jsMind使用踩坑记录与个人总结(vue2+elementui)
首先是安装包,目前版本是0.8.7
npm install jsmind
注意,如果你也是vue2,那直接引入的时候可能会失败。
import 'jsmind/style/jsmind.css' //样式 import jsMind from 'jsmind' //这个是正常引入 //import jsMind from 'jsmind/js-legacy/jsmind.js' //引入失败的话可以试试这个,不过该方式下引入将无法使用新版选项更改样式或渲染方式之类的
如果要正常引入,则需要在vue.config.js中添加如下代码
module.exports = { transpileDependencies: ['jsmind'], ……
如果是vue3,则不会有问题。
接下来是使用,具体选项配置可查看官网文档get-started | zh | docs | jsMind
主要是几个坑:
1、绘图必须要存在实体才能进行,因此若是要用弹窗等形式展示的话,最好确保包裹的父元素出现了再进行初始化
1 handleClick(){ 2 this.dialogVisbile = true //弹窗显示 3 this.jsMindLoading = true //加载 4 this.$nextTick(()=>{ 5 this.jsChart = new jsMind(this.jsoptions) //初始化jsmind实例 6 this.jsChart.show(this.mind) //加载数据,渲染节点 7 }) 8 },
2、jsmind不提供自带的销毁api,因此如果是在弹窗之类的进行渲染的话,再次点开会导致上一次的图还保留着,同时再次重复渲染一次(即使元素id理论上来说不能重复),所以需要手动销毁
1 handleClose() { 2 if (this.jsChart) delete this.jsChart //删除实例对象 3 const container = document.getElementById('jsmind_container') 4 while (container.firstChild) container.removeChild(container.firstChild) //获取父容器,并循环删除其下节点,如果加了el-loading的遮罩层,也可一并删除 5 this.mind.data.children = [] //这里是子节点的数据,可以在请求接口时清空,或者此时清空 6 this.dialogVisible = false 7 },
3、可以支持自定义绘制连线与节点(此处是在vue文件的script内)连线可用canvas或svg绘制,canvas方式返回的是canvas上下文,可直接调用方法进行绘制;而svg返回的是"path"这个dom对象,绘制时需要添加属性:
1 export default { 2 data() { 3 const printArrow = ({ ctx, start_point, end_point }, str) =>{ 4 //获取根节点高度与宽度,因为实际终点是在根节点的中心位置,因此需要重新计算其连线的边界y值与x值。这里的nodeid就是根节点的id,也就是数据集mind.data.id 5 let height = document.querySelector(`[nodeid=${str}]`).offsetHeight 6 let width = document.querySelector(`[nodeid=${str}]`).offsetWidth 7 console.log('height', height) 8 //起点始终是子节点,终点始终是父节点,因此基础路径一致,只是箭头方向需要变化 9 //左边的选项 10 if(start_point.x < end_point.x){ 11 //左边——上边的选项 12 if(start_point.y < end_point.y){ 13 ctx.setAttribute('d', `M${start_point.x},${start_point.y} 14 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2},${start_point.y} 15 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2},${end_point.y - height / 2 - 4 } 16 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2 - 3},${end_point.y - height / 2 - 4 } 17 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2},${end_point.y - height / 2 } 18 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2 + 3},${end_point.y - height / 2 - 4 } 19 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2},${end_point.y - height / 2 - 4 } 20 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2},${start_point.y} 21 L${start_point.x},${start_point.y}`) 22 } //左边——中间的选项 23 else if(start_point.y === end_point.y) { 24 ctx.setAttribute('d', `M${start_point.x},${start_point.y} 25 L${end_point.x - width / 2 - 4},${start_point.y} 26 L${end_point.x - width / 2 - 4},${start_point.y + 3} 27 L${end_point.x - width / 2},${start_point.y} 28 L${end_point.x - width / 2 - 4},${start_point.y - 3} 29 L${end_point.x - width / 2 - 4},${start_point.y} 30 L${start_point.x},${start_point.y}`) 31 } // 左边——下边的选项 32 else if(start_point.y > end_point.y){ 33 ctx.setAttribute('d', `M${start_point.x},${start_point.y} 34 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2},${start_point.y} 35 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2},${end_point.y + height / 2 + 8} 36 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2 - 3},${end_point.y + height / 2 + 8} 37 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2},${end_point.y + height / 2 + 4} 38 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2 + 3},${end_point.y + height / 2 + 8} 39 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2},${end_point.y + height / 2 + 8} 40 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2},${start_point.y} 41 L${start_point.x},${start_point.y}`) 42 } 43 } //右边的节点,统一一个方向箭头 44 else if(start_point.x > end_point.x){ 45 ctx.setAttribute('d', `M${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2},${end_point.y} 46 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2},${start_point.y} 47 L${start_point.x - 4},${start_point.y} 48 L${start_point.x - 4},${start_point.y + 3} 49 L${start_point.x},${start_point.y} 50 L${start_point.x - 4},${start_point.y - 3} 51 L${start_point.x - 4},${start_point.y} 52 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2},${start_point.y} 53 L${(start_point.x + end_point.x) / 2},${end_point.y}`) 54 } 55 ctx.setAttribute('stroke-width', 2) 56 ctx.setAttribute('stroke', 'rgb(85,89,198)') 57 ctx.setAttribute('fill', 'rgb(85,89,198)') 58 } 59 const printRootBorder = (jm, element, node) => { 60 //jm为jsMind实例,不用 61 //element为节点元素 62 //node为节点数据 63 //返回true则意味着不再渲染该节点,取而代之使用自定义渲染;false则为默认渲染方式 64 if(['root_hardware', 'root_software'].includes(node.id)){ 65 element.innerHTML = node.topic 66 element.style.border = '2px solid red' 67 return true 68 } else return false; 69 } 70 return { 71 jsoptions: { 72 container: 'jsmind_container', 73 theme: 'primary', 74 editable: true, 75 mode: 'full', 76 view: { 77 engine: 'svg', 78 custom_line_render: ({ ctx, start_point, end_point }) => printArrow({ ctx, start_point, end_point }, 'root_hardware'), //可以直接在这里用匿名函数绘制,不过如果有多个图需要绘制,而他们又拥有同样的渲染样式,那就可以抽取出来定义后使用 79 custom_node_render: printRootBorder 80 }, 81 …… 82 }, 83 } 84 }
需要注意的是,开始点永远是在子节点上,而结束点是出于根节点中心位置,因此若是要绘制左右两侧的箭头,那么从左边来的连线就要获取根节点的内置高度与宽度,从而计算出连线与其交汇的位置(上面的方法实现)
如果不更改边框的话,正常来说左侧箭头的上下部分绘制时是加减相同的偏差值(即根节点一半高度+箭头本身高度),但不知为何加入了边框后,下方的箭头必须要加上两倍边框的偏差值才行,否则会被边框挡住……
同样的,因为path绘制默认会连接起点到终点部分,
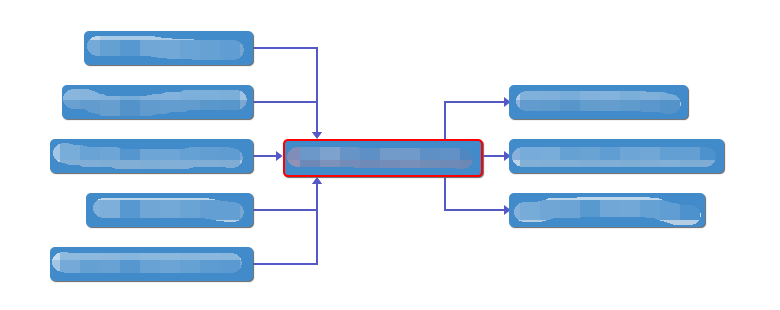
如果为了美观,可以考虑怎么做成曲线连接




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号