为清晰,单链表一旦有连接,上一个就自动断掉
reversehead.next = temp;
temp = next;
}
head = reversehead.next;
}
从尾到头打印单链表(两种方式:1:反向遍历 2:stack栈)
//实现逆序打印还是栈的数据结构最方便
public static void reversePrint(HeroNode head){
if(head == null){
return;
}
Stack<HeroNode> stack = new Stack<HeroNode>();
HeroNode cur = head;
//将链表的所有节点压入栈中
while(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
while(stack.size() > 0){//遍历出栈
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}
复杂链表复制
题目需求:请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
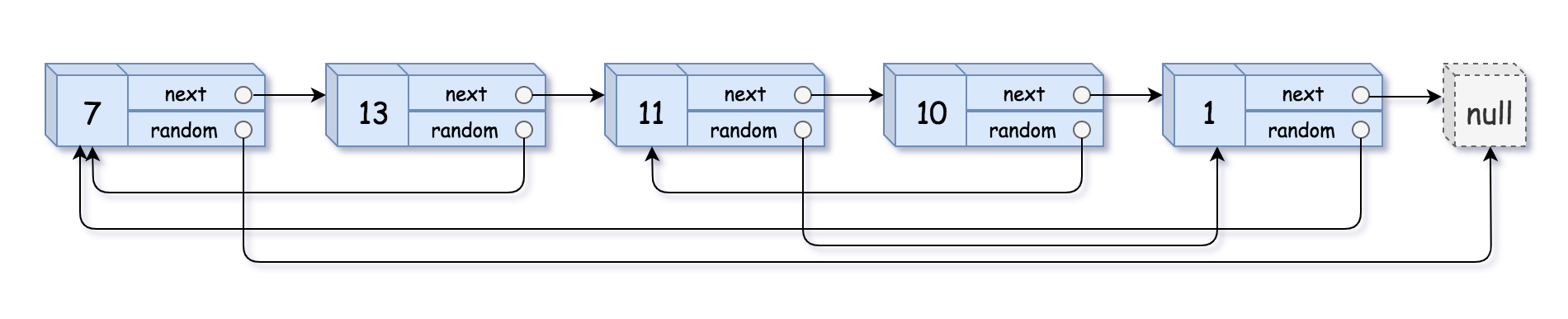
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/fu-za-lian-biao-de-fu-zhi-lcof
1.复制一个新的节点在原有节点之后,如 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> null 复制完就是 1 -> 1 -> 2 -> 2 -> 3 - > 3 -> null
2.从头开始遍历链表,通过 cur.next.random = cur.random.next 可以将复制节点的随机指针串起来,当然需要判断 cur.random 是否存在
class Solution
public Node copyRandonList(Node head){
if(head == null){
return head;
}
Node cur = head;//定义一个辅助节点
//首先是节点的复制
while(cur != null){
Node copyNode = new Node(cur.val);
copyNode.next = cur.next;
cur.next = copyNode;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
//完成链表的随机指针复制
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.random != null){
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
}
cur = cur.next.next;
}
//将链表一分为二
Node copyNode = head.next;
cur = head;
Node curCopy = head.next;
while(cur != null){//拆分两个链表
cur.next = cur.next.next;
cur = cur.next;
if(curCopy.next != null){
curCopy.next = curCopy.next.next;
curCopy = curCopy.next;
}
}
return copyNode;
}
合并K个有序链表(分治算法了解)
链表中的节点与指针
其实可以这么理解,链表中存放数据的节点构成了链表,我们所定义的头结点及后面的指向对象其实都是指针,用来操控节点这一数据载体。
可以理解为链表上的增删改操作是链表结构本身不发生改变,只有链表的指针发生改变。所以才设置一个静态链表指针。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号